Genetic linkage and gene mapping
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Morgan (1900s)
First to associate a specific gene with a specific chromosome
- Nobel prize 1933
Drosophila
Small fruit fly used to study basic mechanisms of inheritance

Morgan's terminology
- normal phenotype: wild type (+)
- alternative trait to wild type: mutant phenotype
- gene takes its symbol from 1st mutant (e.g. eye colour: 1st mutant = white (w), wild type = red (w+)
Morgan's first cross
P- red eye (female) x white eye (male)
F1 results- all red eyes
F1 (red) x F1 (red)
F2 results - 3:1 (red:white)
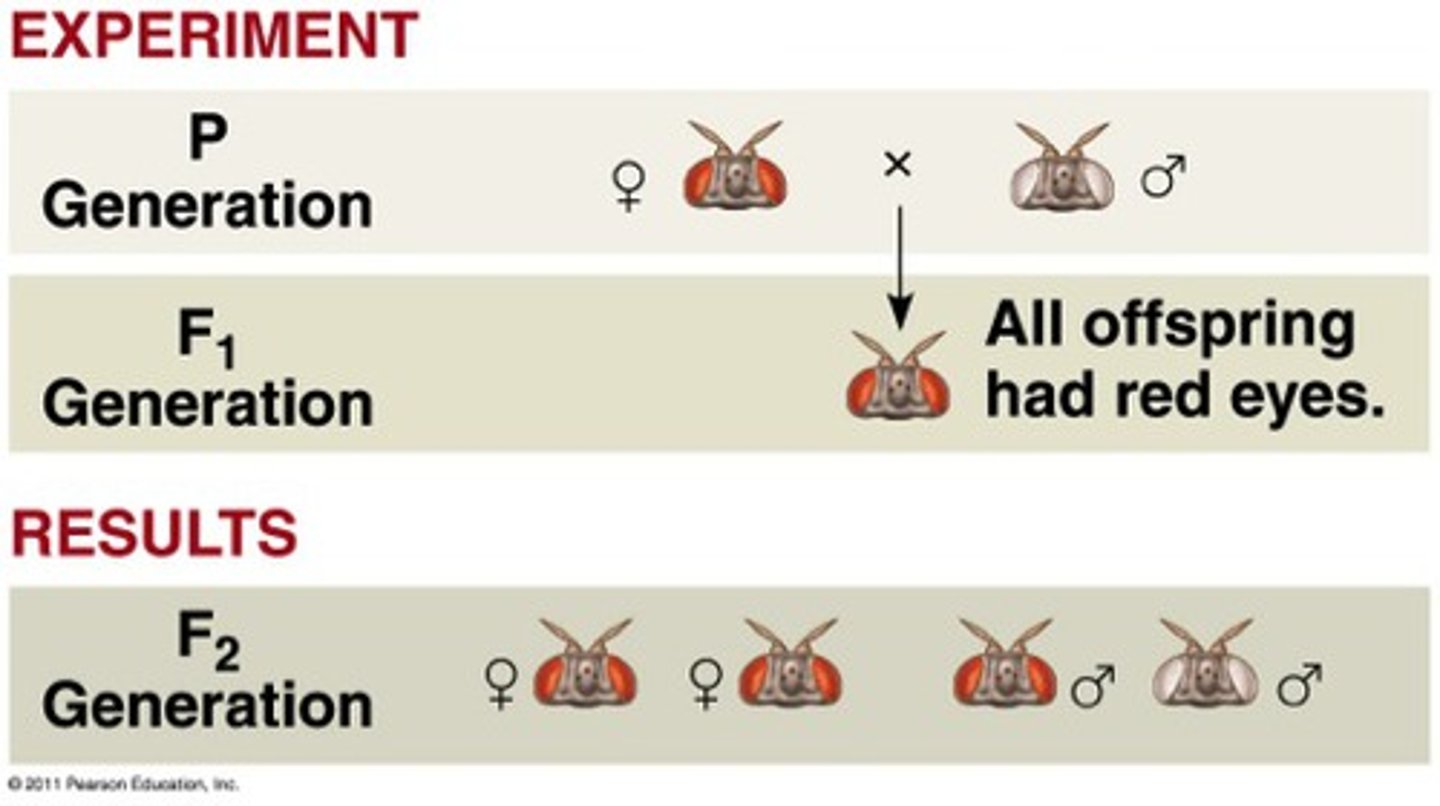
First cross conclusions
- red (w+) dominant
- white (w) recessive
Morgan's second cross
F2 female (red) x F2 male (white)
F3 results: 1:1 (red:white)
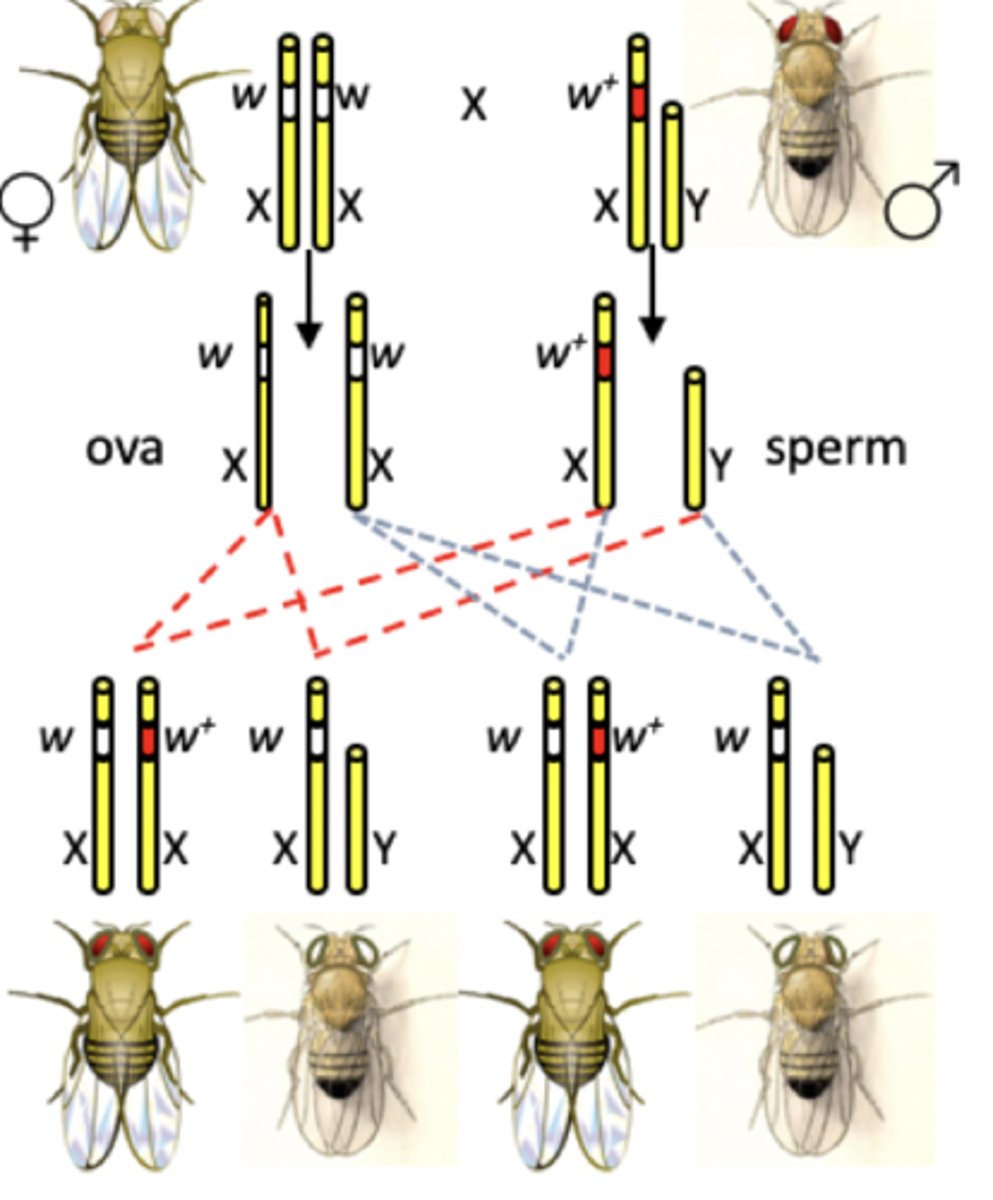
Second cross conclusions
Female flies are heterozygous
Morgan's sex linkage hypothesis
- eye colour gene locus is on the X chromosome
- drosophila sex is determined by XY
- males are 'hemizygous' and possess only one allele -> on their X chromosome
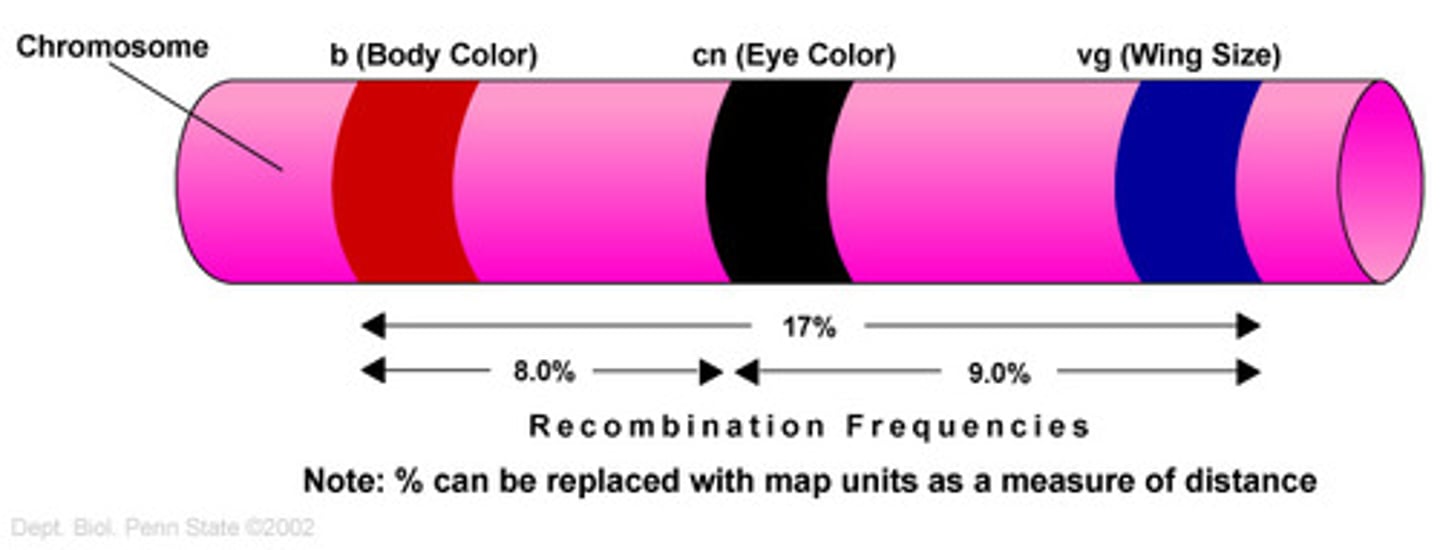
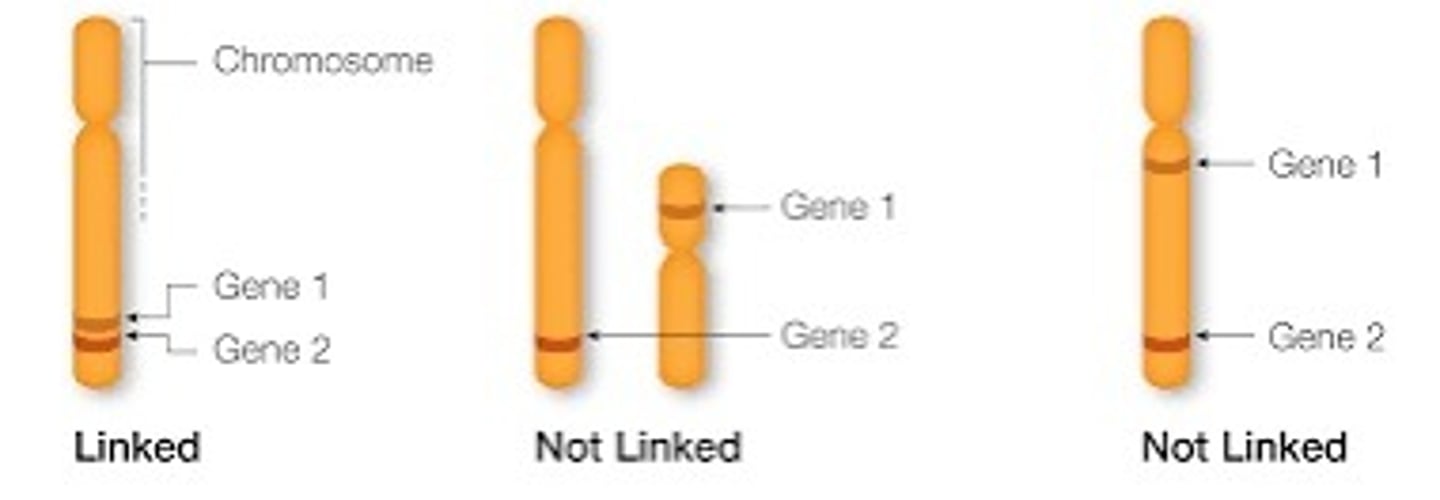
Genetic linkage
Genes on any given chromosome are physically linked together on the same DNA molecule
- tend to be inherited together
- linked genes do not conform to Mendelian patterns
Dihybrid test cross
2 traits crossed at the same time
- crossing an unknown dominant genotype with a known recessive to find out its genotype
- proves independent assortment: 1:1:1:1
Dihybrid test cross involving body colour and wing size
Parent 1: homozygous recessive mutant, phenotype: black and vestigial wings, genotype: bb vgvg
Parent 2: heterozygous wild type, phenotype: grey and normal wings, genotype: b+b vg+vg

Dihybrid cross results
2300 offspring
grey/normal (parent) = 965
black/vestigial (parent) = 944
grey/vestigial (recombinant) = 206
black/normal (recombinant) = 185
Dihybrid cross conclusion
- disproportionate number of parental phenotypes
- alleles tend to be inherited together (linked on the same chromosome)
- smaller number of recombinant phenotypes present due to crossing over
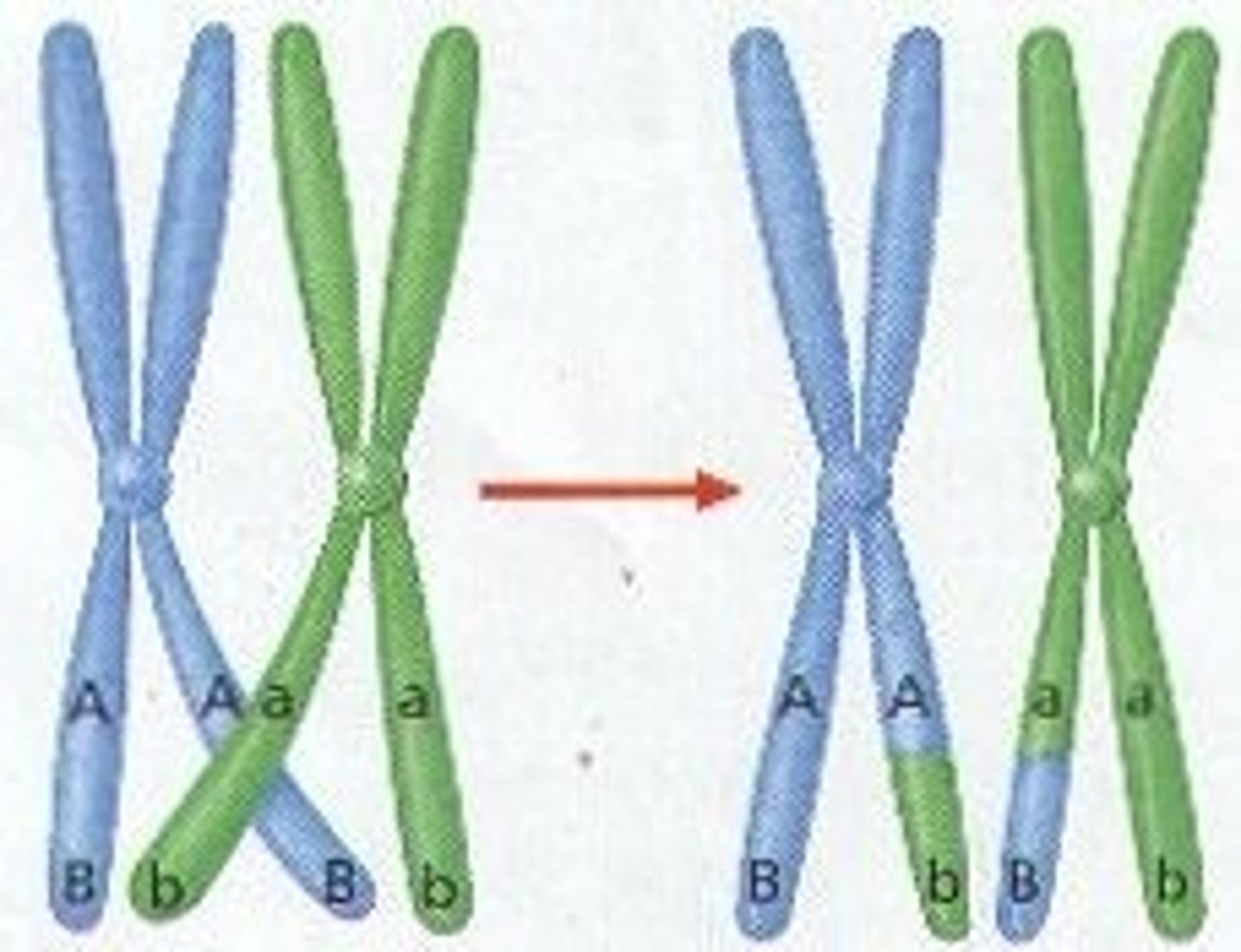
Crossing over
Homologous proportions of 2 nonsister chromatids exchange places
- physically exchange DNA at chiasma
- tension results in DNA duplexes breaking and rejoining crosswise
- occurs during prophase of meiosis 1
- contain both maternal and paternal DNA
Recombinant frequency (RF)
The proportion (or percentage) of recombinant cells or individuals
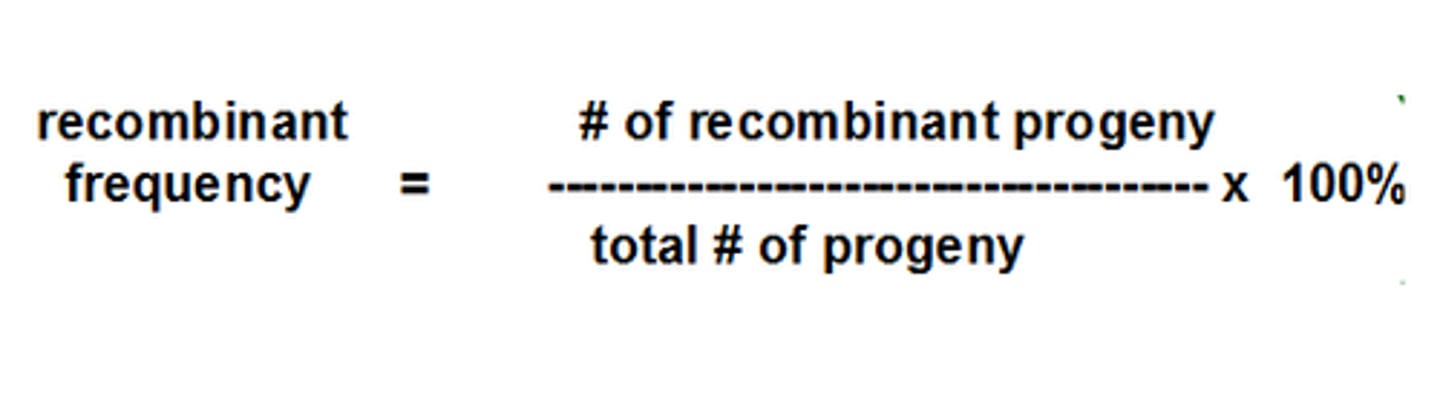
RF conclusions
0%
Sturtevant
The first to realise that Morgans proposal could be used to map genes
- student of Morgan
Genetic mapping
Determining the location of genes on chromosomes
- first genetic map illustrated the sequence of genes along a chromosome and the relative distance between the genes
How did Sturtevant map genes?
Assumed an equal chance of crossing over along a length of chromosome
- if 2 genes are far apart they are more likely to cross over (high RF) -> units 1 & 10 = 10x chance
- if 2 genes are close together they are less likely to cross over (low RF) -> units 1 & 2 = 1x chance at crossing
Stutevant's first map
Analysis of transmission and recombination between 3 mutant traits in Drosophila (yellow body, white eye, miniature wing)
- performed dihybrid crosses, calculated the RFs between each pair of traits
- RFs taken as a measure of distance (one map unit = a centimorgan (cM), 1cM = 1% recombination between 2 genes)
Sturtevants results
1: RF between y (yellow body) and w (white eye) = 6%
2: RF between y and m (miniature wing) = 34%
3: RF between w and m = 40%