Psychology 200 Final Exam Review Ch. 2,3,4,6,7,8,11,12,15, and 16
1/296
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
297 Terms
Parts of a neuron
Soma- cell body
Dendrite- Branch-like extension of the soma that receives incoming signals from other neurons.
Axon- Major extension of the soma.
Nodes of Ranvier- open spaces that are found in the myelin sheath that encases the axon
Myelin sheath- fatty substance that insulates axons
Terminal button- axon terminal containing synaptic vesicles
Synapse- Junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite of the receiving neuron
Synaptic cleft- small gap between two neurons where communication occurs
Synaptic vesicle- storage site for neurotransmitters
Action potential
Electrical signal that moves down the neuron’s axon.
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane
Adrenal gland
Sits atop our kidneys and secretes hormones involved in the stress response.
Agonist and Antagonist
Ag: Drug that mimics or strengthens the effects of a neurotransmitter.
An: Drug that blocks or impedes the normal activity of a given neurotransmitter.
All-or-none
Phenomenon that an incoming signal from another neuron is either sufficient or insufficient to reach the threshold of excitation.
Neuron reaction is all or nothing.
The more intense the stimulus the more neurons will fire and the more often they will fire.
Amygdala
Structure in the limbic system involved in emotional memory and fear responses, helping encode memories more strongly when they are emotionally significant.
Auditory cortex
Strip of cortex in the temporal lobe that is responsible for processing auditory information.
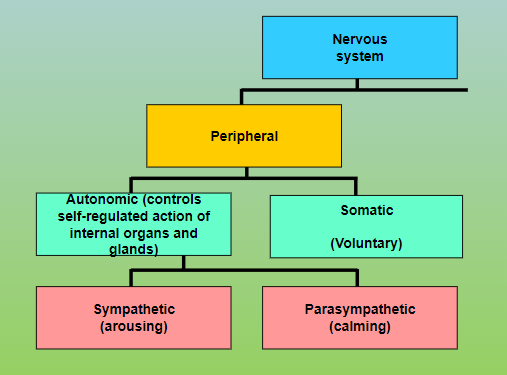
Autonomic and Somatic nervous system
A: Controls our internal organs and glands.
S: relays sensory and motor information to and from the CNS
Biological perspective
View that psychological disorders like depression and schizophrenia are associated with imbalances in one or more neurotransmitter systems.
Broca’s area and Aphasia
BA: Region in the left hemisphere that is essential for language production.
Difficulty producing speech but can comprehend.
A: language disorder that results from damage to specific areas of the brain, usually in the left hemisphere, affecting a person’s ability to communicate
Central (CNS) and Peripheral (PNS) nervous system
CNS: Brain and spinal cord.
PNS: connects the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, organs and senses in the periphery of the body
Cerebellum
Hindbrain structure that controls balance, coordination, movement, and motor skills; important in processing some types of memory.
Cerebral cortex
Surface of the brain associated with our highest mental capabilities.
Computerized tomography (C T) scan
Imaging technique in which a computer coordinates and integrates multiple x-rays of a given area.
Corpus callosum
Thick band of neural fibers connecting the brain’s two hemispheres.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Recording the electrical activity of the brain via electrodes on the scalp.
Endocrine system
Series of glands that produce chemical substances known as hormones.
Epigenetics
Study of gene-environment interactions, such as how the same genotype leads to different phenotypes.
Fight or flight response
Activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, allowing access to energy reserves and heightened sensory capacity.
Forebrain
Largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and limbic system.
Frontal lobe
Part of the cerebral cortex involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
MRI that shows changes in metabolic activity over time.
Glial cell
Nervous system cell that provides physical and metabolic support to neurons.
Gonad
Secretes sexual hormones important for reproduction and mediates sexual motivation and behavior.
Gyrus
Bump or ridge on the cerebral cortex.
Hindbrain
Division of the brain containing the medulla, pons, and cerebellum.
Hippocampus
Structure in the temporal lobe associated with learning and memory.
Hormone
Chemical messenger released by endocrine glands.
Hypothalamus
Forebrain structure that regulates sexual motivation and behavior and homeostatic processes.
Regulates eating, drinking, body temperature, libido, and the “fight or flight” reaction
Limbic system
Collection of structures involved in processing emotion and memory.
Longitudinal fissure
Deep groove in the brain’s cortex.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Imaging technique using magnetic fields to produce pictures of tissue.
Medulla
Hindbrain structure that controls automated processes like breathing and heart rate.
Membrane potential
Difference in charge across the neuronal membrane.
Midbrain
Division of the brain located between the forebrain and hindbrain.
Motor cortex
Strip of cortex involved in planning and coordinating movement.
nervous system
made up of billions of neurons and controls our thoughts, responses, and movements; divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
neuron
cells in the nervous system that act as interconnected information processors, which are essential for all of the tasks of the nervous system
neuroplasticity
nervous system's ability to change
neurotransmitter
chemical messenger of the nervous system
occipital lobe
part of the cerebral cortex associated with visual processing; contains the primary visual cortex
pancreas
secretes hormones that regulate blood sugar
parietal lobe
part of the cerebral cortex involved in processing various sensory and perceptual information; contains the primary somatosensory cortex
pituitary gland
secretes a number of key hormones, which regulate fluid levels in the body, and a number of messenger hormones, which direct the activity of other glands in the endocrine system
polygenic
multiple genes affecting a given trait
pons
hindbrain structure that connects the brain and spinal cord; involved in regulating brain activity during sleep
positron emission tomography (PET) scan
involves injecting individuals with a mildly radioactive substance and monitoring changes in blood flow to different regions of the brain
prefrontal cortex
area in the frontal lobe responsible for higher-level cognitive functioning
psychotropic medication
drugs that treat psychiatric symptoms by restoring neurotransmitter balance
range of reaction
asserts our genes set the boundaries within which we can operate, and our environment interacts with the genes to determine where in that range we will fall
receptor
protein on the cell surface where neurotransmitters attach
resting potential
the state of readiness of a neuron membrane’s potential between signals
reticular formation
midbrain structure important in regulating the sleep/wake cycle, arousal, alertness, and motor activity
reuptake
neurotransmitter is pumped back into the neuron that released it
semipermeable membrane
cell membrane that allows smaller molecules or molecules without an electrical charge to pass through it, while stopping larger or highly charged molecules
somatosensory cortex
essential for processing sensory information from across the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain
substantia nigra
midbrain structure where dopamine is produced; involved in control of movement
sulcus
(plural: sulci) depressions or grooves in the cerebral cortex
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic nervous system
S: involved in stress-related activities and functions
P: associated with routine, day-to-day operations of the body
temporal lobe
part of cerebral cortex associated with hearing, memory, emotion, and some aspects of language; contains primary auditory cortex
thalamus
sensory relay for the brain
theory of evolution by natural selection
states that organisms that are better suited for their environments will survive and reproduce compared to those that are poorly suited for their environments
threshold of excitation
level of charge in the membrane that causes the neuron to become active
thyroid
secretes hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and appetite
ventral tegmental area (VTA)
midbrain structure where dopamine is produced: associated with mood, reward, and addiction
Wernicke’s area
important for speech comprehension
What are 2 thing the pituitary does?
secretes hormones that regulate the body’s fluid levels.
secretes messenger hormones that direct the function of the rest of the endocrine glands.
Acetylcholine
Triggers muscle contraction (PNS)
Linked with attention, arousal, memory
In: Muscle action, memory
Effects: Increased arousal, enhanced cognition
Types of Neurotransmitters
Excitatory and Inhibitory
Excitatory and Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
E: increase the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential. Acetylcholine and Glutamate.
I: decrease the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential. GABA and Serotonin
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
primary inhibitory neurotransmitter for the central nervous system (CNS).
Reduces neuronal excitability by inhibiting nerve transmission.
The balance between inhibitory neuronal transmission via GABA and excitatory neuronal transmission via glutamate is essential for proper neurologic function.
In: Brain function, sleep
Effects: Decreased anxiety, decreased tension
Serotonin and Dopamine
Inhibitory neurotransmitter.
Necessary for a stable mood and to balance any excessive excitatory (stimulating) neurotransmitter firing in the brain.
Also regulates carbohydrate cravings, sleep cycle, pain control, and appropriate digestion.
Help people with depression by preventing the neurons from "vacuuming" up excess serotonin, so that there is more left floating around in the synapses.
In: Mood, sleep
Effects: Modulated mood, suppressed appetite
Dopamine: In: Mood, sleep, learning
Effects: Increased pleasure, suppressed appetite
Beta-endorphin
In: Pain, pleasure
Effects Decreased anxiety, decreased tension
Glutamate
The balance between inhibitory neuronal transmission via GABA and excitatory neuronal transmission via glutamate is essential for proper neurologic function.
In: Memory, learning
Effects: Increased learning, enhanced memory
Norepinephrine
In: Mood, sleep
Effects: Modulated mood, suppressed appetite
sensory neurons
carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the central nervous system.
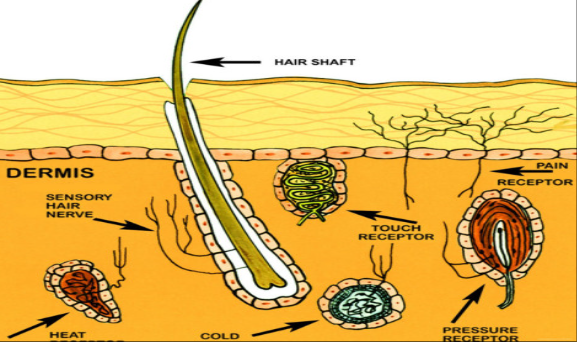
Motor Neurons
Carry outgoing information from the CNS.
Located mostly in the spinal cord.
Normally, signals cause muscles to contract
Neuronal communication
often referred to as an electrochemical event.
The movement of the action potential down the length of the axon is an electrical event.
The movement of the neurotransmitter across the synaptic space represents the chemical portion of the process.
Localization
The theory that specific parts of the brain are responsible for specific behaviors or cognitive processes.
Although we know that some parts of the brain do play specific roles in behavior, rarely does a part of the brain work in complete isolation .
H.M. Milner
Naturalistic Observation
A research method in which subjects are observed in their natural environment without any manipulation or intervention by the researcher, allowing for the collection of data on behavior in real-world settings.
Cross sectional research
A research method that analyzes data from a population at a specific point in time, allowing for comparisons across different groups.
Longitudinal research
A research method that involves repeated observations of the same variables over long periods, often years or decades, to study changes and developments in individuals or groups.
Correlational research
A type of non-experimental research method that examines the relationship between two or more variables to determine if they are associated or correlated.
Experimental research
A research method that involves manipulating one variable to determine if changes cause an effect in another variable, often conducted in controlled conditions.
Single and Double Blind
Single: A study in which the participants are unaware of whether they are receiving the experimental treatment or a placebo, but the researchers know.
Purpose:
To reduce participant bias in the results.
Double: A study in which neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving the experimental treatment or a placebo.
Purpose:
To reduce both participant and researcher bias, ensuring more objective results.
Significant results
Findings in a study that are unlikely to occur by chance, often indicated by a p-value below 0.05.
Reliability
The consistency or repeatability of a measure; a test is reliable if it produces the same results under the same conditions.
Validity
The extent to which a test measures what it is intended to measure and accurately reflects the concept being studied.
Left and Right Hemisphere
L: The side of the brain typically responsible for language, logical reasoning, analytical thinking, and mathematical skills.
Example: Processes tasks like speech production (Broca’s area) and comprehension (Wernicke’s area).
R: The side of the brain associated with creativity, spatial awareness, emotional processing, and recognizing faces.
Example: Plays a key role in visual and spatial tasks, such as reading maps or interpreting art.
Michael Gazzaniga
His work with split-brain patients revealed the distinct roles of each hemisphere, demonstrating lateralization of brain functions. For example, he found that the left hemisphere is dominant in language processing, while the right specializes in spatial and non-verbal tasks.
Phineas Gage
His case provided early evidence of the role of the frontal lobe in personality, decision-making, and emotional regulation, as his behavior and temperament changed drastically after the accident.
Wilder Penfield
conducted brain surgery experiments in which he stimulated specific areas of the brain and observed the effects, helping to identify the functional areas of the brain, such as the motor and sensory cortices. His work significantly advanced the understanding of brain localization
Long-term potentiation
a process that strengthens the connections between neurons, leading to long-lasting increases in their communication efficiency.
Arborization and Pruning
A: The process by which neurons form new branches (dendrites) and synaptic connections to increase their surface area and improve communication.
Significance: Important for the development of neural networks and plasticity, especially during early brain development.
P: The process of eliminating excess synaptic connections and neurons that are no longer needed.
Significance: Helps refine neural circuits, increasing efficiency and strengthening important connections for learning and development.
Charles Spearman and “g”
suggests that a general intelligence, or "g," underlies all cognitive abilities.
He believed that cognitive tasks could be explained by a single factor influencing performance across a wide range of activities.
Crystallized and fluid intelligence
CI:
Refers to knowledge and skills acquired through experience and education.
Increases with age as people accumulate information and problem-solving strategies.
Example: Knowing facts, solving crossword puzzles.
FI:
Refers to the ability to reason, think abstractly, and solve new problems, independent of past knowledge.
Peaks in early adulthood and declines with age.
Example: Solving puzzles or adapting to new situations.
Divergent and convergent thinking
DT:
The ability to generate multiple creative solutions to a problem.
Focuses on exploring many possible answers or ideas.
Example: Brainstorming ideas for a new project.
CT:
The ability to identify a single, correct solution to a problem.
Focuses on narrowing down options to find the best answer.
Example: Solving a math equation with one correct solution.
Robert Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
defines intelligence through three components:
Analytical Intelligence: Logical reasoning and problem-solving.
Creative Intelligence: Innovation and adaptability.
Practical Intelligence: Real-world problem-solving or "street smarts."
Emotional Intelligence
the ability to recognize, understand, manage, and effectively use emotions in oneself and others.
Key Components:
Self-Awareness: Recognizing your own emotions.
Self-Management: Controlling and regulating emotions.
Social Awareness: Understanding others' emotions.
Relationship Management: Using emotions to build and maintain healthy relationships.
Howard Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
intelligence is not a single ability but consists of distinct types:
Linguistic: Language and communication.
Logical-Mathematical: Problem-solving and reasoning.
Musical: Sensitivity to sound and rhythm.
Bodily-Kinesthetic: Physical coordination and skill.
Spatial: Visualizing and manipulating space.
Interpersonal: Understanding others.
Intrapersonal: Self-awareness.
Naturalistic: Recognizing patterns in nature.