2b- Biological Molecules: Proteins and Enzymes
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What are proteins?
polymers made up of 1 or more chains of amino acid monomers forming polypeptide chains
What elements do all proteins contain?
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
What are all amino acids made of?
amine group
carboxyl group
a side chain
How many different amino acids are there?
20
What does an amino acid look like?
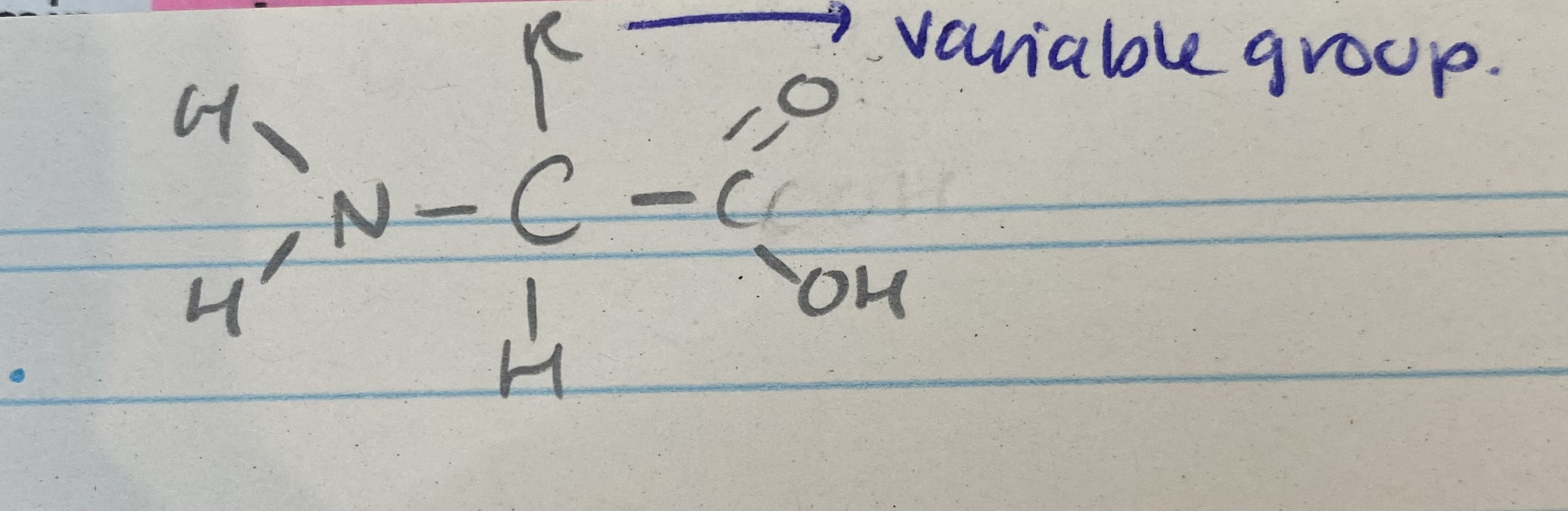
What is a dipeptide?
2 amino acids joined together
What is a polypeptide?
many amino acids joined together
What bond is formed between amino acids?
peptide bond
Describe how amino acids join together
Condensation reaction which removes a water molecule between the carboxyl and amine group of different amino acids, forming a peptide bond
Describe the primary structure of a protein
Sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, joined by peptide bonds
Describe the secondary structure of a protein
Folding of the polypeptide chain due to hydrogen bonding between amino acids
What are the 2 structures formed in the secondary structure?
a helix
B pleated sheet
Describe the tertiary structure of a protein
3D folding of polypeptide chains into a specific shape due to interactions between R groups forming hydrogen and ionic bonds, and disulphide bridges
What is the order of strength of these bonds from weakest to strongest?
hydrogen
ionic
disulphide
Where do hydrogen bonds form in the tertiary structure?
between amine and carboxyl groups of different amino acids
Where do ionic bonds form in the tertiary structure?
between variable groups
Where do disulphide bridges form in the tertiary structure?
between any variable group that has a sulphur atom
Describe the quaternary structure of a protein
protein containing more than 1 polypeptide chain
Describe the food test for proteins
Add biuret reagent (sodium hydroxide + copper II sulphate). Positive result blue to lilac. Indicates presence of peptide bonds
What is a fibrous protein?
Form long parallel chains with cross-bridges
Very stable
Have a structural role in organisms
What is a globular protein?
Carry out metabolic functions e.g. enzymes and haemoglobin
What are some examples of fibrous proteins?
collagen
keratin
elastin
What is chromatography used for?
used to separate mixtures of monosaccharides or amino aids
Why does chromatography work?
the molecules have different molecular sizes and solubilities
In chromatography, what does it mean if the molecule is smaller and more soluble?
the further it will be moved in a solvent
What is the equation to find the Rf value?
Rf= distance from origin to solute (spot) / distance from origin to solvent front
What are enzymes?
they are biological catalysts and act by lowering activation energy (never used up)
What is activation energy?
minimum amount of energy required to start a reaction
Why do we have enzymes in our body?
without, temperature would be too low to support life
What is meant by metabolism?
sum of all chemical reactions in the body
Distinguish between intracellular and extracellular enzymes
act inside and outside cells
What type of protein is an enzyme?
globular
Describe the ‘lock and key’ model
substrate fits exactly into active site as it is complementary. Enzyme-substrate complex formed. Reaction takes place and products are released
Describe the ‘induced fit’ model
the substrate does not fit perfectly into the active site (not complementary). The active site changes shape to allow the substrate to bind. E-S complex forms, causing bonds in substrate to distort, lowering activation energy to break bonds
Explain the specificity of enzymes
Specific tertiary structure determines shape of active site= dependent on sequence of amino acids
Active site is complementary to a specific substrate
Only this substrate can bind to active site, inducing fit and forming an enzyme-substrate complex
What are the 2 calculations for rate of reaction?
rate= amount of product / time taken
rate= 1 / time
What are the units for per second?
S -1 (smaller -1)
What does it mean when the line levels off in a graph?
stopped-all substrate converted to products
Why is the enzyme reaction faster at the start?
the substrate used up as reaction progresses= more substrate at start so more ES complexes
What does the temperature graph for enzyme rate of reaction look like?
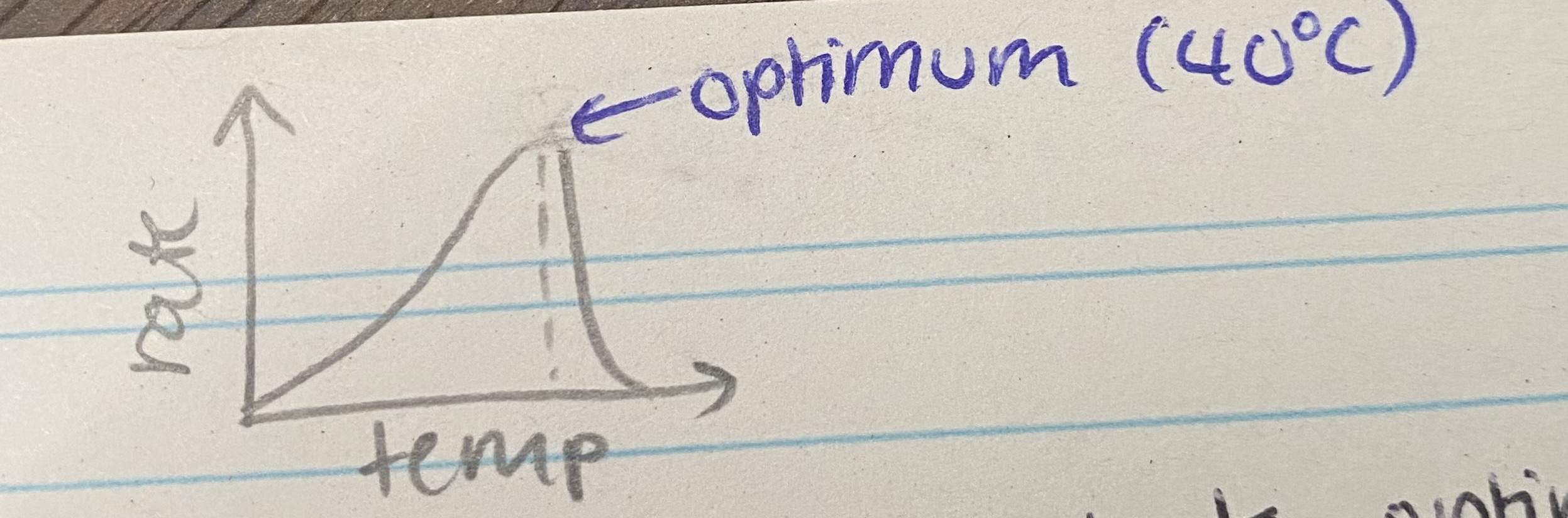
Describe and explain the effects of temperature on enzyme rate of reaction
As temp increases up to optimum, rate increases= more kinetic energy so more collisions so more ES complexes form
Temp above optimum, rate decreases= enzymes denature, bonds break so tertiary structure + active site change shape so no longer complementary so fewer ES complexes form
What does pH refer to?
concentration of hydrogen ions
What happens to enzyme rate of reaction when you change pH by 1?
changes aqueous H+ conc by 10 times
What is used to control pH in an enzyme investigation?
a buffer
Why is pH a log scale?
there is a huge range of H+ conc involved
What does the pH graph for enzyme rate of reaction look like?
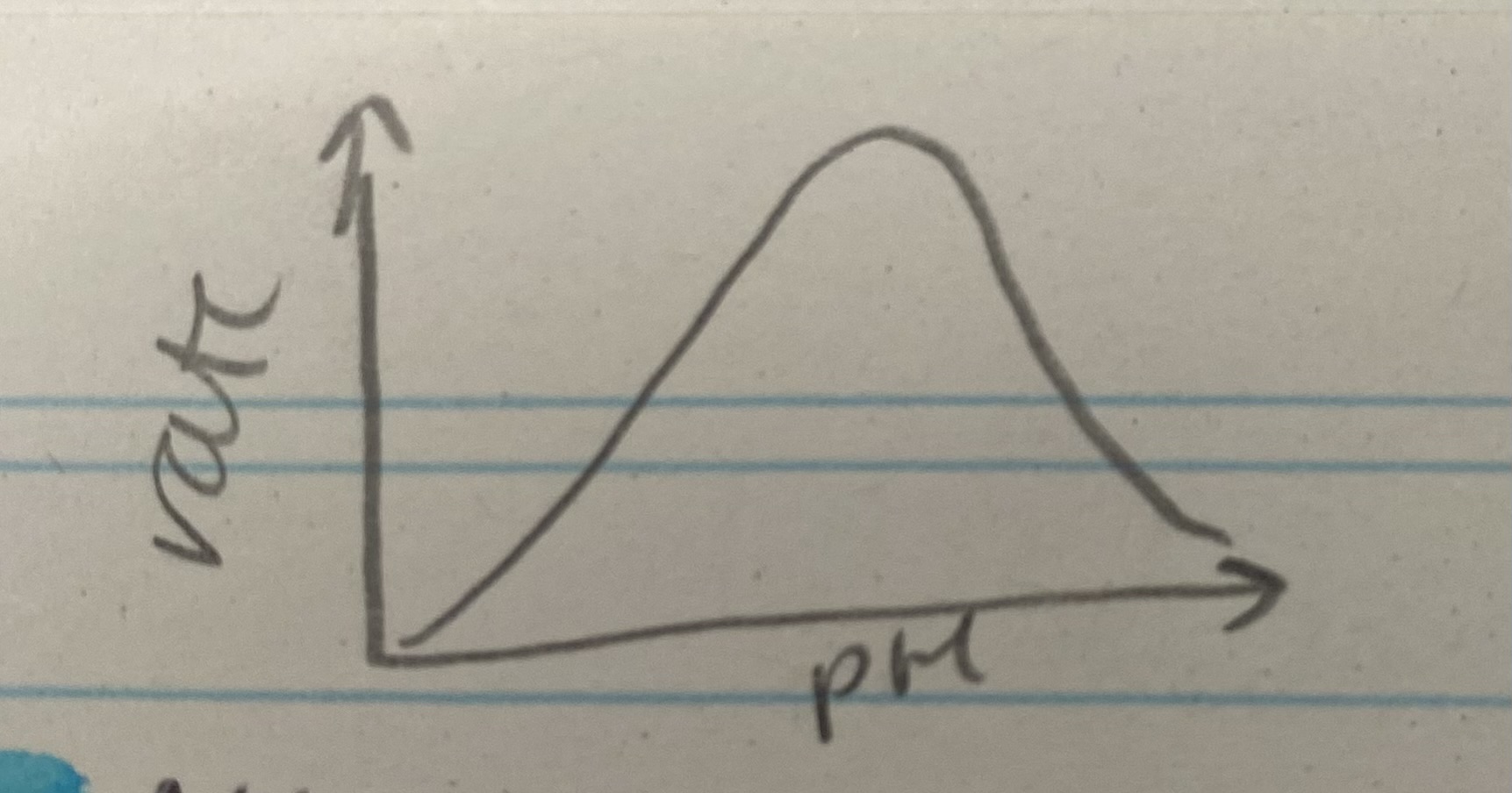
Describe and explain the effects of pH on enzyme rate of reaction
When not optimum= alters charges on amino acids which affects bonding= breaks bonds that hold tertiary structure and reform in different places= change shape of active site= not complementary= no ES complexes form= enzyme denatures
What does the substrate concentration graph for enzyme rate of reaction look like?
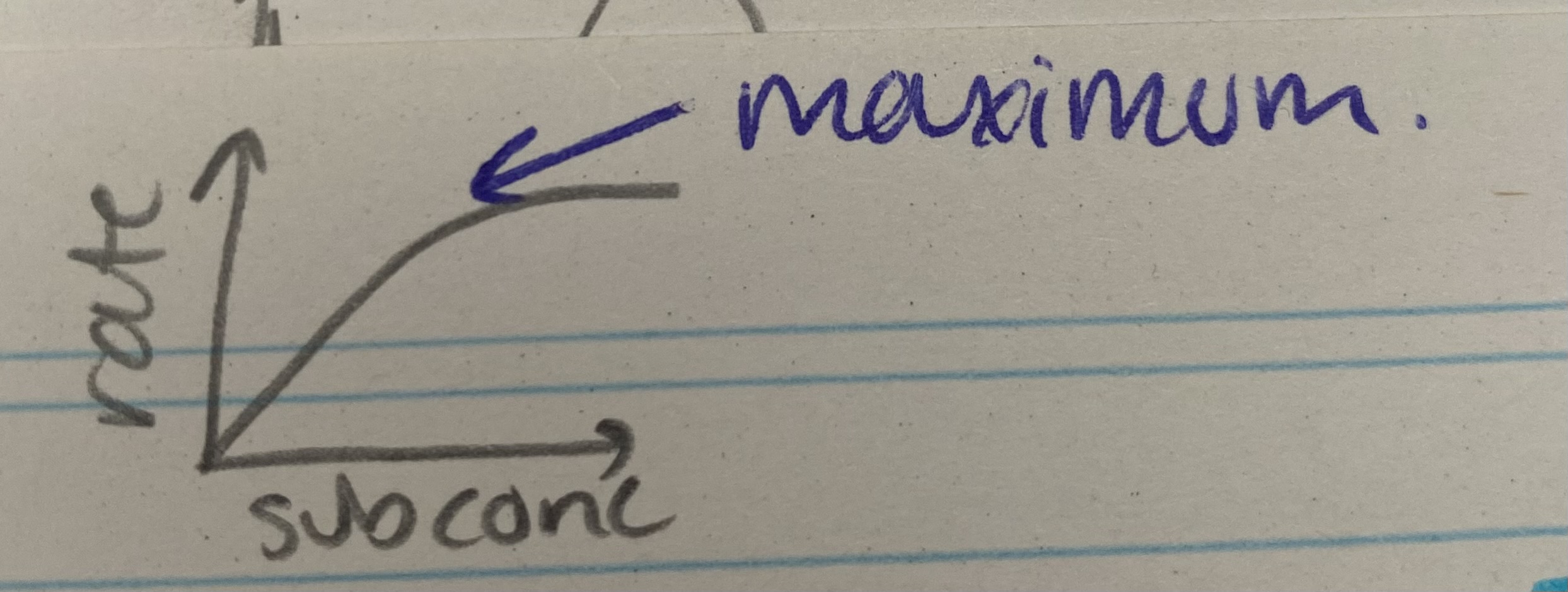
Describe and explain the effects of substrate concentration on enzyme rate of reaction
As sub conc increases, rate increases= sub conc is limiting factor (too few enzymes to occupy all active sites)= more successful collisions= more ES complexes formed
At maximum, rate stops increasing= enzyme conc is limiting factor as all active sites are saturated/ fully occupied
What does the enzyme concentration graph for enzyme rate of reaction look like?

Describe and explain the effects of enzyme concentration on enzyme rate of reaction
As enzyme conc increases, rate increases= enzyme conc is limiting factor (excess substrate)= more available active sites= more ES complexes form
At certain point, rate stops= substrate conc is limiting factor= all substrates in use
What is an inhibitor?
a substrate which decreases the rate of an enzyme- controlled reaction and may bring it to a halt
What are the 2 types of inhibitor?
competitive
non- competitive
What is a competitive inhibitor and how does it work?
Have a similar shape to that of the enzyme’s substrate
competes with substrate as it binds to the active site of the enzyme
Active site is blocked so can’t be occupied by substrate= fewer ES complexes formed= reduced rate
What does the competitive inhibitor graph for enzyme rate of reaction look like?
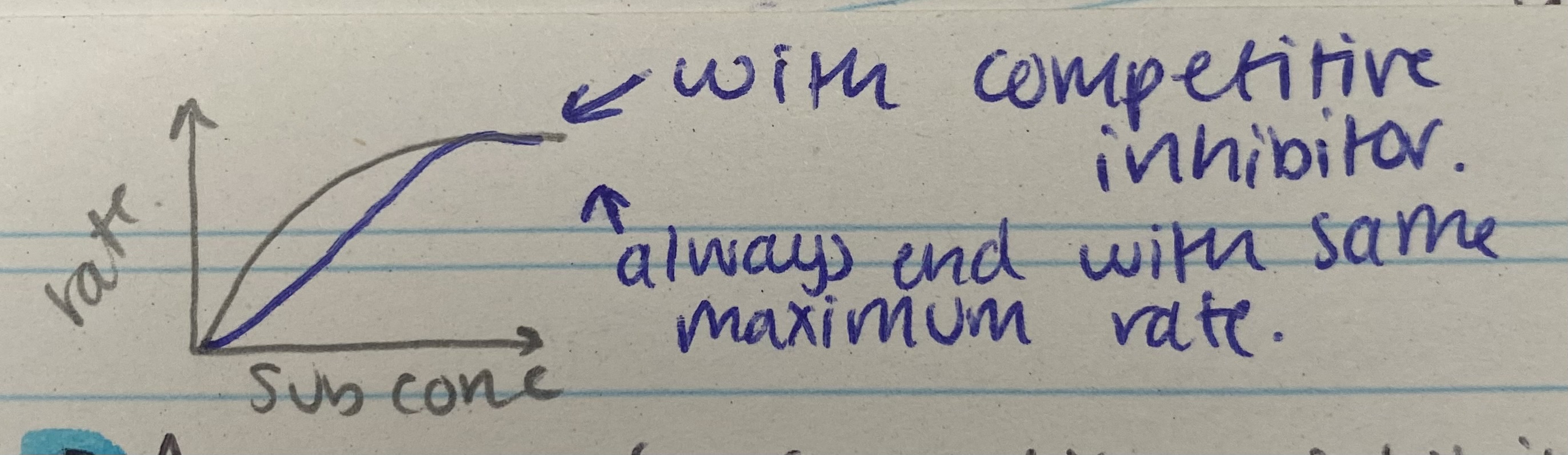
Describe and explain the effects of competitive inhibitor on enzyme rate of reaction
As conc of competitive inhibitor increases, rate decreases= similar shape to substrate= competes/binds/blocks active site= so substrate can’t bind= fewer ES complexes formed
Increasing subsrate conc, reduces effect on inhibitors
What is a non-competitive inhibitor?
Not similar shape
Binds to another region of the enzyme (allosteric site)
Changes tertiary shape therefore active site shape= substrate can’t bind= fewer ES complexes formed= rate decreases= once added, inactivates enzyme
What does the competitive inhibitor graph for enzyme rate of reaction look like?
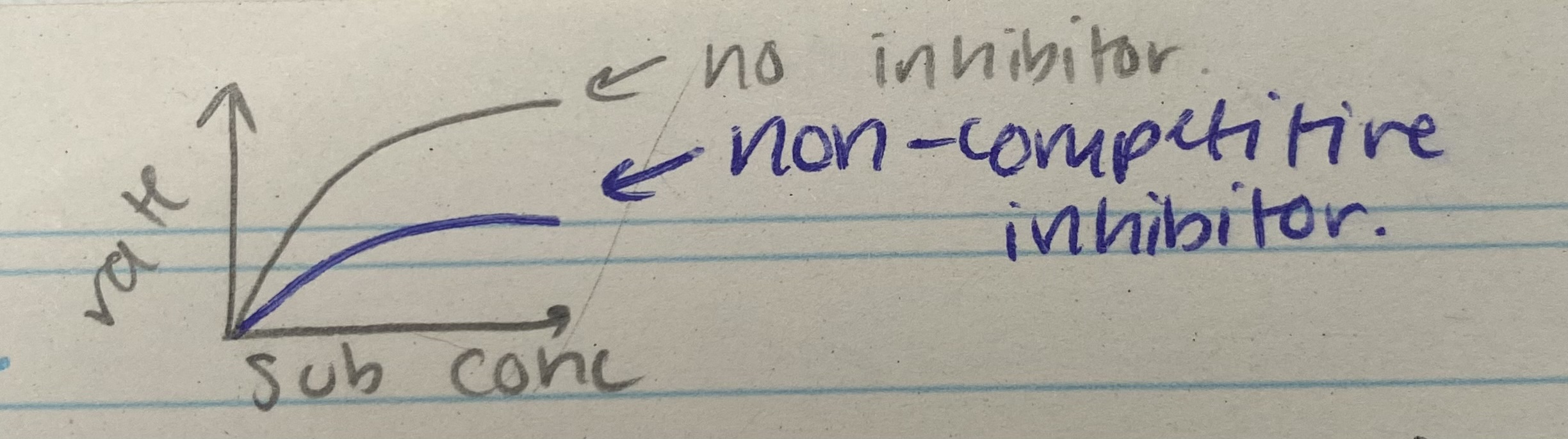
Describe and explain the effects of enzyme concentration on enzyme rate of reaction
As conc of non-competitive inhibitor increases, rate decreases= binds to allosteric site= changes active site shape= no longer complementary to substrate= can’t bind= fewer ES complexes formed
increasing sub conc has no effect on rate, as change to active site is permanent