KNR 225 Exam 2 (Ch, 5,6,7,8)
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
Prenatal Factor Affecting Motor Development
- a number of factors, many of which can be controlled, affect motor development during infancy and beyond
Leading Causes of Infant Mortality
1. congenital malformation
2. low birth weight
3.) sudden infant death syndrome
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
common causes...
-not practicing safe sleep in crib
-cord + placenta complications
-mother being young
-bacterial sepsis of newborn
-diseases of circulatory system (viral infections, pericarditis)
-neonatal hemorrage
Cord and Placental complications
-cord around baby's neck
-cord is either too long to too short
-knotting of cord
-placenta malnutrition and injury
Bacterial Sepsis of Newborn
-cured with antibiotics
Disease of circulatory systems
-viral infections
-pericarditis
Neonatal Hemmorage
stroke
average age of women having first child
27.3 years old.... it is increasing... in 2011 it was 25.6. Could be due to women wanting to get their education/career beforehand, socioeconomic, etc
Factors in high risk pregnancy
-maternal malnutrition
-lack of access to quality medical care
-air pollution
-cig smoke/tobacco/vaping
-viruses or infections
-drug use, medication, prescription or over the counter
-alcohol
-medical history
Considerations for maternal drug use
-timing during pregnancy
-dosage of the drug
-length of consumption
-genetic disposition
Reasons for malnutrition
-dietary habits
-poverty/socioeconomic staus
-stress
Types of malnutrition PRIOR to birth
-placental malnutrition: supply transport issues
-fetal malnutrition: fetal metabolism complications
-maternal malnutrition: inadequate nutritional intake
genetics during pregnancy
-union of sperm and egg
-chromosones
-determines sex, hair, eye color, body size, physical structure
Typical development of chromosomes
2 pairs of 23 chromosones, 46 in total
chromosomal based disorders
-atypical development
-miscarriages, 43% of pregnancies end in miscarriages
-most miscarriages are bc of chromosomal abnormalities
Chemical Teratogens
any substance that may cause the unborn child to develop in an abnormal manner.
Alcohol impacting mother and infant
-the leading cause of birth defects in the US
-approximately 40,000 newborns/year are impacted
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD)
-formerly known as fetal alcohol syndrome
-when the mother ingests alcohol during pregnancy
-permanent
-100% preventable- dont drink while pregnant
-results cognitive and physical defects such as central nervous system defects and physical features.
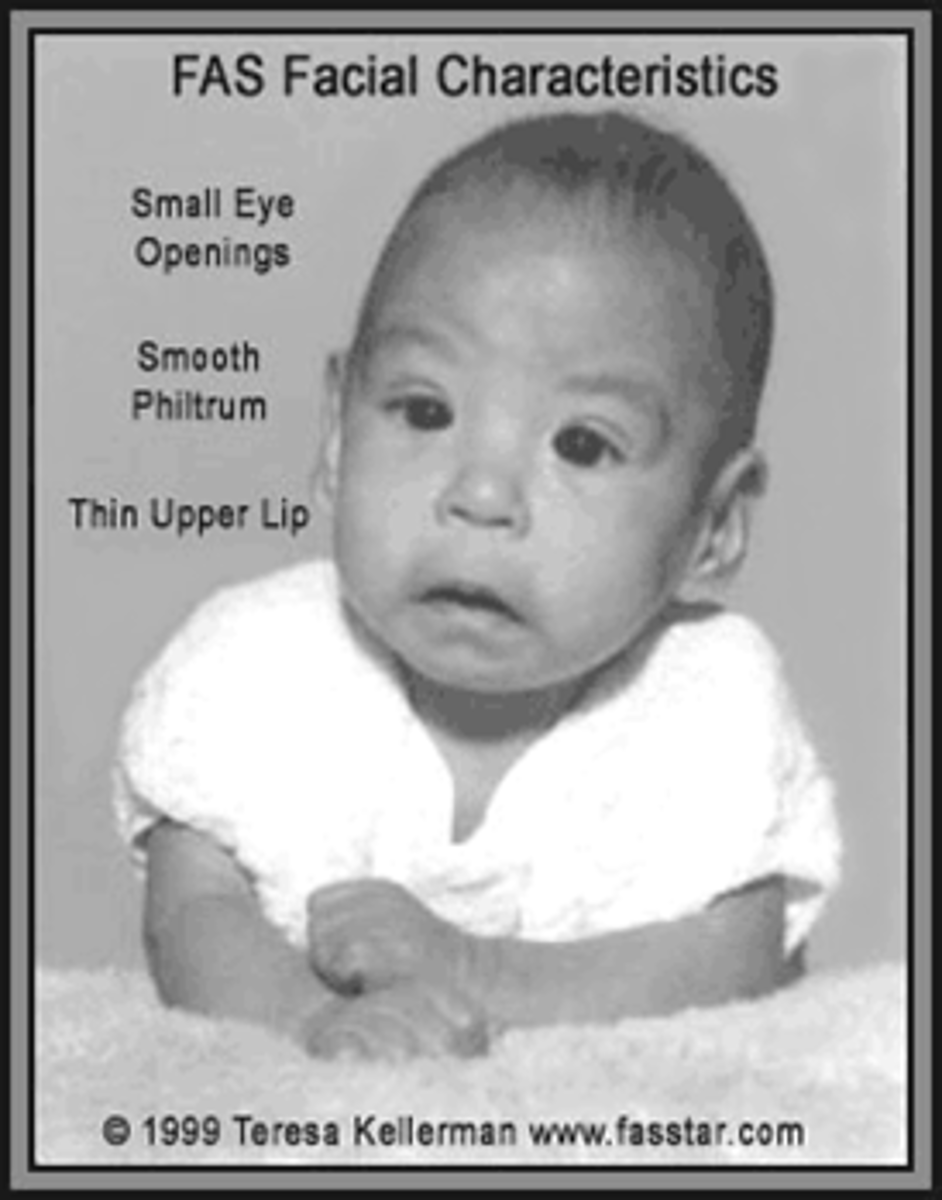
fetal alcohol spectrum disorder physical features
-smooth ridge (philtrum) between nose and upper lip, thin upper lip, small eyes
Tobacco and Liquid Nicotine impacting mother and infant
-maternal smoking is linked to SIDS.
-also increases chance of miscarriage
-speeds up fetal heart rate
-increases chance for early deliveries
-1 in 5 babies are LBW if mother smokes
babies in utero AND after birth are 3-4x more likely to die from SIDS when the mother...
smokes. (2nd hand smoke for after birth)
Drugs impacting mother and infant
-necessary maternal drugs
-over the counter drugs
-illegal drugs
-impacts infant reflex scores
if the mother does illegal drugs while pregnant it can
-cause permanent brain damage
-low birth weight
-learning disabilities
-or death of baby
Chromosonal Disorders
-duchenenes muscular dystrophy
-prader willi
- trisomy- 21 (down syndrome)
the term for down syndrome
trisomy-21
Down Syndrome
-most common chromosomal alteration
-tied to the mother
-extra chromosone
-if mother is 35 or older, increases chance of DS
down syndrome traits
-premature
-short
-cognitive delays
-intellectual disability
-heart conditions
-decreased muscle strength (hypotonia)
-poor vision
down syndrome motor skills
-poor balance
--bilateral coordination issues
-normal sequence of motor dev, just delayed
Atlanto-axial subluxation
-the ripping away of vertebrae in the neck
-not able to put any sort of pressure on the neck (like headstands)
-greater chance of this in ppl with down syndrome, but anybody can have it
Chris Nickic
-man with down syndrome who runs triathlons, has many endorsements, and a business called 1% better (bc he has an extra chromosone)
motor development research and infants with down syndrome
-delays in emergence of reflex
-delays in attaining motor milestones
Dr. dale ulrich treadmill study
treadmill group walked 180 before the group that didn't get the didn't. once walking starts other voluntary and fundamental movements begin.
Prader- Willi Syndrome
-chromosomal
-intellecutal disability
-severe obesity
-extreme severe appetite
-passed down by the father
-hyperphagia (the person never feels full)
-poor sucking reflex at birth
-low muscle tone at birth
Duchenne's muscle dystrophy
-mom is the carrier
-only in male children
-always ends in death- 20s or 30s
-around age 7, all motor skills start regressing. even walking, writing, etc.
-must use wheelchair. all muscle strength gone, even the heart
high risk pregnancy
a pregnancy characterized by risk factors that make it likely the birth will be surrounded by problems such as premature delivery, difficult birth, delayed growth, birth defects, or SIDS
prenatal malnutrition
- common cause or later developmental difficulties
-results in 3 factors: placental factors, fetal factors, maternal factors
-mothers poor nourishment due to poverty, low SES class, anxiety, stress, and trauma
-can cause birth defects (spinal bifida)
Placental Malnutrition
-problems with the supply and transport of nutrients to the baby
Fetal malnutrition
-inability on the part of the developing fetus to use the nutrients available to it
-complication with metabolism of fetus that interrupts normal use of available nutrients
maternal malnutrition
-deficiencies in mother's diet both prior to and during pregnancy can have harmful effects on child
- a sound nutritious diet is absolutely essential for the mother's health and that of her unborn child.
-poverty/socioeconomic status
-stress
malnurishment
-Mother and child not receiving the proper nutrients through their normal daily intake of food
Factors considered on influence of drug on unborn child
-the point in the pregnancy at which the drug is taken
-the dosage of the drug
-the length of time the drug is taken
-the genetic predisposition of the fetus
-how the preceding factors interact
Common maternal drugs
-pregnant women need to take extra precautions with any kind of drug use
-Maternal drugs and medications frequently affect the fetus and later motor development
-
"Necessary" maternal Drugs
-drugs that a mother needs to take due to an underlying chronic illness
-example: chemo, epilepsy, migraines
-may need to be modified with pregnancy
Psychoactive Drugs
-drugs that act on the nervous system to alter states of consciousness
-opiates, cocaine, meth, marijuana, and heroin
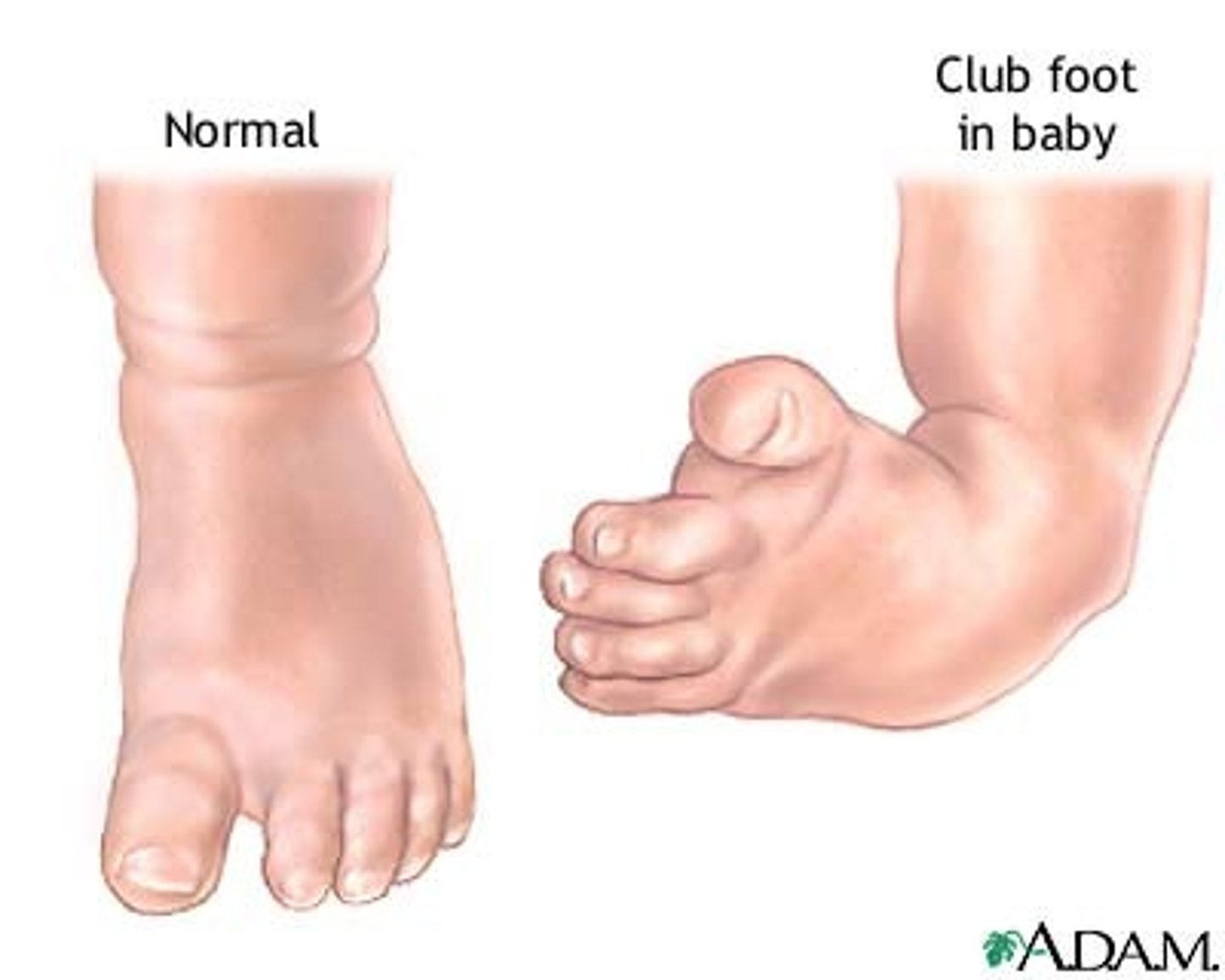
Talipes (club foot)
-three forms: equinovarus, calcneal, and metastarus
-one of most common birth defects
Equinovarus
foot twisted inward and downward
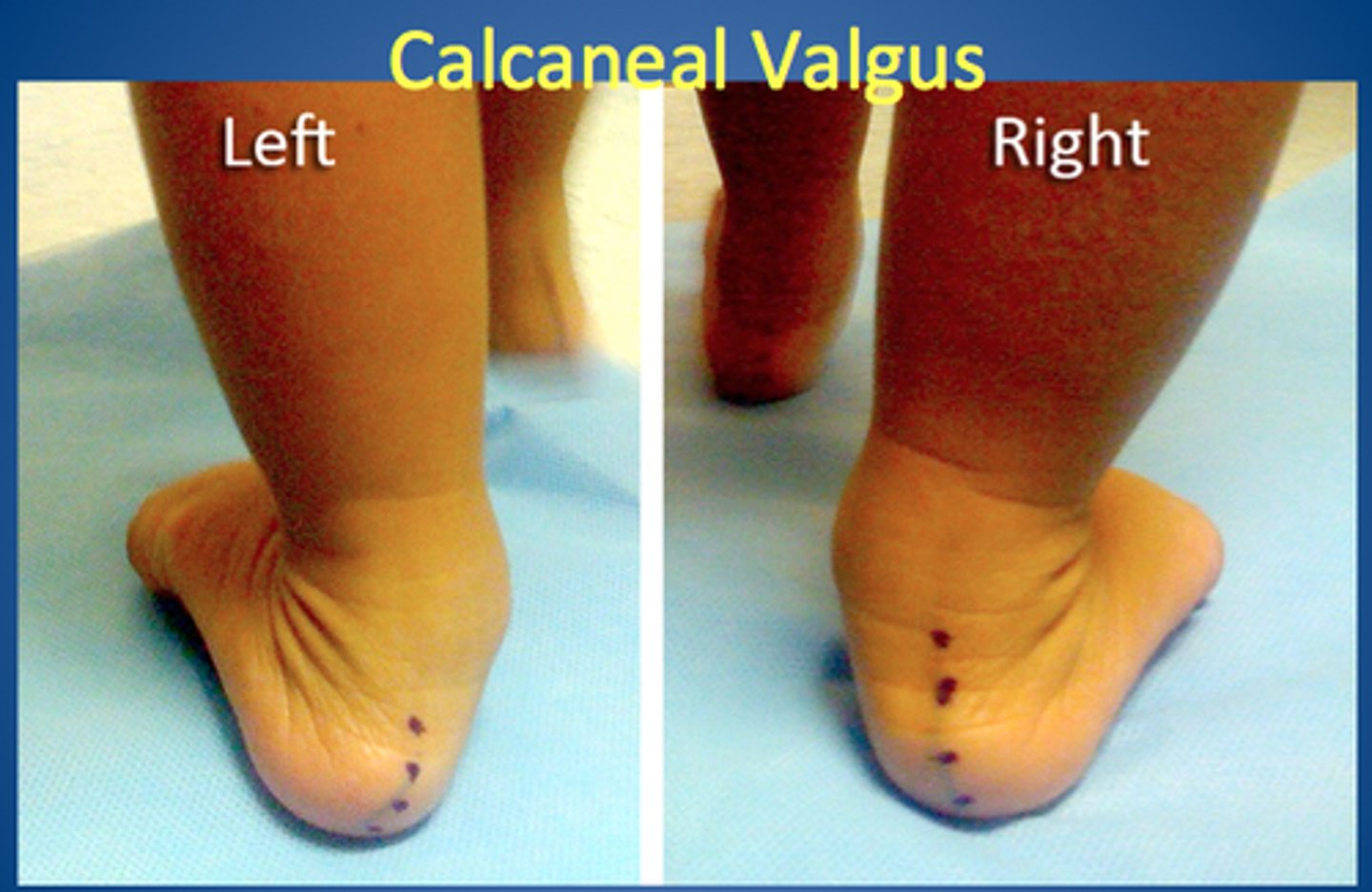
Calcaneal Valgus
most common, foot sharply angled at the heel and pointing up and outward
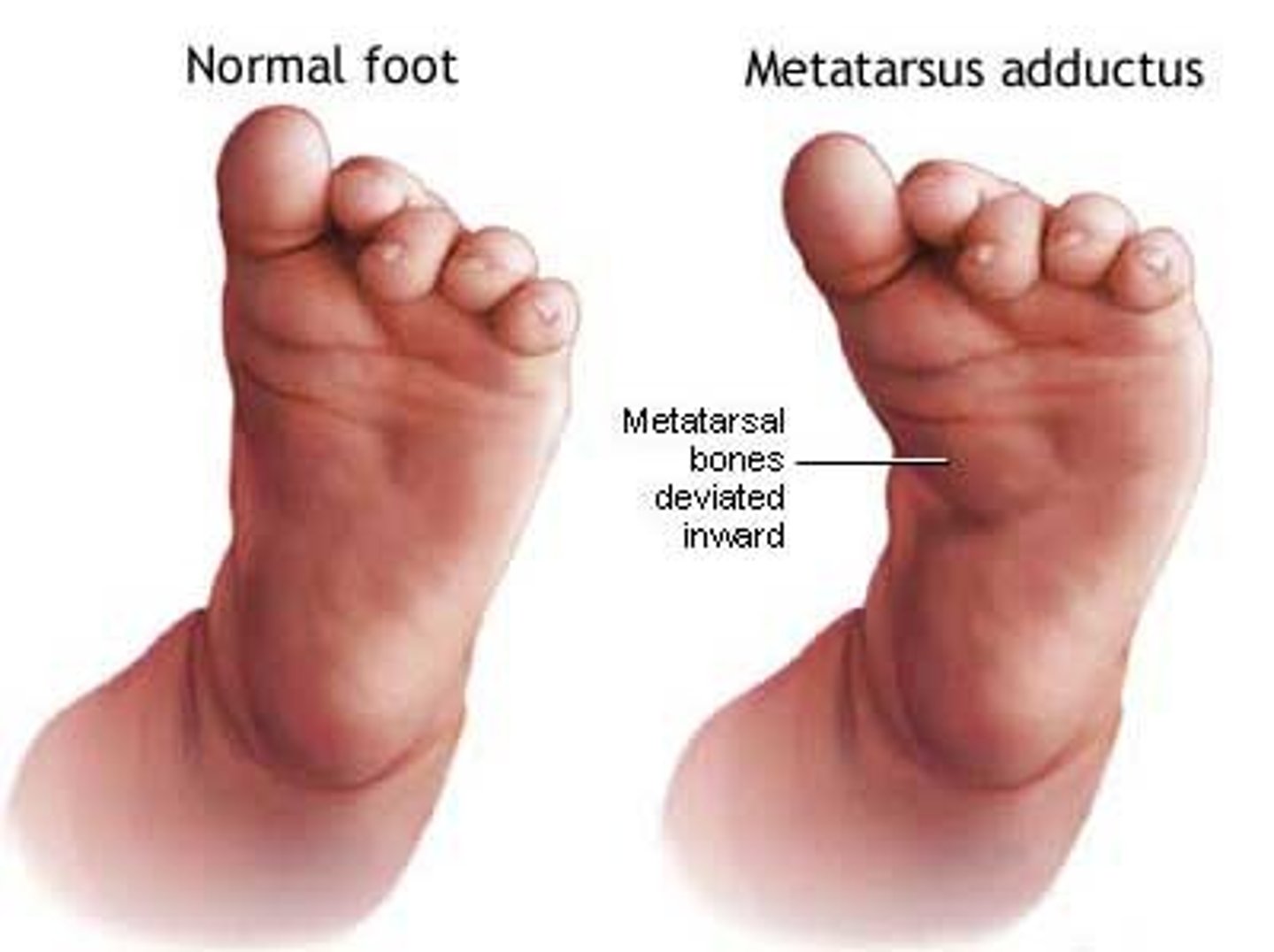
Metatarsus Varus
mildest, front part foot turned inward
Sickle Cell Disease
-Inherited disease that affects red blood cells
-growth and motor dev of individuals with this disease are often impaired. shorter stamina and short of breath.
Tay-Sachs Disease
-gene based disorder that typically affects central and eastern european jews
-appears in infancy with the baby losing motor control, bildness and paralysis follow
-death by age 5
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
-metabolic disorder that is the result of a recessive gene that stops production of phenylalanine hydroxylase , which is necessary to convert the amine acid phenylaline to tyrosine
-w/o the enzyme, the child cannot digest many foods such as dairy products
-if untreated, it will result in severe cognitive impairment, seizures, and physical growth delays/motor dev
-if treated within a week of birth, these issues can be greatly decreased or completely avoided
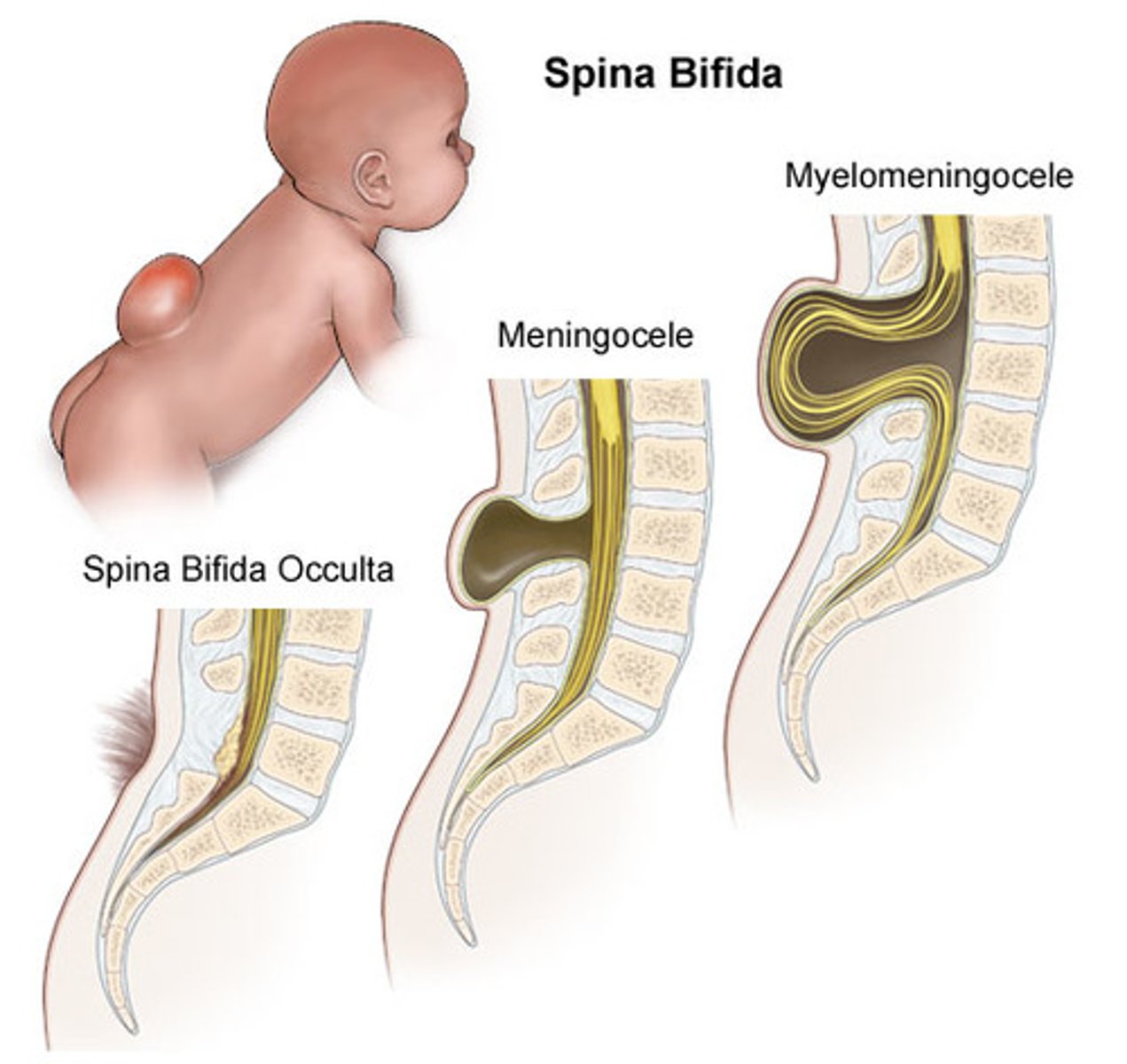
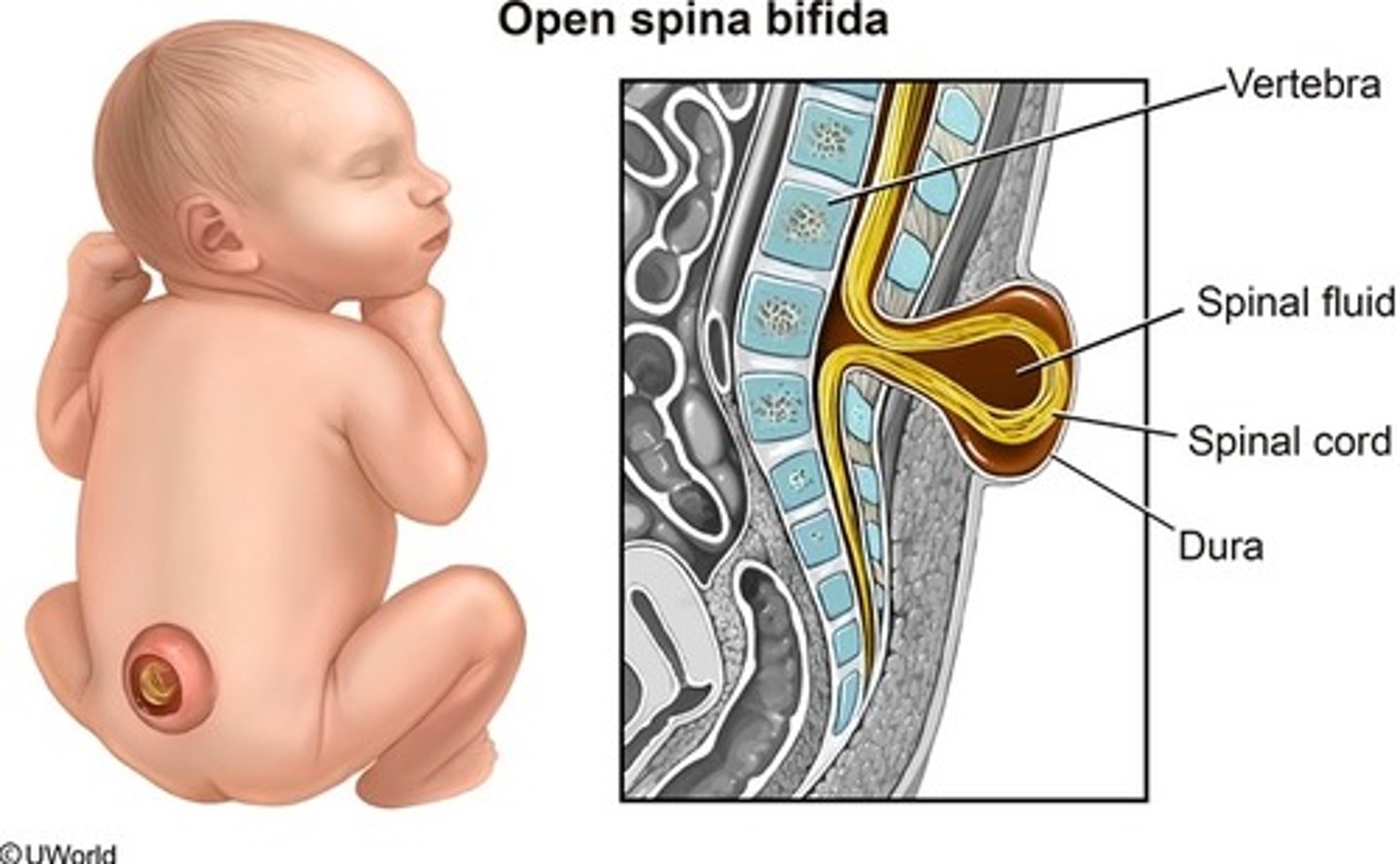
Spina bifida
-3.5 in every 10,000 babies (in US)
-impacts spinal column/doesn't form properly
-typically apparent at birth
-Myelomeningocele sack on back exposing nerves (see pic)
cause of spina bifida
lack of folic acid during pregnancy
spina bifida occulta
-no symptoms
-small gap in vertabrae
-spinal nerves not involved
-tuft or hair or dimple/birthmark on back
-requires spinal ultrasound or MRI
myelomeningocele
most severe form of spina bifida in which the spinal cord and meninges protrude through the spine
prenatal diagnostic procedures
-ultrasound
--high frequency sound waves
--pictures of fetus, abnormalities
-amniocentesis - needle in abdominal wall
Environmental factors to infant
Radiation, chemical pollutants
Radiation
An exposure to the fetus of more than 25 rads would be considered high dosage.
Chemical Pollutants
toxic metals such as lead, mercury, and lithium, and PCBs have been linked to birth defects
Genital herpes
brain damage or death in baby
Chlamydia
premature, stillbirth, pneunomia, eye infections in baby
Gonorrhea
ectopic pregnancies, eye damage in baby
Syphilis
severe illnesses, nervous damage system, death in baby
Acquired Immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
fever, weight loss, lethargy, diarrhea, pneunomia, death in baby
Maternal Infections
Rubella, STDs, AIDS and HIV, Rh incompatibility, Toxoplasmosis
Rubella
-if mom has rubella the baby/child has a high risk of deafness, heart defects, intellectual disabilities, liver and spleen damage, LBW
Rh incompatibility
-results from the mismatch of blood types between mother and child
Teenage Pregnancy effects on Infants
-higher risk of serious health problems
-high young or small-for-date
-psychological stress
-low socioeconomic status
-drug and alcohol abuse
-inadequate parenting behaviors
-poor or nonexistant medical care
erythroblastosis fetalis
-caused by Rh incompatibilty
-anemia and jaundice
-occurs when father is Rh positive and mother is Rh negative
Toxoplasmosis
-starts in mice that a pet (usually cats) can catch from the mouse and pass to pregnant mother
-most times symptoms develop later in life, like blindness or brain damage
-occasionally, newborns have serious eye or brain damage
prenatal diagnosis and Treatment
-diagnostic procedures have recently become available
-used to detect the presence of fetal developmental abnormalities
-valuable tools determining status of developing baby
Amniocentresis
-a technique where a hollow needle is inserted into the pregnant woman's abdomen
-performed around the 15th week of pregnancy
- a small amount of Amniotic fluid is withdrawn to detect for;
-chromosomal abnormality, multiple metabolic disorders, structural effects
Chronic Villus Sampling
-chorionic villi fragments from the developing placenta are extracted
Ultrasonography
-uses high-frequency sound waves, can be done from 5 weeks-birth
birth process factors
-3 stages
-when the cervix reaches 2cm dilated, labor begins
-amniotic sac breaks (water breaks)
-complete dilation is 10cm and then the 2nd stage of labor begins
-expulsion stage: the baby is pushed with a lot of pressure down the birth canal
-third stage begins after baby has emerged and continues until after the umbilical cord and aferbirth have been delivered
CHAPTER 6-prenatal and infant growth
--
Prenatal growth
-growth begins at the moment of conception and follows in a sequence throughout the prenatal period.
-uniting of sperm and ovum
-zygote production
-mitosis
zygote
-occurs when sperm meets egg
-fertilized egg with 46 chromosomes
-genetic potential is determined
mitosis
-zygote splits into two
-then 4, then 8
Zygotic Period
-Conception- 1st week
-period of zygote
-zygote is still small (0.01 of an in)
-pregnancy does not begin until the zygote is implanted on the uterine wall
-alcohol, drugs, and tobacco can be lethal to zygote
Embryonic Period
- second week- 2 months
-layer developed= beginning period of embryo
-Ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
highly sensitive period for susceptibility to congenital malformations
embryonic period
embryo
-the human organism that begins at the time when the cells differentiate into 3 layers and continues until it is firmly implanted in the uterine wall and receiving nourishment through the placenta and umbilical cord
ectoderm
-outer covering
-sensory-end organs and central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, skin, hair, and nails develop
mesoderm
middle layer; develops muscular, skeletal, circulatory, and reproductive systems
endoderm
-inner layer; formation of digestive, respiratory, and glandular systems
congenital malformations
- abnormal conditions when an infant is born
-may be bc of genetics, nutrition, environment, infections
-difficult to identify the cause
-greatest during the embryonic period
Early Fetal Period
-3-6 months
-rapid growth, height and weight double
-gender, teeth, stomach, and kidneys begin to function, and vocal cords appear
-reflexes are felt in the belly
-by end of 6th month, fetus is structurally complete/functionally mature
Later Fetal Period
-7-9 months
-triples in weight
-7 month is a quiet period resting up for the big day
-The last two months of fetal life are a time for filling out in preparation for birth
-fetus becomes more active
-a birth process initiated by the placenta and uterine musculature
normal gestation
38-42 weeks
normal length and weight of baby
19-21 inches, 6-8 ibs
Major event at conception
genetic inheritance is determined
Major events at 1 week prenatal
germinal period, period of rapid cell differentation
Major events at 2 weeks prenatal
implantation in the uterus
major events at 1 month prenatal
endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm formed, growth organized and differentatied
major events at 2 months prenatal
rapid growth period, begins to take on human form, weak reflex activity
major events at 3 months prenatal
sexual differentiation, stomach and kidney function, eyelids fuse shut
major events at 4 months prenatal
rapid growth period, first reflexive movements felt, bone formation begins
major events at 5 months prenatal
half birth weight, internal organ completion, hair over entire body
major events at 6 months prenatal
eyes reopen, vernix caseosa forms, structurally complete but functionally immaure