PPFA 13- Good manufacturing practice and documentation
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
explain both large- scale and small scale manufacturing approaches , identify reliabke sources for product formulations and apply core principles of good manufacturing practice
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What do you need to know to understand pharmaceutics ?
To achieve this, one needs knowledge of:
• Fundamental physical chemistry
• Human body systems and drug kinetics
• Formulation science and product design
• Both small- and large-scale manufacturing processes
• Methods to prevent and control microbial contamination
pharmaceutics- transforms an active drug into a usable medicine
What is the PQS and what do they do ?
Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) ensures medicines are consistently made to required quality standards:
Responsibility led by senior management; commitment from all
staff essential.
Integrates GMP principles and Quality Risk Management (QRM).
Emphasizes thorough design, documentation, monitoring, and.
continuous improvement.
Applies across all stages: from development and tech transfer to full -scale commercial production
What are the GMP s for medicinal products ?
Processes must be clearly defined and validated
Requires qualified staff, proper facilities, and suitable equipment
All steps documented with clear procedures and records
Deviations must be investigated and addressed through Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
What is the GMP quality control ?
Quality Control
• No product released without thorough testing
• Detailed records of tests and release decisions kept
• Samples retained for future checks
What is GMP risk management ?
Product Quality Review
• Annual reviews assess process consistency and trends
• Supports ongoing improvements and revalidation
What is GMPs Quality risk management ?
Quality Risk Management
• Risk assessments based on scientific evidence and patient safety.
• Level of formality and documentation depends on risk severity.
What are the types of GMP documentations ?
Specifications for materials- is it amorphous or crystalline (starting, packaging, intermediates, finished products).
Manufacturing formulae and processing instructions.
Packaging instructions.
Batch processing and packaging records.- for the safety of the patient - no variations between batches
Standard operating procedures (SOPs) for receipt, sampling, testing, etc.
Why are documentation principles importance and what are some good key features ?
Documentation Principles are critical for demonstrating GMP compliance and traceability.
key features :
Documents must be accurate, clear, and available at points of use.
• Corrections should not obscure original entries.
• Records retained for a defined period (usually at least 1 year after expiry).
What are the 2 type of scale considerations ?
large scale manufacturing
small scale manufacturing
Describe large scale manufacturing
Large scale focuses on mass production - products are not tailored to individual patients needs
Focuses :
precise , standardized processes
use rigorous quality control , testing procedures
uses large- scale , specialized equipment
includes both sterile and non-sterile production settings
uses packaging to maintain stability
products licensed and approved
Describe small - scale manufacturing ?
small - scale manufacturing- to meet specialized needs like early-stage clinical trials, personalized medicine, or niche markets
In pharmacy - extemporaneous dispensing
•Community settings
•Hospital settings
•Specials manufacturing
Generally , less expensive - used only when no alternative exists
reasons for use:
•No licensed product available
•Product has been discontinued
•A specific individual dose is needed
•A tailored formulation is required
•For veterinary use
What is specials small scale manufacturing ?
Specials manufacturing
• Custom-made medicines
• Typically used for toxic or complex formulations
• Involves high costs for each individual prescription
The NHS is working to lower the expenses
associated with specials manufacturing
Large vs small scale GMP ( summary )
Large vs Small Scale
GMP principles are the same regardless of scale.
Large scale: higher complexity, more automation, larger volume of documentation, more formalized controls.
Small scale: systems may be simpler but must still ensure equivalent product quality.
Documentation
• Fundamental for compliance and audit readiness.
• Covers specifications, SOPs, batch records, quality control data, CAPA records.
• Good Documentation Practices (GDP) essential for both scales.
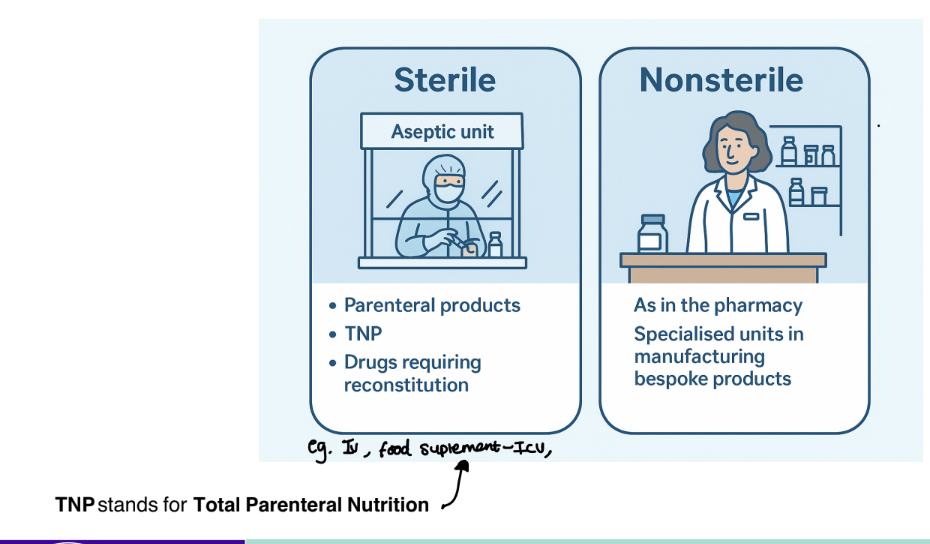
what are the 2 types of hospital extemporaneous dispensing ?
sterile
non sterile
What is the risk assessment GPhC ?
Use a formula from an authoritative source, such as an official pharmacopoeia
Verify the preparation method (for example, using the pharmacopoeia method)
Double-check all calculations
Ensure the use of appropriate specialist equipment
Assess and minimize the risk of contamination
Implement strict hygiene measures
Confirm the quality and safety of ingredients and starting materials
Ensure the premises are suitable for preparation
Verify that staff have the necessary skills, training, and competence
Define the situations that would require a new risk assessment
How do you make sure to have quality control ?
equipment is suitable and functional
formula and dose are accurate and safe
raw materials are properly sourced
calculations are correct
records are complete
labelling is correct
staff are well trained
What are the requirements for record keeping ?
Legal requirement:
• Must be kept for a min of 2 years (5 years)
• The pharmacist is responsible and so must ensure
accuracy of final product
• Name + signatures of staff involved in the production
What do records include ?
Formula + source
• Calculations - checked!
• Ingredients - checked!
• manufacturer, quantities, batch number and expiry
• Names and signatures of all people involved in the preparation of the product
• Date prepared
• Expiry date + BN
• Date supplied
• Pt details
• Drs details
• Label
What are key techniques from GPhC ?
Combining liquids: Mix thoroughly by careful stirring or shaking to ensure even distribution.
Dissolving solids in liquids: Reduce particle size (e.g., by grinding or sieving) to improve solubility and accuracy.
Blending solids:
Use a pestle and mortar to achieve uniform mixing.
For equal small amounts, simple mixing is appropriate.
For unequal quantities, adopt the geometric dilution method to ensure even blending.
Mixing semi-solids (e.g., creams and ointments):
Use a smooth, clean surface (e.g., ceramic tile).
Add ingredients incrementally to achieve a homogeneous final product.
How is stability checked over time ?
Appearance: no visual changes
Chemistry: ingredients stay the same
Microbiology: remains sterile or has acceptable microbial levels
Effectiveness: therapeutic action unchanged
Safety: no new toxic effects
What is the expiry date guidance ?
The date after which the product must not be used.
Large-scale manufacture: expiry set using accelerated stability testing.
Extemporaneous dispensing: expiry guided by official monograph.
If no standard available, use a cautious approach:
Stable products (solids for internal or external use): up to 3 months.
Less stable products (liquids or semi-solids for internal or external use): up to 4 weeks; considered "recently prepared."
Some liquids: up to 2 weeks; considered "freshly prepared."
What are the use of preservatives ?
Purpose:
To prevent bacterial growth, especially in aqueous (water-based) liquid preparations.
What are commonly used preservatives 🇦:
chloroform spirit , water - these are available at single strength , double strength
According to GPhC guidance, pharmacists must ensure correct preservative concentrations, validate preparation methods, and document calculations to protect patient safety and product stability.
What are common packaging used for extemporaneous preparations ?
Packaging must protect quality, safety, and
stability:
Amber glass bottles
Dropper bottles
Jars (plain or amber)
Cartons
Summary
GMP Principles essential to understand before making any medicine.
All types of manufacturing require strict good practice.
Detailed records must be kept for extemporaneous preparations.
Product stability determines its expiry date.