A&P Lab midterm practice 2
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
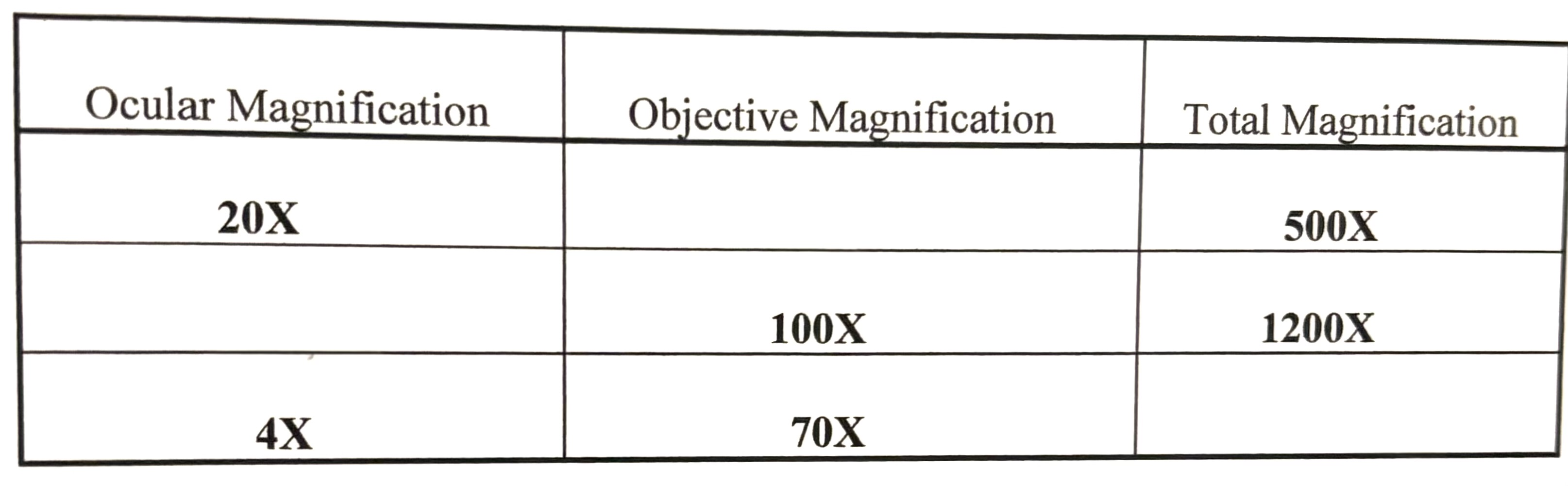
Calculate the missing values in the table below:
25X — 12X — 280X
Define: parfocal microscope
a type of compound light microscope designed so that when you switch from one objective lens to another, the specimen remains nearly in focus.
Name an example organ associated with each of the following organ systems:
a) nervous system
b) lymphatic system
c) urinary system
a - brain
b - spleen
c - uterus
Rank the following levels of biological hierarchy from 1 to 6 in ascending order, with 1 being the lowest (most simple) level and 6 being the highest level (most complex).
tissue level ___ organism level ___
organ system level ___ organ level ___
cell level ___ organelle level ___
organelle level - 1
cell level - 2
tissue level - 3
organ level - 4
organ system level - 5
organism level - 6
Name an example organ found within each of the following body cavities:
a) abdominal cavity
b) cranial cavity
c) pericardial cavity
d) pleural cavity
a - large intestines
b - brain
c - heart
d - lungs
Define term: parietal peritoneum
The layer of the peritoneum that lines the inner wall of the abdominal cavity.
Define term: visceral pericardium
The inner layer of the pericardium that directly covers the surface of the heart.
Define term: medial
refers to a position closer to the midline of the body.
Define term: distal
refers to a position farther from the point of attachment or origin of a body part.
Define term: parasagittal plane
It is a vertical plane that divides the body into unequal left and right portions, parallel to the midsagittal plane.
Define term: contralateral
refers to something occurring on or affecting the opposite side of the body.
Give the regional name for each of the following body parts.
a) armpit b) neck
c) sole of foot d) anterior knee
e) posterior knee f) eye socket
a - axillas
b - cervical
c - plantar
d - patellar
e - popliteal
f - orbital
Name the body cavity in which the following structures are found. Be as specific as possible in giving the smallest possible cavity that correctly answers the question.
a) stomach b) spinal cord
c) lungs d) urinary bladder
a - abdominal cavity
b - vertebral cavity
c - pleural cavity
d - pelvic cavity
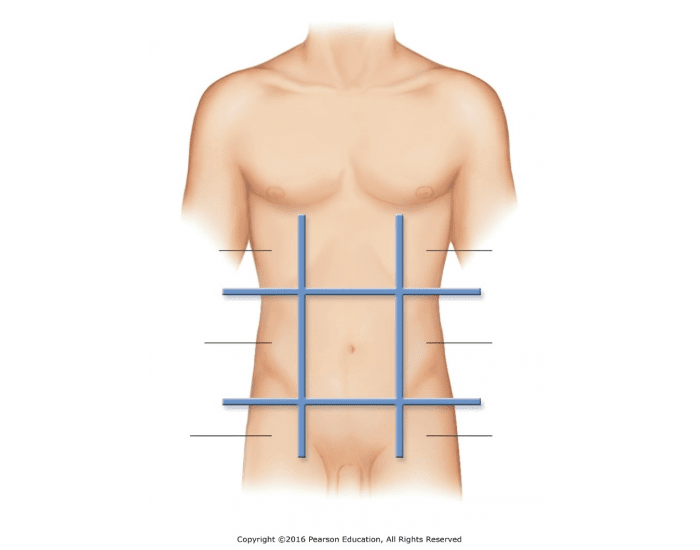
Name the abdominopelvic regions indicated on the diagram:
right hypochondriac
right lumber region
right inguinal (iliac) region
epigastric region
umbilical region
pubic region
left hypochondriac
right lumbar
left inguinal (iliac) region
Give the correct description/function of each of the following cellular structures:
Golgi apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum for storage in the cell or secretion outside the cell. “post office”
Give the correct description/function of each of the following cellular structures:
mitochondria
Produce energy for the cell by converting nutrients into ATP through cellular respiration. “powerhouse”
Give the correct description/function of each of the following cellular structures:
lysosome
Contain digestive enzymes that break down waste materials, old cell parts, and foreign substances. “garbage crew”
Give the correct description/function of each of the following cellular structures:
nucleolus
Produces ribosomes by assembling ribosomal RNA and proteins.
Give the correct description/function of each of the following cellular structures:
cilia
Short, hair-like structures that move fluids or materials across the cell’s surface.
State ONE difference between rough ER and smooth ER.
Rough ER has ribosomes on its surface, while smooth ER does not.
Name the stage of the cell cycle during which each of the following occurs within a cell:
a) chromosomes line up on the equator of the cell
b) The cell is not actively dividing
c) cleavage furrow separates daughter cells
d) DNA is replicated
e) nuclear envelope reforms and spindle fibers
a - Metaphase
b - Interphase
c - Cytokinesis
d - Interphase (S phase)
e - Telophase
List the three basic components of a typical cell:
nucleus
plasma (cell) membrane
cytoplasm
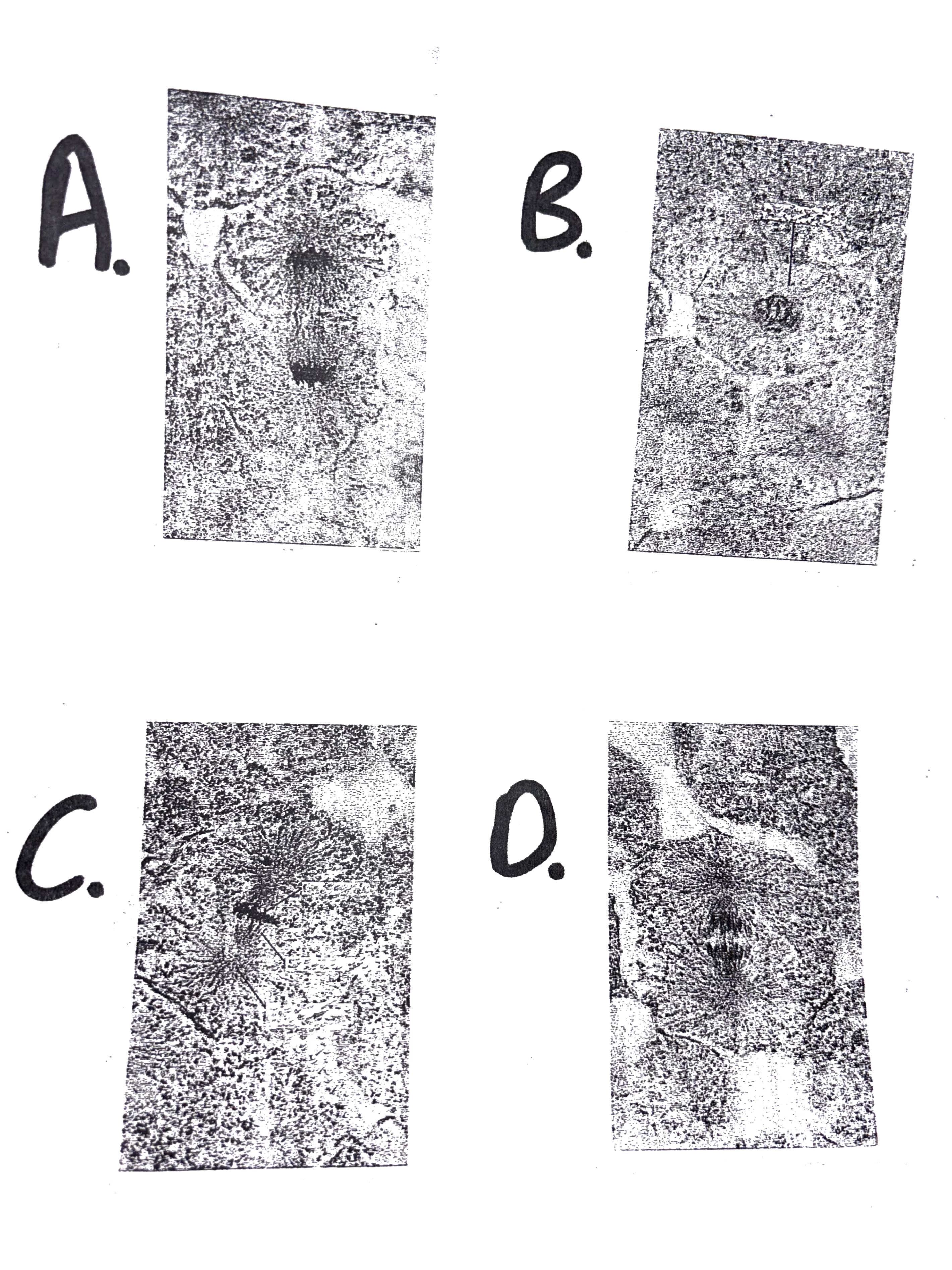
Identify the specific stage of mitosis as shown in the attached diagram.
A – Anaphase
B – Metaphase
C – Prophase
D – Telophase
Given the four tissue types in the human body, which one:
a) sends and receives messages?
b) is responsible for secretion and absorption?
c) contracts to produce movement?
d) fills void spaces in the body?
a - Nervous tissue
b - Epithelial tissue
c - Muscle tissue
d - Connective tissue
Give one location within the body where the following tissues may be found:
a) dense irregular
b) simple cuboidal c) hyaline cartilage
d) cardiac muscle e) transitional (Furothelium)
a - dermis of the skin
b - kidney tubules
c - ends of long bones or in the trachea
d - walls of the heart.
e - urinary bladder
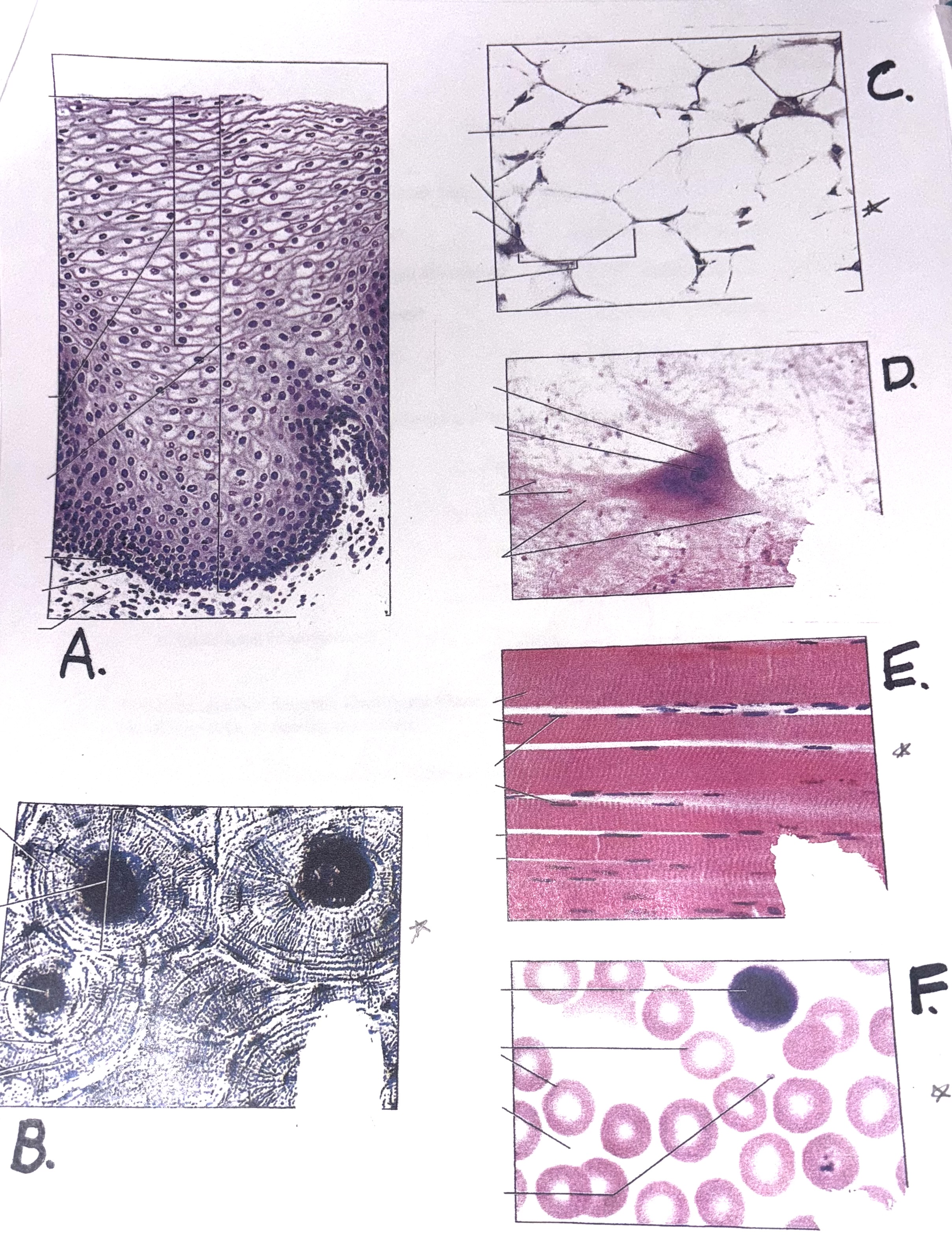
Using the attached diagram, identify the tissues and write their correct names in the blanks below. Be very specific in naming the tissues.
a - Stratified squamous epithelium
b - Compact bone
c - Adipose tissue
d - Nervous tissue
e - Skeletal muscle tissue
f - Blood (vascular tissue)

The dermis is subdivided into two sublayers. Fill in the blanks below:
a) Superficial sublayer – Papillary layer → Areolar connective tissue
b) Deep sublayer – Reticular layer → Dense irregular connective tissue
What is the name of the smooth muscle associated with a hair follicle?
arrector pili muscle
List two ways in which hair and nails are similar
Both are made of keratin, a tough, protective protein.
Both are produced by epidermal cells that grow from specialized structures in the skin.
What is the function of:
a) sweat gland
b) melanin
c) hypodermis
d) Meissner's corpuscle
a - Regulates temperature and removes waste
b - Gives skin color and protects from UV rays
c - Insulates and anchors the skin
d - Detects light touch
List the sublayers of cells that comprise the superficial layer of the skin in correct anatomical order:
(superficial) __________
_____________
_____________
_____________
_____________
(deep) _________
1. corneum
2. lucidum
3. granulosum
4. spinosum
5. basale
What layer of cells undergoes active mitosis?
Stratum basale – the primary layer where mitosis happens.
Stratum spinosum — cells here can also divide, but less actively than in the stratum basale

Match each of the following bones of the skeleton into their proper category:
scapula - E
distal phalange - A
mandible - C
sternum - E
patella - D
tarsal - B

Match each of the following bones of the skeleton into their proper category:
A. axial skeleton
B. appendicular skeleton
B - femur
A - cervical vertebrae
B - clavicle
A - hyoid
Describe a sutural bone.
It is a small, irregular bone that sometimes forms within the sutures (joints) between the flat bones of the skull.

Fill in the blanks regarding surface landmarks on bones.
______ a bony tunnel through a bone.
______ a wide, shallow depression, a pronounced.
______ enlargement, typically at the proximal end.
______ a small, flat, smooth surface.
metuas
fossa
head
facet