medphysics final essays
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
electromagnetic radiation
em spectrum, waves catgorised by
RIVUXG
light has wave particle duality
light fastest in vaccum
e= h (c x w)
n = c/v
reflection refraction
reflection
refraction
total internal reflection
absorption
scattering
rreflection diagram
refraction diagram
a = E x c
range
nonionising
sources
uv bands and ranges
a 315-400
b 280-315
c 200-280
+ve and -ve of uv bands
ct mutation
protection
diagram is spectrum
infrared
non ionising
range
sources
propereties; thermal effect, law diffraction
uses; IR imaging and therapy
spectrum
bands
a 0.76 - 2.5um
b 2.5 - 50um
c 50 - 1000 um
bio action; increase tissue temp, vasodilation
thermodivision; detects heat emitted from body e.g. inflammation
luminescence
what; electric transition from excited > ground state
photoilluminescene
flurescence short illumination lasts less than 10-9
phosphorescence emittion after excitation stops, longer than 10-6
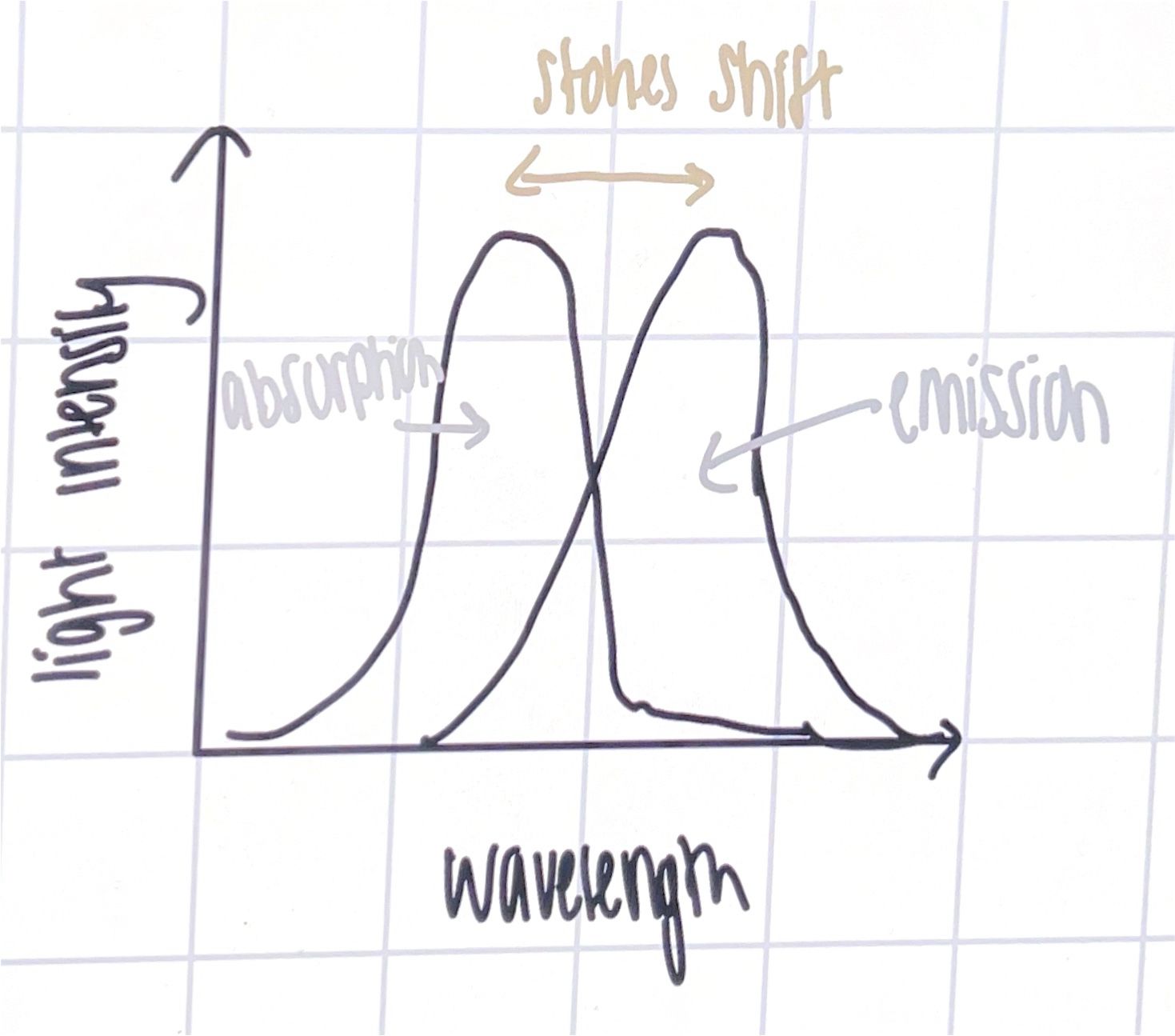
stokes law Wlum > W ex
vavilovs law; no of excited photons if proportional to no of luminescent photons
diagnostic methods;
flurescence, cancer detection,
chemilluminescence, blood tests
parameters of laser radiation
wavelength
intensity
pulse duration
spot size
monochromaticity
coherence
directionality
medical applocations; oncology, dermatology, surgery, opthamology
microscope
instrument to observe microobjects
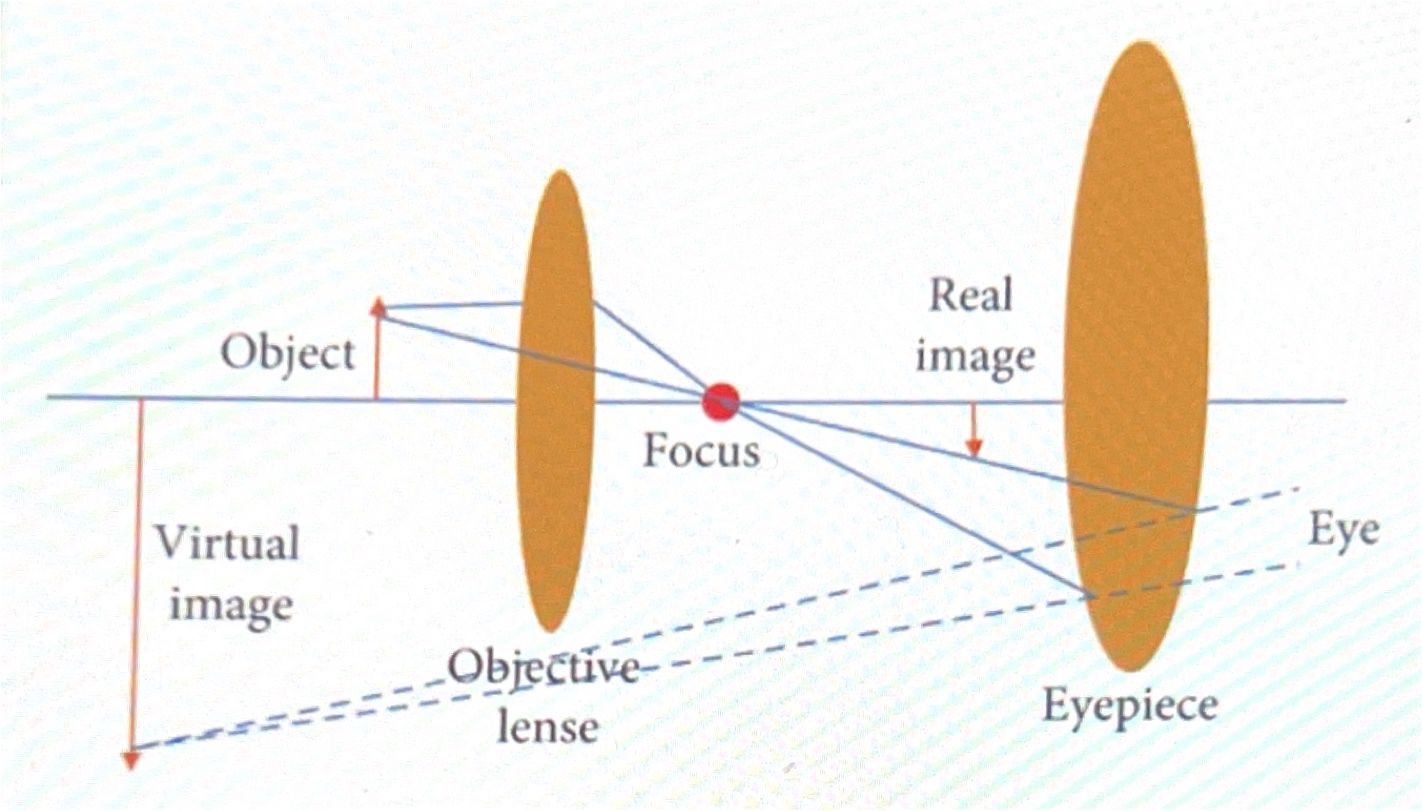
opticsal microscope uses visible light and lenses to magnify small images = 2d, high M low R
optic scheme,, eyepiece, objective
components of M
magnification'
mag eq
resolution
observation modes
bright field microscopy, sample illuminated from below, observed from above
dark field microscopy, live microO, not visible or stained
phase contrast microcopy converts phase differences into brightness differences
lasers
def; coherent light with properties
monochromatic
directional
coherent
polarised
types of lasers
visible light
gas lasers
infrared
absorption; atom E0, atom energy by incident photon so E1
spontaneous emission; excited atom on e1 spontaneously emitts photon so moves to e0,, photon emitted in rando direction
stimulated emission; excited atom, stimulated to fall to e0 as photon interacts w atom,, 2 identical photons released
population inversion; more atoms in excited than ground by pumping
pumping; energy to lasers active medium so theyre raised to higher level e.g. laser pumping
metastable state; when atom is excited state, stays for time
3 level laser scheme; pumping moves atom e0>e2,, unstable state now so falls to metastable state = population inversion at e1.. photon allows e1>e0
4 level laser scheme; atom e1>e3,, unstable so fall to metastable state where pop inv,, atoms stimulated and fall to e1 = laser radiation
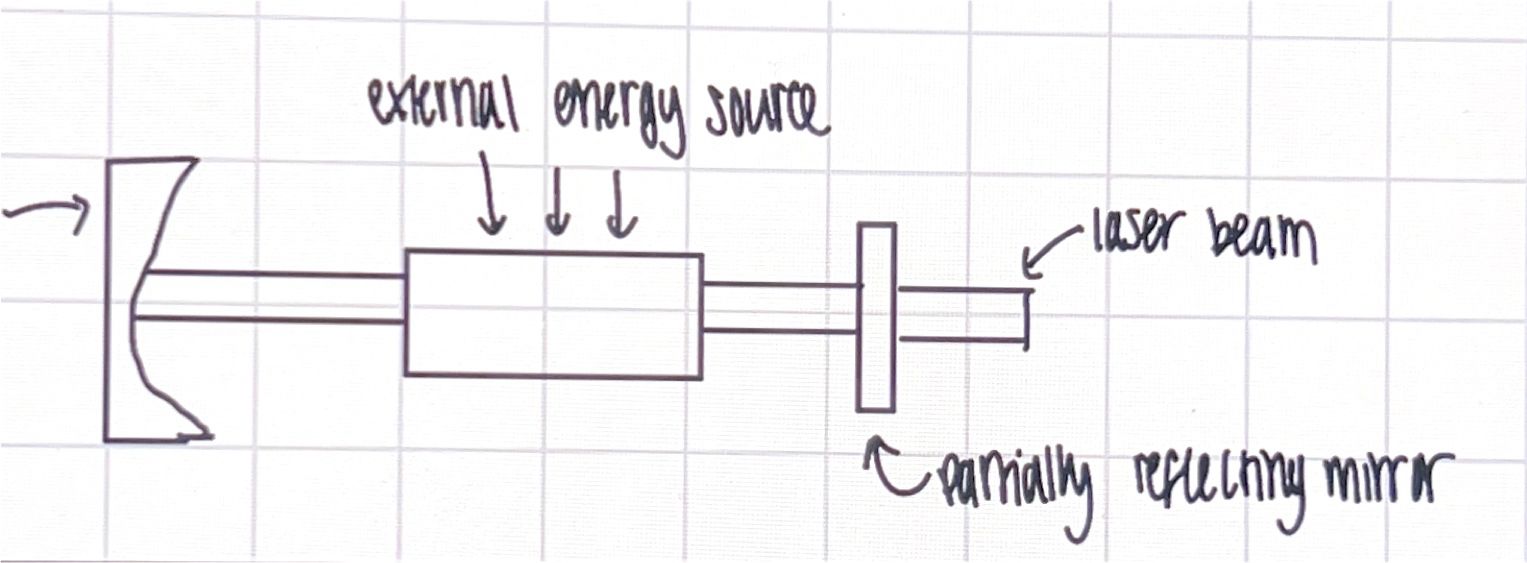
component of laser
active medium
pumping system
optical resonator
human eye
opticsl system
cornea
retina
lens
anterior chamber
optical nerve
refractive power,, ability to bend light + focus on retina
n = c/v
refraction
reduced schematic eye; cornea and lens act as single convex lens
optical lens types; cylindrical, spherical
spectral sensitivity; eye responds to light 400-700
emmetropia; normal
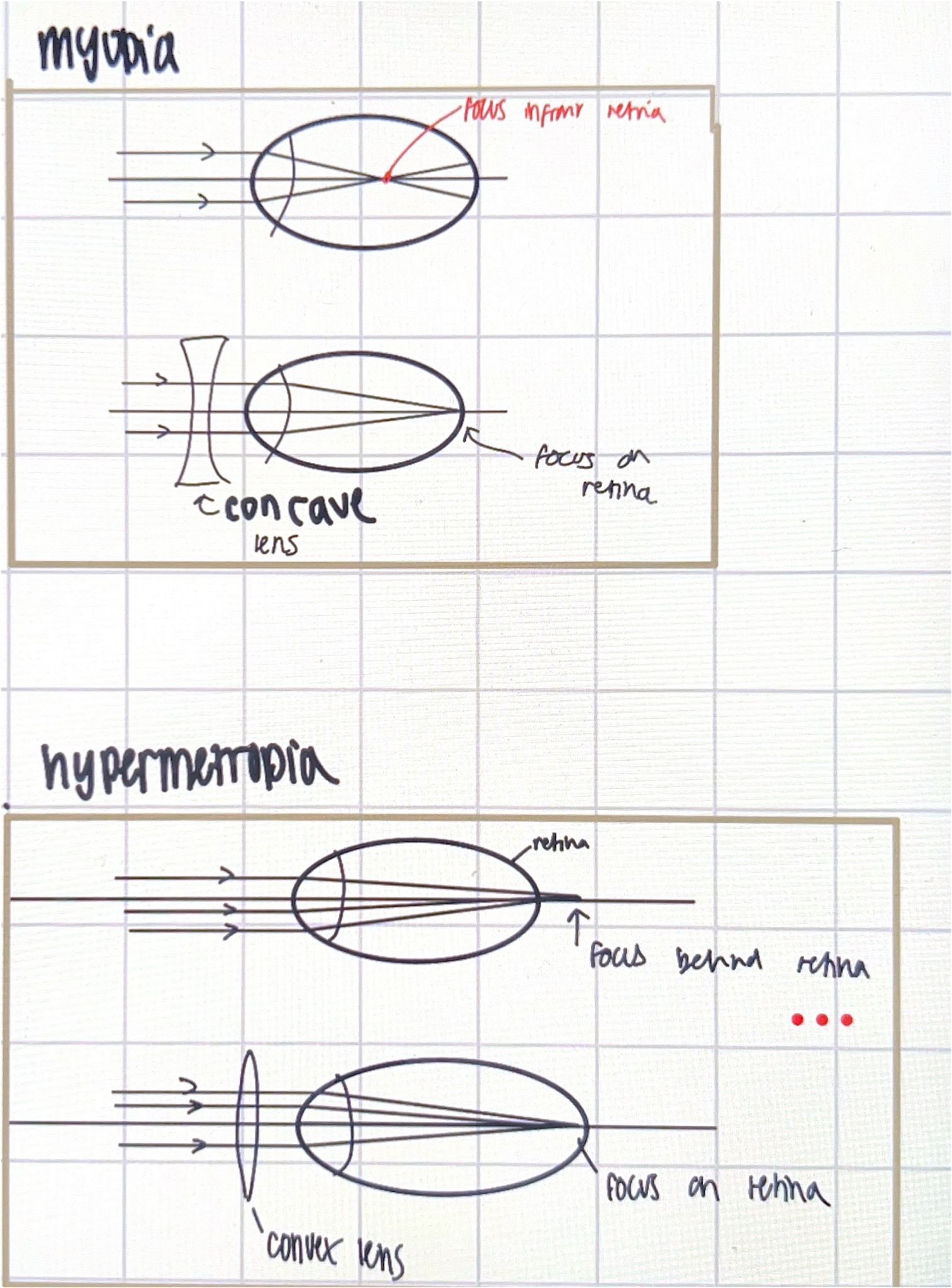
myopia; short sighted,, image projected before retina,, high OP,, corrected by concave lens so rays spread and converge later
hypermetropia; far sighted,, image proj after ret,, low OP,, corrected my convex lens which bends light so rays meet earlier
astigmatism; light rays focussed on multiple points in retina,, cylindrical lens corrects this by meeting in one
strabism,, muscles in the eye lack coordination
ionising radiatiations
high energy radiation to remove e- from materials
non ionising 10³ > 10^-8
ionising 10^-8 > 10^-13 ,, x ray and gamma
direct ionsising radiation,, charged particles, e- and photons
indirect ionsiing radiation,, secondary charged particles,, gamma and x ray photons
how indirect radiation interacts with matter
incoherenet scattering; partial energy transfer
photoelectric absorbption; complete energy transfer
couple production; e- > e+
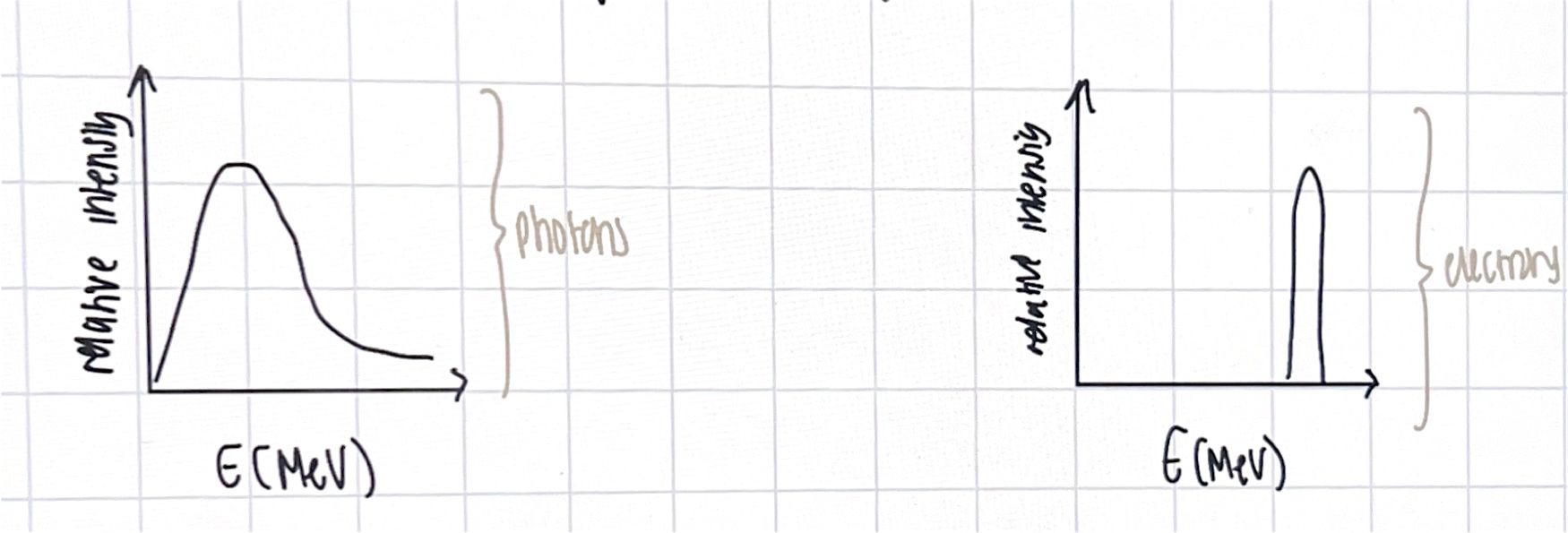
x-rays
type of ionising radiation called roentegen radiation
EM radiation
10nm - 2pm
produced by roentegen tube as e- hit the tungsten target so energy is converted to xrays
characteristic radiation; e- jump between shells to then produce xrays
braking radiation; e- slow down, energy released to produce xrays
medical application of x rays
x ray image formation; dense structures hv high absorption
x ray imaging; radiography, radioscopy etc
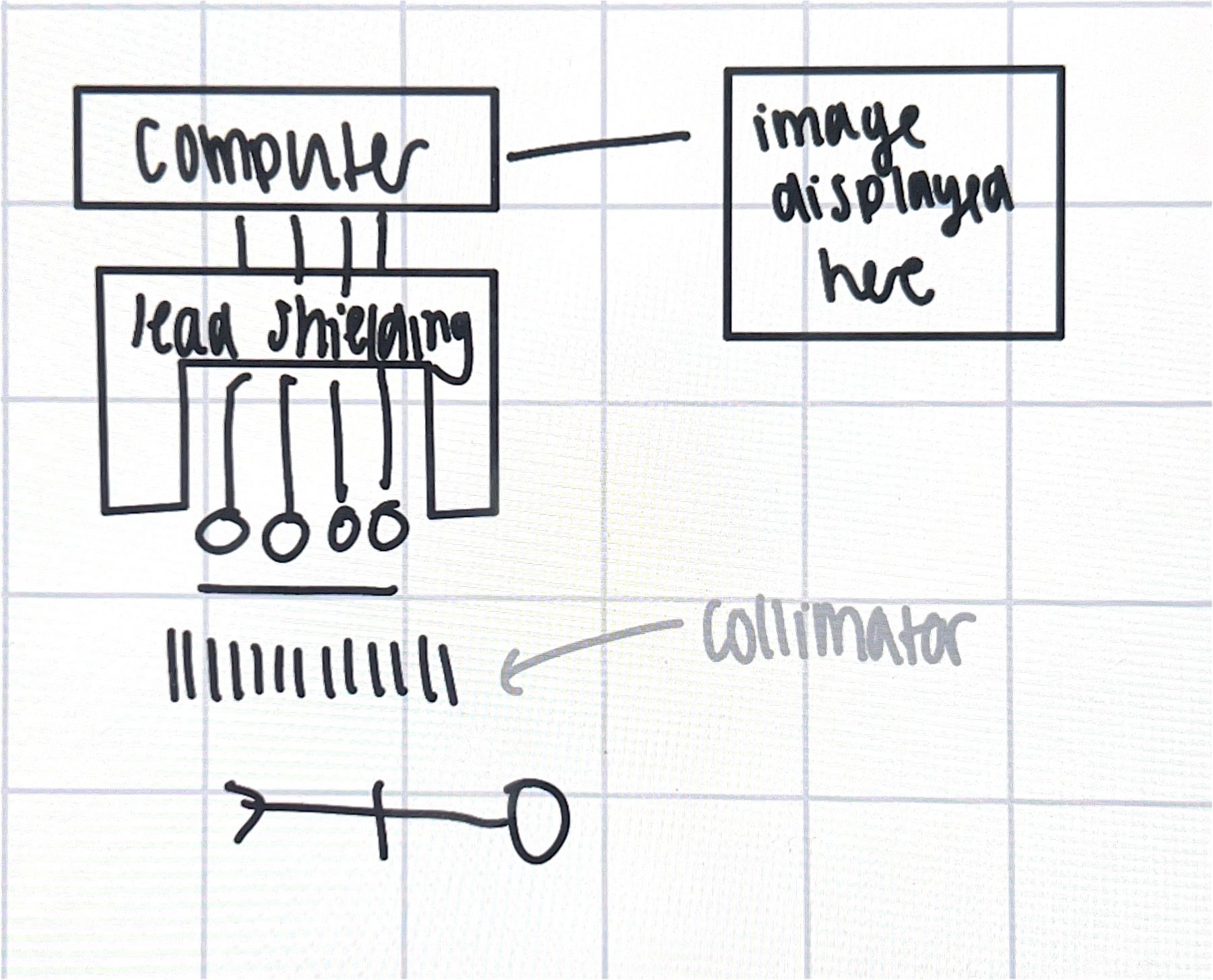
computer tomography; gives cross sectional images of body as machine rotates and takes images at diff sngles and are combined
hous=nsfield scale; scale in CT scans that state how much xray absorbed at tissues
radioactivity
atoms emitts energetic particles from nucleus
atom strucutre
radioactive decay; random emittion of radiation from nucleus to make it more stable (a, b, gamma rays emitted)
alpha decay, a particle emitted
beta minus decay, radionuclide has +1 neutron
beta plus decay nucleus emitts positron
gamma decay, nucleus excited > low energy state
decay laws;
half life; time for half nucleides to decay > Thalf = 0.693/w
nuclear decay
radiopharmaceuticals; drugs w radioactivity, used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes
nuclear medicine imaging
tomograph; 2d image of thin tissue layer of organ
somputed tomography, explain from previous point
SPECT, gamma cameras used to form images
PET, pateint injected w radioactive tracer to detect emittion of radioactivity
gamma cameras; detect emittion of gamma rays from radiopharmaceuticals in the body
dosimetry of ionising radiation
measurment and calculation of radiation dose in body and tissue
exposure; amnt of radiation produced in air by x or g
absorbed dose; radiation absorbed per unit mass of tissue/ Gy
equivelent dose; how harmful radiation is/ unit, Sv
effective dose; overall biological risk radiation has on body/ unit, Sv
radiation weighting factorbiological effectivness of different radiations
tissue weighting factor; hpw sensitive tissue/organ to radiation
radiotherapy
medical use of high energy radiation to treat cancer
LINAC; xray beam directed at tumour to treat it
CYBERKNIFE robotic RT tracking tumour movement
BRACHYTHERAPY; radiation source v close to tumour
direct and indirect ionising radiation
linear accelerators; accelerate charged partices

mechanical waves
waves which vobrate particles to transfer energy
sound waves; longitudinal mechanical waves, produce hearing perception
physical characteristics of sound
physical characteristucs of sound
pressure'
wavelength
frequency
intensity
prop speed
acoustic impendance'
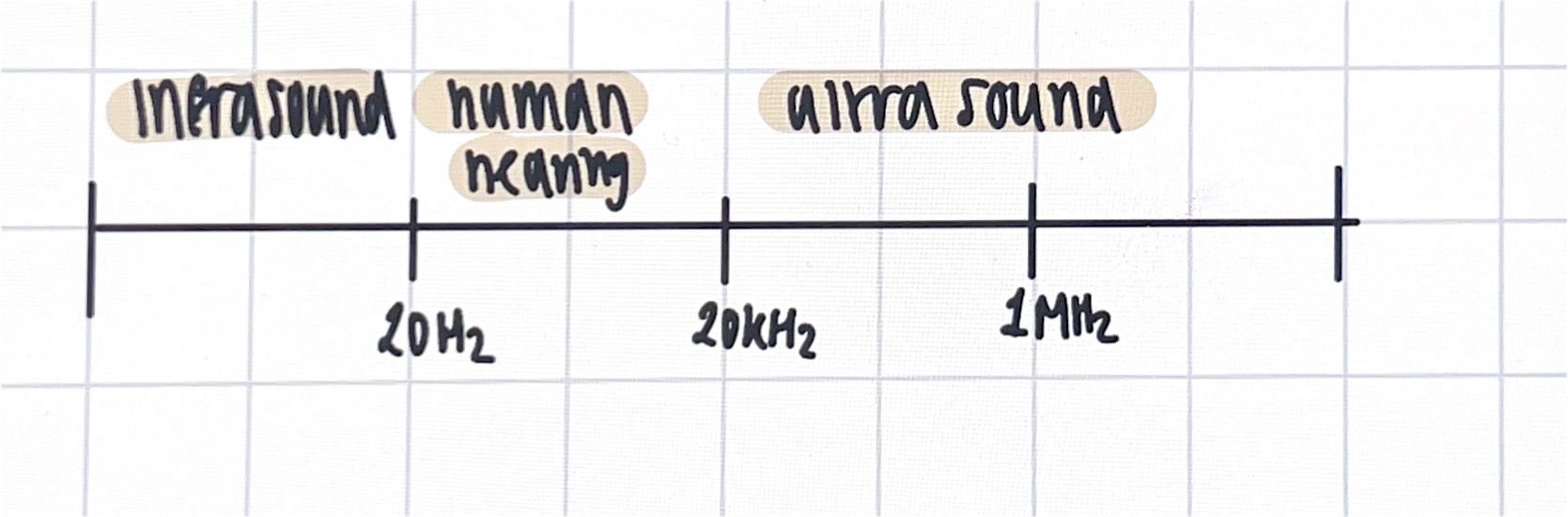
spectrum
paychophysical properties of sound
how human ear percieves sound
intensity, power per area
pitch, frequencies of sound
loudness
timbre, quality
sound diagnostics and therapy methods
auscullation, hearing internal body sounds to assess health
BP, sphygmomameter and steth hearing kortokoff sounds
audiogram
phonocardiography, graph of heart sounds
ultrasound
non invasive diagnostic technique, high f sound waves to measure movement of blood/fluids
properites; mechanical waves, high F low W
20Hz - 1MHZ
PEIZOELECTRIC EFFECT, give us waves for medical use
heart imaging and blood flow
ultrasonography
medical imaging technique to visualise muscles, tendons, joints
US pulse sent into tissue, sound waves hit boundary between tissues, reflected waves used to see distance between probe and tissue
doppler effect; frequency change as source and recievr of sound move close or further away
ultrasound- sonophoresis
US waves used to enhance penetration of drugs inbody, via gel or cream
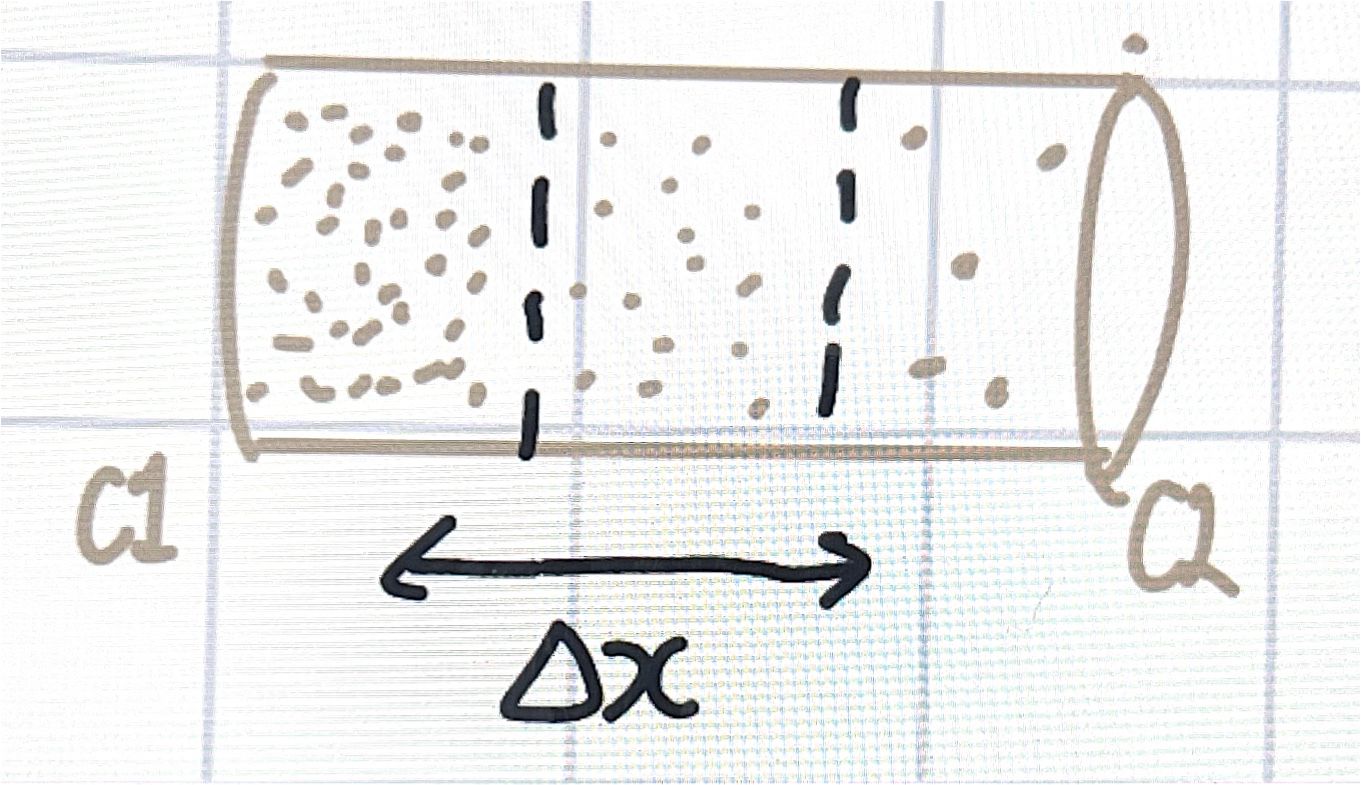
gradients
variation in physical quantity
diffusion of molecules,, conc gradient
internal friction, resistance o f flow in fluid bc friction in layers
heat conduction, heat transfer thru material by temp gradient
medical method; haemodialysis, tubing, dialyser, solution, opposite directions, urine and creatine removed
st

structure of liquids
liquids lossly packed
intermolecular forces; cohesion adhesion VDW, h bond
molecular pressue; ITMF = attraction = pressure
surface tension, cohesive forces between molecukes give elastic stretched memb
laplace pressure;
emobilisim, obstruction of blood vesslel
movement of fluids
ideal fluids hv constant density and 0 velocity
laminar; smooth no mixing, healthy person
turbulent, irregular motion, strong mixing, in aorta
steady flow, constant
poiseuilles law; rs of fluid flow rate in cylindrical pipe
reynolds no
blood flow
laminar
reynolds no is 2000
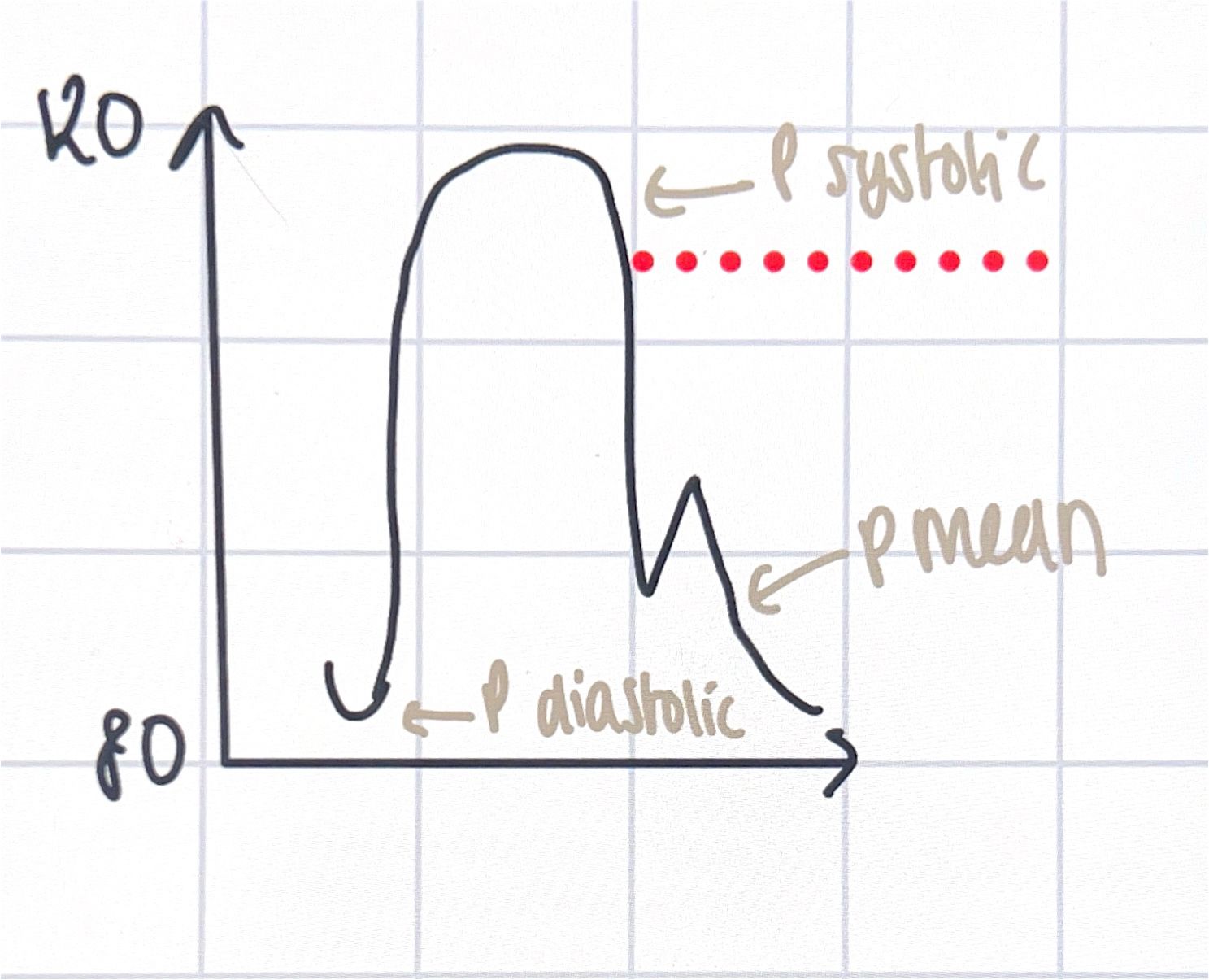
pulse pressure= s-d
systole, contraction
diastole relax
pulse wave; elastic deformation as artery walls stretch when blood moves in
mechanics of breathing
change in pressure and volume in chest allows air in and out of lungs
inspiration, diaphragm contacts
syrfactant, lining in alveolis prevents collapse and reduce surface tension
laplace law; p=2T/r
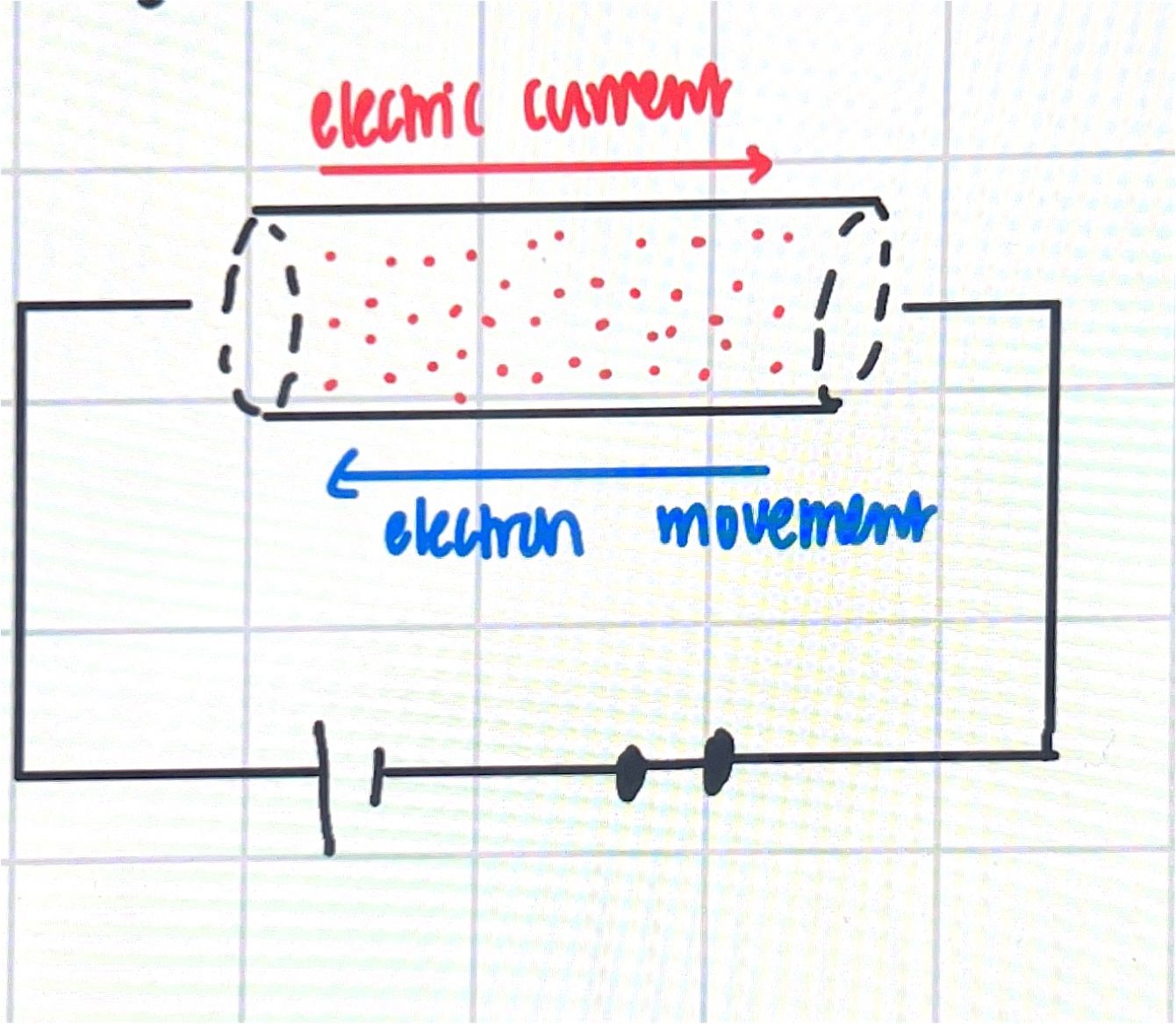
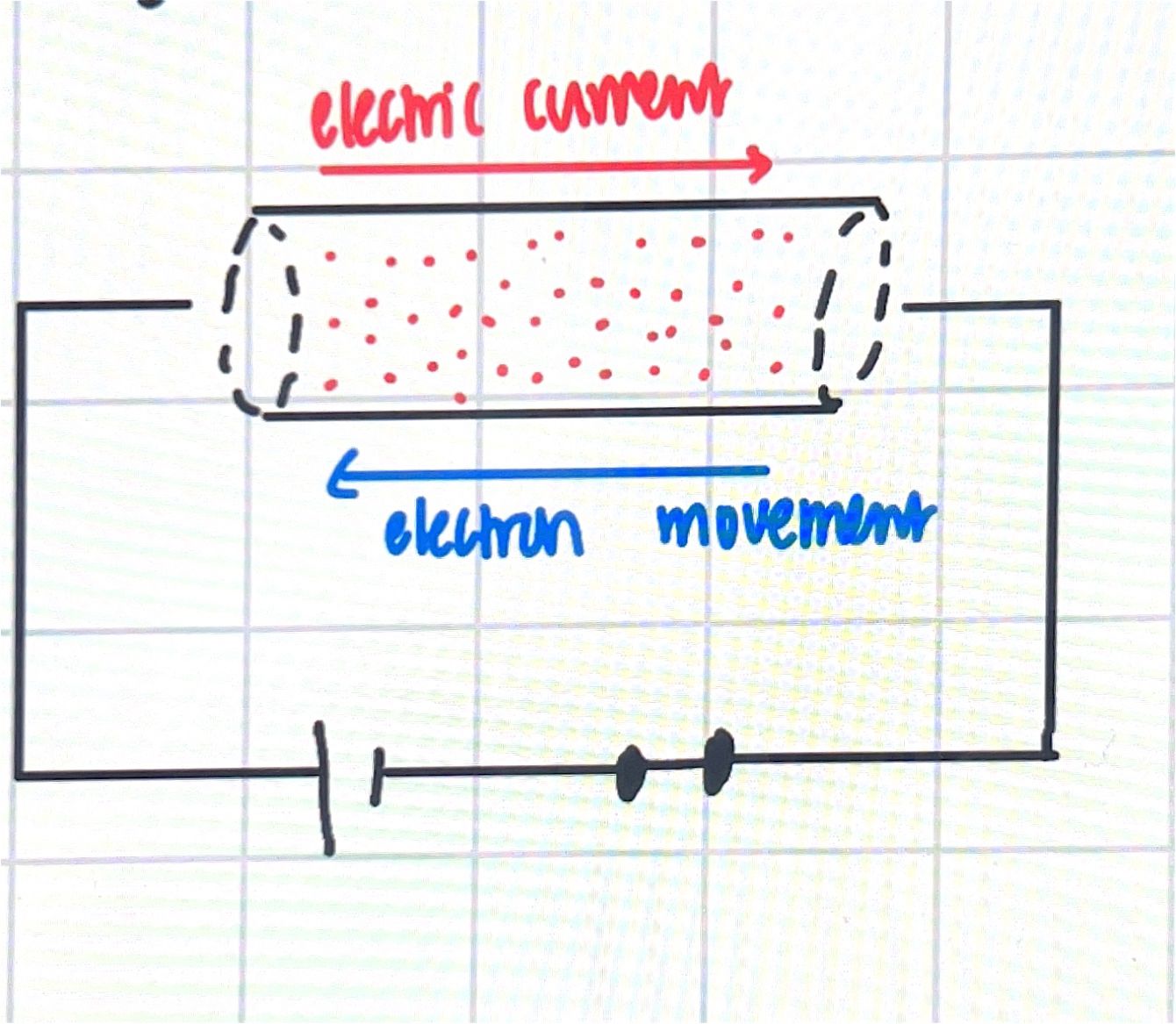
electric current
movement of charge or ions
current = charge/time
electric conductivity; electric field applied, how easily charge moves… high conductivity = easy charge flow
conductors, high conductivity bc free e-, silver
semiconductors, intermediate conductivity, temp dependant, sillicon
dielectric, no conductivity bc e- tightly bound e.g, glass
dir
direct, pulsing, ac
DC, constant flow of e- in one direction
AC changes direction and magnitude
pulsing current, current flow in discrete bursts
circuit components; switch, resistors, voltage, conductors
impendance resistance in ac
ohms law; v= I x r
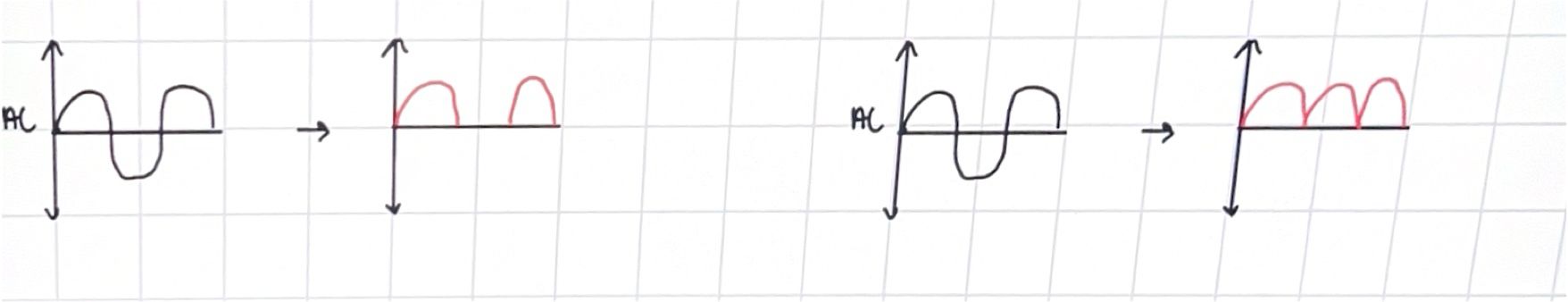
ONE AND TWO WAY CURRENT RECTIFICATION
ac > dc
one way; diode used allowing half of ac waveform to pass forming pulsating dc
two way; 2 diodes used allowing both ac waveform halves to pass
electrodiagnostics