Thẻ ghi nhớ: Unit 1: Ecosystems | Quizlet
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
predation
An interaction in which one organism kills another for food.
Parasitism
One organism benefits and the other is harmed
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
symbiotic relationship
The relationship between two species that live in close association with each other
competitive exclusion principle
Ecological rule that states that no two species can occupy the same exact niche in the same habitat at the same time
resource partitioning
the differentiation of niches that enables similar species to coexist in a community
temporal partitioning
using resources at different times
spatial partitioning
using different areas of a shared habitat
morphological partitioning
using different resources based on different evolved body features
pathogen
a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease
weather
local area's short term physical conditions
climate
a region's average weather conditions over a long period
Nutrient availability for the tropical rainforest
nutrient poor soil because the high temp & rainfall causing rapid decomposition of organic matter
nutrient leaching
Loss of nutrients from soil due to water movement.
Nutrient availability for the boreal forest
nutrient poor soil (low temp & low decomposition rate of dead organic matter)
Nutrient availability for the temperate forest
nutrient rich soil (lots of dead organic matter - leaves & warm temp/moisture for decomposition)
2nd law of thermodynamics
each time energy is transferred some is lost as heat
10% rule
in trophic pyramids, only about 10% of the energy from one level makes it to the next level; the other 90% is used by the organism & lost as heat
Lithosphere
soil, land, and earth's crust
fossil fuels
a natural fuel such as coal or gas, formed in the geological past from the remains of living organisms.
what are the effects of human activities on the nitrogen cycle?
- adding gases when we burn gasoline and other fuels that contribute to acid rain
- adding nitrous oxide to the atmosphere through farming practices (commercial fertilizers) which can warm the atmosphere and also deplete the ozone
- contaminating groundwater from nitrate ions in inorganic fertilizers
- releasing nitrogen into the troposphere through deforestation
What factors decide aquatic zones?
sunlight and nutrient availability
economic and health services of coral reefs
- enzymes, algae, and pigments contribute to cancer, HIV, and other ailments
- supports fisheries and tourism
- 500 million people rely on coral reefs worldwide for food and income
- provide globally $375 billion/year in goods and services
streams
narrow channels of water, often beginning in mountainous areas, where water (from melting glaciers) moves rapidly across rocks and down waterfalls
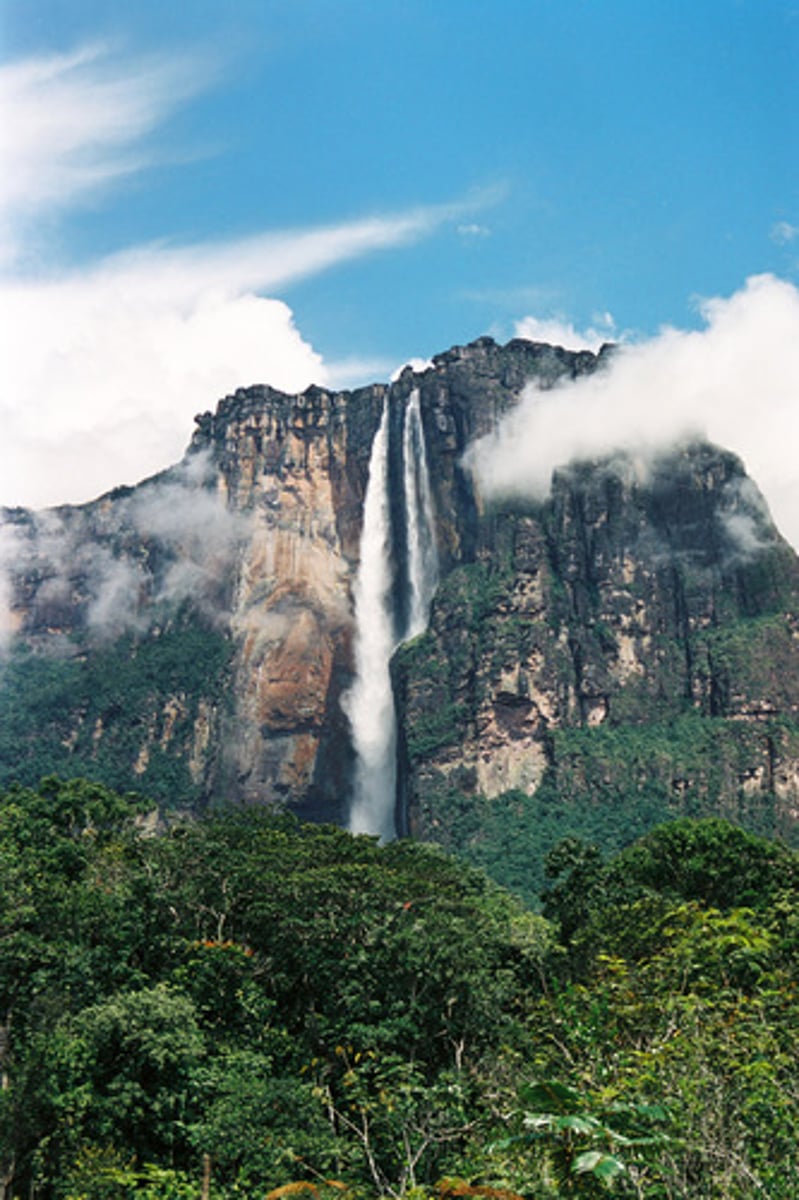

Floodplain Zone
low-lying areas that experience wide, slow-moving rivers that will occasionally flood and deposit material from upstream; water continues to warm, oxygen levels decrease, nutrients continue to increase
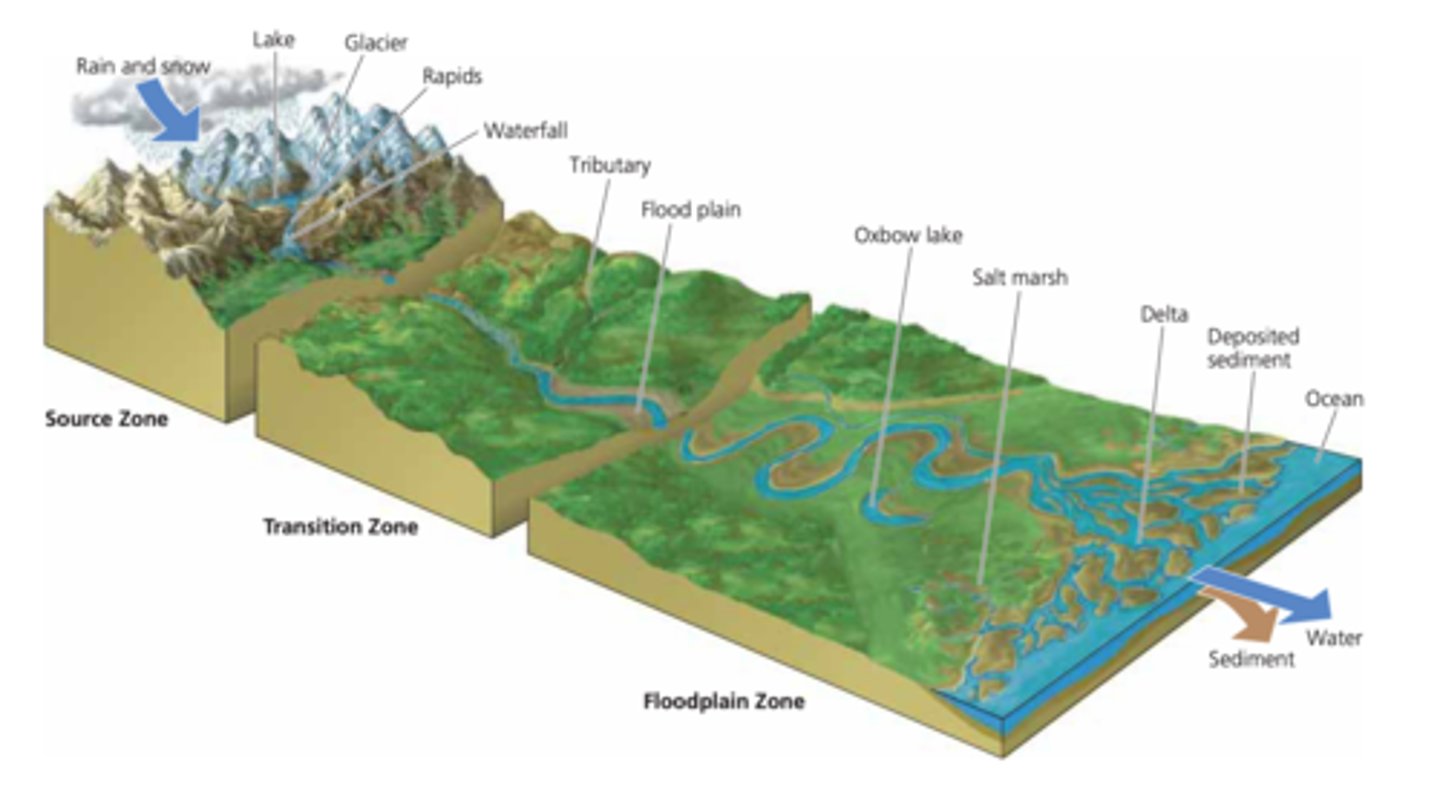
evapotranspiration
the combined process of water evaporating from the land and plant surfaces and transpiring from plants, ultimately moving water from the Earth's surface to the atmosphere
how can the 2nd law of thermodynamics be applied to food webs?
the amount of useable energy decreases as you move up the food chain; because available energy decreases with each step up the food chain
why is the producers' trophic level for oceans as small?
phytoplankton are eaten as fast as they produce
are mushrooms heterotrophs or autotrophs?
heterotrophs
trophic cascade
removal or addition of a top predator has a ripple effect down through lower trophic levels
gross primary productivity (GPP)
RATE at which biomass (all plant material) is made by producers during photosynthesis in an ecosystem
Net primary productivity (NPP)
RATE at which biomass is made by producers minus RATE at which the producers use what they produce respiration
ecological efficiency
the portion of incoming solar energy that is captured by plants and converted into biomass
law of conservation of matter
matter cannot be created nor destroyed but can be transformed
biosphere
region occupied by living organisms
atmosphere
air and space
Hydrosphere
areas covered by water such as rivers, lakes, and oceans
extraction and combustion
digging up or mining FFs & burning them as energy source; releases CO2 into atmosphere
sedimentation and burial
slow geological process that stores carbon in underground sinks
exchange of carbon
transfer of carbon between different reserviors
Photosynthesis
plants take in CO2
Respiration
organisms release CO2
carbon sink
reservoir that accumulates more carbon than it releases (ex. ocean (algae & sediments), plants, soil)
carbon source
reservoir that releases more carbon than it takes in (fossil fuel (oil, coal, natural gas) combustion, animal (cow burps & farts = CH4), deforestation (releases CO2 from trees))
direct exchange
CO2 moves directly between atmosphere and the ocean by dissolving into and out of ocean water at the surface
sedimentation
calcium carbonate precipitates out as sediment and settles on ocean floor
nitrogen reserviors
plants, soil, atmosphere
nitrogen fixation
process of N2 gas being converted into biologically available NH3 (ammonia) or NO3- (nitrate)
bacterial fixation
certain bacteria that live in the soil or in symbiotic relationship with plant root nodules convert N2 into ammonia (NH3)
synthetic fixation
humans combust fossil fuels to convert N2 into nitrate (NO3-)
assimilation
plants and animals taking nitrogen in and incorporating it into their body
ammonification
soil bacteria, microbes, & decomposers converting waste & dead biomass back into NH3 and returning it to soil
nitrification
conversion of NH4 into nitrite (NO2-) & then nitrate (NO3) by soil bacteria
denitrification
conversion of soil nitrogen (NO3) into nitrous oxide (N2O) gas which returns to the atmosphere
What is phosphorus cycled through?
cycled through water, soil, and sediment but NEVER in the atmosphere
Does the phosphorus cycle move slowly or quickly?
VERY slowly
What is the major natural source of phosphorus?
weathering of rocks that contain phosphorus minerals
What are synthetic sources of phosphorus?
mining phosphate minerals and adding to products like synthetic fertilizers and detergents/cleaners
Assimilation of Phosphorus
Phosphorus is absorbed by plant roots and assimilates into tissues; animals assimilate phosphorus by eating plants and other animals
excretion/decomposition of phosphorus
animal waste, plant matter, and other biomass is broken down by bacteria/soil decomposers that return phosphate to the soil
Sedimentation
phosphate doesn't dissolve very well into water so a lot of it forms solid bits of phosphate that fall to the bottom as sediment; phosphorus sediments can be compressed into sedimentary rock over long periods of time by weight of overlying water
geological uplift
tectonic plate collision forcing up rock layers that form mountains; P cycle can start over again with weathering and release of phosphate from rock
Eutrophication
too much nitrogen and/or phosphorus causing algae to bloom which covers the surface of water blocking sunlight and killing plants below the surface; algae eventually die-off, bacteria that break down the dead algae use up all the O2 in the water and lower O2 levels in the water kills aquatic animals causing bacteria to use even more O2 (creates a positive feedback loop)
What causes eutrophication
too much nitrogen/phosphorus; can occur form fertilizer runoff or human/animal waste contamination
Precipitation
the falling to earth of any form of water (rain or snow or hail or sleet or mist)
Condensation
Gas to liquid
Evaporation
Liquid to gas
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
Runoff & Infiltration
Precipitation (rain) either flows over earth's surface into a body of water (runoff) or trickles through soil down into groundwater aquifers (infiltration)
aquifers
An underground water reservoir
how does infiltration and runoff help ground and surface water?
precipitation recharges groundwater through but only if groundwater is permeable; runoff recharges surface waters but can also carry pollutants into water sources
effects of human activities on the water cycle
- withdrawing large amounts of freshwater
- clearing vegetation and eroding soils
- polluting surface and underground water
- contributing to climate change -> water cycle tends to run faster in warmer climates
Sulfur cycle
mostly stored underground in rocks and minerals and in ocean sediments as sulfate salts; enters atmosphere through volcanic eruptions, sea spray, dust storms, forest fires; cycles back to land through rainfall
Effects of Human Activities on the Sulfur Cycle
- we add sulfur dioxide to the atmosphere by:
- burning coal and oil
- refining sulfur containing petroleum
- sulfur dioxide in atmosphere reacts to form acid rain
acid rain
rain containing nitric and sulfuric acids
ocean hemisphere
Land-ocean hemisphere

What abiotic factors influence aquatic ecosystems
- salinity (dissolved salt in water)
- water temperature
- amount of sunlight
- availability of dissolved oxygen
- nutrients such as nitrates and phosphates
- turbidity (cloudiness of the water)
- pressure
plankton
free-floating or weakly swimming organisms
Phytoplankton
Microscopic, free-floating, autotrophic organisms that function as producers in aquatic ecosystems
zooplankton
"animal-like" plankton that consume phytoplankton (ex. krill, jellyfish)
nekton
strong swimmers and consumers (ex. fish, whales, sea turtles)
benthos
Bottom-dwelling organisms (ex sea stars, lobsters, mussels, etc)
photic zone
Portion of the marine biome that contains sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis
aphotic zone
dark layer of the oceans below the photic zone that contains little to no sunlight
benthic zone (abyssal zone)
The bottom surface of an aquatic environment; no sunlight reaches here
coastal zone
warm temperature, nutrient-rich, extends from shallow water to continental shelf; life is plentiful due to an abundance of sunlight and nutrients
estuaries
partially enclosed bodies of water where seawater mixes with freshwater
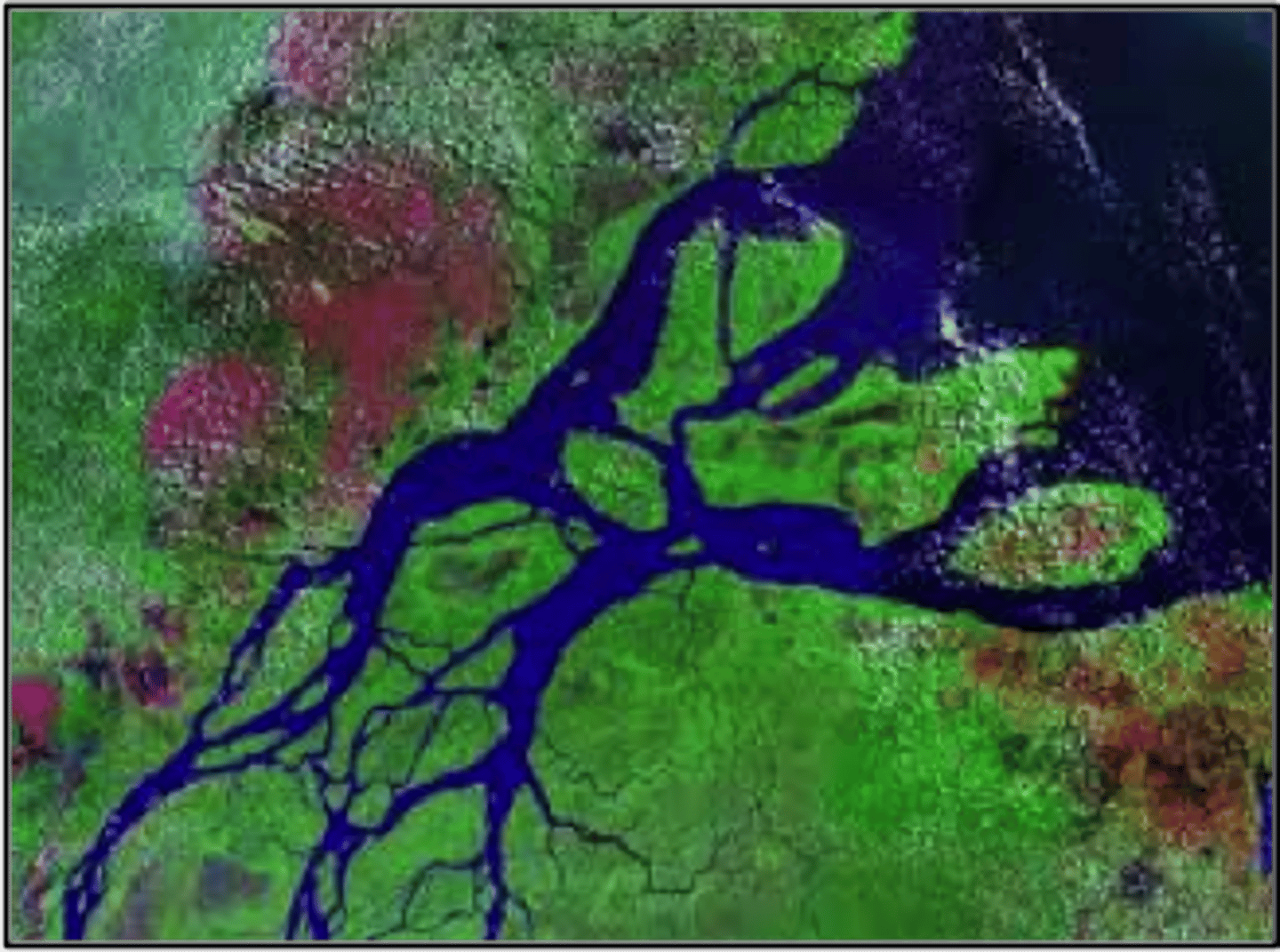

coastal wetlands
areas of land that are fully saturated with water at least part of the year
types of coastal wetlands
- salt marshes
- seagrass beds
- mangrove forests
- swamps
- bogs (usually inland)
Salt Marshes
coastal wetland regularly flooded by tides and dominated by herbs, grasses, and shrubs (few/no trees)
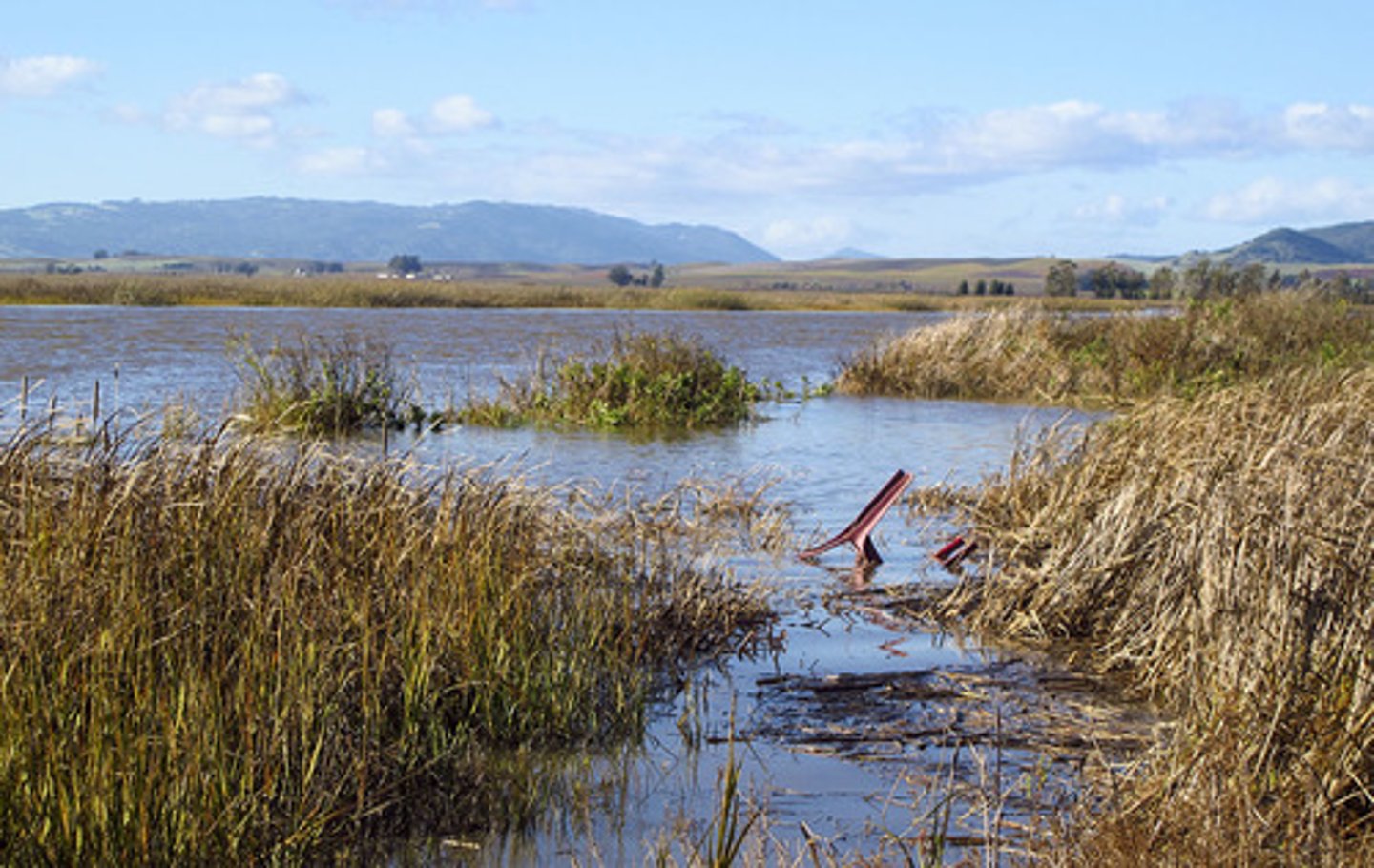

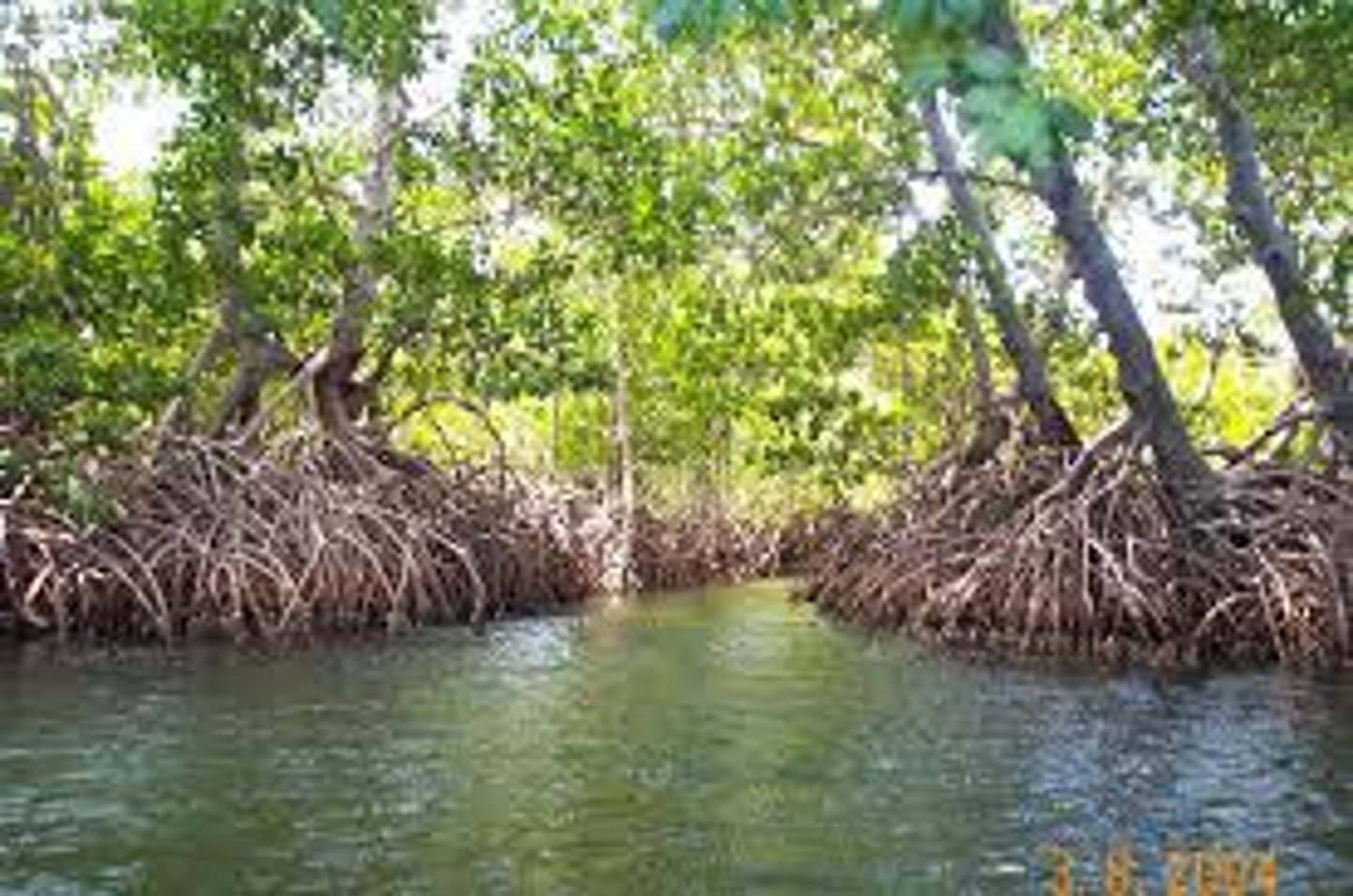
mangrove swamps
Coastal wetlands with trees that have evolved to survive in the high-salt, low-oxygen water

benefits of wetlands
- highly productive ecosystems that support great deal of biodiversity
- can slow and hold influxes of water, helping to prevent flooding
- water that passes through wetlands tends to come out cleaner, with less sediment and pollution
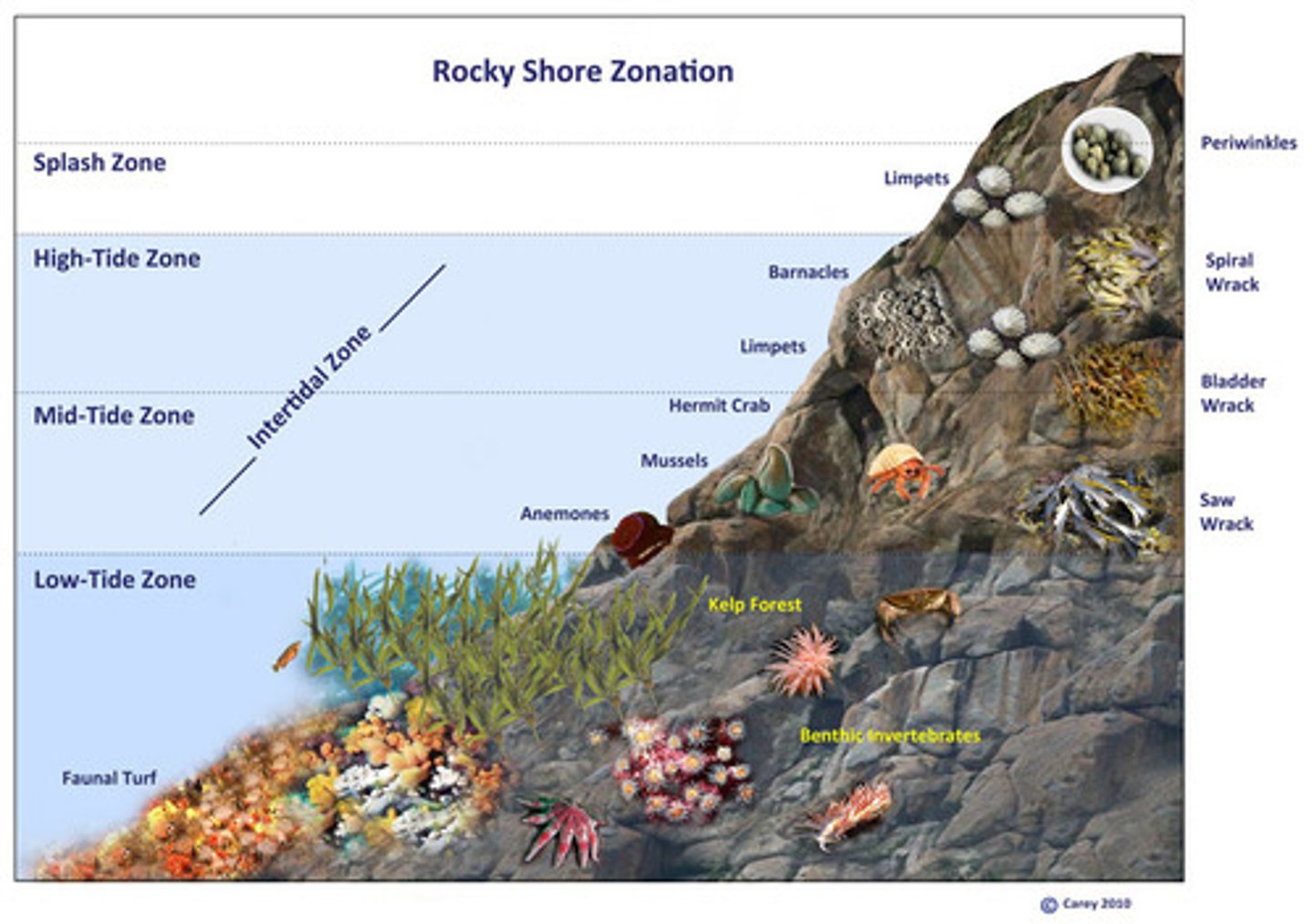
intertidal zone
Portion of the shoreline that lies between the high and low tide lines
rocky shores
type of intertidal zone found on coasts with heavy wave activity
sandy shores
type of intertidal zone found on coasts with gentler wave action; color of sand indicates the source material that eroded to form it (black = volcanic; brown = granite; white = coral)

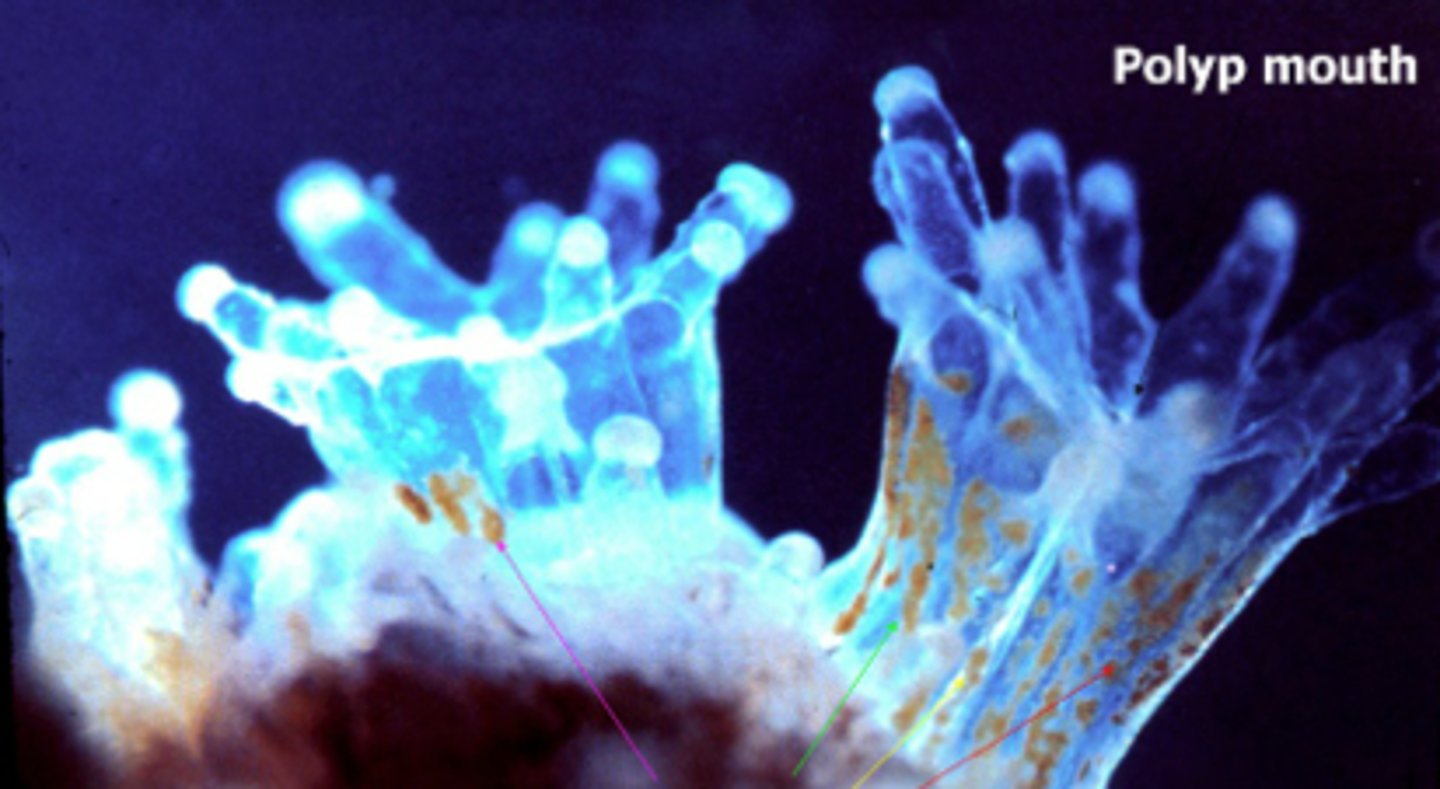
coral polyps
small animals that live in the warm coastal waters of the tropics and subtropics; have a mutualistic relationship with photosynthetic algae; as the polyps grow they produce a calcium-based external skeleton, when the polyps die the skeletons are left behind and are built upon by other polyps
Coral Reefs
The most diverse marine biome on Earth, found in warm, shallow waters beyond the shoreline