SAS 13-14: PROGRAM PLANNING
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
planning
the process of planning is a dynamic one
E.C. Banfield said “plan is a decision about a course of action”
the process itself must remain fluid and flexible which are responsive to the presentation of new factors and issues.
the planner should consider that one of the most important things to look into aside from the statistics present is the human element
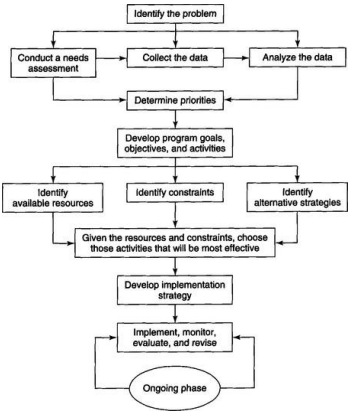
a systematic approach to defining the problem, setting priorities, developing specific goals and objectives and determining alternative strategies and a method of implementation.
2 perspectives about planning
planning by the person within the system or organization who is usually a full-timer
planning by someone brought in from the outside whose job is to help the organization in formulating new proposals and/or making recommendations for changing some existing plans.
insider
can make decisions more quickly regarding appropriate action
advantage: has a true understanding of the issues and operation of the system including its subtle conditions
disadvantage: might already have acquired certain biases about the system which could influence his/her objectivity
outsider
advantage: might bring a fresher outlook, less bias and a greater sense of objectivity
disadvantage: requires more time to understand the system to sufficiently plan an appropriate course of action
conducting an assessment
may be necessary for issues of a medical nature.
requires significant financial, labor, and time resources
the choice of method depends on the target population and the nature of the assessment
the information needed and the methodology for data collection should be clearly defined
planners may partner with other organizations or utilize existing surveys when funds are limited
considerations include the number of participants, the severity of the issue, and the attitudes of those surveyed
data can be obtained through various techniques: survey questionnaires, clinical examinations, or informal communications
formal methods are suited for larger, more severe issues, while personal communications may better capture individual attitudes
reason for conducting a needs assessment
to define the problem and its extent and severity
to obtain a profile of the community to find out the real cause of the problem
to evaluate the effectiveness of the present program if there is which can be accomplished by obtaining baseline information and measuring the progress achieved in solving the problem.
such profile should be included
rate of growth
ethnic backgrounds
general health profile
diet and nutritional levels
public and private school system
number of individuals in the population
geographic distribution of the population
patterns and distribution of dental disease
population density and degree of urbanization
amount and type of public services and utilities
standard of living, including the types of housing
other questions that should be included
what types of programs exist?
how successful was the program?
what was the community’s acceptance of the program?
are the programs oriented toward prevention, treatment, education, research or a combination?
who or what organization is responsible for the planning, implementation and or administration of the program?
aspects that need to be explored
who are the financial leaders?
who sets the policies for the community?
what is the organizational structure of the community?
what are the community leaders’ attitudes toward the oral health and community dental programs?
questions to ask regarding the funds
what is the source of funds for dental care?
questions to ask regarding the facilities
are the facilities accessible?
are the dental services provided well?
how many dental care offices are available?
what are the existing facilities for dental care?
how well are the facilities used by the population?
questions to ask regarding the labor
is there a dental school in the area?
how many laboratory technicians are available?
how many active dentists and dental assistants or dental aides are available?
general information on how the population should be obtained
utilize clinical examinations, dental records, and governmental data for epidemiologic data
assess dental disease incidence and distribution, and history of community dental programs
examine community resources for effective program implementation
understand fluoride presence in drinking water to avoid duplication
in small communities, health departments typically have data on health status, morbidity, and health service utilization
understand socioeconomic structure to determine community's ability to afford dental care
address cultural and language issues by identifying population breakdown and age distribution
use educational status to understand community values and health awareness programs
guide healthcare facilities by guiding types and costs of services
keep fluoride status updated for accurate dental planning
support school-based dental programs.
determining priorities
involves applying values and judgments to raw data
it serves purposes like ranking problems and solutions
identifying the target group based on dental issues is crucial
community representative involvement aids in program implementation and acceptance
planners should establish program goals and objectives following target group identification.
2 types of objectives
outcome objective
process objective
outcome objective
provides a means by which it measures quantitatively the outcome of a specific objective
ex: by the year 2019, more than 50 % of the population aged 5-12 years in Barangay Mahimsog will not lost any teeth due to caries.
process objective
will state a specific process by which a health problem can be reduced and prevented
ex: By 2015, Barangay Mahatagon will have a public fluoride program to guarantee access to fluoride exposure via the public water supply.
the objectives should specify the following:
where: the geographic areas of the program
what: the nature of the situation or conditioned to be attained
extent: the scope and magnitude of the situation or condition to be attained
who: the particular group or portion of the environment in which attainment is desired
when: the time which the desired situation or condition is intended to exist using the words “at” or “by”
program goals
broad statements on the overall purpose of a program to meet a defined problem
program objectives
the specific avenues by which goals are met
more specific and describe in a measurable way the desired end result of program activities
program activities
this will describe “how the objectives will be accomplished”
how to bring about the desired result of the program, after the program goals and objectives have been stated.
3 components of program activities
who will be doing it
when will it be done
what is going to be done
criteria of identifying resources
appropriateness: the most suitable resources to get the job done
effectiveness: the capability of the resources in completing the job
efficiency: the cost and the time that might be spent to complete the job
adequacy: the extent or degree to which the resources would complete the job
identifying constraints
at least 1 or 2 alternative strategies are acceptable
often arise during the planning stage of programs, presenting obstacles to achieving objectives
may stem from organizational policies, resource limitations, or community characteristics
identifying it early allows for modifications to the program's design, leading to a more practical plan
community members can propose alternative solutions to achieve the program's goals and objectives
engaging a group of concerned citizens can help as they are knowledgeable about local politics and community structures
implementation phase
the process by which the plan is put into operation
will involve also the individuals, organization and the community
there should be teamwork between the individuals and the environment so that its implementation can be a success.
developing implementation strategy
why the effect of the objective is to be achieved
when is the chronological sequence of activities
who are the individuals responsible for each activity
how much are the cost estimate of materials and time
what are the activities required to achieve the objective
how are the materials, methods and techniques to be used including the documentation
rules for implementation strategy development
identify the constraints that will need to be addressed
specify the resources that will be needed and their source
determine the date when each step should begin and end
make sure that the time allotted for each step is sufficient
check for the missing steps which might need to be added
properly listing down the order by which the activity must occur.
the activity should be clearly specified. (as to who will do it, what for, for whom)
make sure that all people involved will know what is/are expected from them and when
a point person who will be responsible for the whole activity and to coordinate between all the individuals who will carry out the different tasks should be identified
consult with whoever will be affected by the activity or activities. this can be individuals or organizations. identify the potential problems or opportunities
identify all the preparatory steps prior to doing the activity. (for example the preparation of the training manual, preparations of the materials, acquire equipment, train volunteers, determine treatment protocol and camera for documentation)
monitoring, evaluating and revising the program
program revisions possible before or during implementation
understanding recipient perspectives for varying satisfaction views
continuous monitoring of program activities for success assessment
both formal and informal evaluations for work quality and recipient attitudes
proactive identification of potential problems for timely program improvements
evaluation of individual performance, equipment functionality, and facility adequacy
importance of evaluation
plan revision and modification
measure the progress of each activity,
measure the effectiveness of each activity,
identify problems in carrying out the activities,
justify the cost of administering the program and if needed, justify the need for additional funds.
the summary of all the steps needed in planning a program