3.1 Asynchronous
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
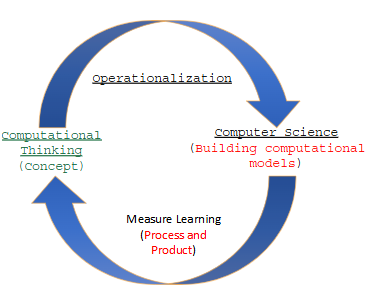
Why is teaching K-12 students how to build computational models so valuable?
Develops Problem-Solving Skills
Encourages Experimentation
Strengthens Understanding of Abstraction
Real-World Application
Prepares for Future STEM Opportunities:
Develops Problem-Solving Skill
Building models requires students to think critically about the problem, break it into smaller parts, and understand how different elements interact. This process helps students learn to structure and approach problems logically, a core part of computational thinking
Encourages Experimentation
By creating and testing models, students can explore "what-if" scenarios, tweaking variables to see the impact on outcomes. This hands-on experimentation builds their understanding of cause and effect, feedback loops, and how systems work.
Strengthens Understanding of Abstraction
Modeling encourages students to focus on the essential aspects of a problem while setting aside irrelevant details. This skill of abstraction is essential in computer science and other STEM fields, as it allows students to manage complex information.
Real-World Application
Many real-world systems—such as climate, economics, or ecosystems—are complex. Computational models help students grasp these concepts by providing a simplified, interactive version of the system, which deepens their comprehension.
Prepares for Future STEM Opportunities
Computational thinking and modelling are foundational in STEM careers. Early exposure to these concepts gives students an edge and helps them appreciate the relevance of math, science, and technology in solving real-life problems.
Space
Investigating natural systems and their interactions deepens one's understanding of the living world, Earth, and space.
Computer Science
Problem-solving and scientific inquiry are developed through the knowledgeable application of creativity, design, and computational thinking.
Computational Model for Orbit Around the Sun
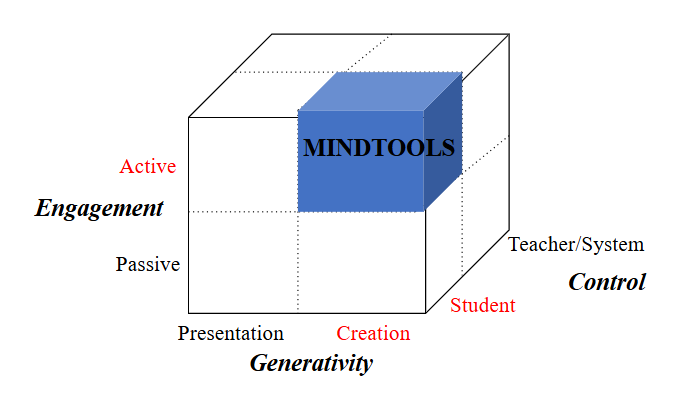
In this context, Scratch is viewed as a mindtool
The learning process is constructionism
I don’t know how to write notes about this (maybe rewatch the video?)
Point and Click on a Grid, Step-by-step (physically make student walk around in circle?), Incorporating the formula for circle: x2+y2=r2 , Computational model the solar system, Ellipse
A simple set of computational model
Scratch as a Mindtool
Constructionist Learning Theory
Abstraction
Decomposition
Pattern Recognition
Algorithm
How would a teacher teach musical notes to children?
Teach notes in relation to other notes
Computational model for Elementary Music
New sounds may be created using instruments in new ways, by inventing new instruments or by electronic methods.
Skills required: Listening, Reading and Writing, Creating & Computation Modeling (Coding)
Computational Model: Design, Develop, Implement the “Cat Music Creator and Player”
Possible Design ideas:
Input the keys you want to play and let Scratch play them back to you! Implemented for Piano.
Etc…
CT Model Building Summary