BTEC applied science unit 1 - Chemistry
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What are the physical properties of elements
Atomic Radius
Ionic radius
Electronegativity
first ionsiation energy and trends
electron affinity
MP BP
what is the general trend in atomic radius ACROSS the period?
the atomic radius decreases across a period because the extra electrons added are added to the same s and p sub shells not new shells so size doesn’t increase
what happens to the atomic radii as you go DOWN a group?
the atomic radii goes increases down a group this is because the extra electons are added to new shells not same shells.
describe the effect of the protons that are added across the group
the protons are added creating an increase in nuclear charge, increased nuclear charge attracts the extra electrons and pulls them closer together decreasing atomic radius ACROSS the group
what group does this slightly not apply for and why?
this slightly doesn’t apply for the transition metals group 3-12 D block, their radii stays similar across the group due to the additional nuclear charge being balanced by the extra shielding of the electons in the 4s subshell
what is the general trend in ionic radii going DOWN a a group?
Extra electons are added to new shells increasing the radii going down a group.
More specifically descibe the ionic radius in cations
Cations have a smaller radius than their corresponding atom
as you go ACROSS the period the cations ahve the same electronic stucture
they are isoelectronic (same number if electrons)
the protons/nuclear charge increases therefore pulling the electrons to the centre of the ion decreasing the ionic radius.
more specifically what is the ionic radius in anions?
Anions have a larger radius than the corresponding atom because of higher electron repulsion
going ACROSS the electrons are isoelectronic
the number of protons increases therefore decreasing the ionic radius
what is an isoelectronic element?
they contain the same number of electrons
what is the difference between the trend in ionic radius in a cation and anion?
Cations have a smaller radius than the corresponding ion
Anions have a larger ionic radius than the corresponding ion due to higher electon repulsion
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativty is the tendancy of an atom to attract to a bonding pair of electrons.
What is the general trend of electronegativity ACROSS a period?
electronegativity increases going across a period.
the bonding pair will be shielded by the same number of electrons .
the protons will increase
What is the general trend of electronegativity DOWN a period?
electronegativity decreases down a group
there is more shielding from inner electrons and the bonding pair of electrons are further from the nucleus, causing less pull on the binding pair from the positivly charged nucleus.
What is the most electronegative element
Flourine group 7
what does electronegativity depend on?
Number of protons in the nucleus
the distance from the nuclus the bonding pair of electrons is
how much shielding there is from inner electrons
what does similarity in trends mean?
they may form similar bonds or show similar chemistry.
What is first ionisation energy?
the minimum energy needed for one mole of the outermost electrons to be removed from the one gaseous atom forming positive ions.
what does ionisation energy show?
periodicity, the repeating pattern seen by the elements in the periodic table
What is the trend in periodicity across a period?
It takes more energy to remove an electron as you go across a period because the number of protons increase so the positive nuclear charge increases which pulls the electrons in more.
what is the equation for 1st ionisation energy?
what are the factors affecting ionisation energy?
There are three main factors
The attraction of the nucleus (The more protons in the nucleus the greater the attraction)
The distance of the electrons from the nucleus (The bigger the atom the further the outer electrons are from the nucleus and the weaker the attraction to the nucleus)
Shielding of the attraction of the nucleus (An electron in an outer shell is repelled by electrons in complete inner shells, weakening the attraction of the nucleus)
what is the general rule for ionisation energy?
the more protons in an element the higher the ionisation energy required, the closer the shell to the nucleus the more energy
. Why do first ionisation energies decrease down a group?
As one goes across a period the electrons are being added to the same shell which has the same distance from the nucleus and same shielding effect. The number of protons increases, however, making the effective attraction of the nucleus greater.
what is electron affinity?
An atoms ability to gain an electron and become a negative ion
What are the first ionisation energies?
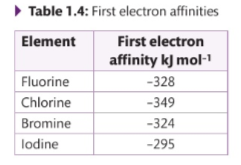
Describe The electron affinity trend clown group 7
Going down the group ,energy released decreases
What element is an exception to the trend in election affinity, and why?
Fiourine 1s an exception I flourine is a very small atom , when fiourine gains an electron to become fluoride , This new electron is added to an region that is already full of electrons and so there is a repulsion from these .
wnat predicts The type of bonding in an
Electronegativity .
What depends on MP and BP?
The melting point and boiling point depends on the strength of the forces between atoms
what is the trend in melting point across groups 1-3
1-3 metals have Increasing nuclear charge, because the protons are always increasing .
meaning they nave a Stronger melting and boiling point because the metallic bonds are strong.
. MP and BP increase across the group
wnat is the trend in MP and BP for me non metals?
In groups 5-7 they have smaller separate molecules therefore lower MP and BP
Define malleable ?
can be hammered into shape without breaking
Define ductile ?
Can be hammered thin or Stretched into wires without breaking
Describe reactivity with oxygen.
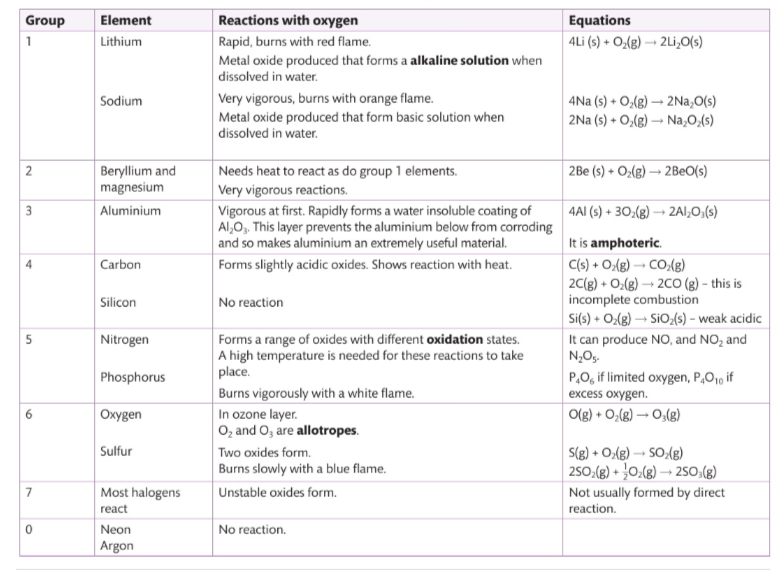
Describe group 1 reactivity with water
These alkali metals react win water to produce a basic solution.
How do group 3 metals react Witn water
They arent very reactive .
Describe reactivity with dilute acids.

what is the order of reactivity and why ?
Group 2, Group 2, group 3 . . group 4 , group’
Going across the period the nuclear charge increases, therefore harder to react.
What is oxidation State?
The number assigned to an element in a Chemical compound , positive or negative depending on now many electrons lost or gained.
Define redox
The transfer of electrons during chemical reactions
Define reduction.
Wren an atom/ ion gains electrons
What is oil rig?
Oxidation Is Gain Reduction Is loss
Wrat is a redox reaction?
Wren the oxidation state has been changed.
Assigning Oxidation State steps

wny do transition metals have a different oxidation state ?
They nave variable stales
Due to their nignest energy electrons being in the cl-subshellDue to their nignest energy electrons being in the cl-subshell
mainly used as catalyst.
wnat is an oxidisation agent ?
Halogens
.They withdraw electrons from other atoms.
Applications
