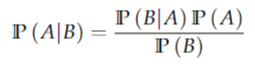P1. Probability
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Sample Space.
The set Ω. It contains all possible outcomes that we are considering.
Event
A subset of Ω (including Ω itself)
Event space
A set of subsets of Ω which must satisfy certain properties. The event space defines the set of all describable events to which we want to assign probabilities
Probability
A function P that assigns, for all events in F:
P(A) >= 0 for all A in F
P(Ω) = 1
If A1, A2, … in F are mutually exclusive, then P(A1 U A2 U…) = P(A1) + P(A2) + …
The complement rule
The probability that an event occurs is always equal to 1 minus the probability that the event does not occur
The Probability of the Union of Two Events Rule
The probability of A or B is:
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) − P(A ∩ B)
Bounds on Probabilities Rule
The probability of A or B is weakly less than the
sum of their probabilities:
P(A ∪ B) ≤ P(A) + P(B)
Logical consequence rule
If B logically entails A then P(A) ≥ P(B)
Kolmogorov definition of a conditional probability
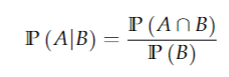
Law of total probability
This says that given a partition {B1, B2} of Ω then for any event A:
P (A) = P (A ∩ B1) + P (A ∩ B2)
P (A) = P (A|B1) P (B1) + P (A|B2) P (B2)
Two events A and B are independent if (intersect)
P (A ∩ B) = P(A)P (B)
Two events A and B are independent if (conditional)
P(A|B) = P(A)
Bayes’ Rule