theme 3
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
structural components that gram+ bacteria use to induce inflammation
thick peptidoglycan contains → lipoteichoic acid
lipoteichoic acid binds to TLR on phagocytes → they start producing cytokines → mediate inflammation
structural components that gram- bacteria use to induce inflammation
thin peptidoglyan layer + LPS
LPS binds to TLR on phagocytes → cytokines → mediates inflammation
capsule is a virulence factor to hide → but what do they do
prevents compelement-mediated phagocytosis
normally C3b binds to bac surface
factor H degrasdes C3b and binds well to capsule → leads to less opsonization
mps are now not activated
which 3 pathogens have a capsule
streptococcus pneumoniae
heamophilus influenza
neisseria meningitidis
streptococcus pyogenes → what kind of patho, diagnos (3), gram
primary pathogen → transient carrier (throat)
diagnostics
catalase test/beta hemolytic
microscopy → gram stain
culture → blood agar plates
gram+
streptococcus pyogenes ENTER
they enter by adhesion
through pilus/pili + F protein + lipotehcoic acid
on pili → protein M
streptococcus pyogenes KICK → 3
make streptolysin → class of pore-forming exo-toxins
kills host cells → erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets
helps evade imm sys → induces inflammation with peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid
pore forming (membrane active) exotoxins
causes H2O to get in → swelling → host cell lysis → death (bc osmolarity = high)
cytoplasmic contents get out → low osmolatiry
enzymes produced by s. pyrogenes = 3
hyaluronidase → easier for bac to spread infection
streptokinase → lysis of clot → easier to spread
C5a peptidase → inact C5 = no effector pw of classical pw
so no phagocyte recruitement and peptide mediators of inflamma
M protein
surface protein on s. pyrogenes
binds host/H factor → prevents opsonization by C3b
immune evasion → prolonged infection → inflamma response
toxins and superantigens
10% of s. pyogenes has superantigenic toxin
leads to toxic shock sd
superantigenic toxin can bind to a lot of TC (master key)
influenza A virus virulence mechanisms = 5
hemagglutin = HA spike → to enter
neuroaminidase = NA → to cut
RNA polymerase
antigenic drift
antigenic shift
hemagglutin spike of influ A
it’s surface glycoprotein on the virus → so for adhesion
binds sialic acid residues on host cells receptors → mediates viral entry via endocytosis
neuroaminidase of influ A
is like scissors (enzyme) → this happens at exit
cleaves sialic acids → allows release of new virions from infected cells
RNA polymerase of influ A
to replicate its genome → causes cell death
had no proofreading bc its RNA → mutations are therefore frequent
antigenic drift
small (evolutional) genetic changes in influenza virus
caused by errors/mutations during replications
pre-existing ab’s bind less effectively because spike proteins are now a bit altered
antigenic shift
major change in influ virus
happens when 2 diff influ A strains infect same host cell
genome segments reassort → new combo of HA and/or NA
can lead to pandemics
diagnostics of influ A
DNA/RNA → PCR
direct immuno-fluorescence → Ag testing
HIV → 4 kenmerken waaronder 3 enzymen
reverse transcriptase → make DNA of the RNA in virus
integrase
HIV protease
exists by budding
integrase = to evade immune sys
inserts viral DNA in genome of CD4 cell
CD4 TC is main target for HIV → progressive destruction of CD4 cells → immunodef = AIDS
HIV protease → 2
HIV only works/replicates if HIV protease cuts the polyproteins (pp) in pieces
it cleaved long viral pp into functional proteins → necessary to infect other cells
HIV diagnostics → 2/3
PCR + combo test
serology + antigens testing = combo test → ab and ag detection
what are commensals
non harmful bacteria → normally present in every person, no symptomps
all the bac that are there to stay
harmless unless impaired immune sys → opportunists
on your skin you mostly have gram …
positive bac
inside of your body you mostly have gram …
mostly gram neg, but little bit of gram pos too
colonization resistance
presence of normal microbiota
protects against adherence of other mo
what causes fever
when immune cells (like macrophages) release cytokines → act on hypothalamus
raises body set point → heat production
colonization
presence of a microbe without disease
could be commensal or pathogen
this is called exposure and not infection
source of infection → endogenous
commensals
colonization → primary pathogens
commensals on body parts → skin, throat, vag, bowel
skin → staph epi
throat → strep pneu, strep pyog, neisseria, candida albicans
strep → throat/vag.na
bowel → e. coli, bac fragi, clos dif
colonization organisms
kenmerkend → 3
nog 2
all have capsule → s. pneu, n. mening, h influ
s aureus (nose), s pyo (throat)
sourc of infection → exogenous
other person
zoonosis
vector
environment
staph epidermis → what kind og pathog, def, when inf
opportunistic + commensal on skin
granulocytopenia
foreign body → adhesion to IV catheter/prothesis = biofilm
staph aures → what kind of patho, def host
primary pathogen + 30% carrier in nose
no risk factors required, but higher risk if
granulocytopenia
foreign body
IV drug use
what happens if skin is disrupted
granulocytes will act up → next in line of defense
but catheter is already in bloodstream → granu cant reach that far → bloodstream infection
staph epidermis infection
bowel surgery infections
e coli
b fragilis
clostridium species → some can form spores
functionally causes of impaired barrier function → uri cat, gastric acid, tears, airway, other causes
urinary catheter → e coli
lack of gastric acid → salmonella, vibrio cholera
lack of tears → heamophilus influ
disturbance of normal airway cleanig → strep pneu
litterally causes → wounds, insect bites, penetration of skin etc.or impaired colonization resistance
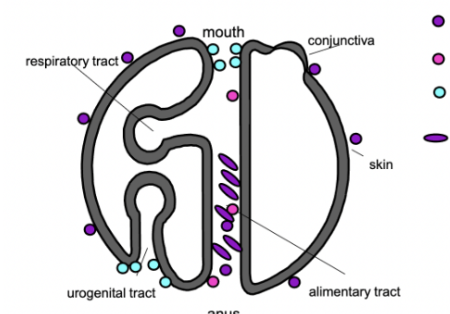
where belongs G=, c. albicans, G+ and clostr diff
gram +
gram -
candida
clos diff
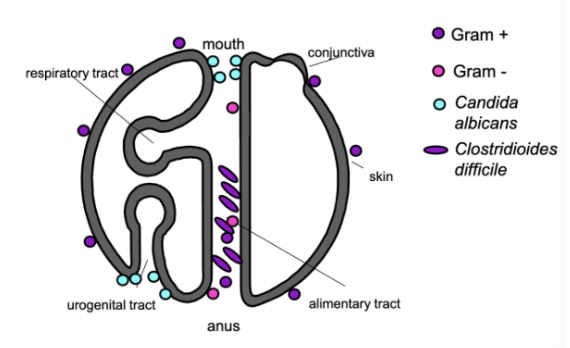
having candida but havent taken antibiotics
how do they grow on plate vs in vivo
candida stomatis/oesophaitis → this infection is associated with TC immune deficiency (HIV)
on a plate → not much food → grow as yeast
in vivo → grow as pseudohyphae
no bacteria → which mo can now grow
c difficile
the cytotoxin (virulence factor) causes bowel damage
pseudomembrane consists of → mucus and numerous granulocytes
this membrane is caused by c diffi → seen by colitis
eculizumab
anti-C5 antibodies → blocks MAC formation
complement deficiency
mostly genetic (could be drugs)
leads to infection with extracell bac and neisseria
doesnt always give infection
complement def in classic route
C2, C3, C4
more sensitive to extracell bac → esp capsulated → pneumococcus, h influ
C3 def is the worst → no opsonisation
complement def in alt/MBL route
factor B, D, MBL
also extracell bac → esp pyo
often asymp tho
compl def in terminal complement/MAC
C5-C9
esp risk on neisseria infection → needs MAC to be killed
MAC is important for killing gram- bac
neisseria meningitidis → 4
VF is LOS = same as LPS
LOS in blood → activates TLR4 → cytokine storm
endothelial damage + leakage → disseminated intravascular coagulation = DIC
could also lead to shock next to DIC
this leads to necrotic skin lesion = purpura fulminans
causes of hypogammaglobulinemia (+ its what kind of defect)
defect in antibodies
congenital
X-linked a-gammaglobulinemia
part of SCID
acquired
common variable immunodef (CVID)
B cell malignancies → CML/myeloma
iatrogenic → rituximab = anti-CD20
which organisms can make a person sick with hypogammaglobulinemia → 1/3
all primary pathogens
capsulated bac → s pneu, n. menin, h influ
campylobacter
persistent giardia lamblia or enterovirus infections
this gives frequent or recurrent infections of these pathogens
spleen disorder
spleen takes out bac from bloodstream
causes:
asplenia → congenital or surgery
functional asplenia → chronic hemolysis syndromes, infarction etc.
what mo can we see in spleen disorder patients → consequences
all primary pathogens → often asymptomatic
severe sepsis caused by capsu bac → s pneu, n, men, h influ
severe plasmodium infections → malaria
causes of phagocyte disorder + leads to no … cells
= no granulocytes, macrophages and NK
granulocytopenia is eg → seen in leukemia
or granulocyte dysfunction → chronic granulomatous disease
what mo seen in phagocyte disorders (primary vs opportu)
all the mo’s that are associated with defect in barrier function → mostly bac, fungi and yeast
but in addition:
aspergillus pneumonia/fumi
a-hemolytic streptococci
which mo’s are associated with defect in barrier function → 6 in total
primary
s. aur → colo nose
s pyo → colo throat
opportu
s epi → comm skin
e coli → comm bowel
clostriduim sp → comm bowel
candida albicans → comm throat, vag
impaired cellular immunity → 4 causes
no T cells CD4/8
congenital → SCID
acquired
HIV → less CD4
chemo → less of all cell counts
use of immunosupp drugs
impaired cell immunity leads to infection with
bac → 3
virus → 4
para → 2
primary pathogens
intracell bac → salmonella sp, leg pneum, m TB
(herpes)viruses → CMV, EBV, HSV, VZV
parasites → toxoplasma gondii, s stercoralis
cholera toxin
cholera toxin binds to apical membrane of enterocytes → subunit of cholera enters cell
normally adenylate cyclase (AC) is regulated and produces cAMP only in response to signals
now with toxin → AC stuck in act state → high intracell cAMP → acti CFTR Cl channels → diarrhea
taenia saginata → how infected/life cycle
eggs in fec.es → environment → cattle/vee (int host) infected
in muscle the mo develops → human (def host) ingests them by eating raw/undercooked infected meat
organism attaches to intestine → becomes adult there
1 → 2 model = 1 mo → 2 outcomes
VZV
primo infection → chickenpox
reactivation years later → shingles
legionella can have 2 diff outcomes
legionella pneumonia → severe pneumonia
pontiac fever → mild
1 → 3 model: treponema pallidum
syfilis
1 ulcer
2 fever and rash
gumma
diagnosis
early stages → directly detected
serology, PCR
1 → 3 model: schistosoma
worm can penetrate skin in water thanks to snails
adult worm in human → eggs secreted through fec.es → eggs hatch into snails
entry → swimmers itch
migration → katayama sd
settles → egg formation
1 mo → many outcomes
enterovirus
s. aureus
s. pyo
e coli
m TB
borrelia burgdorferi → 3 stages
stage 1 → erythema migrans
lyme
stage 2 → meningitis, artritis, carditis
stage 3 → neuro(psycho)logical
s pyogenes and s aureus can infect at the same time → how do both present
s pyo presented as red thick stripe → erysipelas
s aureus presented as large light pink vesicle and wound → cellulitis
beta lactam and glycopeptides
doelwit
normale proces
waar werkt het
werking beta
werking glycopep
doelwit = celwand → remmen peptidoglycansynthesis
transpeptidase (tpd) katalyseert laatste stap → cross linking van peptidoglycan
work in periplasmic space
beta lactams binden aan tpds → inhib → geen crosslink → lyse
glycopeptides
binden aan D-Ala-D-Ala op peptideketens → rem carboxypeptidase → geen celwandopbouw
B lactam antibiotics examples
4
1
spectrum
small → 1
broad → 2
penicillin
penicillin G
Flucloxacillin
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid (β-lactamase inhibitor)
Cephalosporins
Cefuroxim
spectrum
Penicillin → small spectrum (Gram+ cocci, anaeroben)
Meropenem, imipenem → very broad, behalve MRSA
glycopeptides example
vancomycin → vooral tegen gram +
reserve by MRSA or allergie
gentamicin → doelwit/remming van, binding, wat gebeurd er
aminoglycoside 30S → doelwit ribosomen → protein syn inhib
irrev binding
misreading mRNA
doxycycline
tetracyclines 30S → doelwit ribosomen → protein syn inhib
blokkeren tRNA binding
clarithromycine
macroslides 50S → doelwit ribosomen → protein syn inhib
blokkeren translocatie
clindamycin
lincosamides 50S → doelwit ribosomen → protein syn inhib
remmen peptide bond formation
bactericidal
kills direct
bacteriostatic
inhibits growth and multiplying of bacs but doesnt kill them immediately
ciprofloxacin/quinolones
DNA syn inhib
remmen DNA gyrase/topoisomerase II + IV
geen supercoiling → geen replicatie
metronidazole
DNA syn inhib
geact in anaerobes and protozoa
forms free radicals → DNA strand breaks → cel death
conditions that are bad for bac replication and therefore bad for antibiotics → 4
lage pH, lage pO2
necrotisch weefsel
abcessen
biofilms
therapy for superantigen of s aureus
flucloxacilline
clindamycin
MIC
lowest conc of an antibiotic that inhibts visible bac growth
so [AB] >>> MIC is good
if [AB] < MIC → AB not active
extended spectrum betalactamase = ESBL
wat doen ze
in welke soort vooral
enzymen die uitgebreide beta-lactams afbreken inc veel cephalosporinen
esp gram - → e coli bv
epstein barr virus infectie → 3
infectieuze mononucleosis
dringt binnen via orofaryngeale mucosa
infecteert met name B cellen → triggeren sterk immuunrespons (vooral door TC)
klinisch beeld EBV = 4
koorts
lymfadenopathie vooral in cervicale regio → veroorzaakt door prolig van imm cellen
atypische lymfocytose → TC hebben afwijkend uiterlijk → wel typerend voor EBV mono
splenomegalie → door prolif en act van imm cellen
EBV reactivering
CD8 TC respons → veroorzaakt verschuiving van bloedcellen samenstelling
normaal gedomineerd door polymorfonucleaire cellen = granulocyten
en nu gedom door mononucleaire cellen = mono en lymfocyten
onder microscoop zie je blasteren van TC
FACS → CD8 als marker gebruiken
neisseria gonorrhoeae kenmerken - 5
gram neg diplokok
non spore vormend
oxidase en catalase positief
heeft antigenische en fasevariatie van pili en opp proteine
kan overleven in neutrofielen
n. gonorrhoeae manifestatie
man → typisch met urethritis
dysurie - brandend gevoel bij plassen
purulente afscheiding → geel/groen
vrouwn → bac vaginitis en cervicitis
ook pijn bij plassen
purulente afscheiding
intermen bloedverlies
kan PID worden → littekenvorming op eileiders
n. gonorrhoeae diagnose
uitstrijking van cervix of urethra
gramkleuring daarna doen
daarna kweek op selectieve media
catalase + of - → hemolyse?
pos → staph
neg → strep → hemolysin test doen
pos → a of b hemo → pneu of pyo
neg → indiff strep
coagulase - or +
pos → stpah aureus
neg → andere sp
welke organismen kunnen leiden tot mononucleosis (beeld)
ebv
cmv
hiv
toxoplasma gondii