PLP 266 Lab Practical
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms

Bipolaris Sorokiniana
Leaf Spot
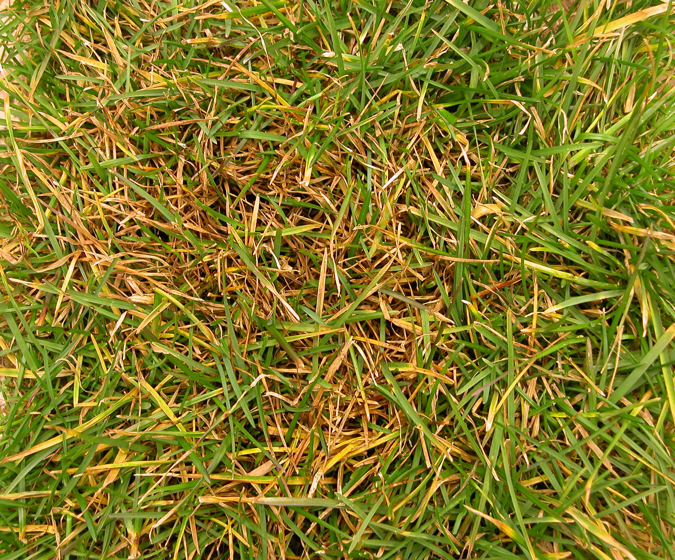

Microscopic signs of Leaf Spot
Large spores (conidium)
y-branching
Crosswalls
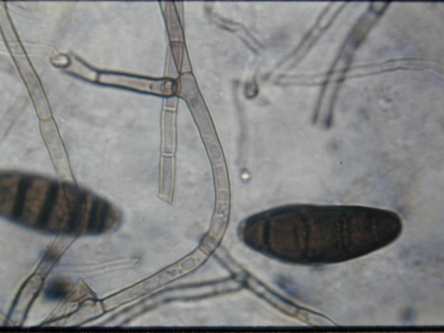
Dark colored spores associated with leaf spot (Bipolaris sorokiniana)
Conidia

Colletotrichum cerale
Crown Rot Anthracnose

Crown Rot Anthracnose (Colletotrichum cerale) microscopic signs
Crescent-shaped spores
y-branching
Cross walls
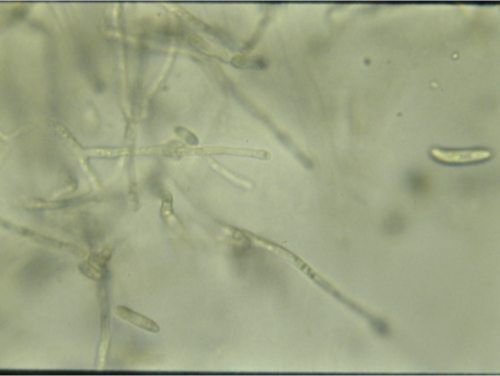
Typhula incarnata
Gray Snow Mold

Gray Snow Mold (Typhula incarnata) microscopic signs
Clamp connections
No spores
y-branching
Cross walls
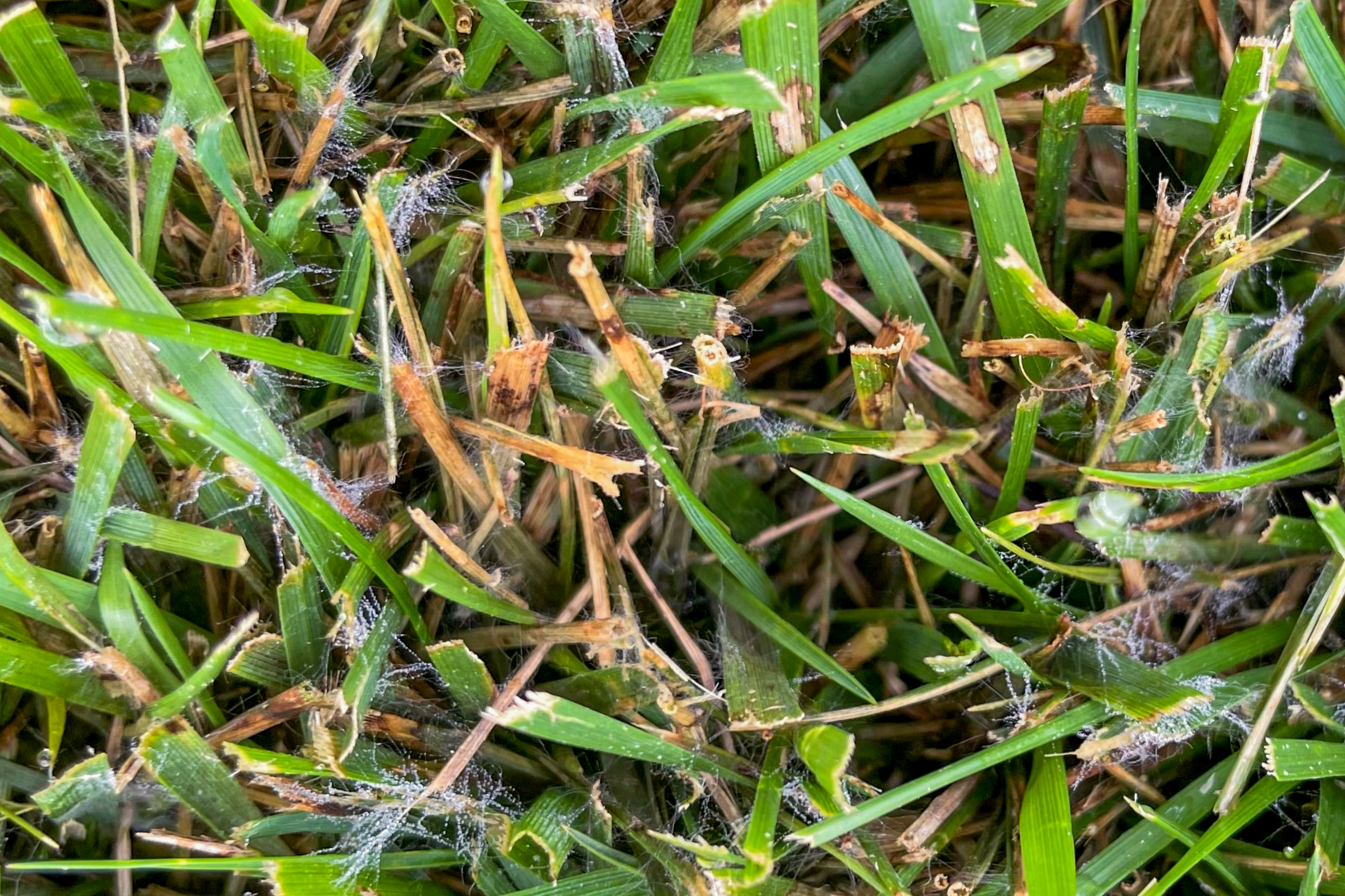
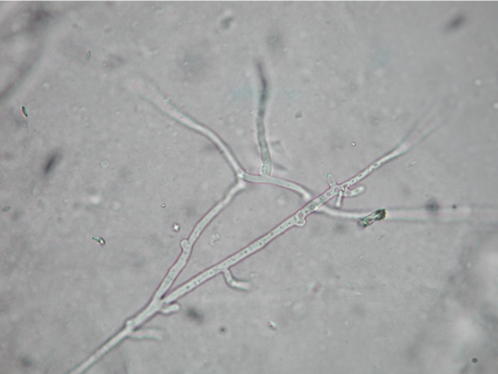

Rhizoctonia solani
Brown Patch

Brown Patch (Rhizoctonia solani) microscopic signs
90 degree branching
No spores
Cross walls
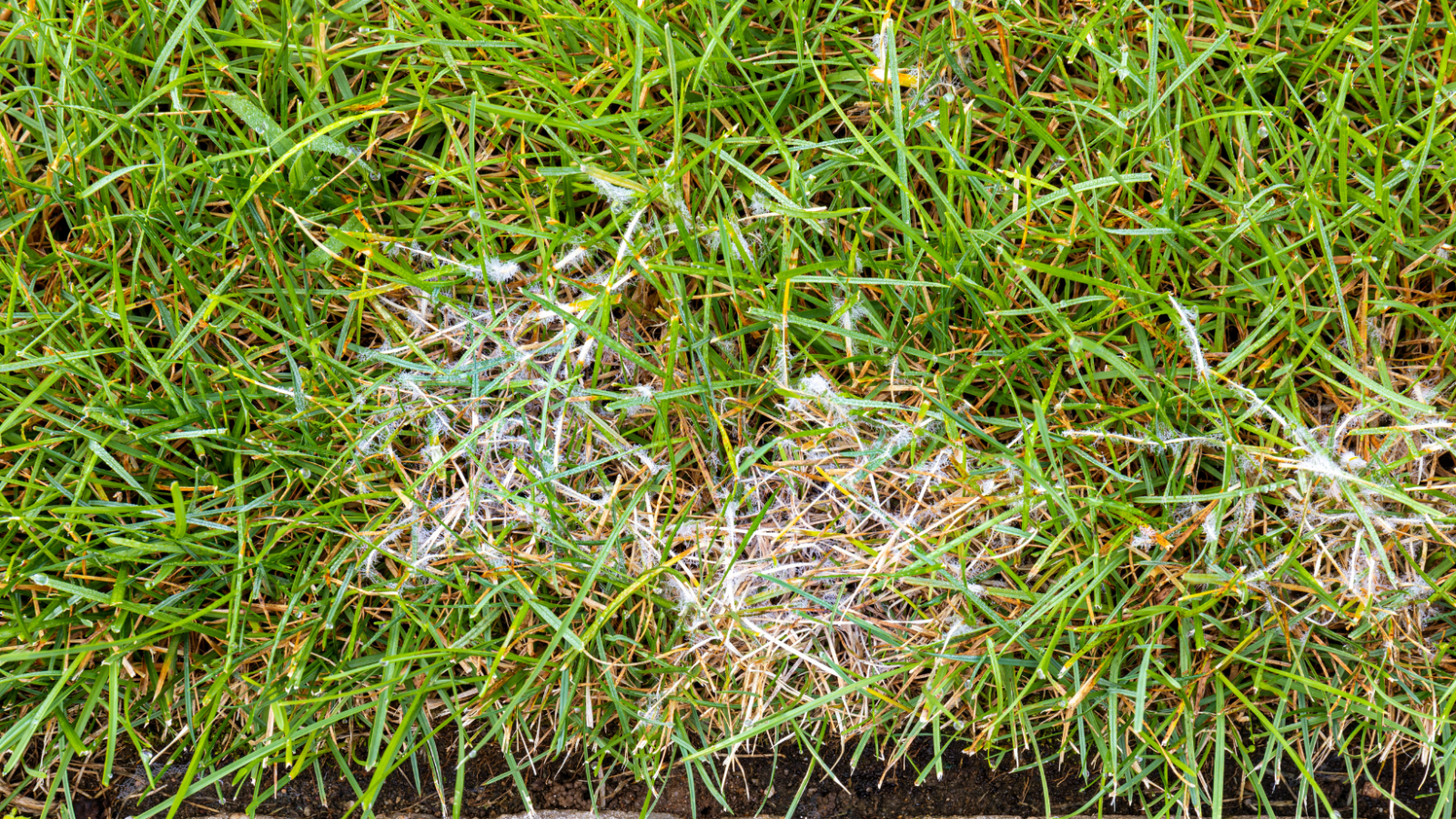
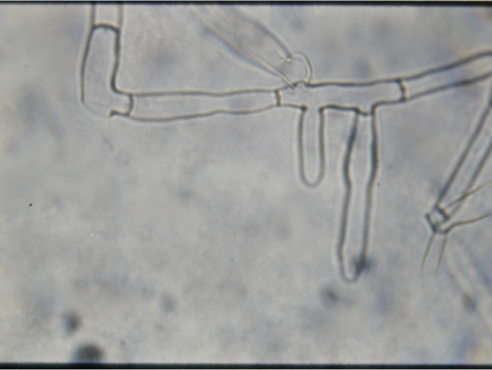

Clarireedia jacksonii
Dollar Spot

Dollar Spot (Clarireedia jacksonii) Microscopic signs
y-branching
Cross walls
No spores
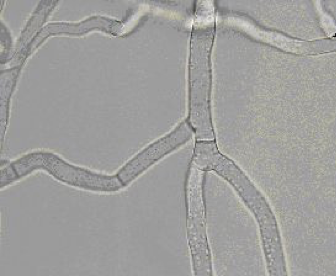
Pythium spp. Microscopic signs
y-branching
No spores
No cross walls
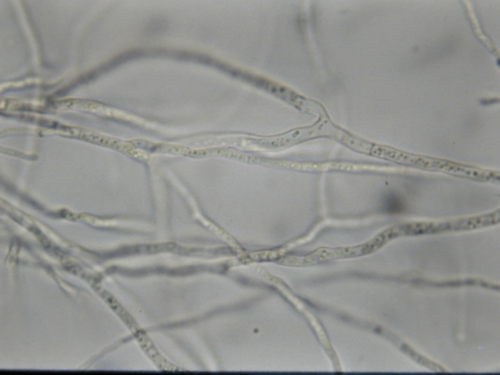

Pythium root rot disfunction microscopic signs
y-branching
oospores within the roots
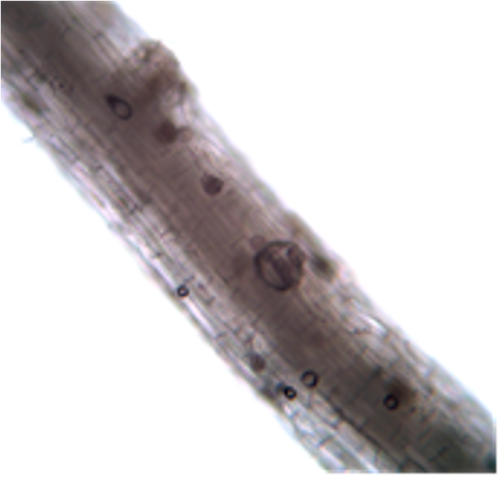


Take all Patch microscopic signs
(Ectotrophic) runner hyphae
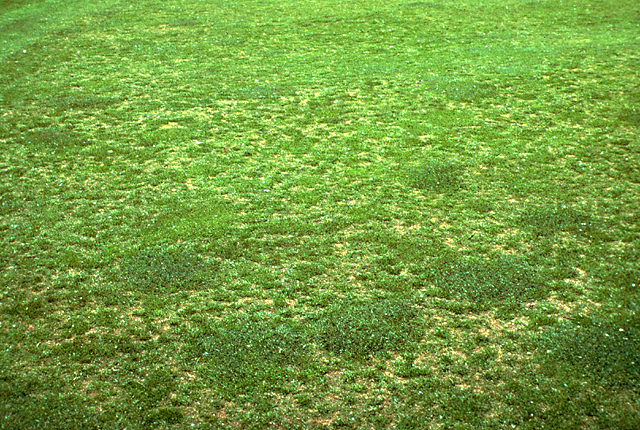

Bacterial wilt microscopic signs
Bacteria flowing out of leaf blade
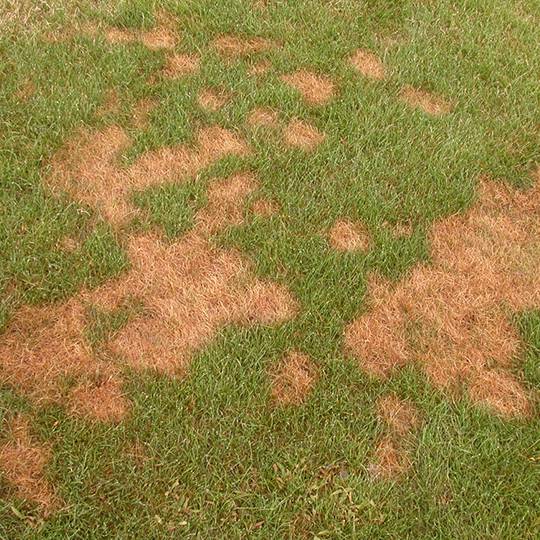

Pythium blight microscopic signs
y-branching
No cross walls
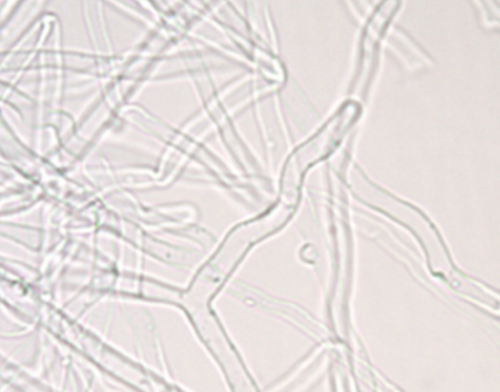
Brown patch occurs with high humidity and what temperature (warm or cool)
warm
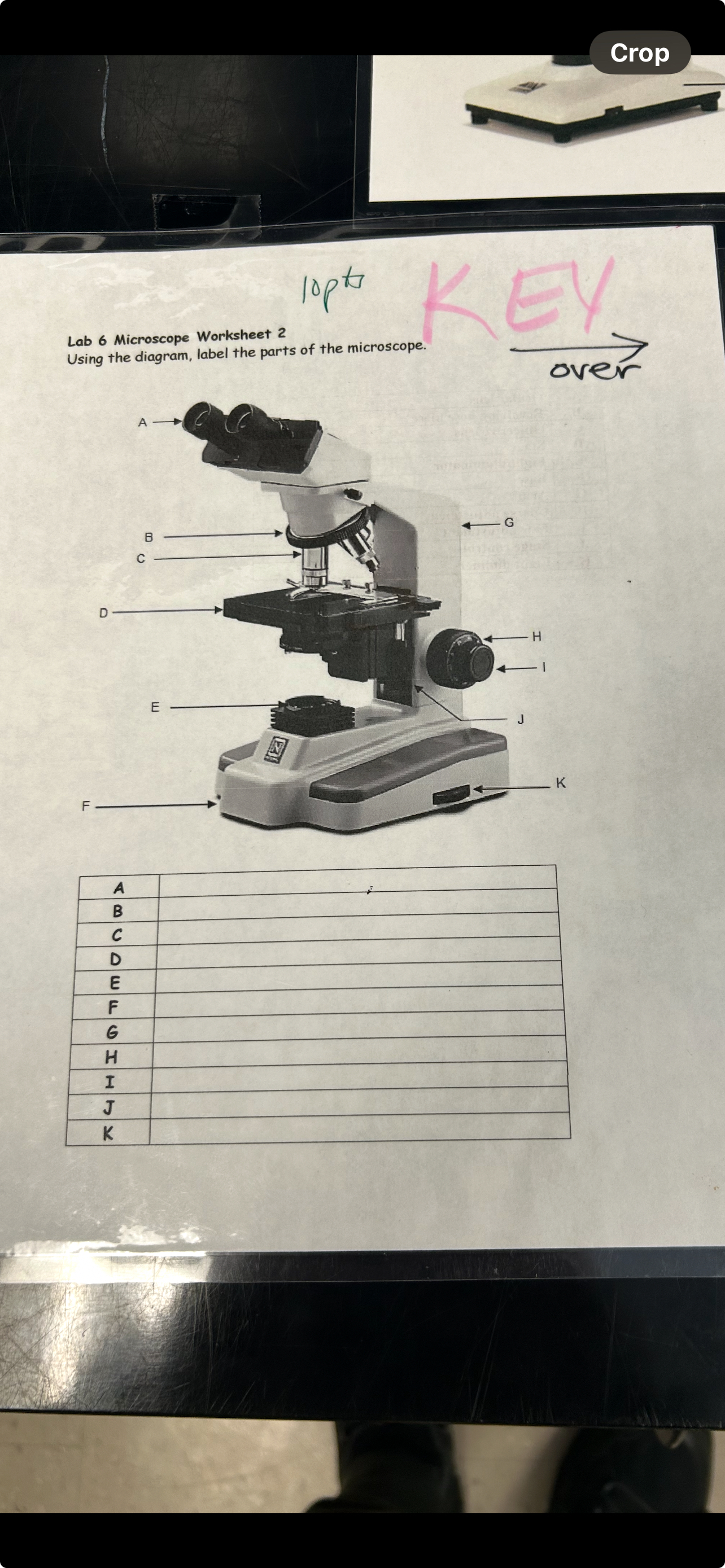
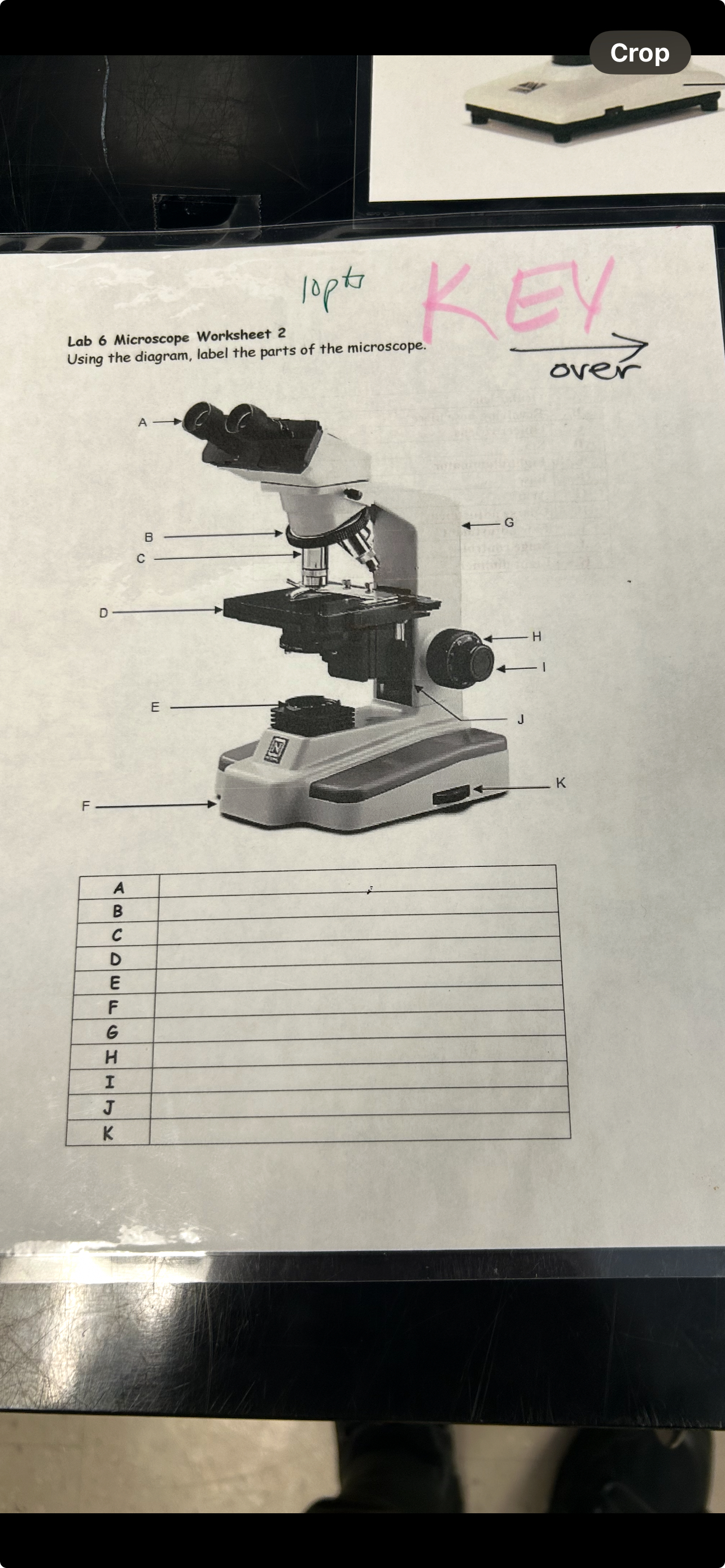
Parts of the Microscope
A- Eyepiece
B- Nose piece
C- Objective Lens
D- Stage
E- Light source
F- Base
G- Arm
H- Coarse focus
I- Fine focus
J- Stage control knob
K- Power switch
Koch’s postulates
The pathogen must be found with the diseased organism (plant)
The pathogen must be isolated from a diseased organism and grown in pure culture
The cultured pathogen must be used to inoculate a disease-free host and cause the same symptoms as first observed
The pathogen must be re-isolated from the inoculated and compared
- Same symptoms
- Same pathogen