Body Fluids Exam 2 + Lab Practical Midterm
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
How will a concentrated (hypertonic) urine affect the appearance of red cells?
They appear crenated
Crenated RBC in urine
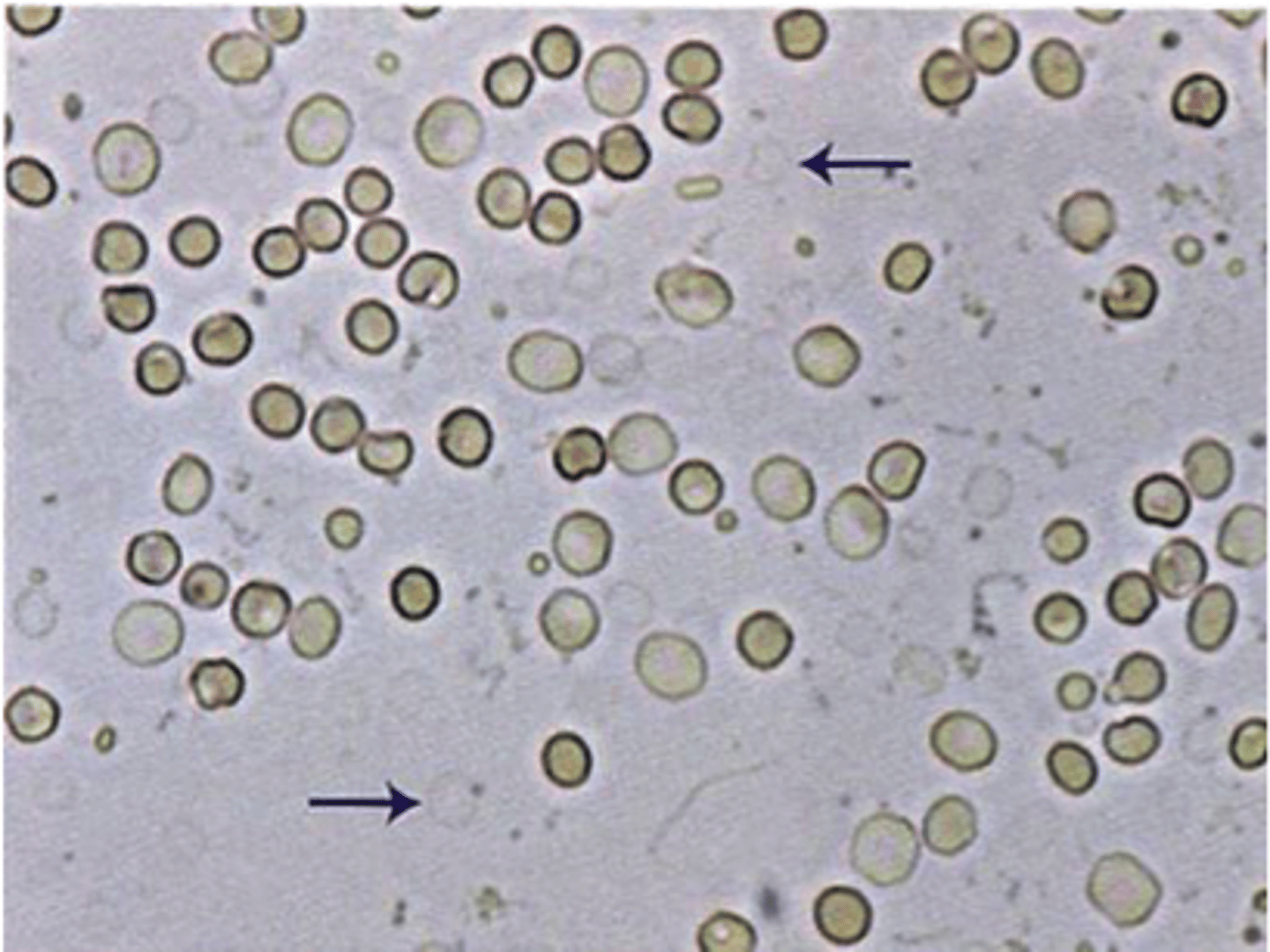
What are ghost cells?
Lysed red cells
Under what conditions might ghost cells be seen?
Dilute or hypotonic environment causes the cells to swell and burst
Ghost cells
What is normal range of RBCs in urine per HPF?
0-2
What are 3 significant causes of blood in urine?
Glomerular damage, trauma, stones, infection or tumors
What is normal range of WBCs in urine per HPF?
0-5
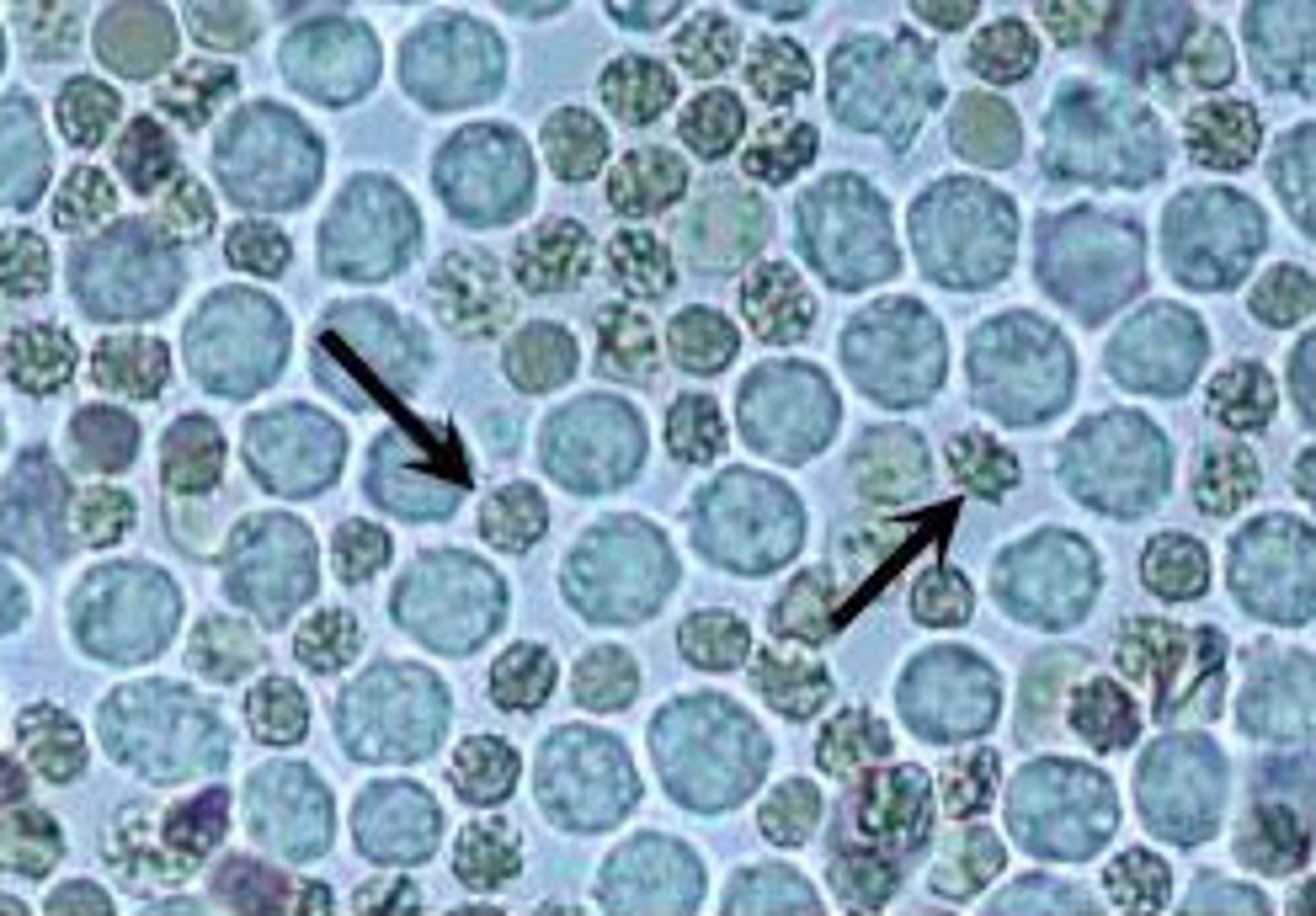
What causes the appearance of glitter cells?
Dilute or hypotonic urine will cause water to move into a white cells
Glitter cells
What is actually glittering in glitter cells?
Granules moving around as the cell swells
What type of cells in urine may indicate a possible kidney transplant rejection?
Lymphocytes
A positive leukocyte esterase plus a positive nitrite is consistent with what condition?
UTI
A positive nitrite in conjunction with a negative leukocyte esterase is most consistent with what situation?
An old or unpreserved urine
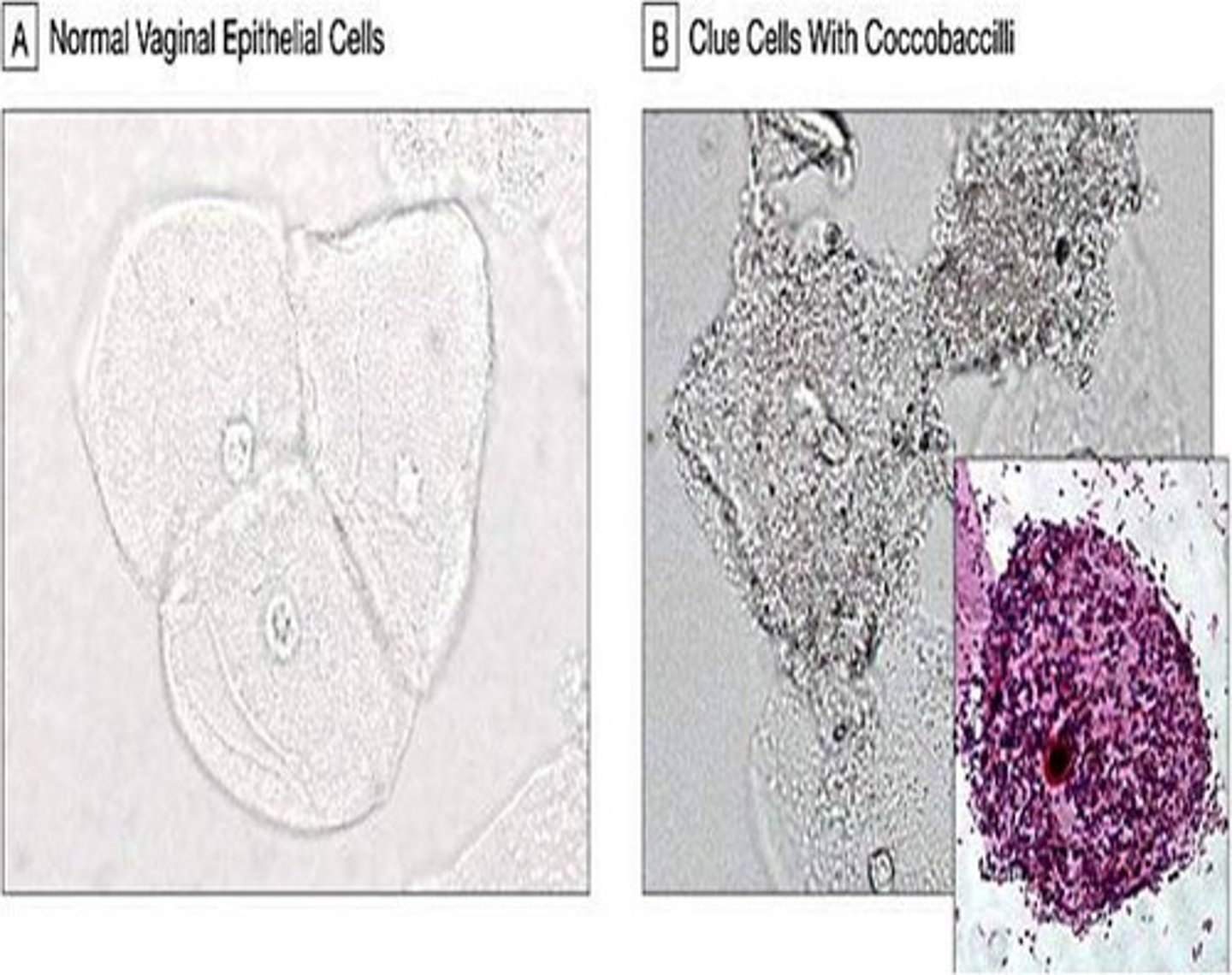
What term is given to squamous epithelial cells covered with bacteria?
Clue cells
Clue cells
What are 3 types of epithelial cells that may be seen in urine?
Squamous, transitional, and renal tubular
Squamous epithelial cell
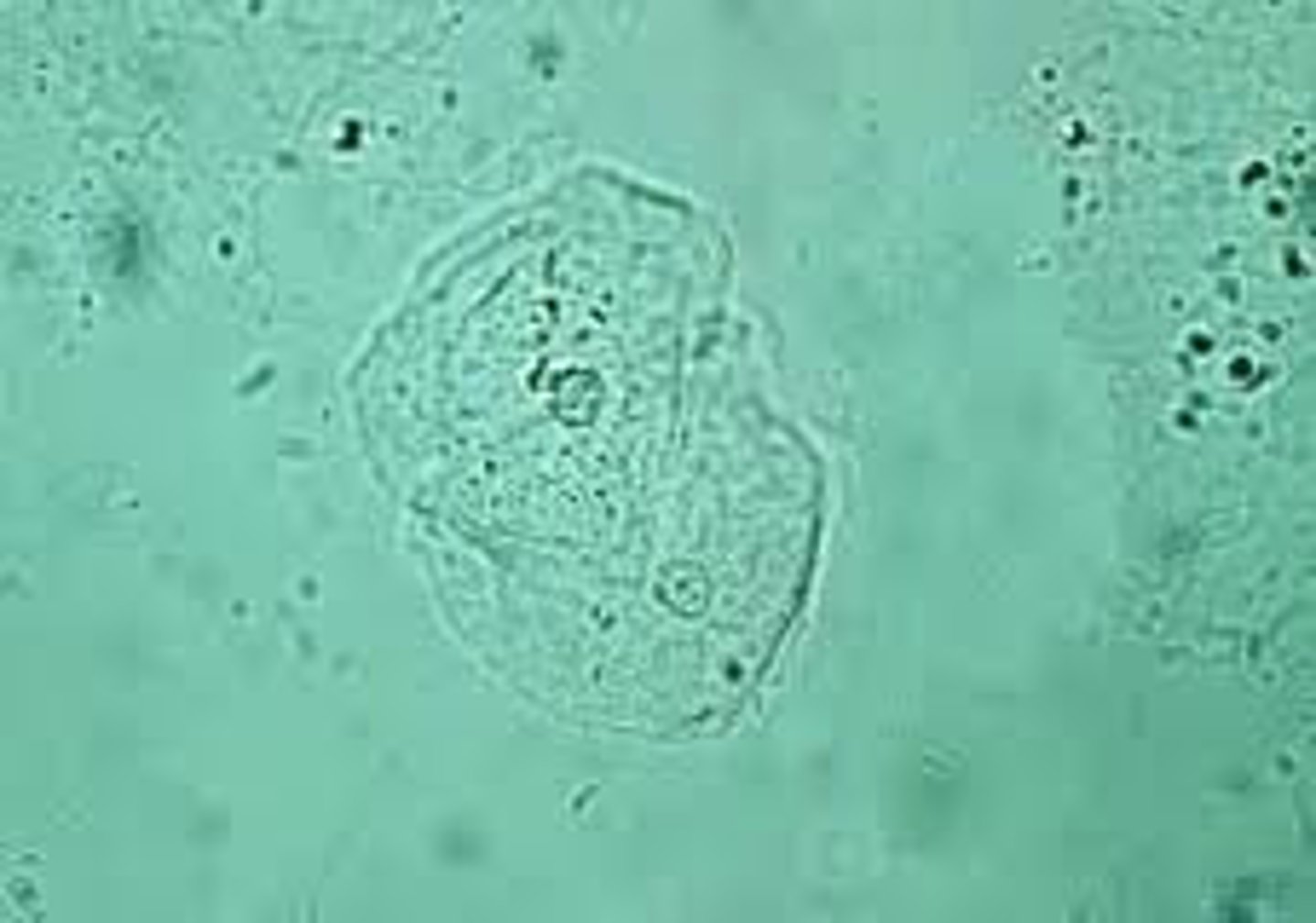
Transitional epithelial cell
Renal tubular epithelial cell
What type of epi is most consistent with bladder infections or catheterization?
Transitional
What type of epi is most clinically significant?
Renal tubular
When might renal tubular epis be seen?
Tubule damage or necrosis from toxins, drugs or kidney transplant rejection
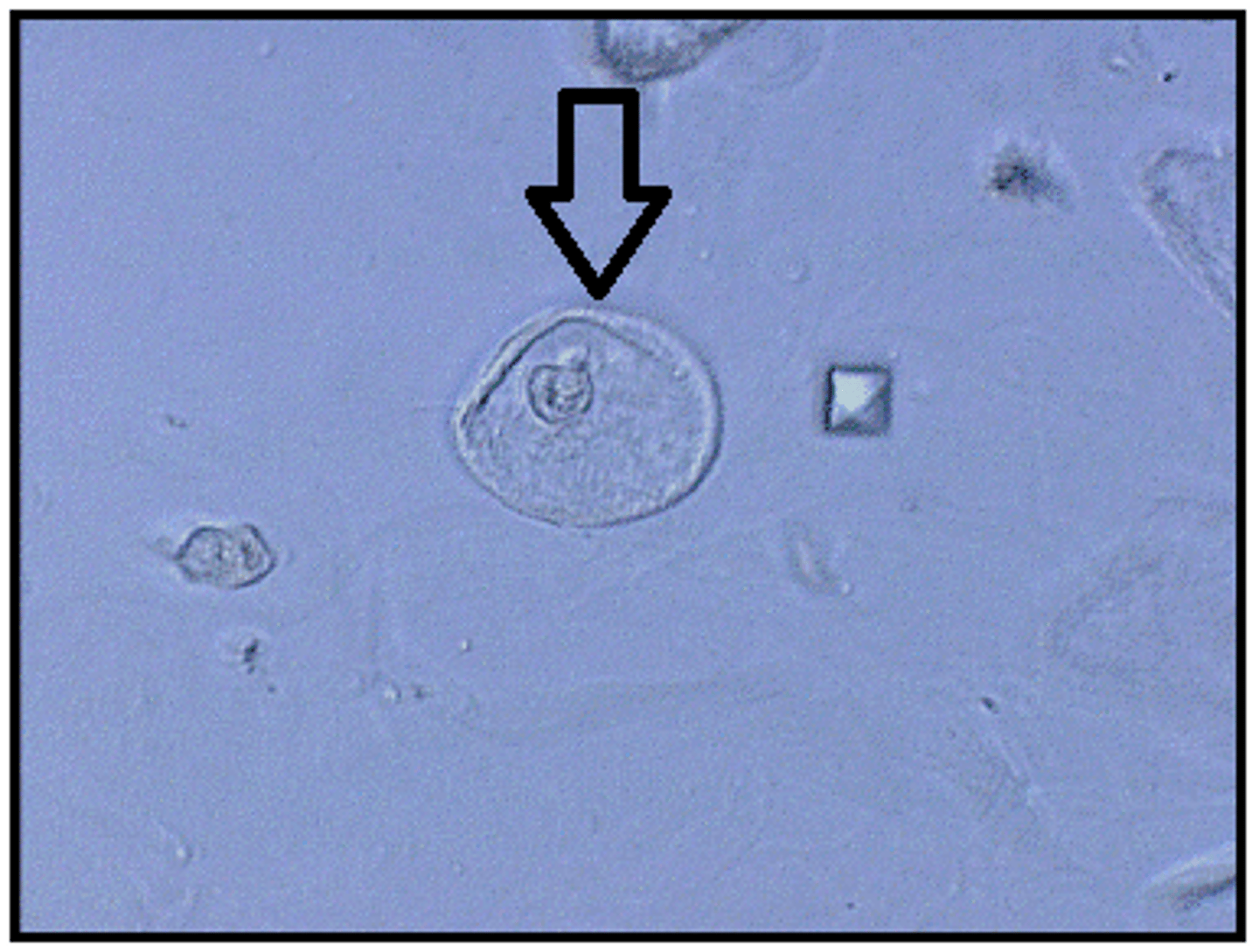
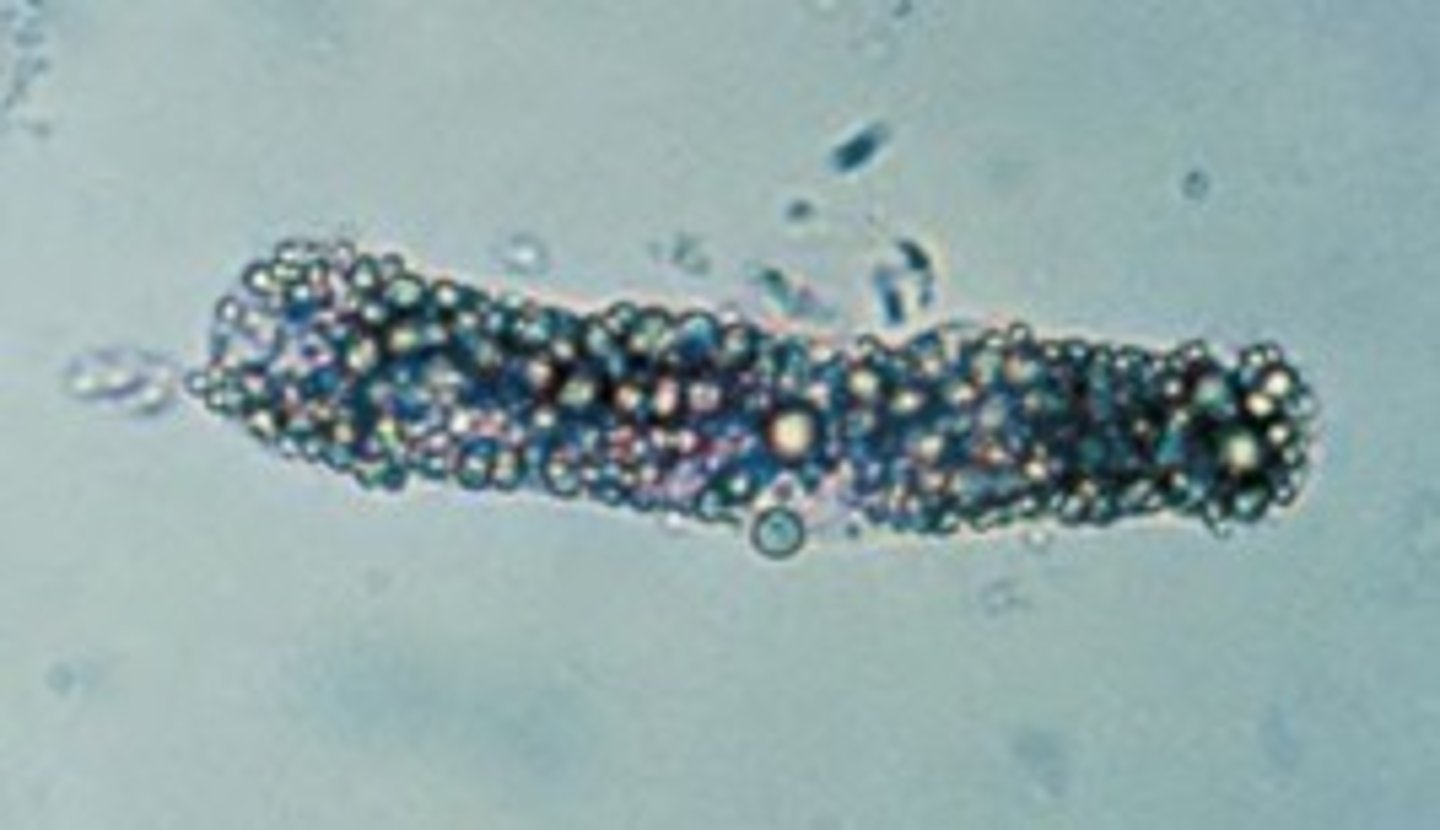
What term is used to describe a renal tubular epi filled with fat globules?
Oval fat body
The appearance of maltese cross forms in a cell or cast denotes the presence of what?
Fat, notably cholesterol
What urine sediment findings are most consistent with nephrotic syndrome?
Oval fat bodies, fatty casts, cholesterol crystals, free fat droplets
What condition can cause the appearance of hemosiderin in urine?
Intravascular hemolysis
What are thread-like structures seen in urine that are increased with inflammatory conditions?
Mucus
Mucus
What cells are rarely seen in urine and indicate bladder or kidney cancer?
Malignant cells
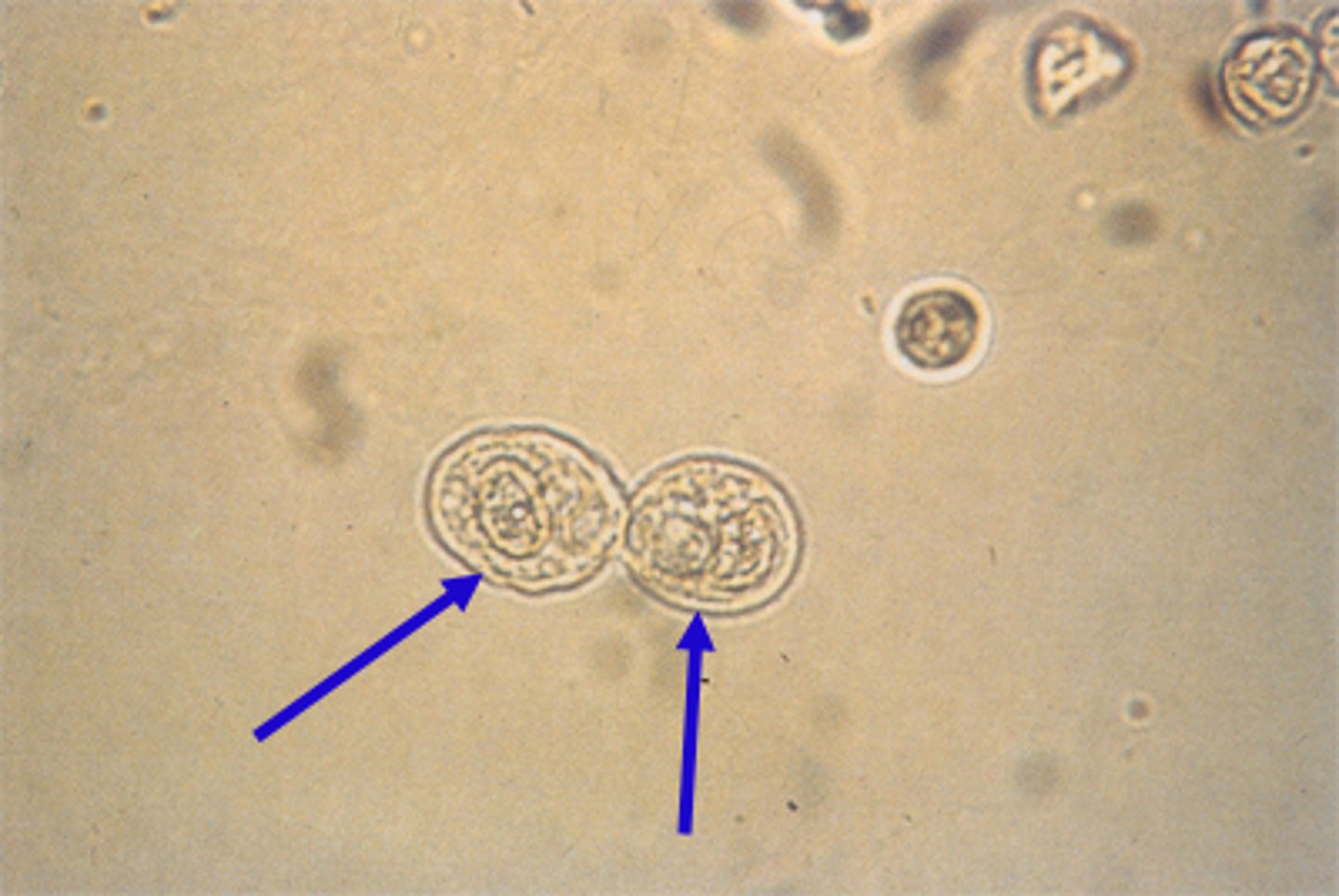
Describe the appearance of yeast in urine
Slightly oval, sizes may vary, often budding, hyphae
What type of organism in urine is pear-shaped, about the size of a white cell, and displays jerky motility?
Trichomonas vaginalis
What protein makes up the basic matrix of casts?
Tamm-Horsfall protein
Other than urine, into what other body fluid can Tamm-Horsfall be secreted?
No other body fluids
What pH environment is needed to enhance cast formation?
Acidic
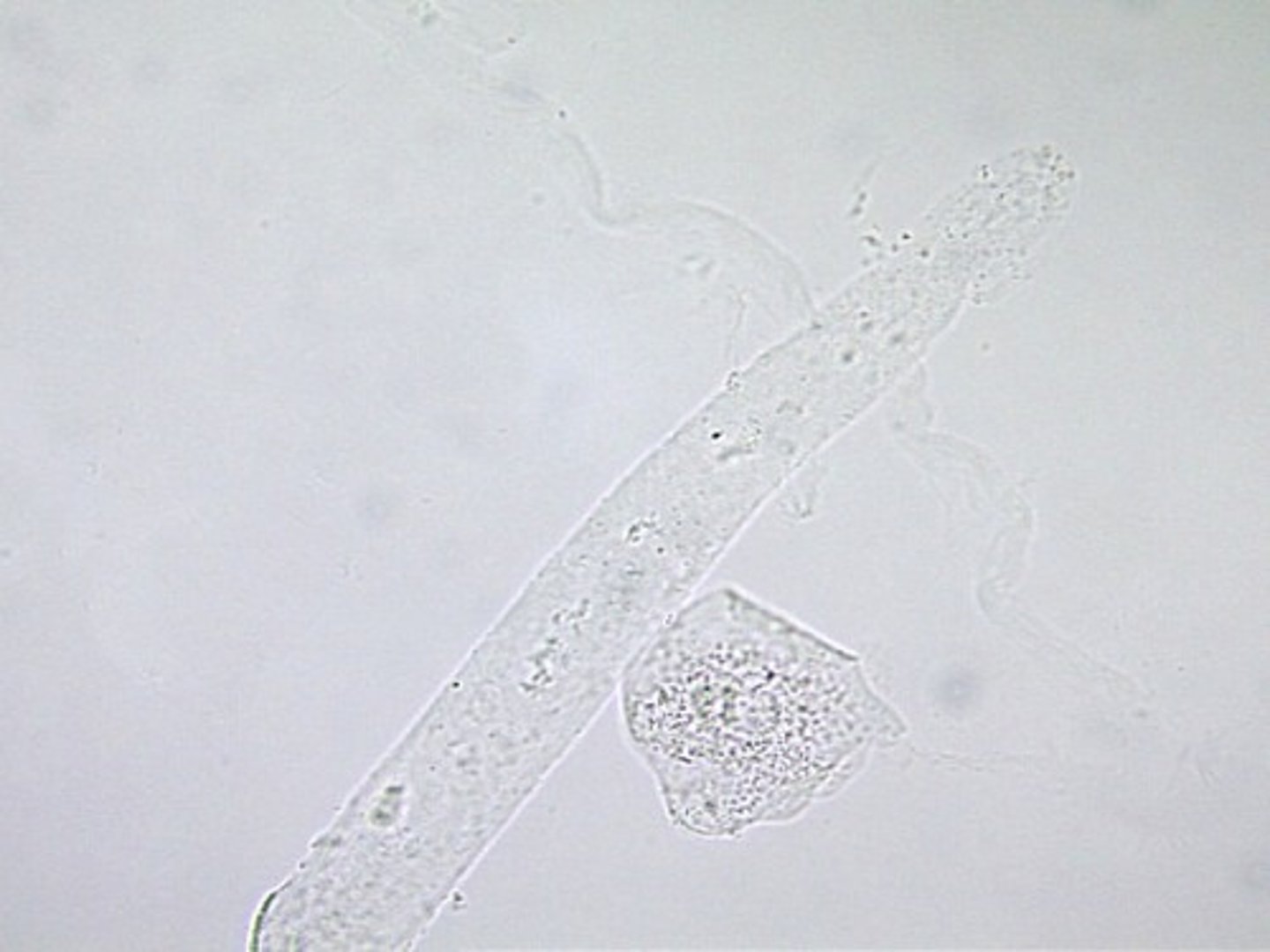
Hyaline cast
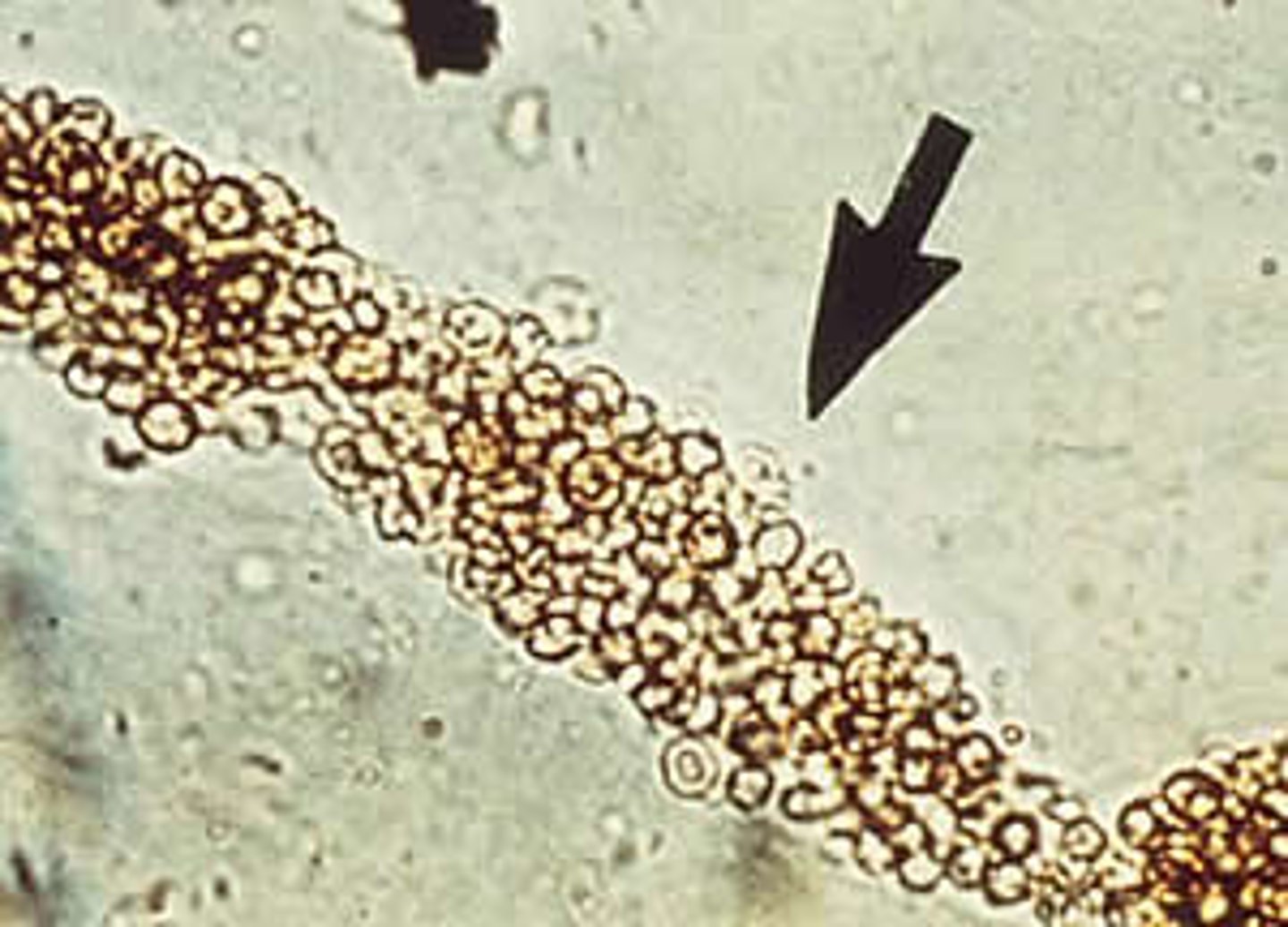
RBC cast
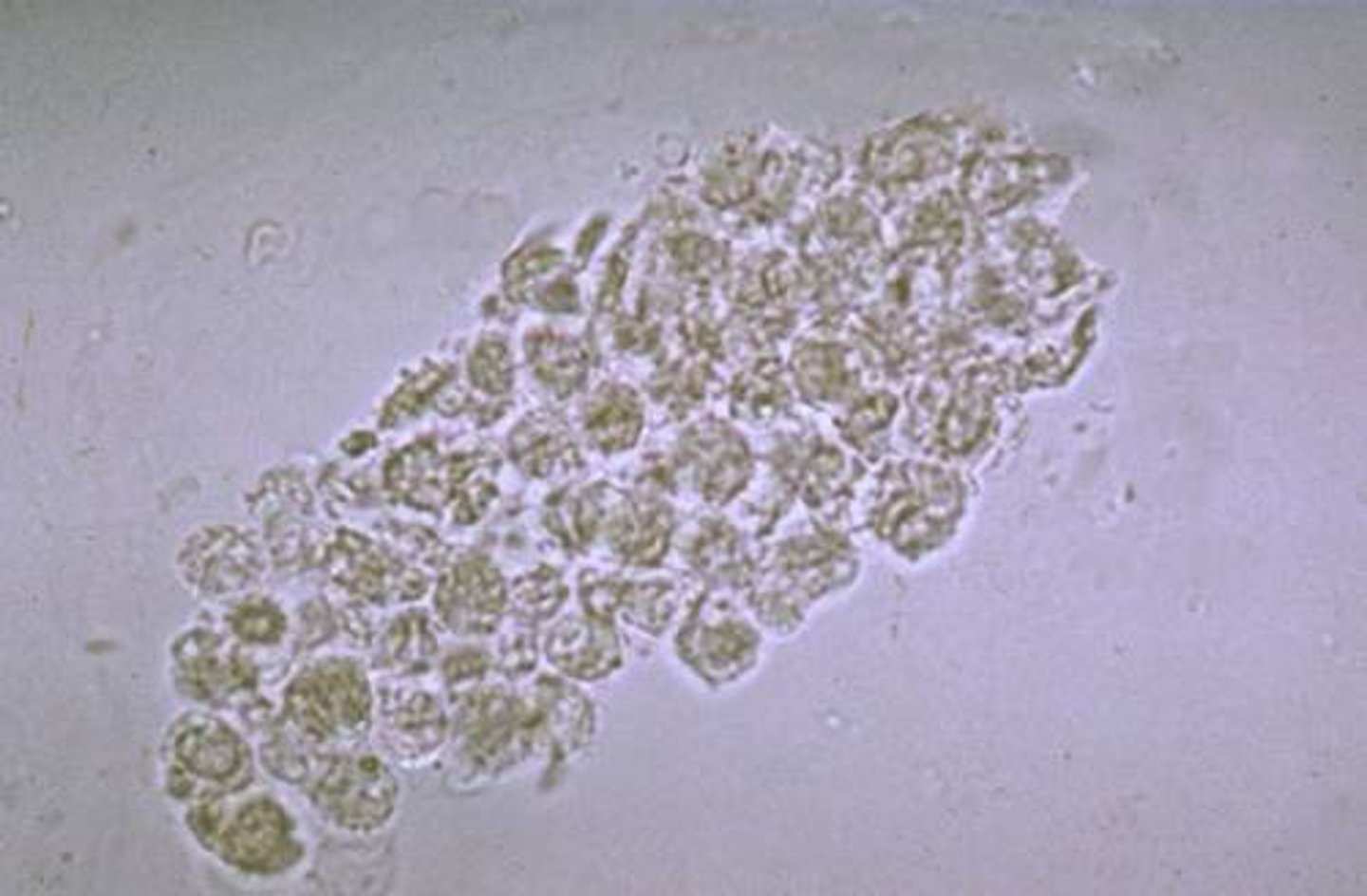
WBC cast
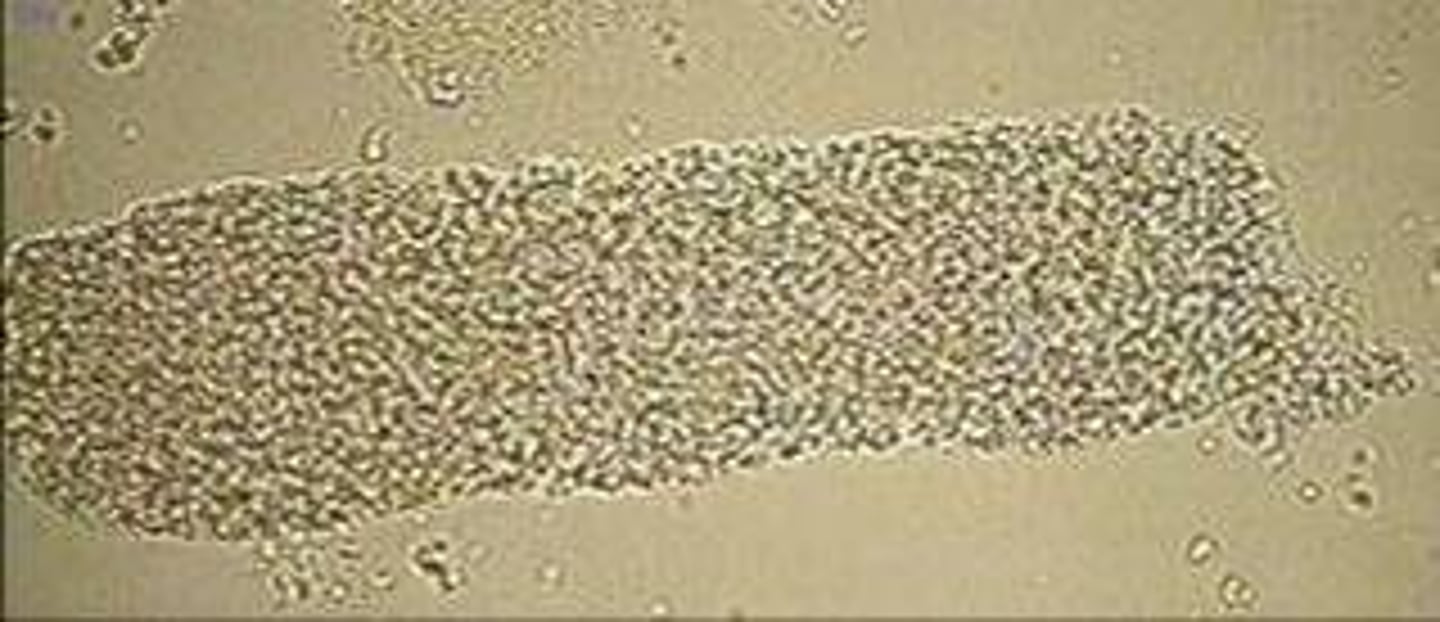
Granular cast
Waxy cast
Broad cast
Fatty cast
Which type of cast is considered to be insignificant?
Hyaline
Describe the appearance of hyaline casts
Colorless, parallel sides & rounded ends
In what conditions will hyaline casts be seen?
Dehydration, stress, or fever
Acute glomerulonephritis is often associated with what type of cast?
RBC cast
White cell casts are often associated with what condition?
Pyelonephritis
A urine is positive for white cells but no white cell casts are seen. What is the most likely condition?
Cystitis (lower UTI)
What type of cast is consistent with indistinguishable cellular debris?
Granular
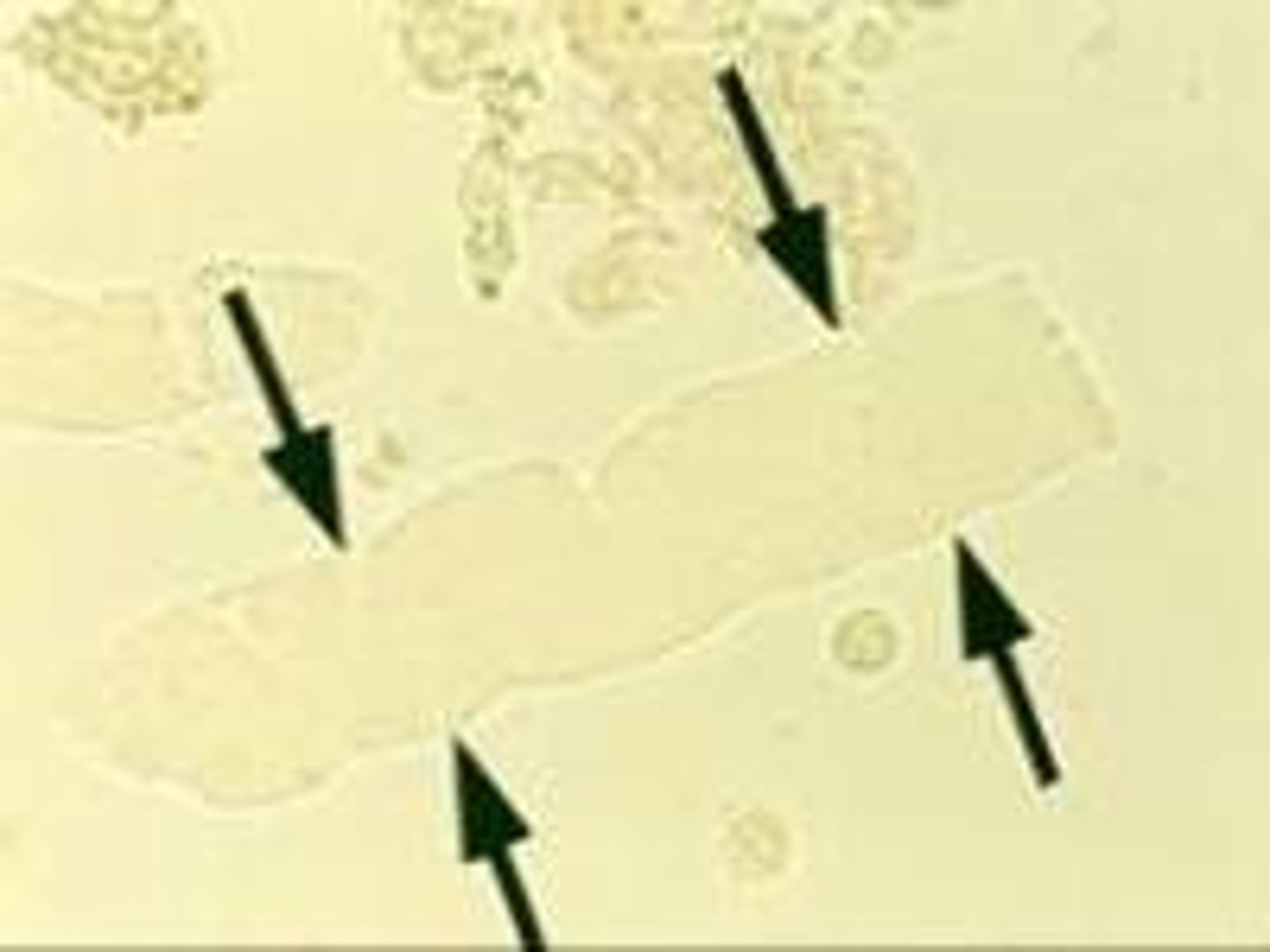
In what portion of the kidney are broad casts formed?
Collecting ducts
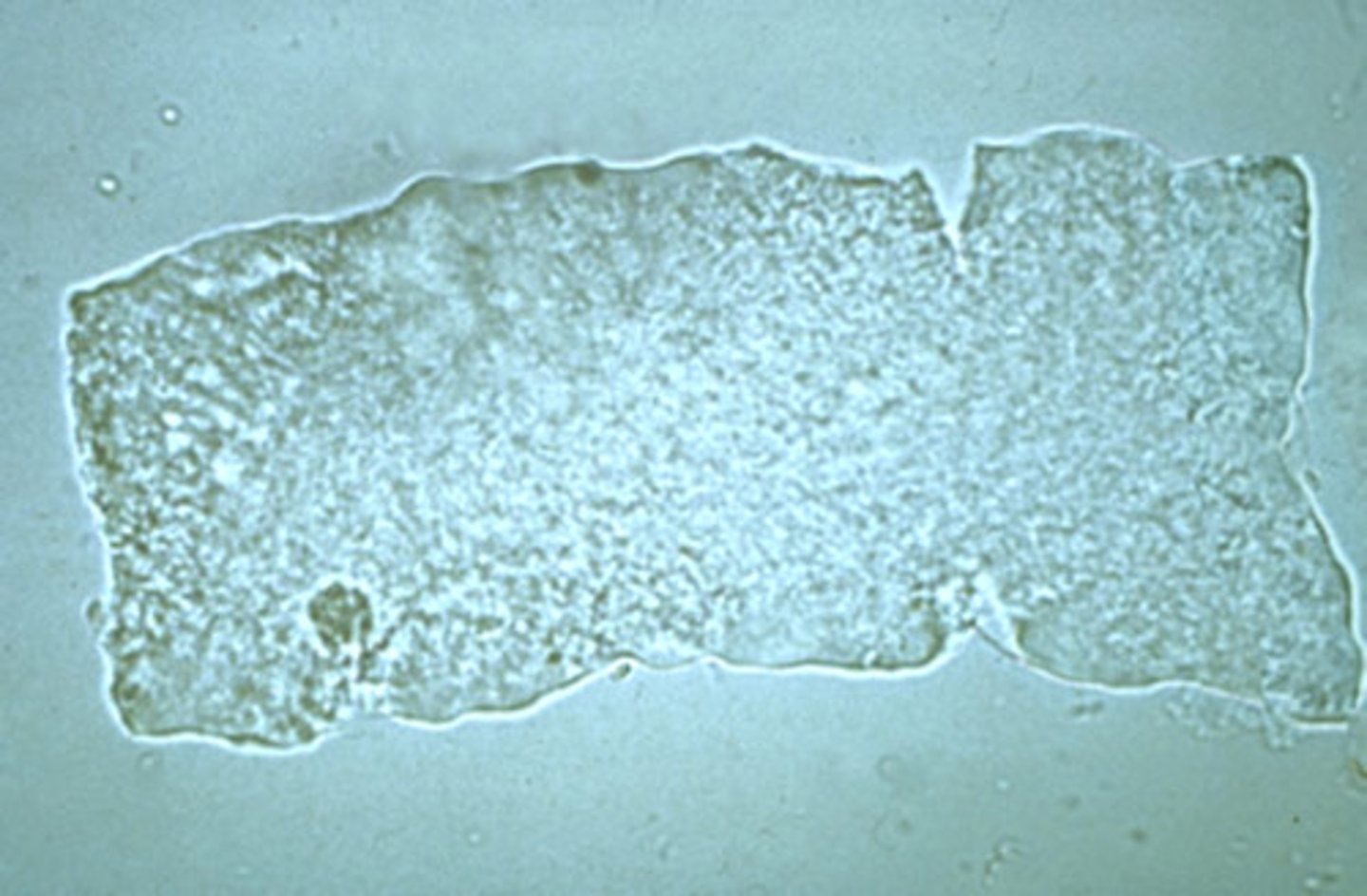
Which 2 types of casts form when urine stasis is at its most extreme?
Broad & waxy
Describe the appearance of waxy casts in urine
Clear, containing minimal debris, ends are blunt & often cracks can be seen along the sides
What are 5 normal types of crystals seen in alkaline urine?
Amorphous phosphates, triple phosphate, calcium phosphate, ammonium biurate, & calcium carbonate
What are 3 normal types of crystals seen in acidic urine?
Amorphous urates, uric acid, & calcium oxalate
What are 7 abnormal types of crystals seen in acidic urine?
Cystine, tyrosine, leucine, bilirubin, cholesterol, radiographic dyes, & drug crystals
Amorphous urates/phosphates
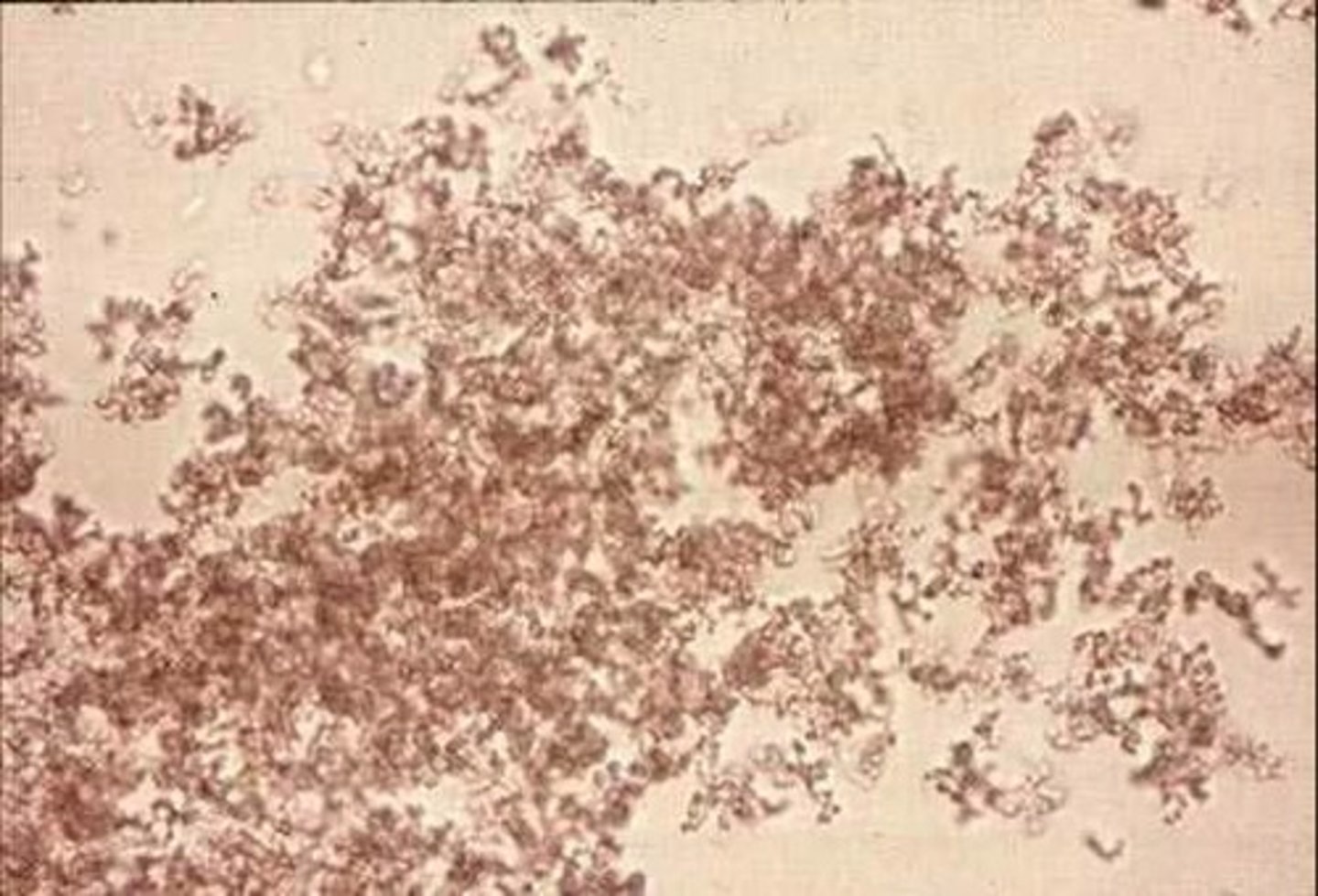
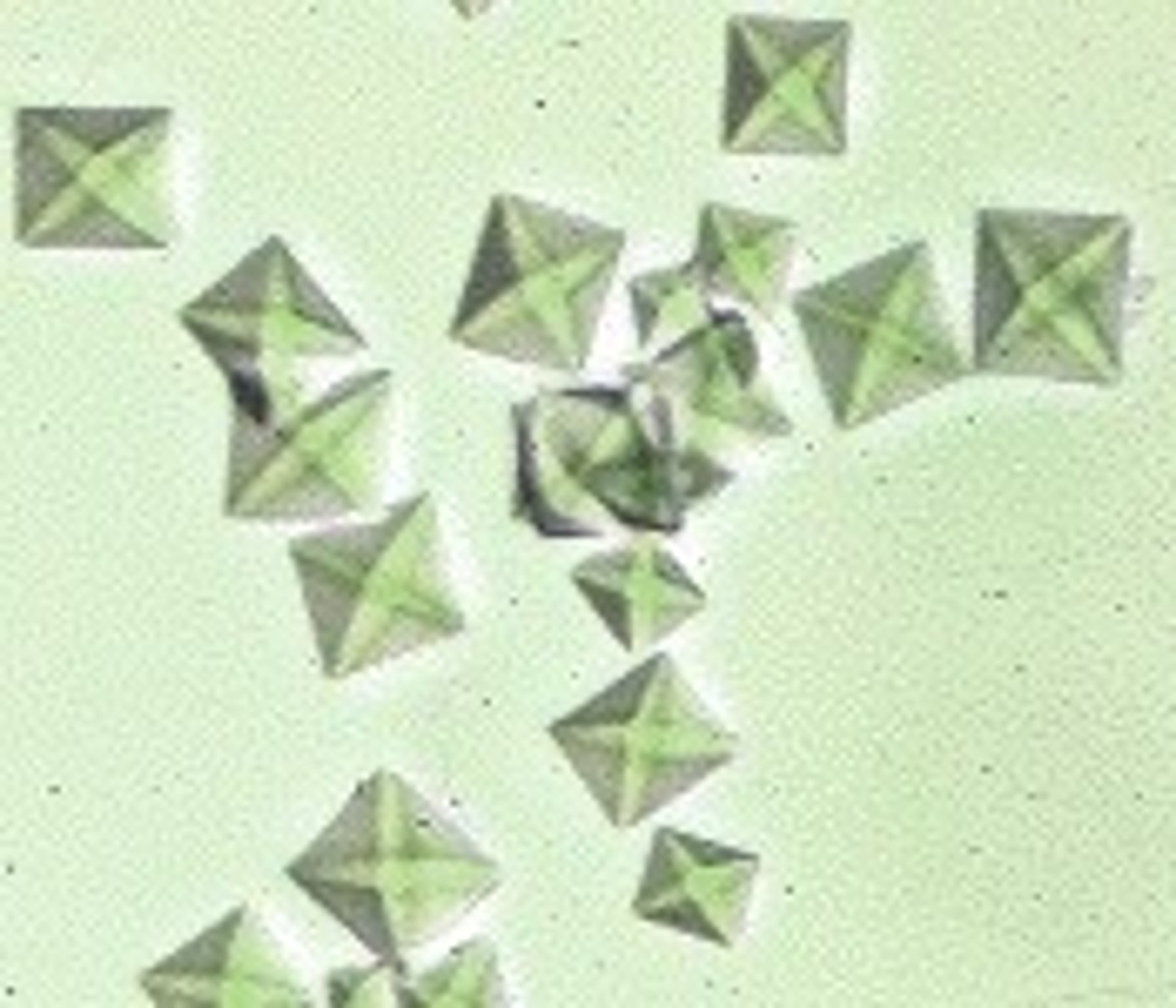
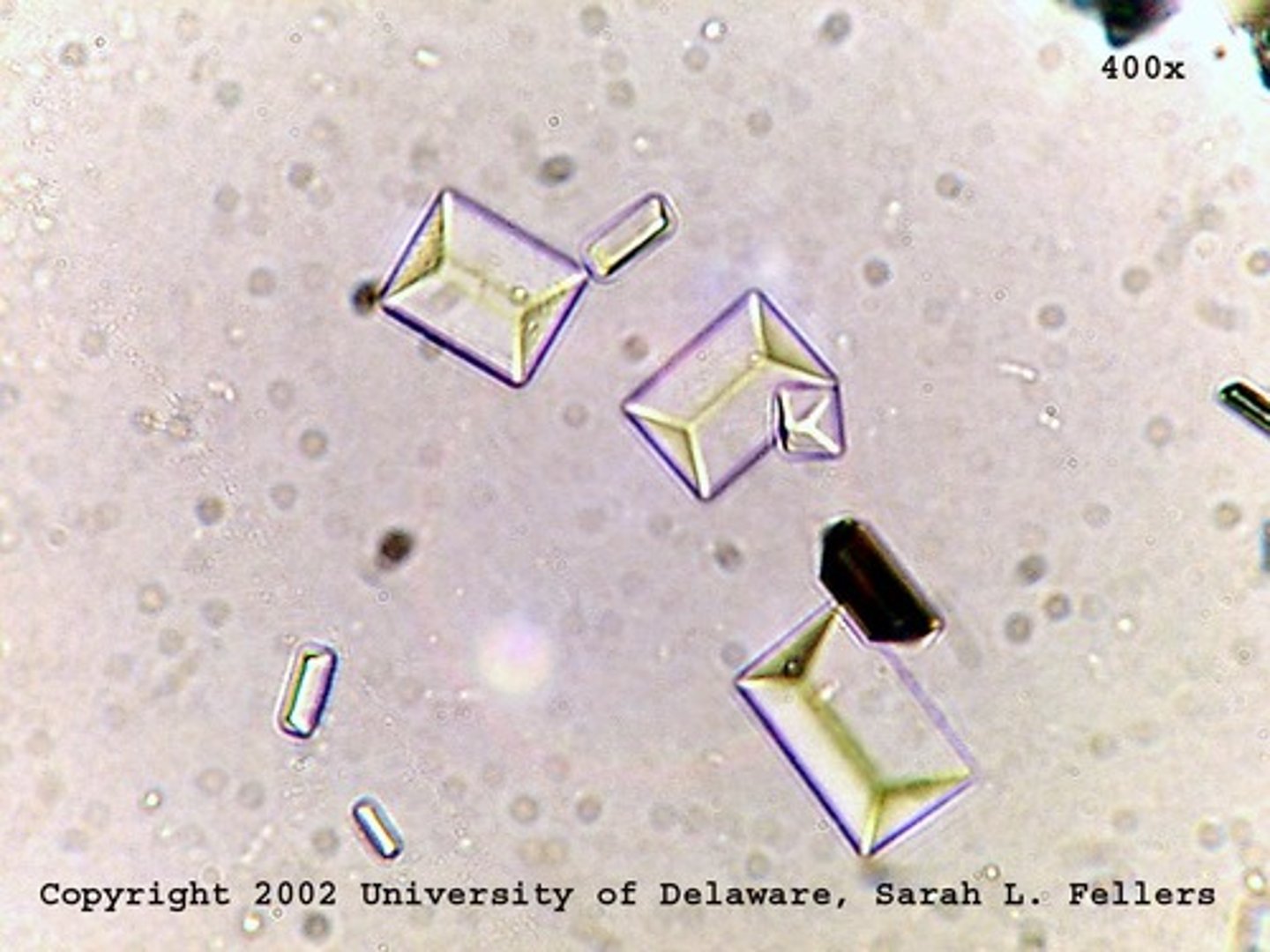
Calcium oxalate

Uric acid
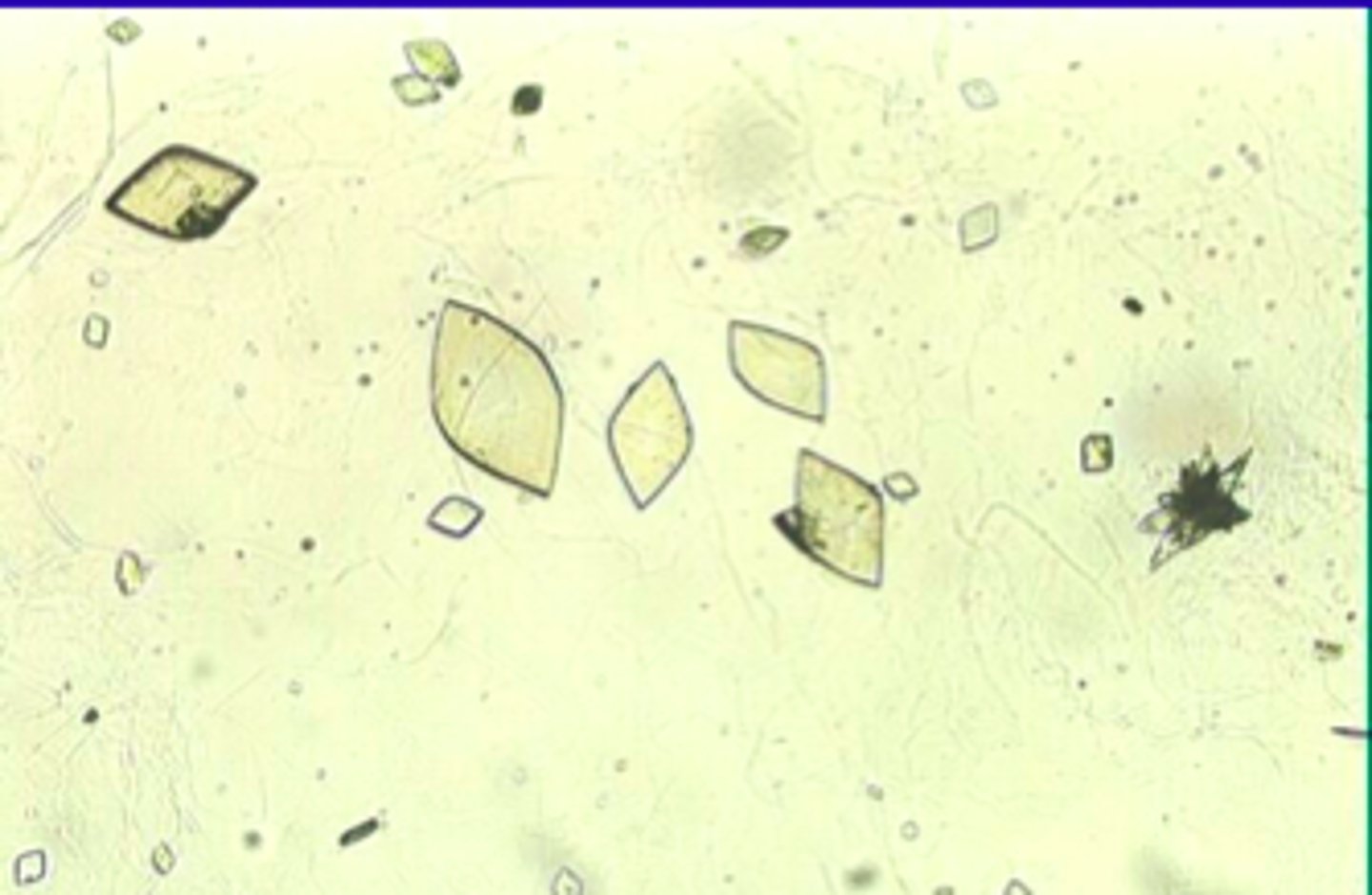
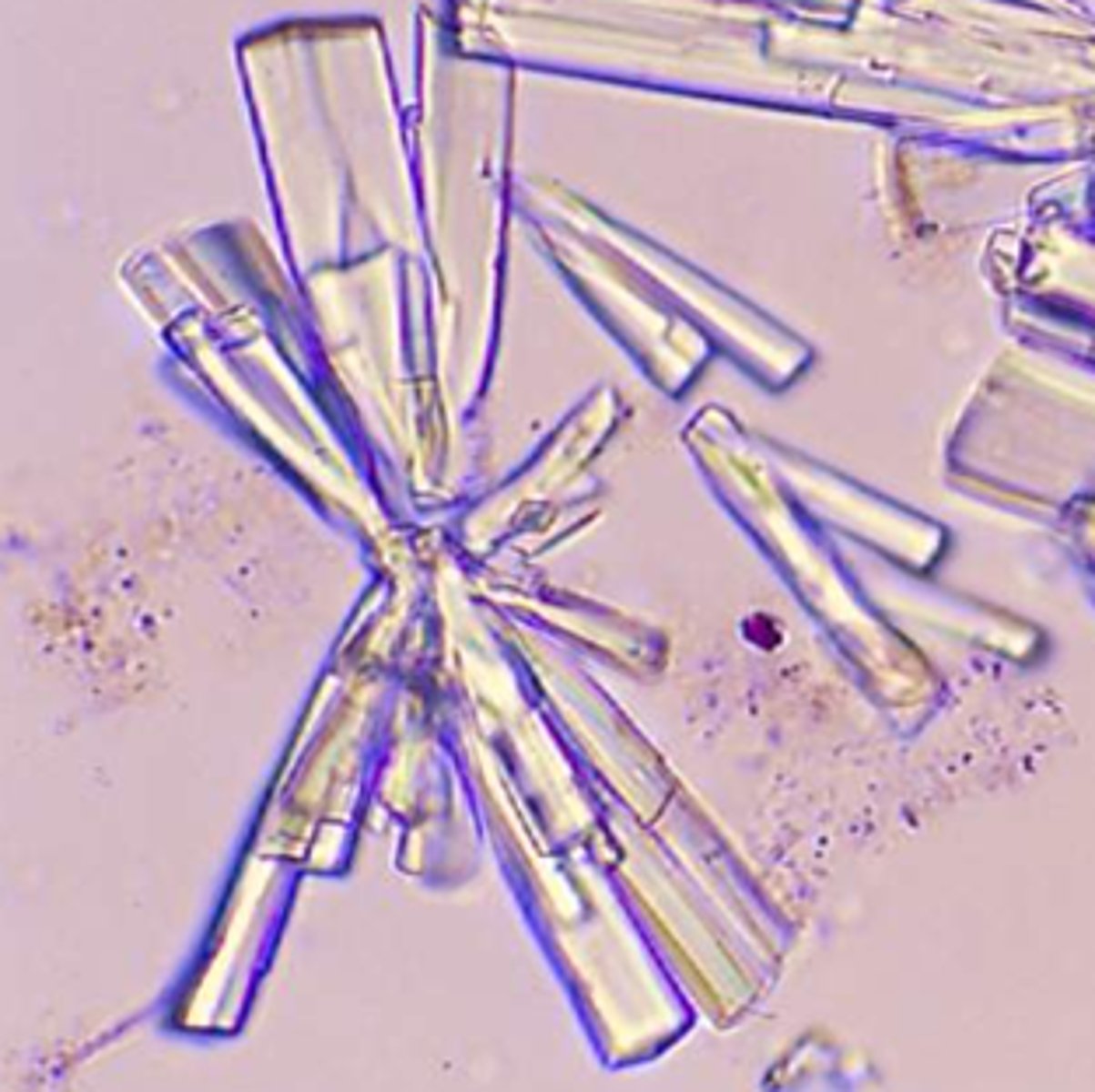
Triple phosphate
Calcium phosphate

Ammonium biurate
Calcium carbonate
Cystine
Tyrosine
Leucine
Bilirubin crystal
Cholesterol crystal
Radiographic dye crystals
Drug crystals
What acid crystal may be seen when there is increased metabolism of purines?
Uric acid
In what condition are increased numbers of oval calcium oxalate crystals seen?
Ethylene glycol poisoning
What are 2 significant causes of uric acid crystals in urine?
Gout, chemotherapy, tumor irradiation
What is the easiest way to differentiate amorphous urates from amorphous phosphates?
Check pH
Acidic = urates
Alkaline = phosphates
What are 2 crystals that may be found in old urine samples?
Triple phosphate & ammonium biurate
What descriptive word do we use for triple phosphate?
Coffin lid
What descriptive word do we use for ammonium biurate?
Thorny apple
What descriptive word do we use for calcium carbonate?
Dumbbells
What descriptive word to we use for calcium oxalate?
Square envelopes
In what pH environment are clinically significant urine crystals typically seen?
Acidic
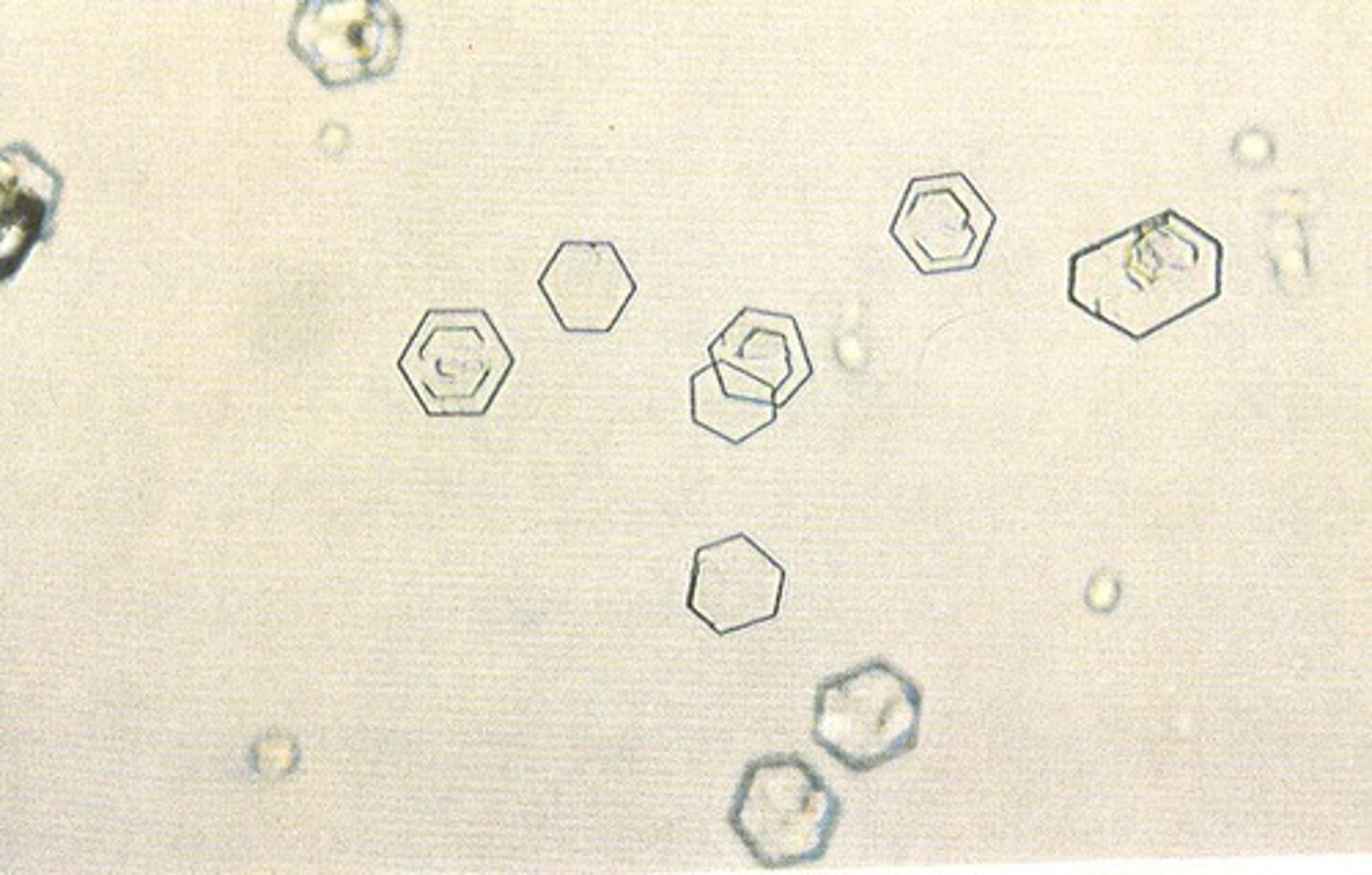
What crystal is described as being hexagonal?
Cystine
In what disorders are cystine crystals seen in urine?
Defect in reabsorption of cystine, may cause kidney stones
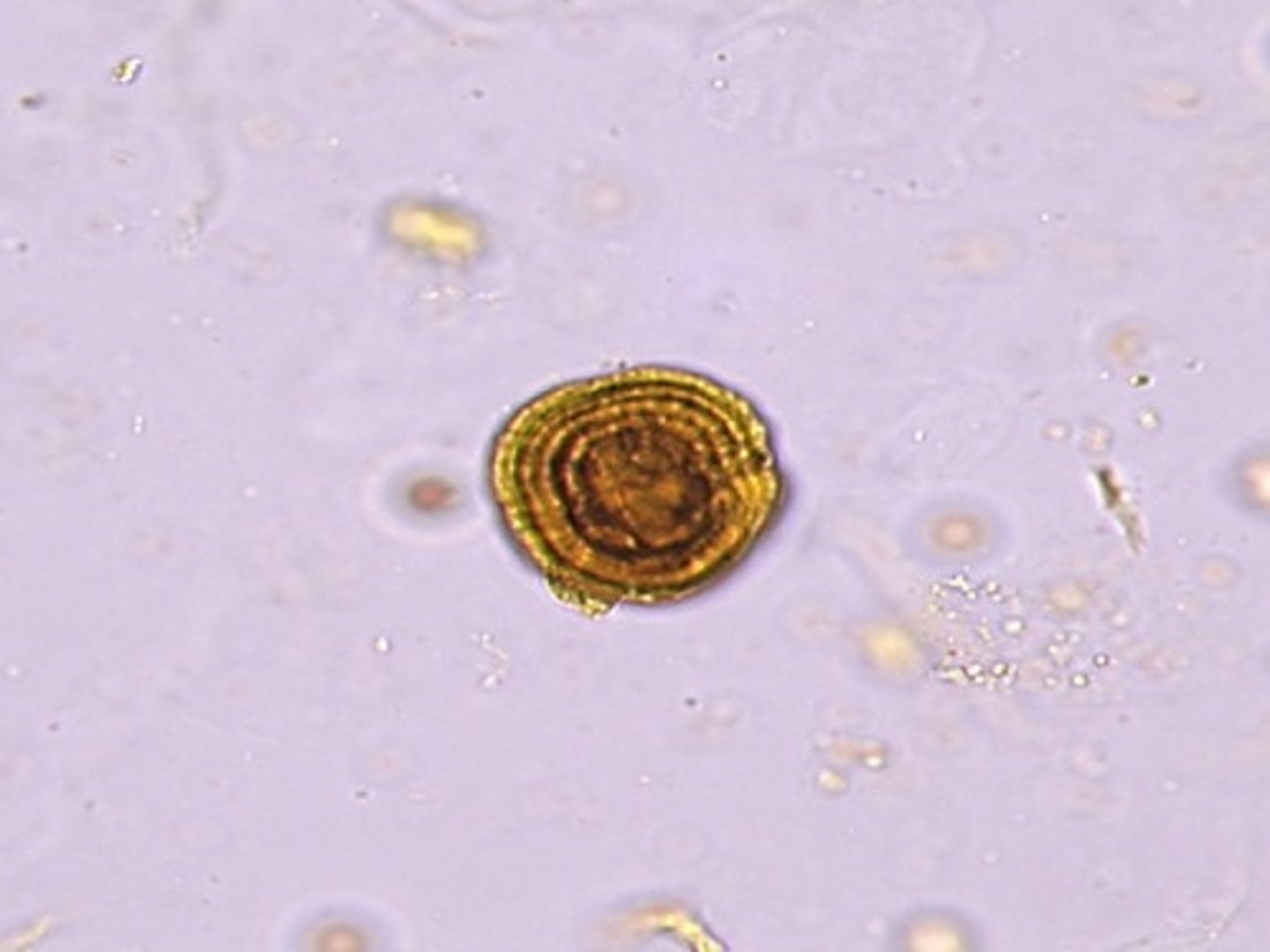
What are 3 crystals that are seen in liver disease in urine?
Bilirubin, tyrosine, & leucine
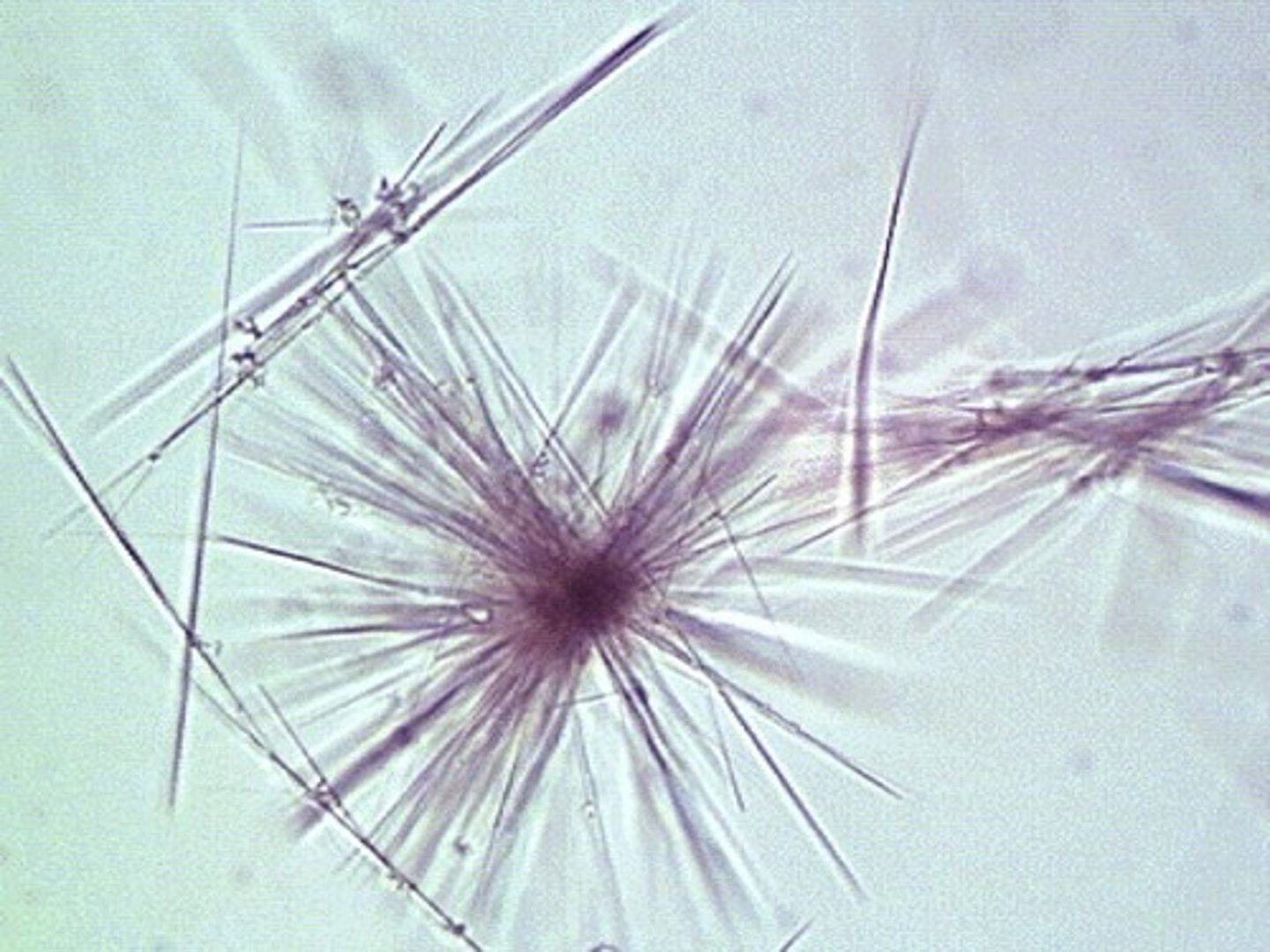
What specific disease is linked to the appearance of leucine crystals?
Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Describe the appearance of leucine crystals in urine
Round with radial striations (TREE TRUNK)
If a patient has hepatitis, what crystal would most likely be seen?
Bilirubin
Why is the appearance of drug crystals in urine considered clinically significant?
Indicates the patient needs hydration, crystals can damage tubules.
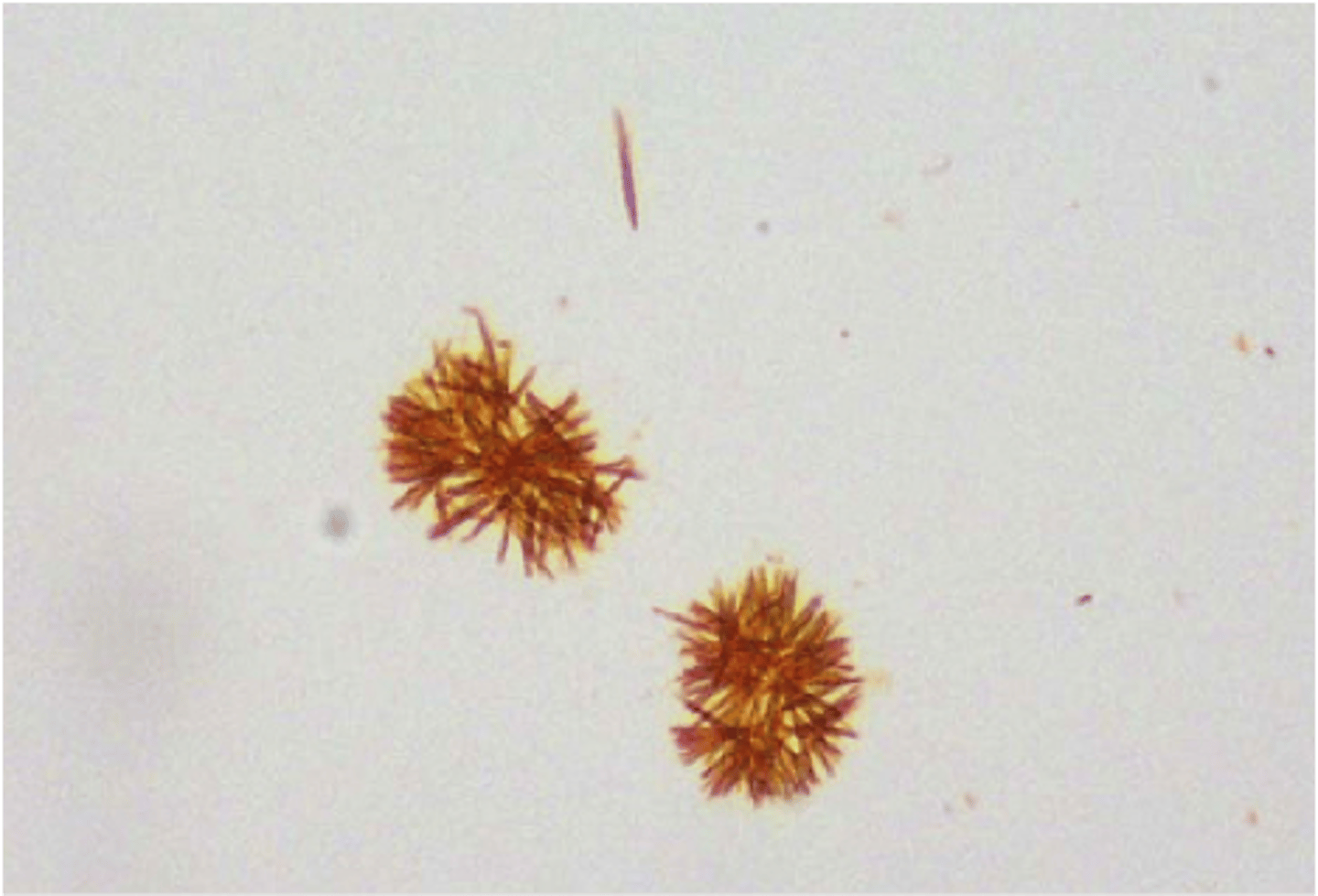
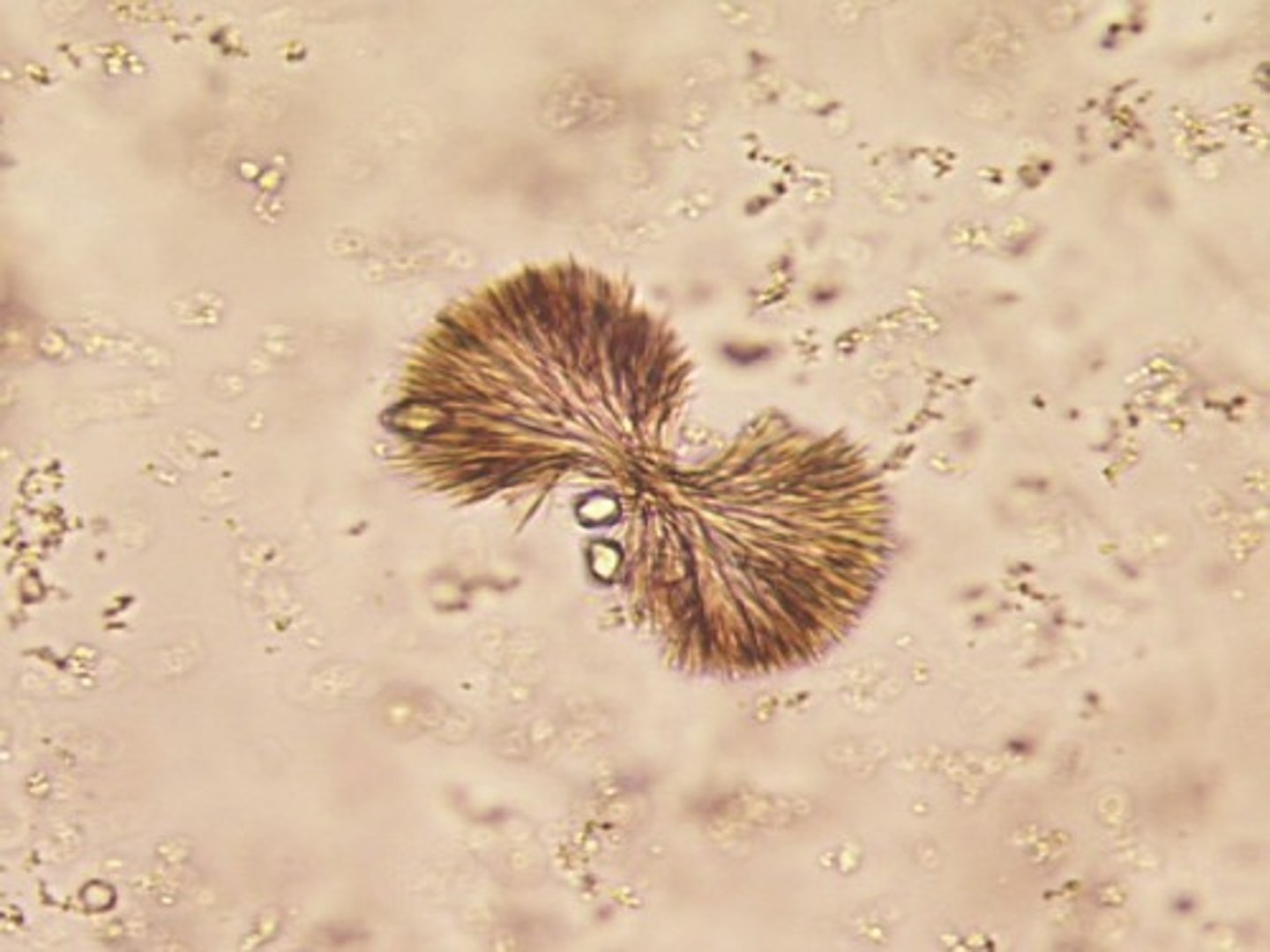
Describe the appearance of cholesterol crystal in urine
Flat plate with notched corners
What contaminant can mimic the appearance of red cells, and will show a maltese cross form when polarized?
Starch/talc
What condition is linked to the appearance of cholesterol crystals?
Nephrotic syndrome
What type of urine collection is preferable for home pregnancy testing and why?
1st morning sample because it's more concentrated
What is the advantage to testing a clean catch urine?
It won't be contaminated by squamous epi cells or skin bacteria
What disease is a 2 hour post-prandial urine designed to help diagnose?
Diabetes
Why are 24 hour or timed urines preferable when testing for the quantity of chemicals?
Because the secretion of chemicals especially hormones varies over the course of a day
What type of urine collection may arrive in the lab in a syringe?
Supra-pubic aspirate
What is a disadvantage to testing a first morning urine?
May contain more amorphous crystals because it's more concentrated
What is the best way to preserve a urine sample?
Refrigerate
When are chemical preservatives most commonly used?
When a sample is being transported & won't be refrigerated
How may ketones be affected if a urine is not properly preserved?
Decrease due to evaporation
How may glucose be affected if a urine is not properly preserved?
Decrease due to glycolysis
How may nitrite be affected if a urine is not properly preserved?
Increase due to bacterial reduction of nitrates