Ch. 11 New Product Development Process
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
New-to-the-world
Products that are entirely new and have never been seen before.
New product lines
Products that are introduced to a new category that the company has not previously offered.
Line extensions
Products that are variations of existing products within the same category.
Improvements/revisions
Products that have been modified or enhanced from their original versions.
Repositioned
Products that are marketed for a different use or to a different audience.
Idea screening
The process of evaluating ideas to determine their feasibility.
Business analysis
The assessment of the market potential and profitability of a new product.
Development
The stage where the product is designed and developed.
Test marketing
The process of introducing a product to a limited market to gauge its performance.
Commercialization
The full-scale launch of a product into the market.
Innovators
Consumers that have a strong desire to have all new products on the market, accounting for 6-10% of the population.
Early Adopters
Consumers who make up 14-18% of the population, love publicity, and act as leaders of opinion.
Early Majority
Consumers who represent 30-33% of the population and are more skeptical about new technologies. Do thorough research before purchasing.
Late Majority
Consumers who make up 30-33% of the population, often buy products due to peer pressure. Lower income, lower education, older.
Laggards
Consumers who account for 6-10% of the population, often live in remote areas and have limited access to media. Oldest, least income and education.
Complexity
The usage of a product.
Compatibility
The degree to which a new product fits with the consumer's existing lifestyle and knowledge.
Relative advantage
The degree to which a product has a better advantage over other products.
Observability
The extent to which the benefits of a new product are visible to consumers.
Trialability
The ability for consumers to try a product risk-free, which increases the likelihood of purchase.
Product Life Cycle (PLC)
The stages a product goes through from introduction to decline.
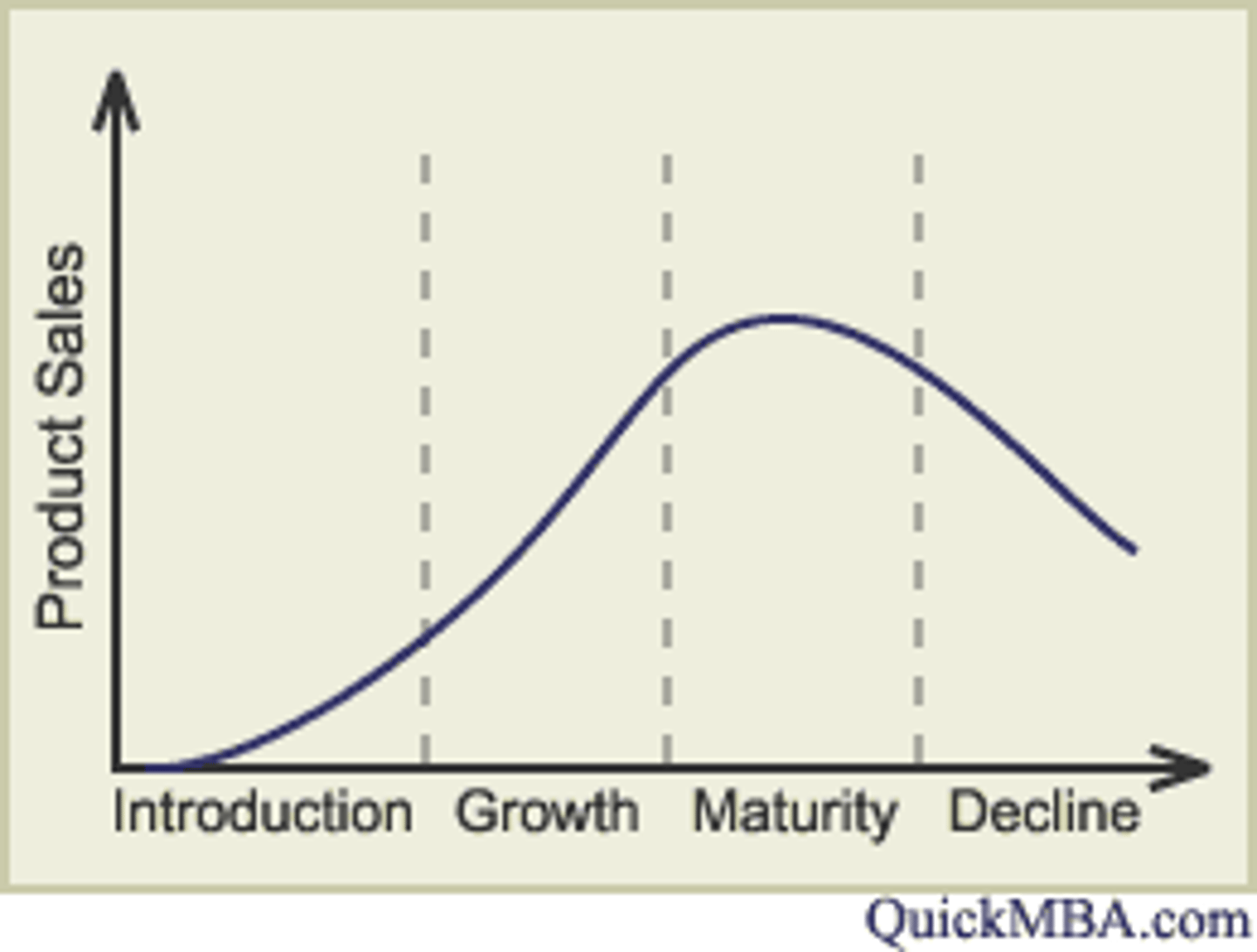
Introductory stage
The phase when a new product is first launched, characterized by low sales and high costs.
Growth stage
The phase where sales increase, costs decrease, and profits rise.
Maturity stage
The phase where sales peak and profits are high, with a stable number of competitors.
Decline stage
The phase characterized by falling sales and profits, with a contracting customer base.
Perishability
The characteristic of services that makes them time-sensitive; unsold services result in lost revenue.
Intangibility
Suggested quality, physical cues to communicate quality of service to consumers.
Heterogeneity
The variability in service quality.
Inseparability
The production and consumption of services are inseparable and spontaneous.
Service Quality
The assessment of how well a delivered service meets customer expectations.
Reliability
Dependability, consistency, and accuracy
Responsiveness
How long it takes for companies to respond back about an issue
Assurance
Ability to convey trust to the customer.
Empathy
Customers being able to relate to the problem.
Tangibles
Physical work and cues to indicate the quality of care in the service.
The Service Gap Model
A framework that identifies gaps between customer expectations and actual service delivery.
Knowledge gap
The discrepancy between what customers want and what the company thinks they want.
Policy gap
Gap between what the company's understanding is of customer expectations versus the policy that they create.
Delivery gap
The difference between the service that was promised and the service that was delivered.
Communication gap
The difference between what was promised to the customer and what actually occurred.
Customer gap
What the customer expects versus what they receive and how they perceive it.
Product (Service) Strategy
The approach taken to deliver services based on how they are processed.
People processing
Services that require customers to be present during the service delivery.
Possession processing
Services that are performed on the customer's possessions.
Information processing
Services that involve the processing of customer information.
Mental stimulus
Services that provide entertainment or mental engagement, such as movies and concerts.
Divesting
Getting rid of old technology and moving on to other products.
Harvesting
Keep the product and market it as a niche product.