15 - Ecotoxicology, Foodwebs, and Biomagnification
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Foodwebs
Interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem
Food chain
A sequence of organisms in which each organism is the food source for the next
Biomagnification
Increase of environmental chemicals in organisms with hierarchical increases in a food chain
Box Models
Models used to represent the flow of organic matter in ecosystems, depicting the input and output
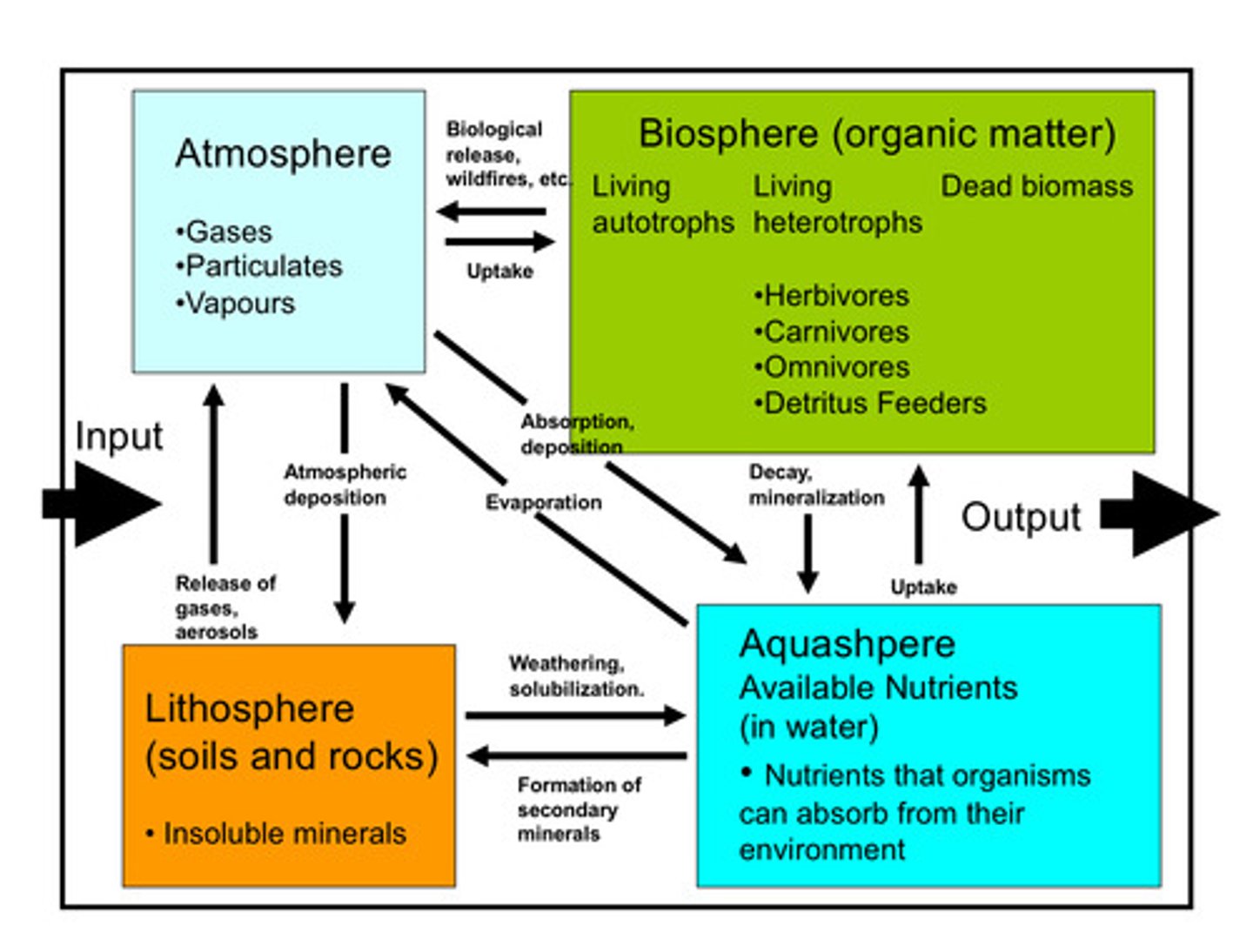
Biosphere
The part of the Earth where life exists, including organic matter
Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding the Earth
Biological release
Release of substances by living organisms, such as through wildfires
Dead biomass
Organic matter that is no longer living
Living autotrophs
Organisms that can produce their own food through photosynthesis
Living heterotrophs
Organisms that obtain their food by consuming other organisms
Uptake
Absorption or intake of gases, particulates, vapours, herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, or detritus by organisms
Mineralization
The conversion of organic matter into inorganic minerals
Atmospheric deposition
The deposition of substances from the atmosphere onto the Earth's surface
Output
The removal or release of substances from an ecosystem
Lithosphere
The solid outer part of the Earth, including soils and rocks
Formation of secondary minerals
The creation of new minerals through chemical reactions
Aquasphere
The part of the Earth that consists of water
Top predator
The highest level predator in a food web
Intermediate species
Species that occupy a middle position in a food web
Basal species
Species that occupy the lowest level in a food web
Node
A point in a network where lines intersect or branch
Trophic Pyramids
Diagrams that show the distribution of energy or biomass among trophic levels
Ecological Efficiency
The efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels in an ecosystem
how does ecological efficiency change as you go up the pyramid?
it decreases, meaning it can support less individuals
Energy transfer
The movement of energy from one organism to another in a food chain
Consumer
An organism that obtains energy by consuming other organisms
Producer
An organism that produces its own food through photosynthesis
Trophic Efficiency
The percentage of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next (10%)
Bioconcentration
Equilibrium distribution of a chemical within an organism and its concentration in the environment through passive absorption and excretion (org:enviro)
Passive absorption
Absorption of a chemical in an organism through the gills or skin
Excretion
The elimination of a chemical from an organism
Bioaccumulation
Build-up of a chemical in an organism through bioconcentration and food inputs
Bioaccumulation factor
The ratio of the concentration of a chemical in an organism to its concentration in the environment, considering all sources
biomagnification
the relative increase of environmental chemicals in the tissues of organisms with hierarchical increases in a food chain, taking into account both bioconcentration AND bioaccumulation
Biomagnification factor
The ratio of the concentration of a chemical in an organism to its concentration in the environment, taking into account bioconcentration and bioaccumulation
Net Trophic Transfer Efficiency
The efficiency of transfer of a chemical through trophic levels in a food chain
ecosystem
A community of organisms and their abiotic environment
why is the ecological system perspective useful?
it allows to understand how everything is dependent on each other - how there are so many factors which influence a living being, allowing us to understand where inputs and outputs are coming from, why they exist, etc.
what is an ecosystem composed of (spheres)?
atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere
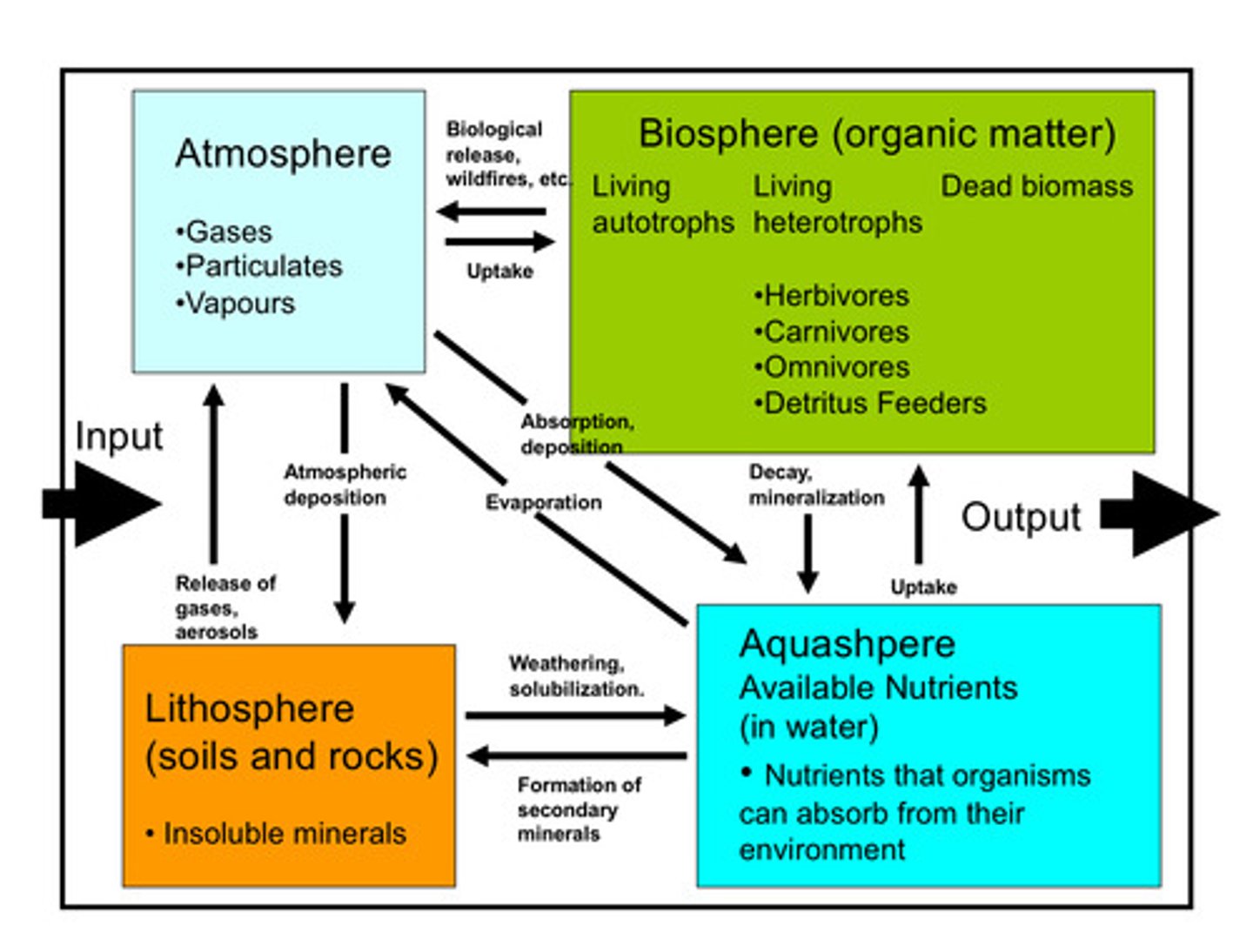
how can particles move between compartments of ecosystems?
biological processes (consumption, decomposition, excretion), physical processes (weathering, sedimentation, erosion, mineralization), hydrological processes (water cycle, groundwater movement), and atmospheric processes (gas exchange (nitrogen, oxygen, carbon cycle), deposition)
why can a human be described using the ecosystem model?
biotic and abiotic factors; biosphere is human body and organisms living on it, including interactions between cells, organs etc.; hydrological and atmospheric processes; cycling elements/nutrients through the body similar to how ecosystem does it