BCR TBL 2: Electrical Properties of the Heart and Rhythm Disturbances
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Are cardiomyocytes polarised or non polarised
Polarised
What does polarised mean
Contains electrical charge
What is the Na/K pump ion movement
2 K in 3 Na out
What are cardiomyocytes connected by
Gap Junctions
What does SAN stand for
Sinoatrial Node
What does AVN stand for
Atrioventricular node
What are the bundle of cells that start a heart beat
Pacemaker cells
Where are pacemaker cells
SAN
When an impulse travels from SAN to AVN what contracts
Atria
When the impulse reaches the AVN what happens before the AVN passes on the impules
Delay
Why is there a delay
All blood can flow of atria
Where does impulse travel after AVN
Bundle of His
Where does impulse travel after Bundle of His
Left and right Bundle fibres
Where does the impulse travel after bundle fibres
Purkinje Fibres
What does the impulse in the purkinje fibres cause contraction in
Ventricles
What percentage of the heart is conductive tissue
1%
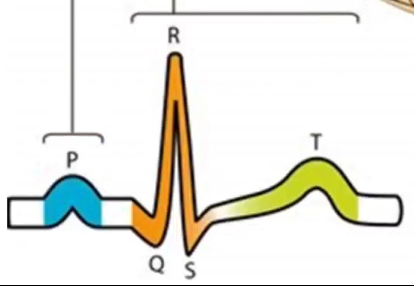
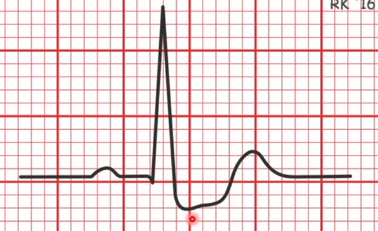
What is happening at
Depolarisation of atria
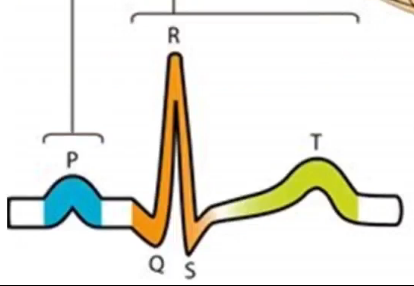
What is the QRS complex showing
Depolarisation of ventricle and repolarisation of atria
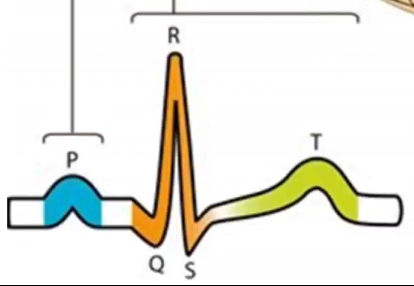
What does the T show
Repolarisation of Ventricle
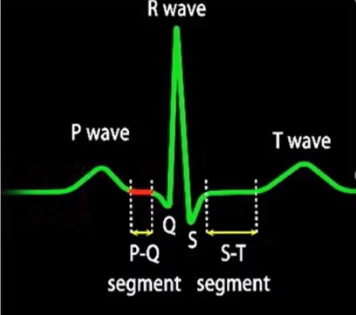
What is the PQ section
Delay
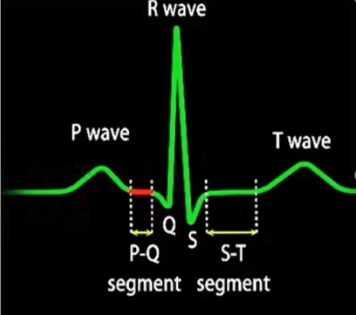
what is the ST section
End of Contraction
In a 12 Lead ECG what color is right arm lead
red
In a 12 Lead ECG what color is Left arm lead
Yellow
In a 12 Lead ECG what color is right leg lead
Green
In a 12 Lead ECG what color is left leg lead
Black
How many chest electrodes
6
Where is V1 Lead
Right side of 4th ICS space
Where is V2 lead
left of 4th ICS space
Where is V3 lead
On 5th left rib
Where is V4 5 6 lead
Laterally from 5th ICS moving Laterally
On ECG paper how much is 1mm in time
40ms
Name of receptor which detects voltage change for calcium channel in action potential
DHPR
What are calcium-activated calcium channels in sarcoplasmic reticulum called
Ryanodine
What are DHPR receptors attached to
Ryanodine Receptors
What kind of K+ channels in cell membrane
Inward Rectifier K+ channels
What is the Nernst Equation
• Vm= Membrane Potential
• R= gas constant = 8.316J K-1 mole-1
• T = absolute temperature (°K)
• F = Faraday’s constant = 96484 coulombs/mole
• z = valency of ion under consideration (z=1 for K+ )
Vm = RT / Zf ln([K+]o / [K+]i)
What is the equilibrium potential for K+
-95mv
What happens if u have an increase in [K+ ]o
Cardiac Arrhythmia or kidney disease
What is RMP(Resting membrane Potential)
-70mV
Why is RMP less than Calculated RMP
Leakage of ions
What does SERCA do (Sarcoendoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase)
pumps calcium from cytoplasm to SR
What does calcium being pumped into SR do
End Contraction
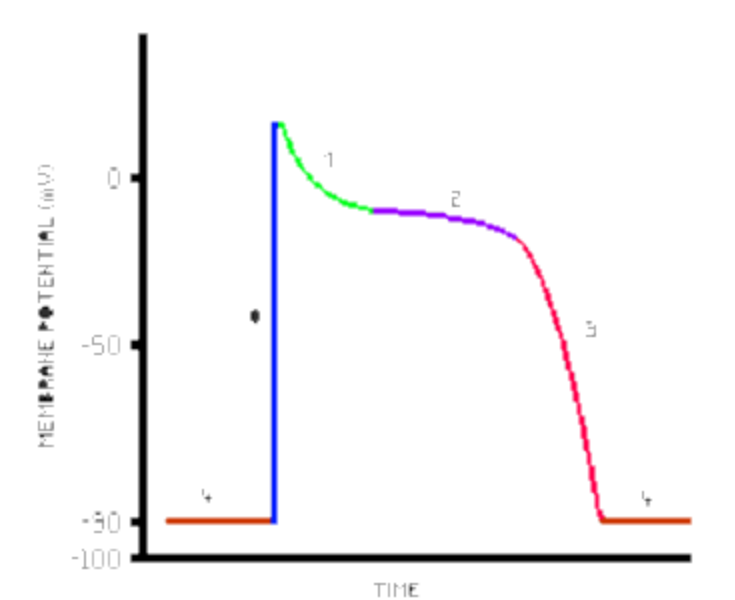
What is blue line
Depolarisation
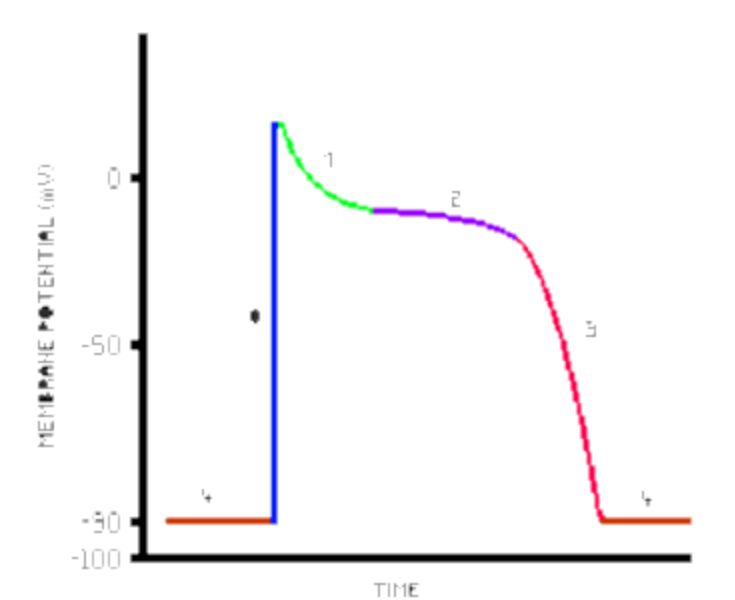
What is green line
Outward flow of K+
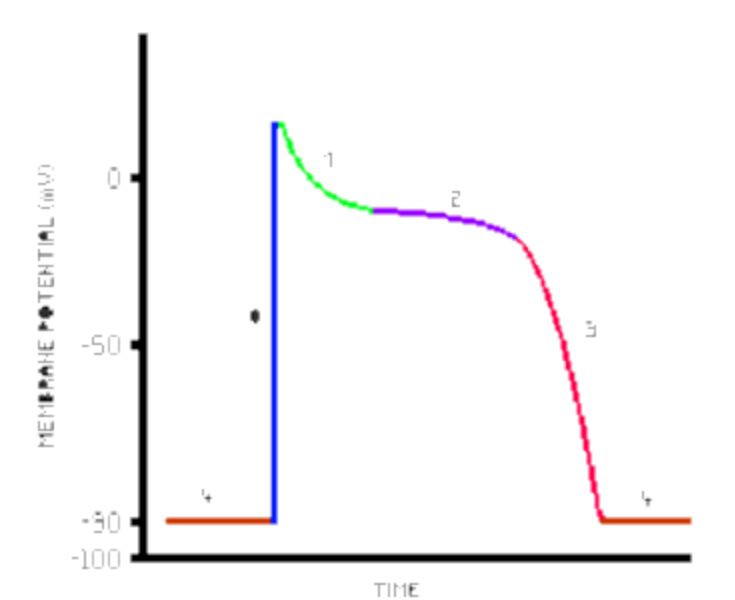
What is purple line
Opening of DHPR
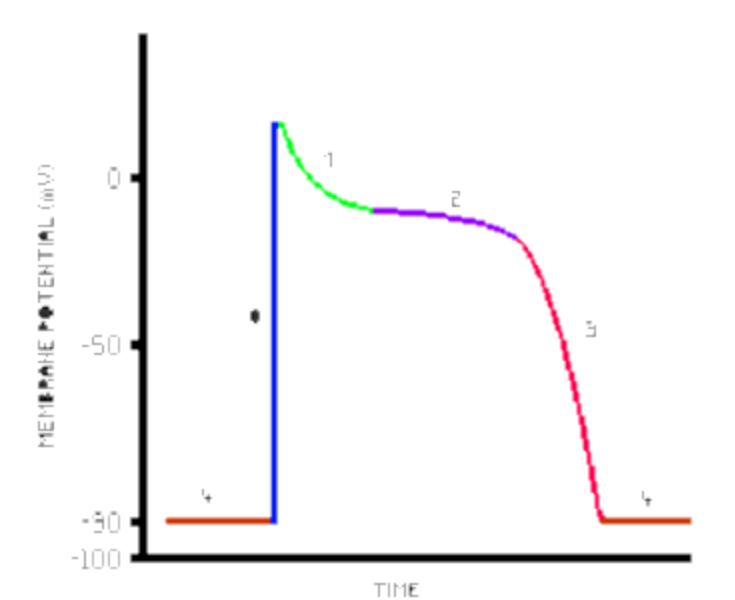
What is Pink line
Calcium channels inactivate
8 Step approach to ECG
Rate Rhythm Axis P wave PR interval QRS complex ST segment T wave
What should ECG rate be roughly
60-100
What can changes in ST phase lead to
Angina
How much is a Small square in ECG in seconds
0.04
How much is a big square in seconds in ECG
0.2
How to work out BPM using RR interval
300/RR
For irregular heart rate how do you work out heart rate
QRSx6
Automaticity refers to
Cells ability to spontaneously depolarise
Conduction block refers to
Impulse encounters non excitable tissue
Re-entrant Circuits are when
Impulse circulates in loop due to non conducting tissue
Triggered Activity is when
Normal AP which triggers Abnormal AP
Is summation possible in cardiomyocytes
No
What are latent pacemakers
Backup pacemakers in lower conducting tissue
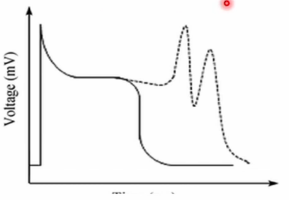
Early afterdepolarisation
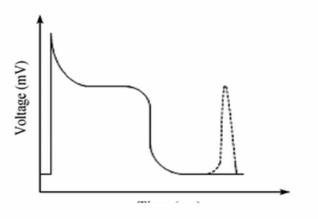
Delayed afterdepolarisation
What is Tachycardia
More than 100BPM
What is BradyCardia
Less than 60BPM
What is the main kind of Conduction block
AV block
What happens in first degree AV block
PR interval is more than 200ms
What is happens in atrial fibrillation
Small Chaotic contractions no P wave narrow QRS complex arrhythmia
What Happens in atrial flutter
Narrow QRS complex sawtooth p wave
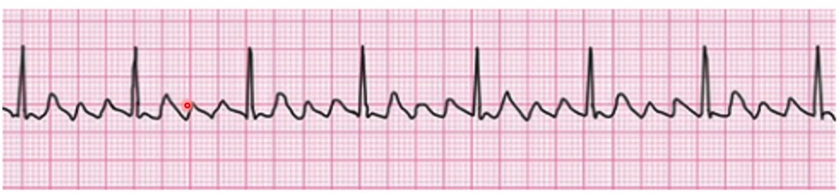
Atrial Flutter
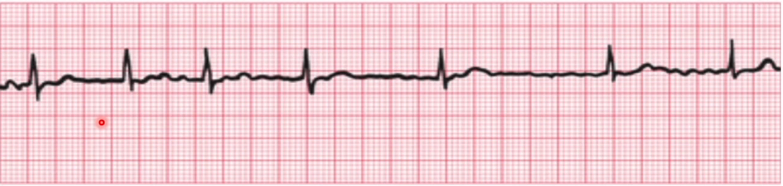
Atrial Fibrillation
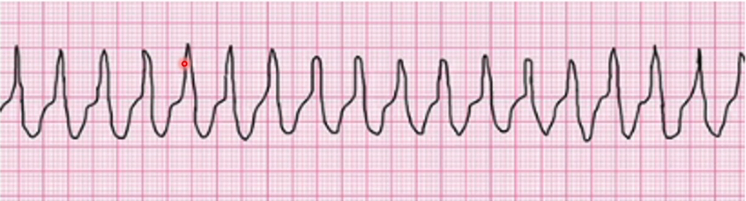
Ventricular Tachycardia
What happens in Ventricular Tachycardia
No p Waves Wide and regular QRS complex no T wave
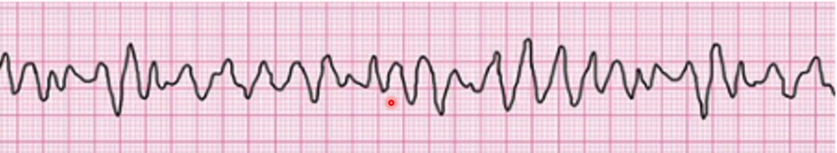
Ventricular Fibrillation
What happens in Ventricular Fibrillation
Irregular peaks No complexed Varying amplitude
What does ICD do
Shock a heart during Ventricular Fibrillation
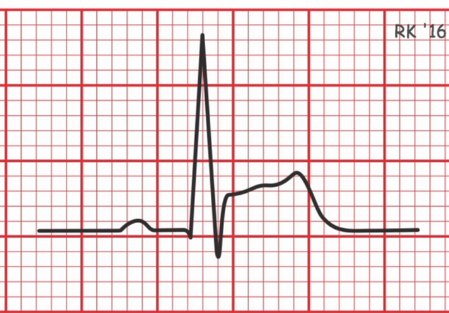
Myocardial Infarction
What happens during myocardial Infarction
ST elevation
Cardiac Ischaemai
What happens in Cardiac Ischaemia
ST Depression
what does the sum of cardiac vectors show
Mean Electrical Vector
If impulse travels to positive electrode which way is projection on ECG
Upwards
If you have Left axis Deviation which leads are inverted
II and III
If you have right axis deviation which leads are inverted
I
If you have extreme right axis deviation which leads are inverted
All of them