common eye issues and tx SA
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What are the clinical signs of acute conjunctivitis?
Hyperaemia, chemosis/oedema, discharge (watery, mucoid, mucopurulent), mild irritation, can be unilateral or bilateral.
What are the common causes of conjunctivitis in dogs?
Primary infectious (viral, bacterial, parasitic), secondary bacterial infections (staphylococcus, streptococcus), non-infectious causes (FBs, irritants, allergies, entropion, ectropion, KCS).
What treatment is first choice for bacterial conjunctivitis?
Topical antibiotic therapy with fusidic acid.
What are the clinical signs of uveitis?
Pain, red eye, miosis, swollen/dull iris, inflammation in anterior chamber, corneal oedema, low IOP.
How is glaucoma diagnosed?
Tonometry to measure IOP, with normal being 10-25; acute glaucoma > 40mmHg.
What are the acute clinical signs of glaucoma?
Pain (blepharospasm, increased lacrimation, photophobia), vision loss, corneal oedema, fixed dilated pupil.
What are common causes of keratoconjunctivitis (dry eye) in dogs?
Immune mediated, congenital (lacrimal gland hypoplasia), neurogenic, toxic, endocrine disease, iatrogenic.
What are the clinical signs of corneal ulcers?
Pain (blepharospasm, lacrimation, photophobia), conjunctival hyperaemia, ocular discharge, corneal oedema.
What treatment is used for superficial corneal ulcers?
Identify and treat underlying cause, chloramphenicol, NSAIDs for analgesia.
What distinguishes keratomalacia or melting corneal ulcers?
Very painful, gloopy/gelatinous discharge, soft edges, marked corneal oedema.
What is the treatment for spontaneous chronic corneal epithelial defect (SCCED)?
Debridement to allow attachment of epithelium, prevent/treat secondary infections, NSAIDs for analgesia.
What are the clinical signs of lens luxation?
Acute painful eye, signs of glaucoma, visible lens outline.
What are the clinical signs of Horner’s syndrome?
Miosis, third eyelid protrusion, ptosis, enophthalmos.
What are the clinical signs of eosinophilic keratitis?
White/pale pink spots on cornea resembling cottage cheese.
What is 'pannus' in veterinary medicine?
Chronic superficial keratitis characterized by cellular infiltrate and vascularisation of the cornea.
What is the treatment for globe prolapse?
Immediate treatment with lubrication, analgesia, GA for globe replacement, and post-operative care.
What is the difference between cataracts and nuclear sclerosis?
Look the same but different…
Cataracts: proteins in eye lens clump together, eye looks cloudy, prevent seeing through pupil. On exam, no tapetal reflex visible.
Nuclear sclerosis: allows viewing of tapetal reflex, harmless
What are the types of cataracts?
Incipient: <15% of lens
Immature: small/partial cataract, clear outer layer
Mature: entire lens/nearly all, can’t see retina on exam
Hyper-mature: lens starts to shrink and wrinkle, see lens-uveitis and can cause glaucoma
What conditions cause conjunctivitis in cats?
Primary infectious causes such as Chlamydia felis, Mycoplasma felis, and viral infections (FHV, FCV).
What is the most common secondary bacterial infection associated with conjunctivitis in cats?
- Chlamydia felis
o Intracellular
o G-ve
o Rod bacteria
o Can’t survive outside host
o Only spread through eye secretions
What diagnostic tests are used for uveitis?
Clinical + ophthalmic exam, blood profile, infectious disease profile, imaging, cytology, histopathology.
What are the symptoms of acute glaucoma?
Pain, vision loss, corneal oedema, episcleral vessel congestion, fixed dilated pupil.
Episcleral vs conjunctiva:
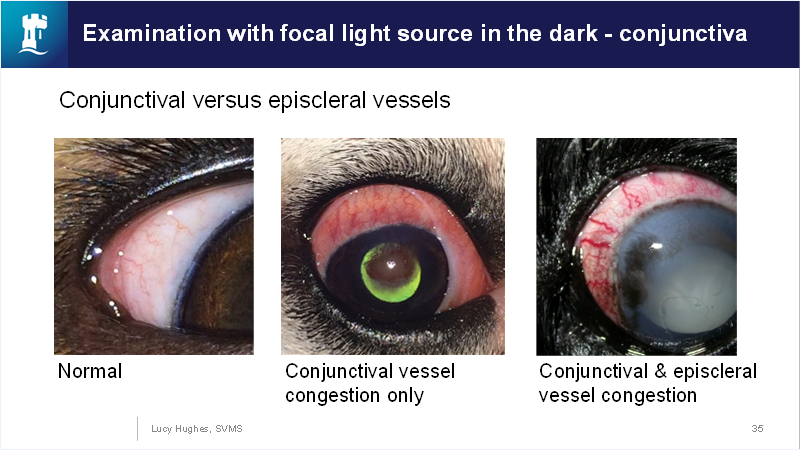
What is the treatment for dry eye (KCS)?
Ciclosporin (optimmune), tear substitutes, and fusidic acid if secondary infection occurs.
What is a common consequence of untreated chronic glaucoma?
Globe enlargement, corneal changes, lens luxation, cataracts.
What are the clinical signs of corneal cytology in cases of infection?
Blepharospasm, discharge, abnormal examination findings.
What imaging can help differentiate between iris neoplasia and cysts in dogs?
Ultrasound.
What are the diagnostic features of corneal ulcers?
Staining with fluorescein, indications of pain, and reflex tests.
What condition is described as a painful, gloopy discharge from the eye?
Keratomalacia or melting corneal ulcers.
What is the management for corneal ulcers that do not respond to medical therapy?
Surgical intervention may be required, such as grafting.
What are the common signs indicative of autoimmune causes in ocular conditions?
Persistent inflammation, conjunctival swelling, and unusual ocular discharges.
What clinical signs are associated with conjunctival swabs and PCR testing?
Detection of infectious agents like Chlamydia felis and FHV.
How do you treat uveitis with systemic involvement?
Topical and systemic anti-inflammatories (steroid) and treatment of underlying causes.
What are the signs of chronic KCS in dogs?
Corneal vascularisation, fibrosis, pigmentation, and reduced vision.
What is the common treatment approach for neoplasia in the eye?
Monitor, and enucleation if tumor growth is rapid or causes discomfort.
What is the first line treatment for an emergency case of globe prolapse?
Immediate lubrication and analgesia.
What signifies secondary infections in keratoconjunctivitis?
Signs like severe irritation and sticky discharge requiring antibiotic therapy.
What sort of eye conditions can be caused by systemic diseases like diabetes mellitus?
Cataracts and dry eye due to metabolic changes.
What is the role of atropine in treating uveitis?
To relieve pain and prevent synechiae.
What indicates a need for surgical intervention in ocular conditions. ?
Failure of medical therapy, e.g., for deep corneal ulcers.
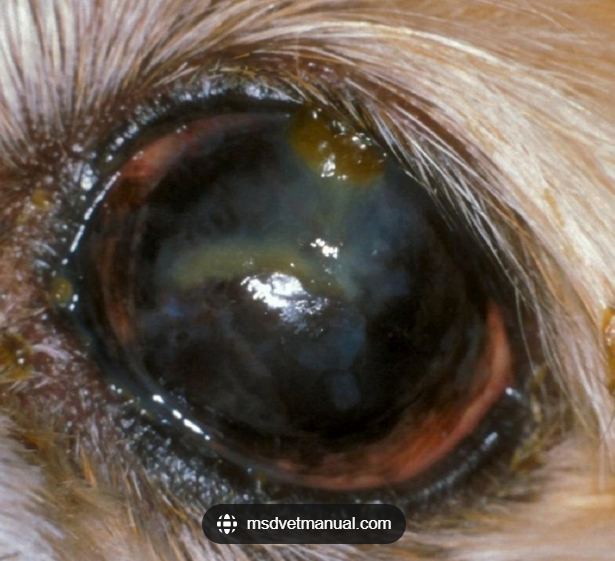
What does ocular discharge in conjunctivitis indicate?
The type of underlying cause, whether infectious or non-infectious.
What are common clinical signs for neoplasia in the eye?
Eyelid masses that are typically benign to malignant growths.
What can lead to excessive tear production in KCS?
Reflex tearing from irritation rather than normal function.
What are the other names for primary corneal disease in brachycephalic breeds?
Superficial keratitis and ectropion.
What is the management strategy for patients with significant ocular pain?
Use of analgesics, anti-inflammatories, and possibly surgical assessments.