AP Biology Unit 3B: Photosynthesis Diagram | Quizlet
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Photosynthesis takes low energy reactants and converts them into high energy products, it also requires the input of energy in order to occur.
Why is photosynthesis considered an anabolic process?
Photosynthesis
process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches
The Sun
What is the energy for photosynthesis supplied by?
Yes
Do plants have a mitochondria?
Yes
Do plants perform cellular respiration?
Energy is absorbed from the surroundings to build up a product, an input of energy is used to turn low energy reactants into high energy products
How is photosynthesis an endergonic reaction?
The Process That Feeds the Biosphere
What is photosynthesis also known as?
Photosynthesis
The process that converts solar energy into chemical energy. Directly or indirectly, ______ nourishes almost the entire living world.
Autotrophs
Organisms that sustain themselves without eating anything derived from other organisms
The producers
What are autotrophs in terms of the biosphere?
Producers
Organisms that producing organic molecules from CO2 and other inorganic molecules
Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, certain other protists, and some prokaryotes
In what organisms does photosynthesis occur?
They don't feed on organisms, they feed themselves through chemical processes using the raw materials in their environment
How do autotrophs sustain themselves?
Biosphere
Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere.
Algae are a type of protists, unicellular protists that can do photosynthesis through chloroplasts and there are bacteria that basically are a chloroplast in the way that they function.
How do unicellular protists and bacteria perform photosynthesis?
Most plants have roots pulling in water, ability to pull in co2 out of the atmosphere and sugars and oxygens come out from that
How do plants and get the water and CO2 that's used in photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the photosynthesis equation?
Leaves are the major locations of photosynthesis
What is the major site of photosynthesis in plants?
Their green color is from chlorophyll, the green pigment within chloroplasts
Where does the green color of plants come from?
Chloroplasts are found mainly in cells of the mesophyll,
Where are chloroplasts mainly found?
Mesophyll
the interior tissue of the leaf
CO2 enters and O2 exits the leaf through microscopic pores called stomata
Where does CO2 enter and O2 exit the leaf?
Stomata
Microscopic pores on a leaf
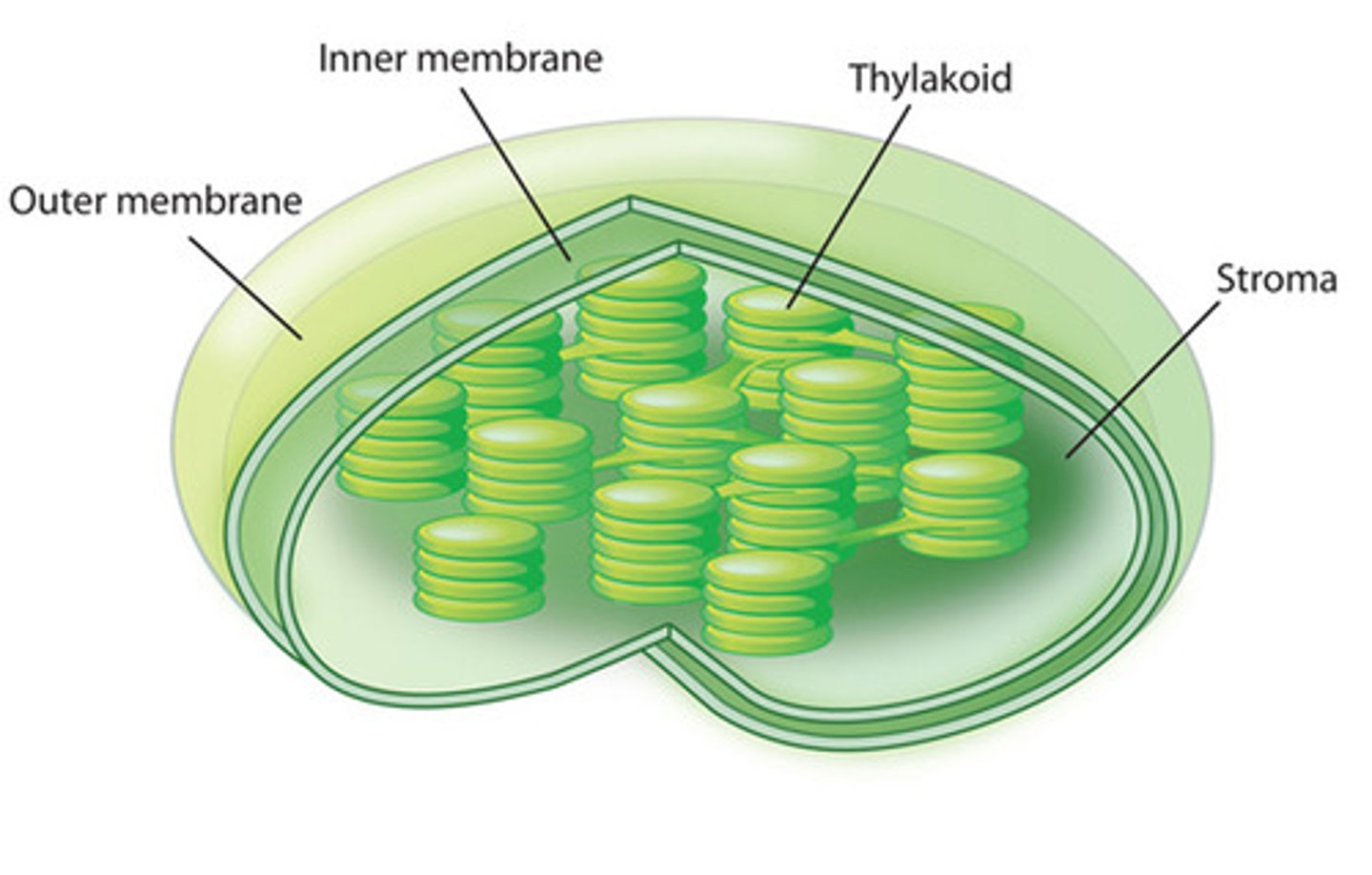
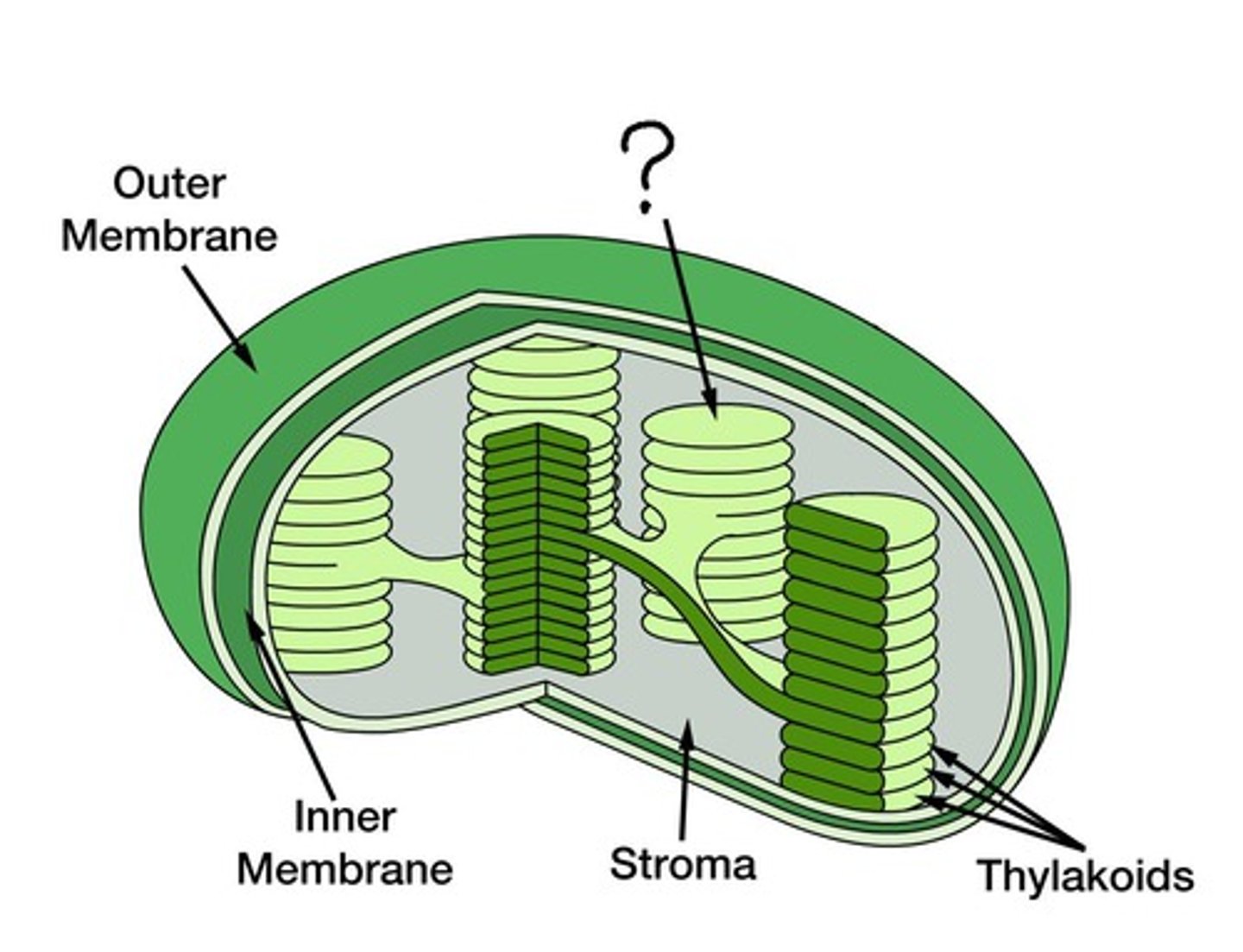
the membranes of thylakoids
Where is the chlorophyll contained?
Thylakoids
Connected sacs in the chloroplast
Stroma
What is the dense interior fluid contained in the chloroplast?
Due to the presence of chlorophyll. The pigment attracts the wavelengths of light that the plant can use to power photosynthesis. Plants are photosynthesis machines and are evolved to do this
Why are plants green?
There is a higher concentration of oxygen inside the plant so it passively diffuses to the exterior of the plant
How does oxygen leave a plant?
Chloroplasts are believed to have once been free living bacteria. They had a lot of characteristics bacteria would have, they're apart of the endosymbiont theory. Very close relationship between early eukaryotes and prokaryotes, they evolved to be just be apart of another cell rather than on their own chloroplasts
What were lone chloroplasts once said to be?
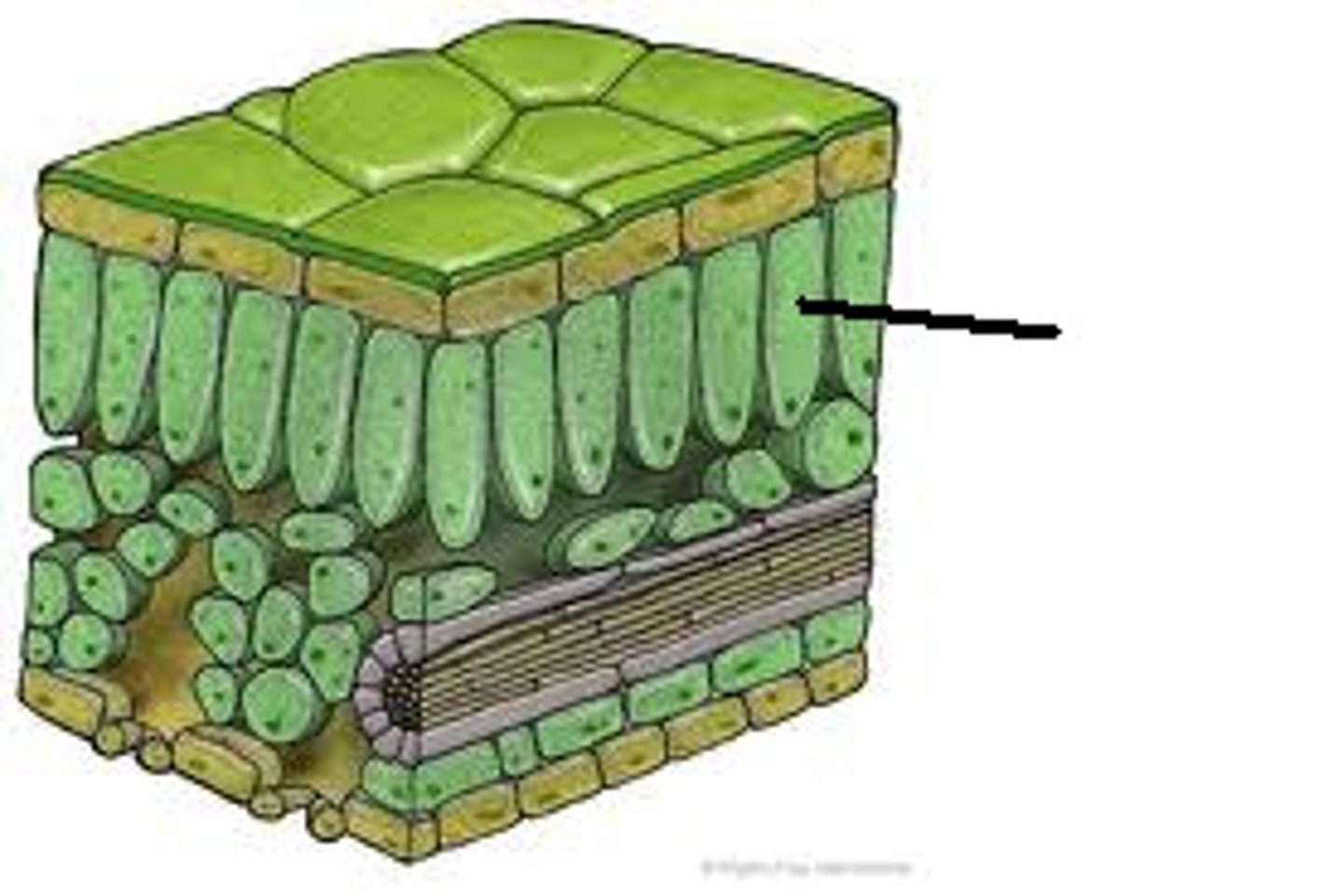
Plants pull in co2 so they can get it to their chloroplasts. They put it in the stroma. The chloroplast has 2 membranes, thylakoids are the thin green discs. When they are in a stack they are called a granum. Stroma is all the fluid in the chloroplasts, the stoma and stomata are the holes in the leaf.
Describe the main parts of the plant.
Mesophyll
What part of the plant is this?
Chloroplast
What part of the plant is this?
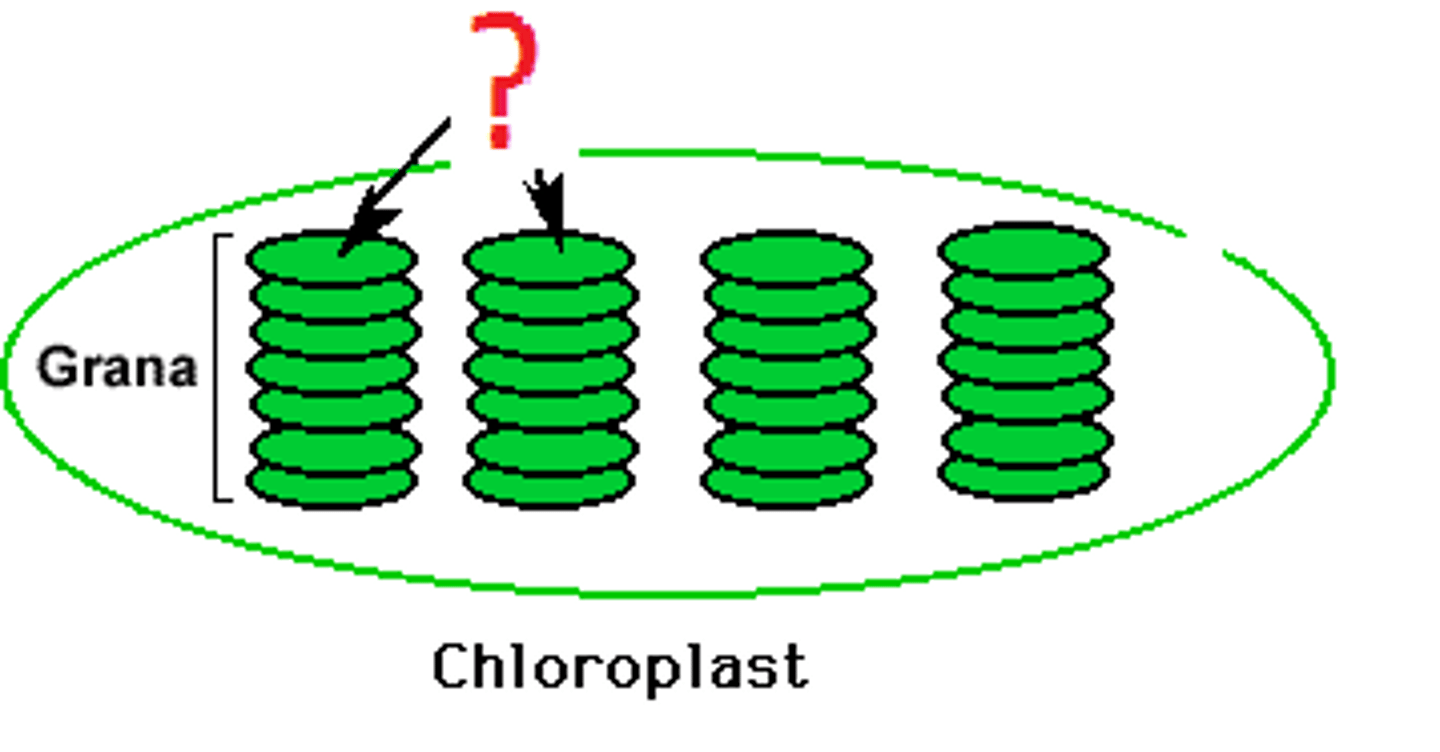
Thylakoid
What part of the plant is this?
Thylakoid Space
What part of the plant is this?
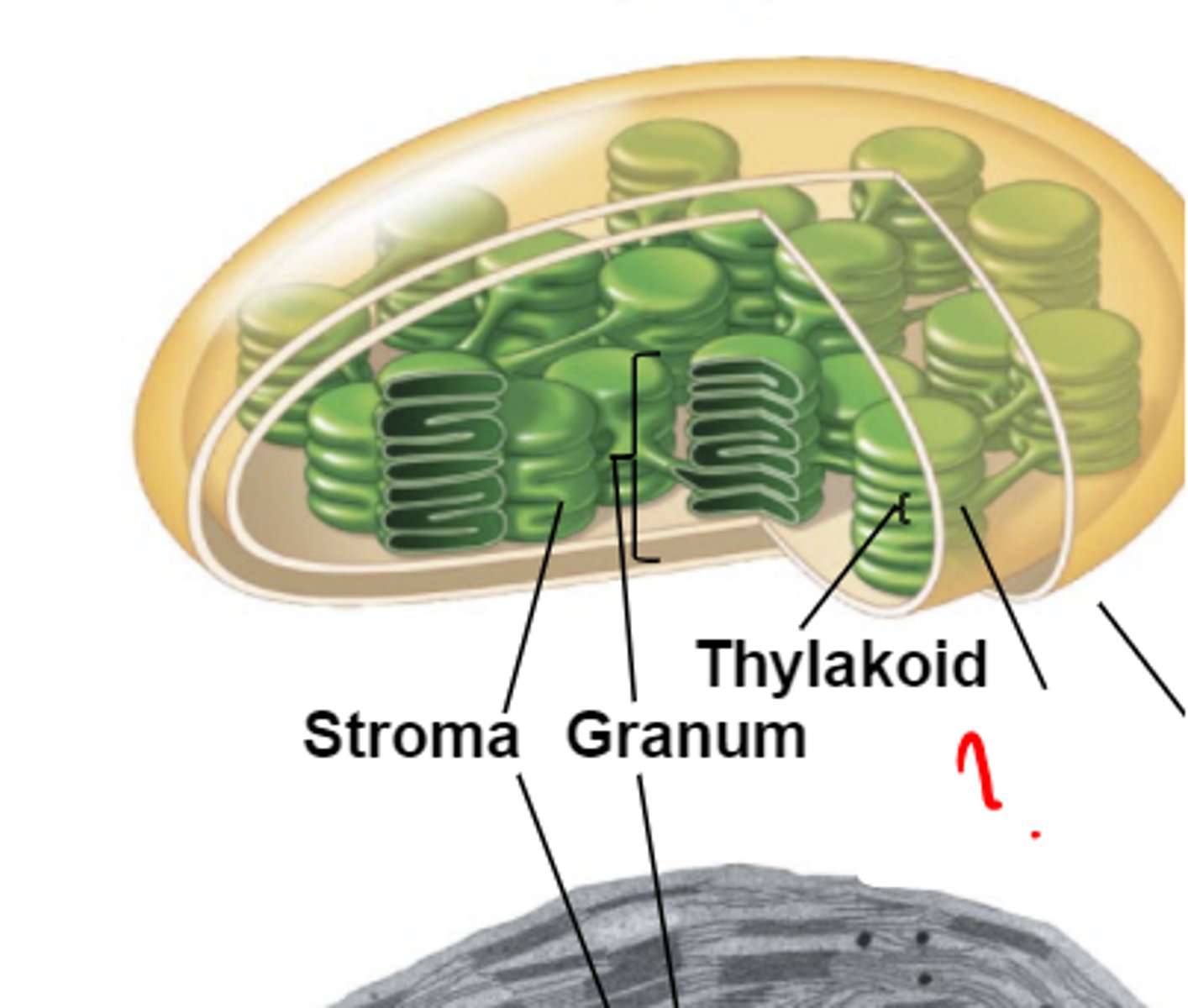
Stroma
What part of the plant is this?
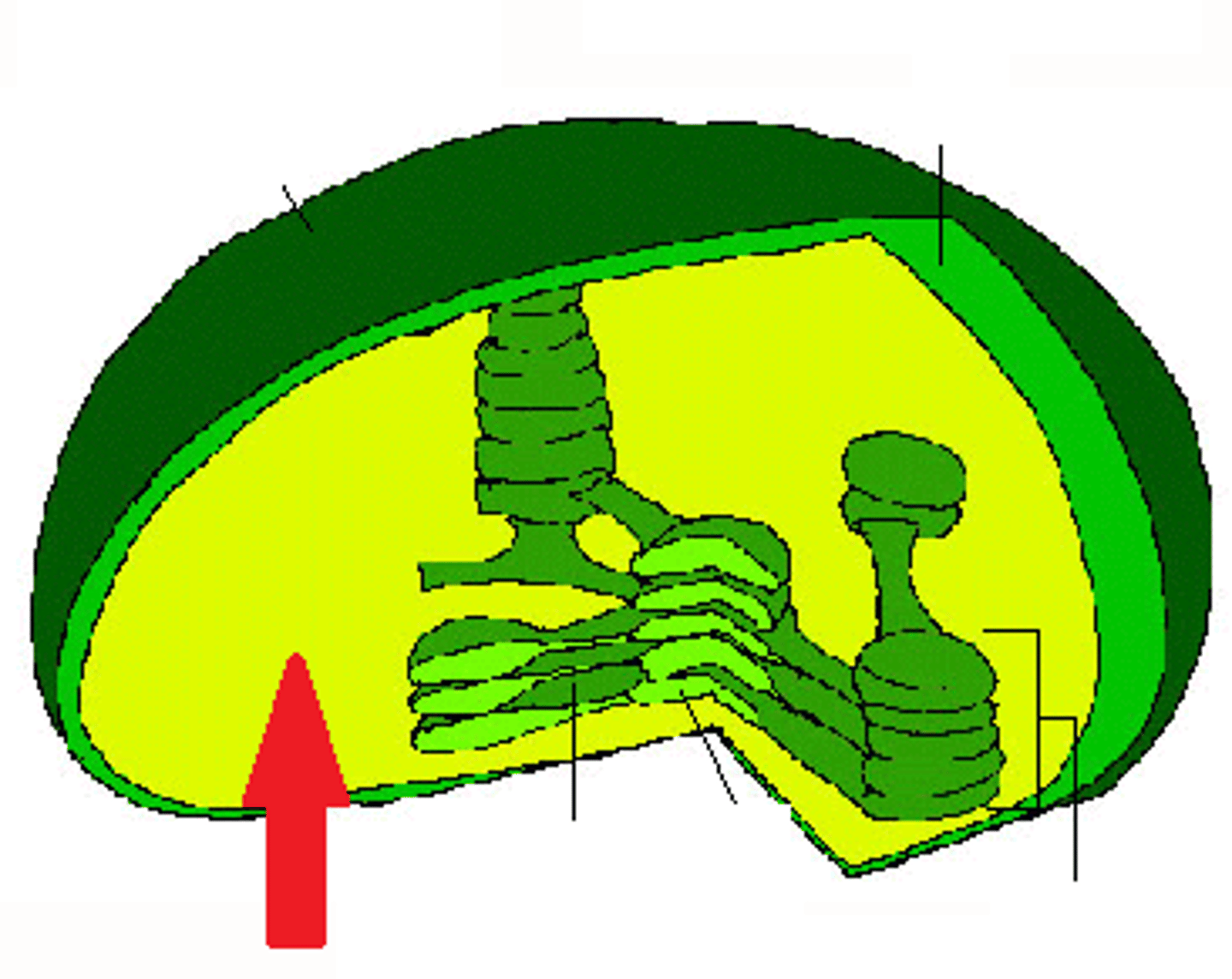
Stomata
What part of the plant is this?
Granum
What part of the plant is this?
The stomata have guard cells that open and close doors. Stomata can be closed to control flow of gases.
What can the stomata do in terms of gas exchange?
Redox Reactions
The transfer of electrons during chemical reactions releases energy stored in organic molecules
This released energy is ultimately used to synthesize ATP. transfer electrons between reactants
Oxidation
a substance loses electrons, or is oxidized
Reduction
a substance gains electrons, or is reduced (the amount of positive charge is reduced)
Photosynthesis reverses the direction of electron flow compared to respiration
What does photosynthesis do in terms of electron flow?
H2O is oxidized
What is oxidized through photosynthesis?
CO2 is reduced
What is reduced through photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is an endergonic process; the energy boost is provided by light. light energy converted into chemical energy stored in the bonds of glucoses, special machinery helps this process occur as well as a myriad of enzymes as well
What type of process is photosynthesis?
Light Dependent reactions and calvin cycle
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
Light reactions
Photo part of photosynthesis
Calvin cycle
Synthesis part of photosynthesis
Thyalkoids
Where do light reactions occur?
Split H2O
Release O2
Reduce NADP+ to NADPH
Generate ATP from ADP by photophosphorylation
What is the goal of the light reactions?
Photophosphorylation
How is ATP generated through the light dependent reactions?
Photophosphorylation
The process of generating ATP from ADP and phosphate by means of a proton-motive force generated by the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast during the light reactions of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis provides the raw material for all of these carbohydrates
What does photosynthesis provide for carbohydrates?
So hydrogen protons and electrons can be used in the photosystems
Why do we split H2O in the light reactions?
NADPH
What is the electron carrier for photosynthesis?
Light independent, dark reactions
What is the Calvin cycle also known as?
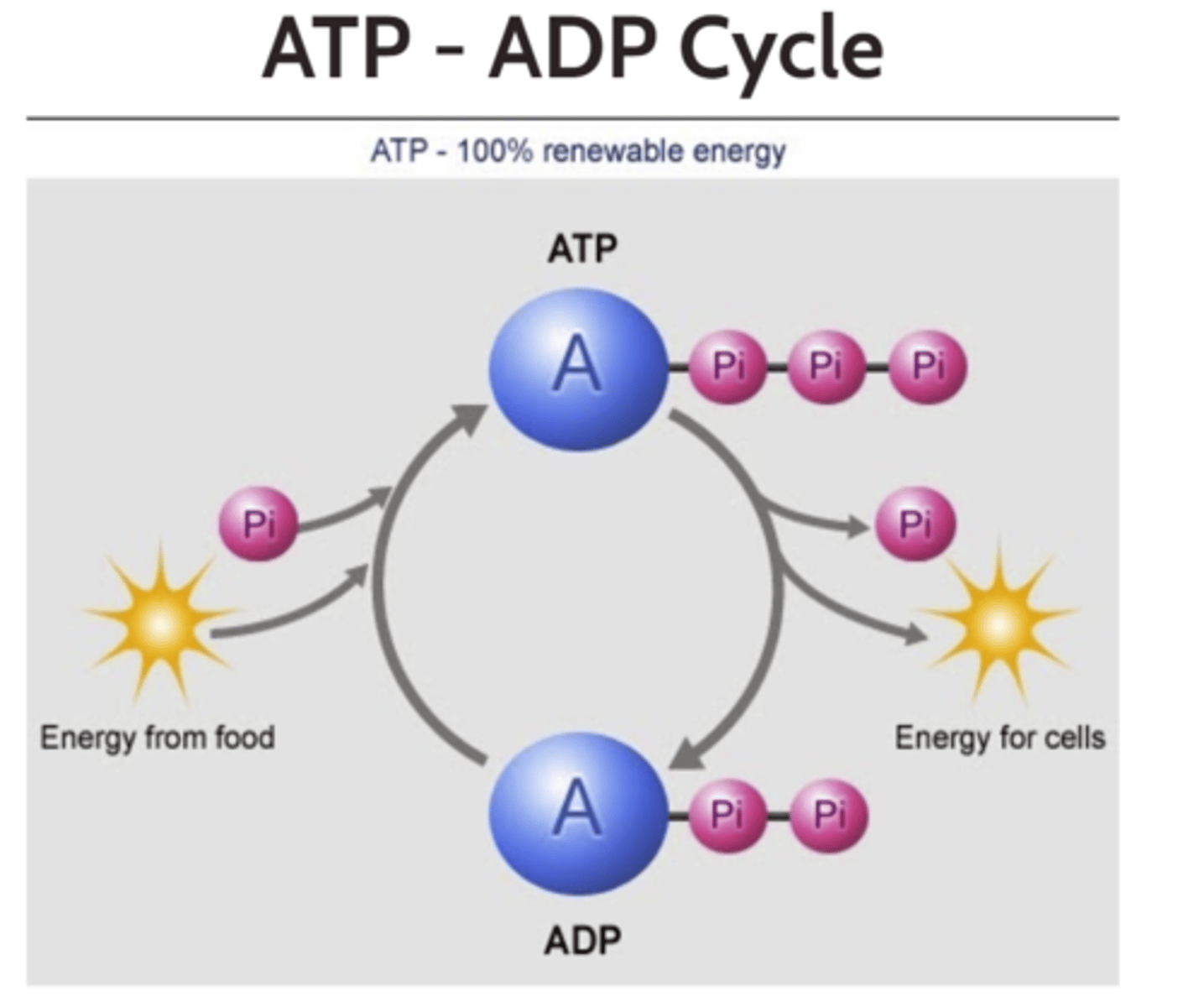
That ATP can be renewed, it is a renewable source of energy
What does this image describe?
NADP+ holds 2 high-energy electrons and an H+ at once
What can NADP+ hold?
NADPH
When NADP+ carries the electrons what does it become?
Light energy is now trapped! Excited electrons are ready to be moved
When NADP+ becomes NADPH what does this mean?
The Calvin cycle (in the stroma) forms sugar from CO2, using ATP and NADPH
What is the main goal of the calvin cycle?
Carbon Fixation
What does the calvin cycle begin with?
Carbon Fixation
incorporating CO2 into organic molecules
Stroma Space
Where does the calvin cycle occur?
surrounds the fluid and thylakoids loaded with enzymes
What is in the stroma space?
The atmosphere
Where is carbon taken from for the calvin cycle?
Light and water go in as well as nadph and atp go
Co2 is also pulled in to create sugars. Water and co2 produce oxygen and sugar Energy goes in, it doesn't come out in excess
Water gets split into hydrogen and electrons, the oxygen leaves, but the hydrogens stay in the electron carriers go in and atp is generated that goes to stage 2 the calvin cycle where co2 is incorporated in and sugar is created
Briefly describe the process of the light reactions.
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation
What is light a form of?
Light travels in waves
What does light travel in?
Wavelength
the distance between crests of waves
Wavelength determines the type of energy
What does wavelength determine?
Light also behaves as though it consists of discrete particles, called photons
How does light behave?
Photons
What doe slight consist of?
The difference in size is shown, especially with radio waves being on the larger side.
What about the size of wavelength is shown?
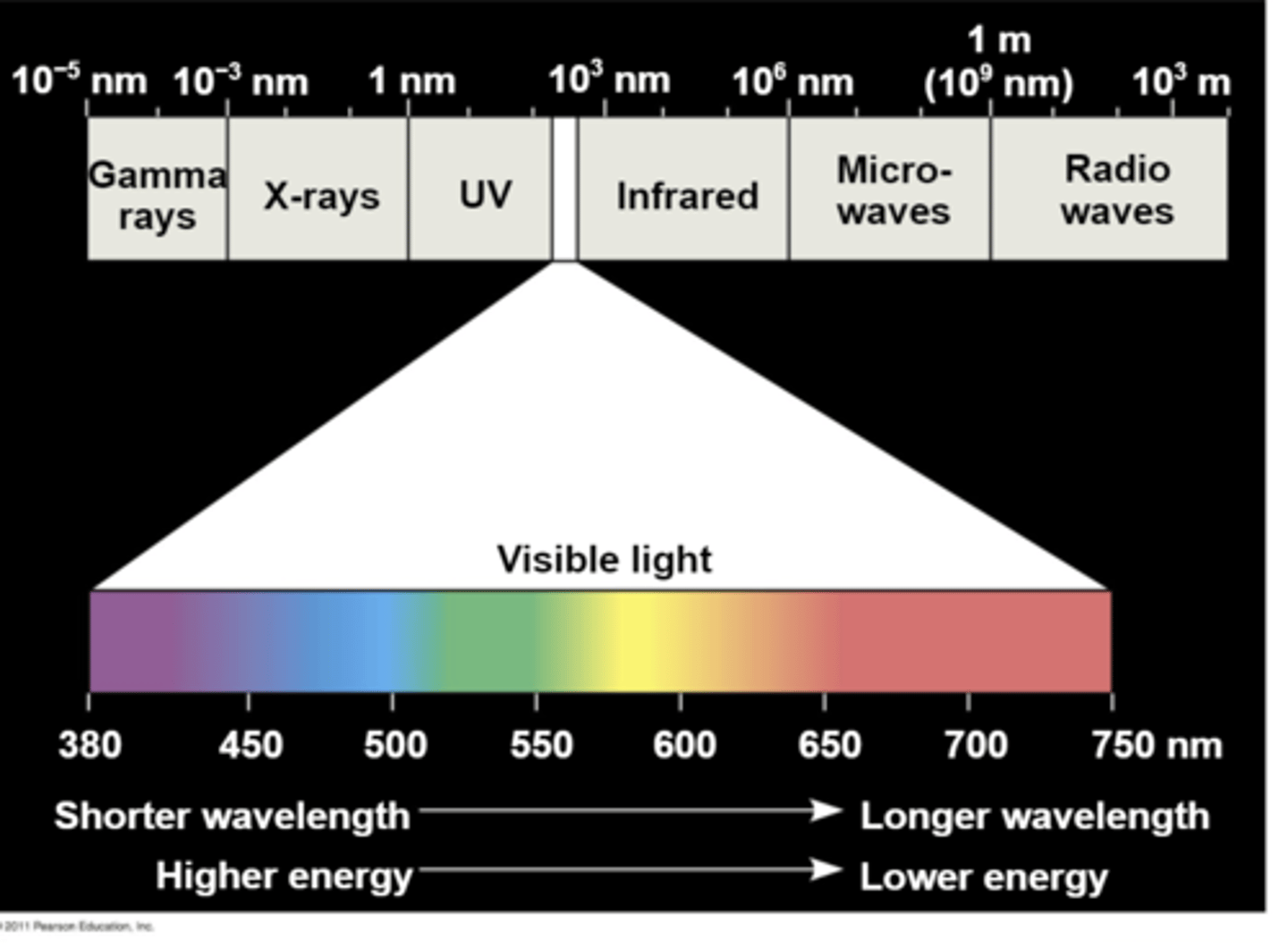
Visible light is the wavelengths that we perceive and are able to see, plants also use parts of this spectrum, difference in wavelength determines what color we have. There is a certain wavelength of interpretation color. Uv and infrared light are around there. Some organisms can see the uv spectrum, we use infrared goggles to see at night but we can't naturally see these wavelengths
What does visible light mean?
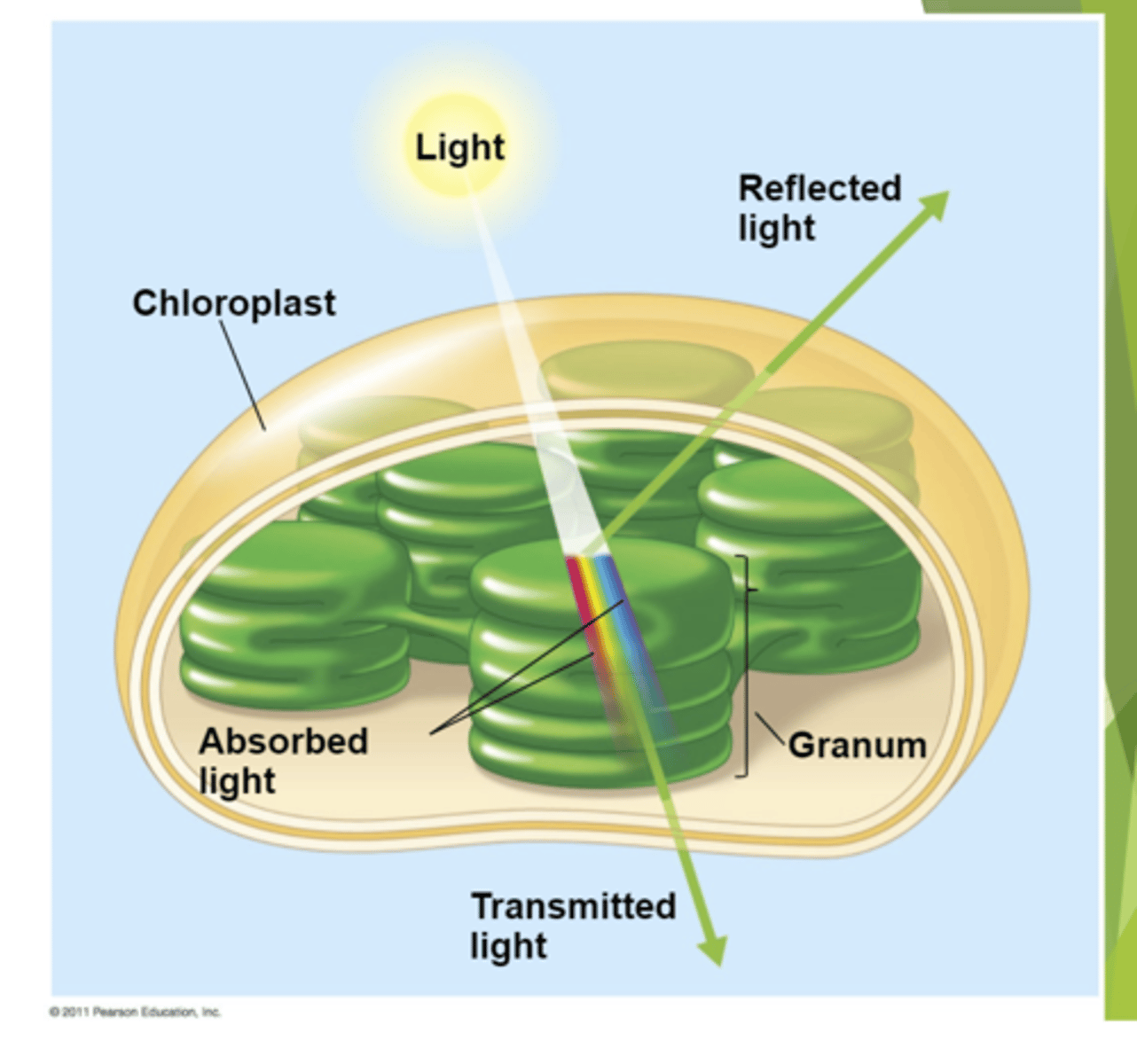
Plants are Green because it reflects certain parts of the white light spectrum and it makes it easier for them to perform photosynthesis.
Why are plants green?
Pigments are substances that absorb visible light
What are pigments?
Different pigments absorb different wavelengths
What do different pigments absorb?
Wavelengths that are not absorbed are reflected or transmitted
What happens to wavelengths that are not absorbed?
Leaves appear green because chlorophyll reflects and transmits green light
Why do leaves appear green?
No
Can we see pigments that are absorbed?
Chlorophyll a
What is the main photosynthetic pigment?
chlorophyll b
What is an example of an accessory pigment?
They broaden the spectrum used for photosynthesis
What do accessory pigments do?
carotenoids
Accessory pigments called _____ absorb excessive light that would damage chlorophyll
Most plants are blasted with light all day, and yet they never get sun burn or cancer. Carotenoids help protect the plants from that.
Why are cartenoids necessary?
If plants absorbed light all the time it would cause major damage to them, with a green plant light is reflected allowing to grow and flourish rather than be scorched. If they were black they'd overheat and get more energy than they need. They don't absorb all light and reflect some of it, pigment help them do that
Why aren't plants black?
Plants Absorbs a lot of the spectrum and reflects some of it. Transmitted light is just light that's gone through, still green the rest gets filtered out.
What does this image describe?
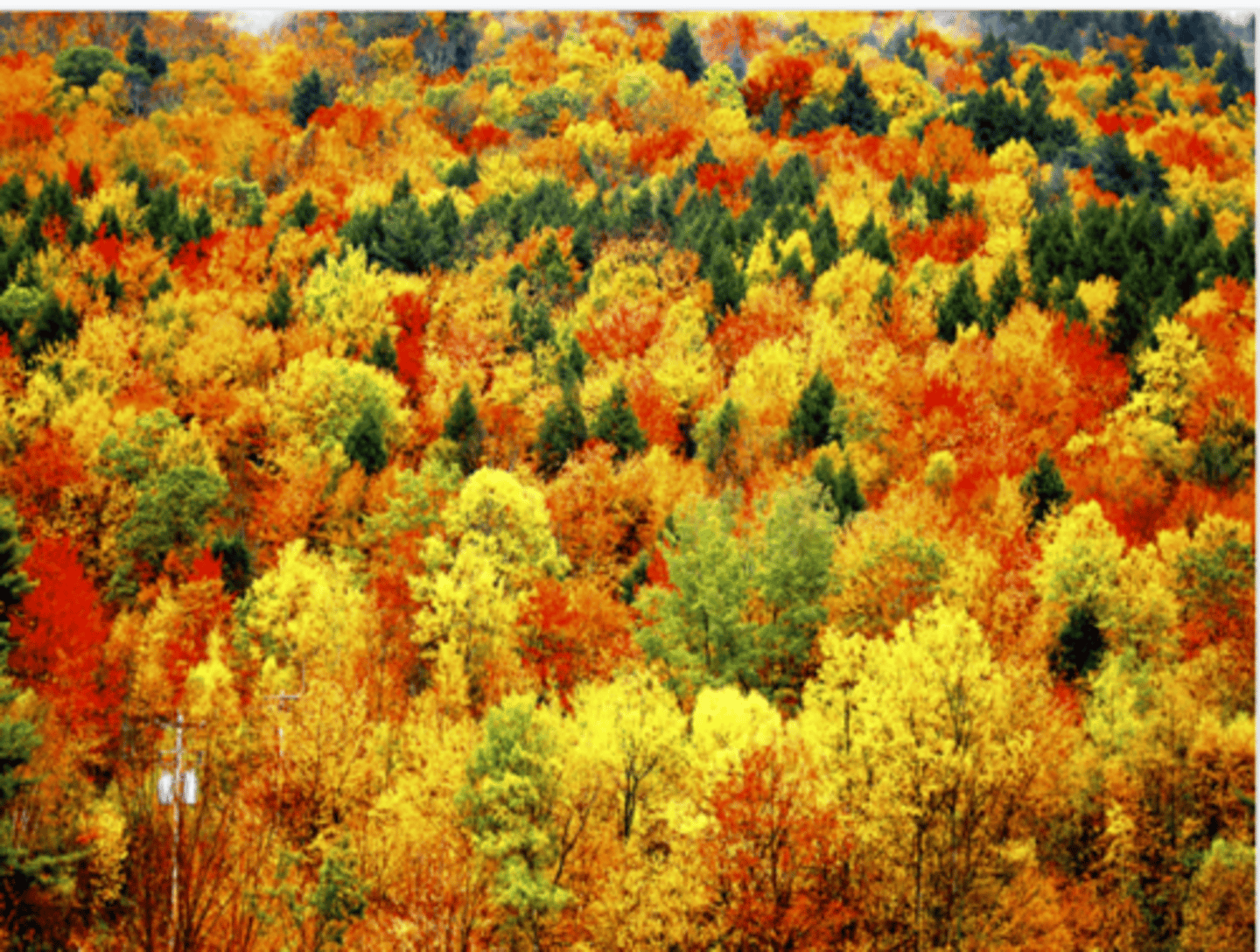
Some of the other pigments that plants have. The carotenoids are different pigments reflecting reds and yellows that are typically not visible because they're masked over by chlorophyll, but once it degraded in the fall we saw all the other colors
Why do we see all these different colors in the fall?

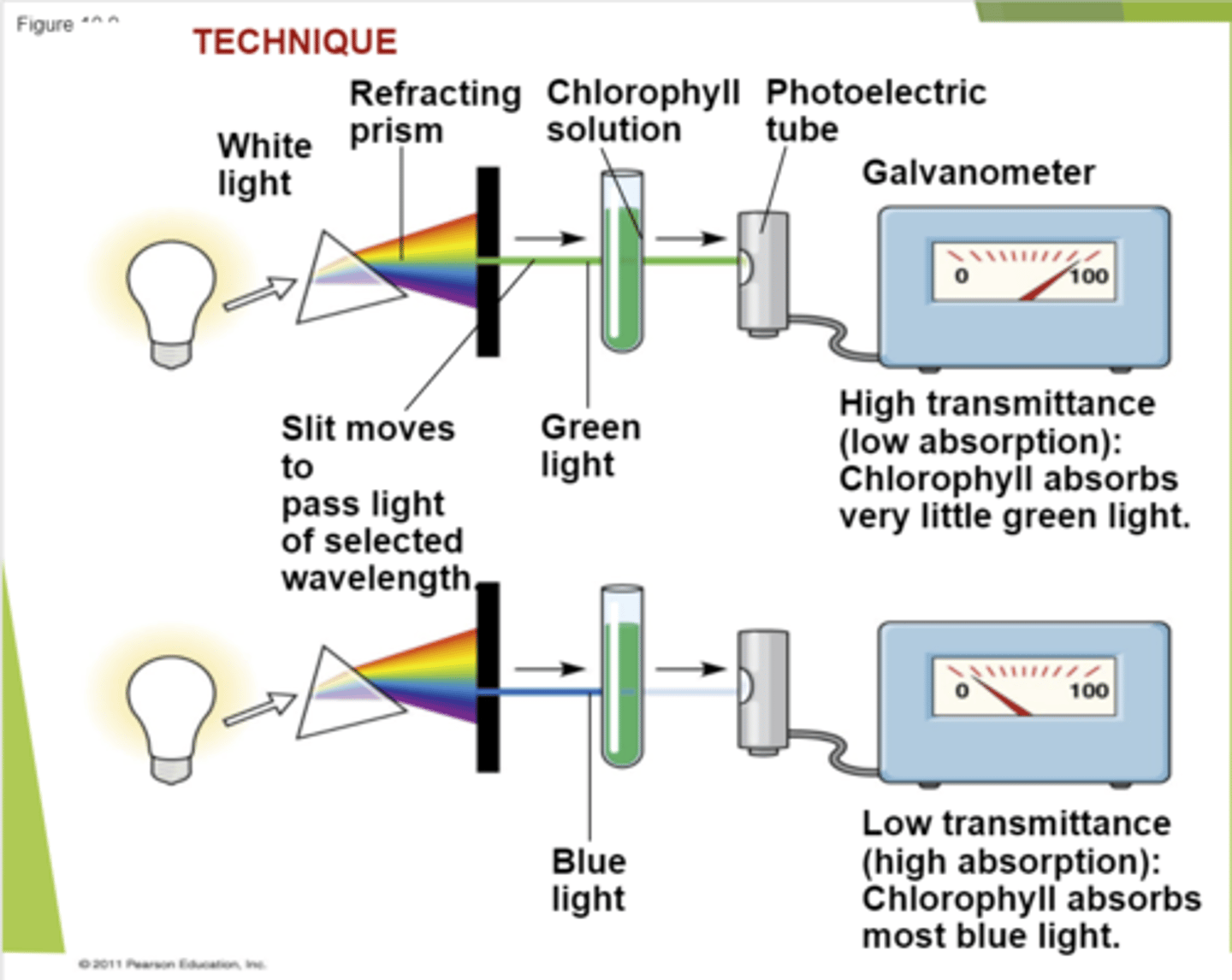
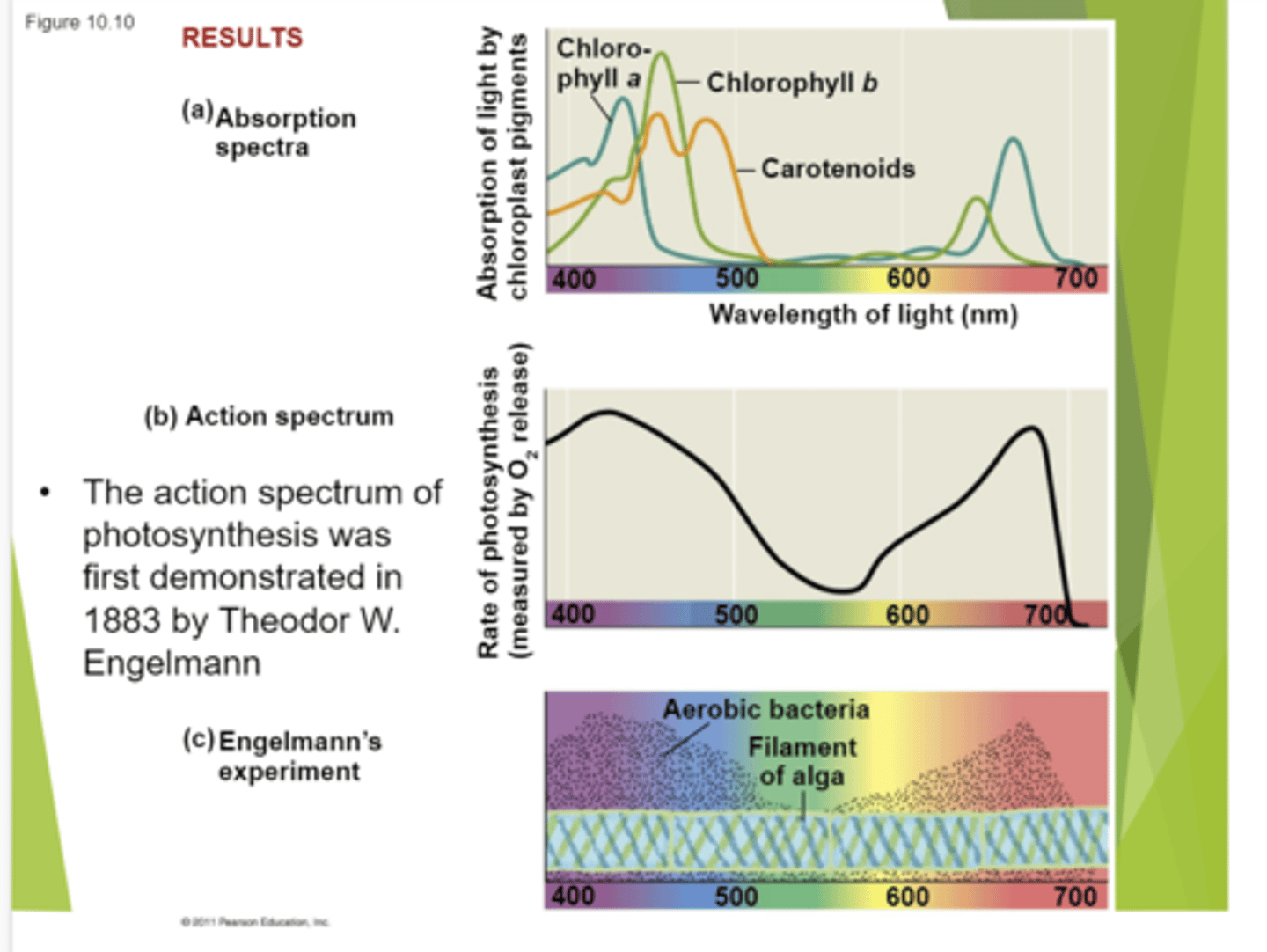
Spectrophotometer
Measures a pigment's ability to absorb various wavelengths.
Absorption Spectrum
a graph plotting a pigment's light absorption versus wavelength.
Action Spectrum
profiles the relative effectiveness of different wavelengths of radiation in driving a process.
Light green light can get through only if chlorophyll is there the green light is almost 100% transmitted.The pigment doesn't reflect the blue light wavelength. There's very low transmittance of blue because chlorophyll doesn't reflect that light, it absorbs it.
What does this image describe?
Scientist created the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a b and carotenoids. Their highest absorption is in purple and blue, lowest is in yellow green which is what they reflect. Carotenoids absorb well in green and purple wavelengths but reflect more in reds and yellows.
The action spectrum, they put aerobic bacteria under light with algae. The algae produced oxygen and food, the aerobic bacteria alive above it. Whenever the best photosynthesis is you produce the most oxygen if they are exposed to certain colors of light they get this profile. Purples and blues and oranges and reds do it best. THey'll grow but not well under a yellow or green light
What does this image describe?
It is a molecule, only difference is the group is ch3 or cho for chlorophyll b Prophyin ring is what interacts with and absorbs light
What is the difference between chlorophyll a and b?
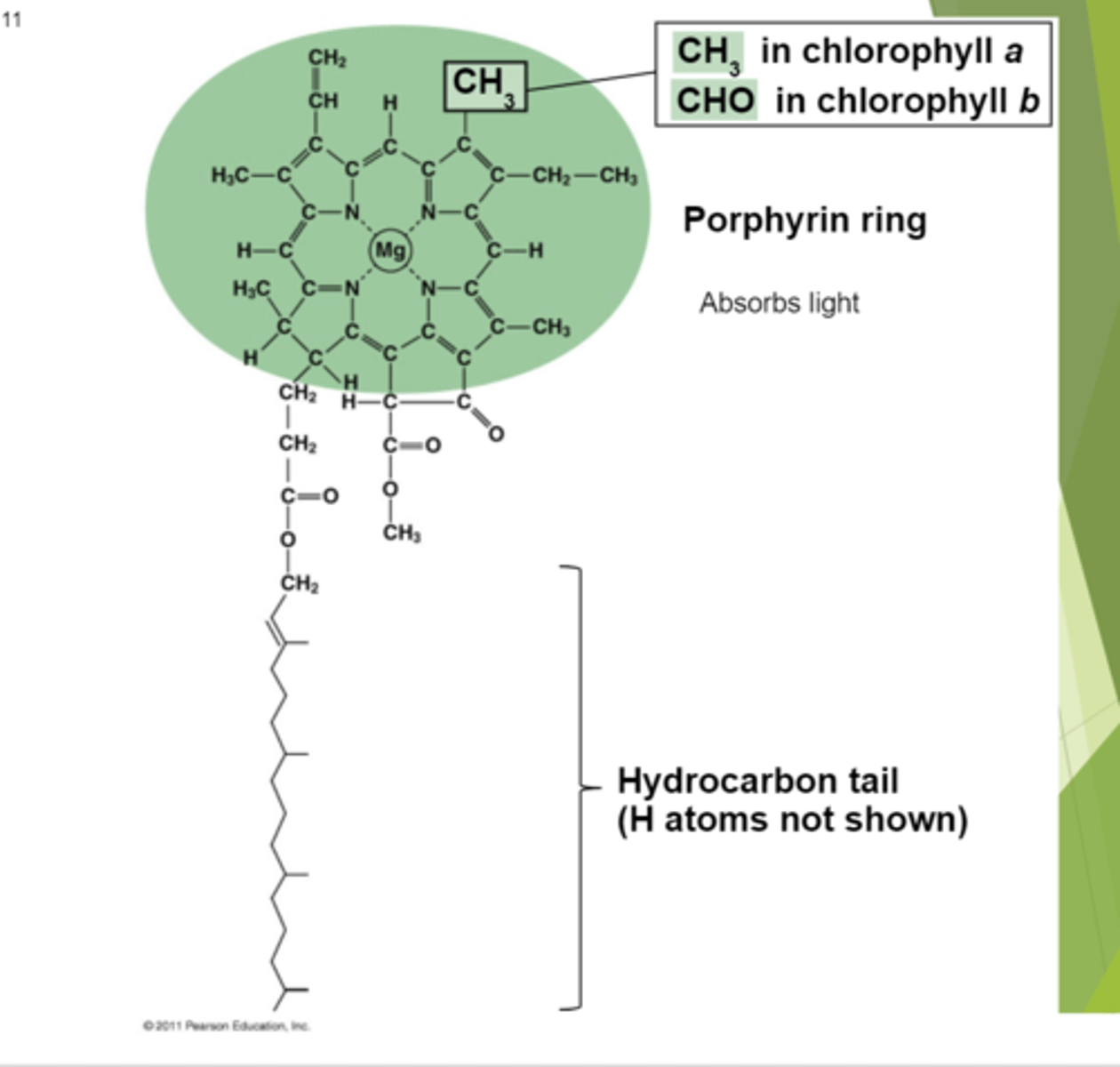
CH3
What is the molecule for chlorophyll a?
CHO
What is the molecule for chlorophyll b?
Chlorophyll reflects or transmits green light because of this structure. The shape of this molecule causes it too interact with light in a certain way, its slightly tweaked between chlorophyll a and b.
Letting the plant slightly tweak light absorption, evolution changes this over time in the genetics of the chlorophyll which can change.
How is evolution evident in this picture?
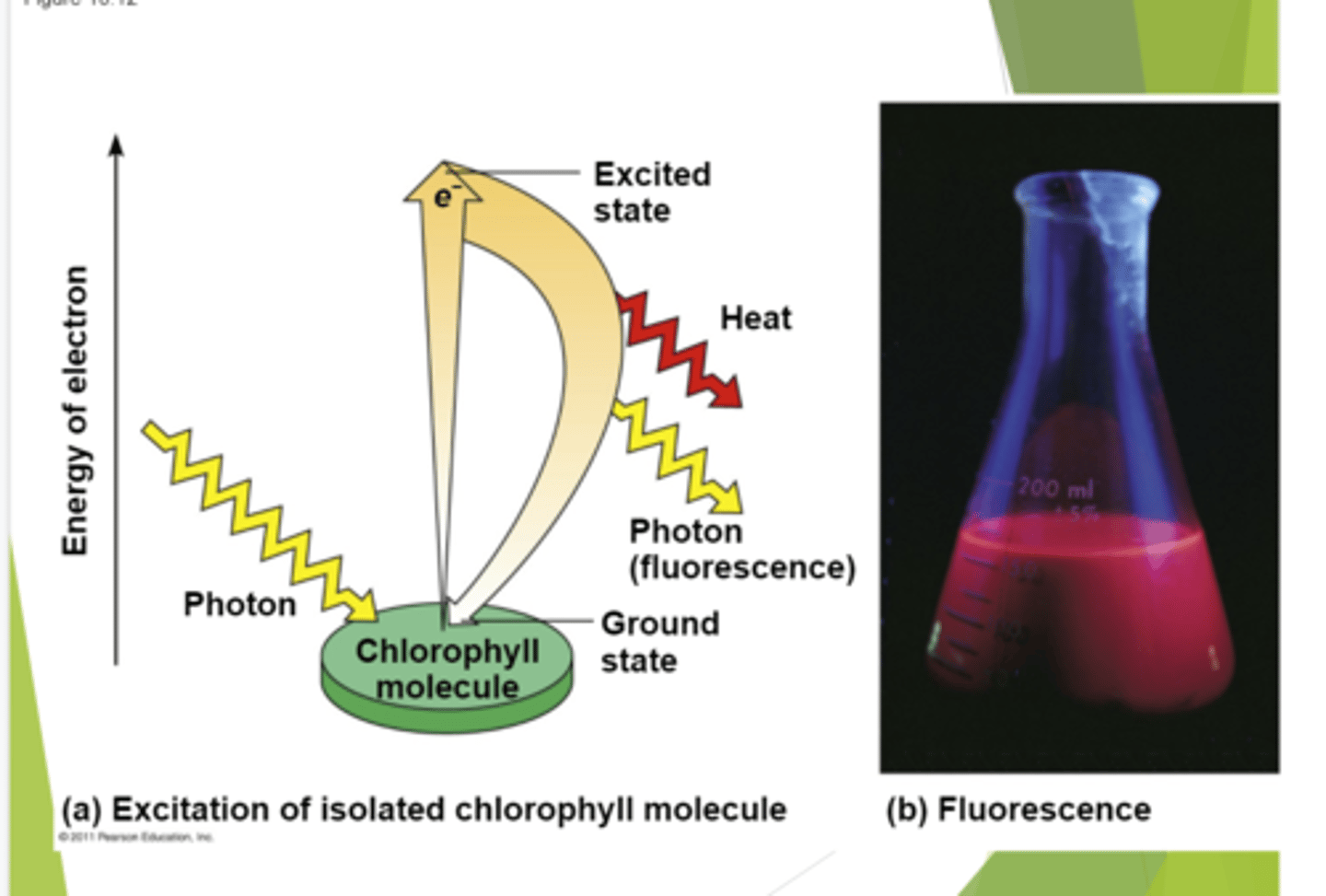
Photons hit the chlorophyll molecule, that excites electrons, they naturally want to go back to their normal state. The plant takes advantage of that energy. The plant if hit with a bunch of light as the electrons lose their energy they release energy as heat and light. This is green chlorophyll in the dark after being exposed to light,a stye go back to their ground state heat and light is released producing this color.Plants don't let be released like that, they siphon it through pathways into the bonds of a glucose molecule. COnversion mechanism for light to chemical energy.
What does this image describe?
Photosystem
A Reaction-Center Complex Associated with Light-Harvesting Complexes