
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
The central dogma
describes the flow of genetic info within a cell
Replication —> Transcription —> RNA processing —> Translation —> Protein Folding
DNA Replication
DNA is copied to ensure genetic material is passed to new cells or offspring.
Transcription
DNA is transcribed into messanger mRNA by RNA polymerase
Translation
mRNA is translated into a protein at the ribosome, with the help of tRNA and rRNA
DNA strcuture
A deoxyribose sugar
A phosphate group
1 of 4 nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine)
A purine always pairs with a _______ to maintain _____ of DNA double helix
pyrimidine; width
A is a _____ and pairs with ______ which is a _____ they share __ hydrogen bonds
purine; T; pyrimidine; 2
C is a ____ and pairs with ____ which is a ______ they share ____ hydrogen bonds
pyrimidine; G; purine; 3
Which base pair is stronger, therefore harder to break
G → C because there are 3 hydrogen bonds
Double Helix structure
DNA strands are antiparallel, meaning one strand runs from 5’ to 3’ while the other runs from 3’ to 5’.
The structure is a right-handed double helix (B-DNA), the most common form in living cells.
Structure of the DNA turns of the helix
10 bases per helical turn, with 0.34nm in between each base pair
Each full helical turn measures 3.4nm
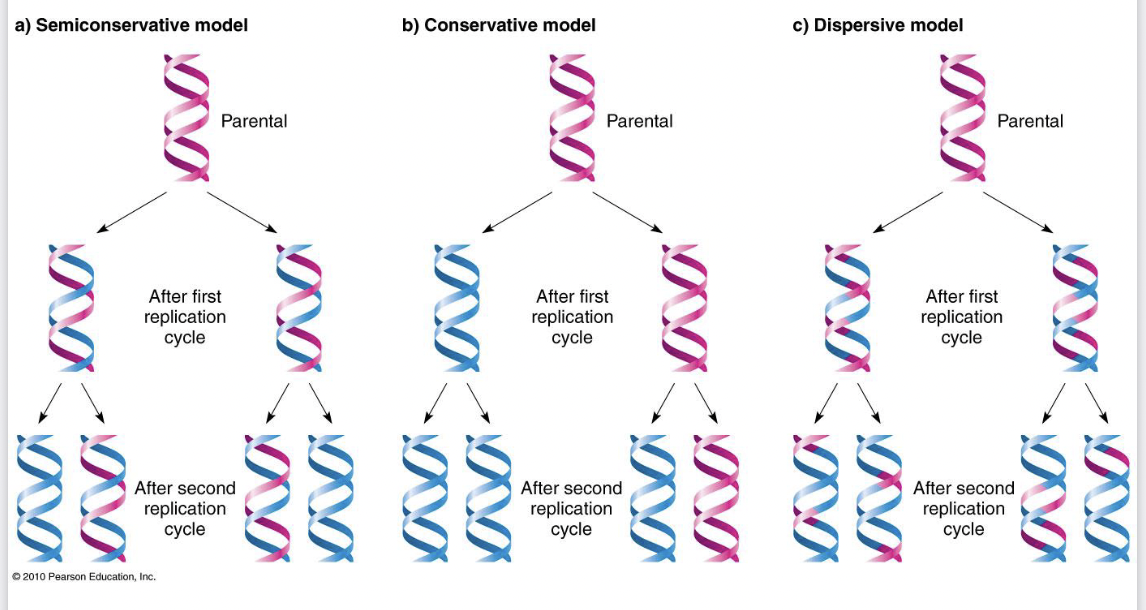
Who proposed the semi-conservative double helical strcuture of DNA?
Watson and Crick
What were the options of models of DNA replication methods
Conservative: the parental model strands conserved and a completely new double stranded DNA molecule is synthesized. Result: one DNA is entirely parental the other is entirely new → incorrect
Dispersive: random sequences are mixed up → incorrect
Semi- the two strands of the parental DNA molecule separate, and each serves as a template for synthesizing a new complementary strand, After one round of DNA replication each DNA contains 1 parental and 1 newly synthesized strand.
Modes of DNA replication
Theta
Rolling circle
Linear chromosome
Theta replication
occurs in circular DNA such as bacterial chromosomes
1 origin of replication
Bidirectional
Theta replication steps
DS DNA unwinds at replication origin, producing two SS templates for new DNA
fork proceeds around circle
Eventually two circular DNA molecules are produced
Rolling circle replication
found in F factor of E. coli and some viruses
1 origin of replication
Unidirectional replication
Rolling circle replication steps
Break in one strand of circular DNA
synthesis begins at 3’ end of broken strand and the unbroken strand is used as a template
5’ end of broken strand flys away after being cleaved
the linear DNA may circularize
the products are multiple circular molecules
Linear chromosome replication (eukaryotes)
multiple origins of replication
bidirectional
Linear chromosome replication steps
At each origin, the DNA unwinds, producing a replication bubble
DNA synthesis takes place on both strands at each end of the bubble as the replication fork proceeds outward
Eventually the forks of adjacent bubbles run into each other and fuse.
This fusing produces two identical linear DNA molecules
If there is no breakage of a DNA strand, like we see in rolling circle…
Then we must pull the strands apart by breaking hydrogen bonds.