Zoology Exam 3
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Echinoderms like sea stars have a unique _____ system.
Water vascular system
Water vascular system
System of canals and tube feet used for locomotion, predation, food and waste transport, and respiration
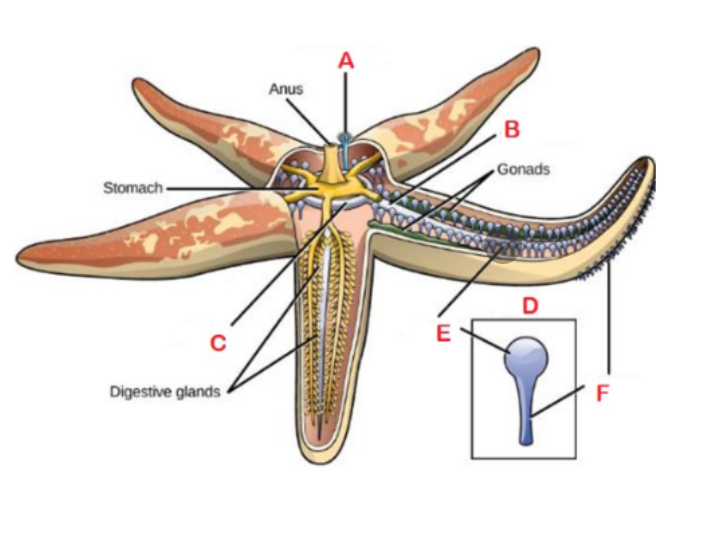
A
Madreporite; Sieve or filter like structure on upper surface that draws in water
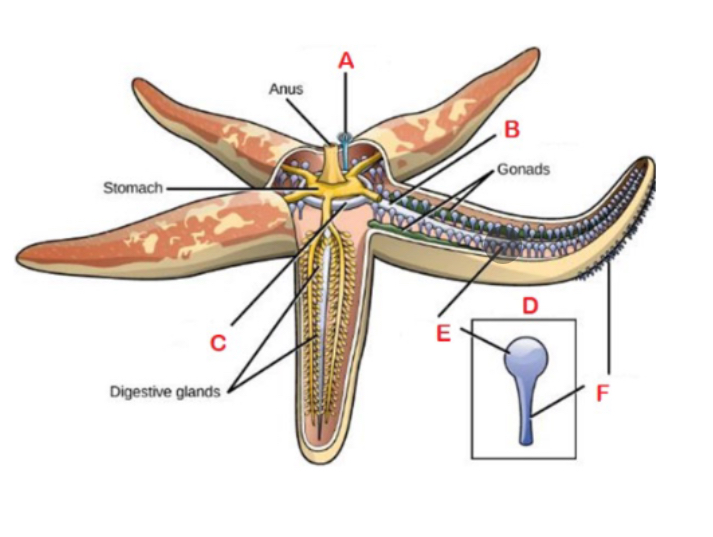
F
Podium; sucker-like structures
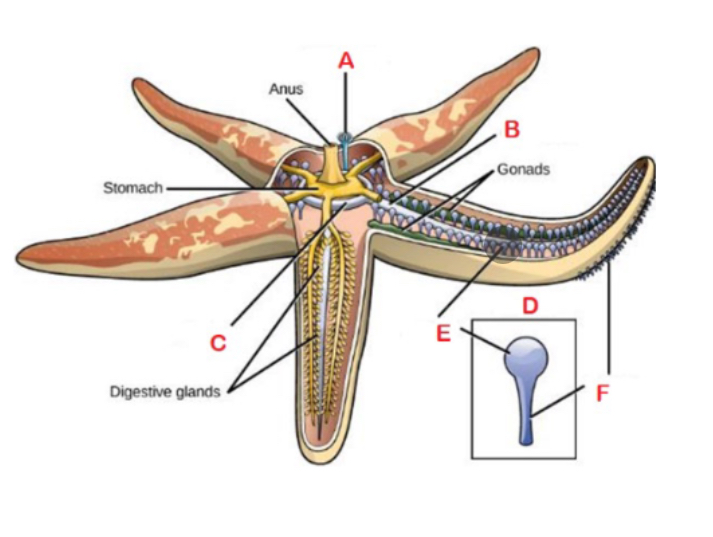
B
Radial canal
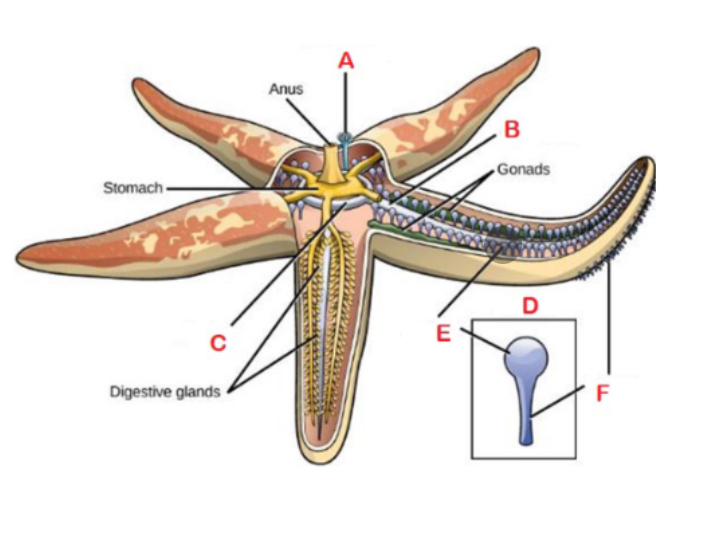
C
Central ring canal
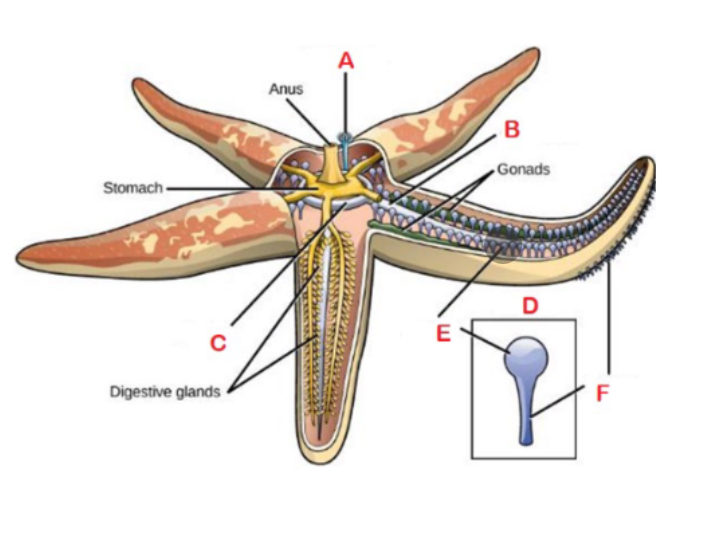
D
Tube foot; made up of ampullae
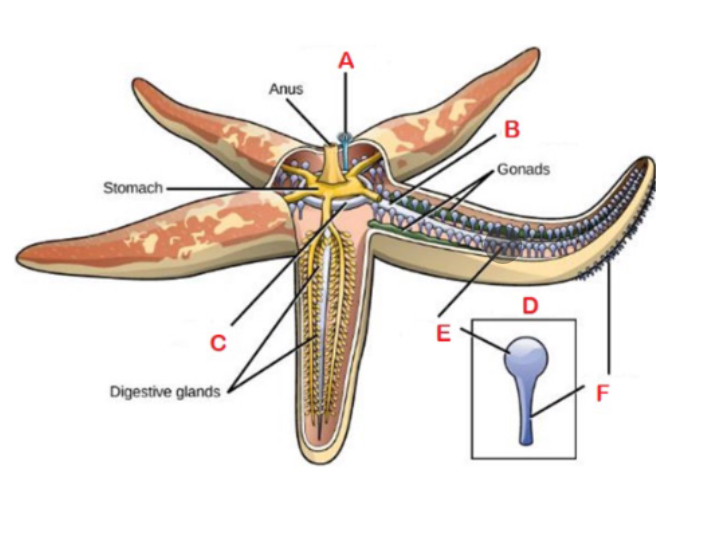
E
Ampulla; bulb like structures
What are two ways that most members of the phylum echinodermata differ from all other bilaterally symmetrical animals?
Adults with pentaradial symmetry; lack of a head region (no cephalization)
Describe the specialized methods for feeding on bivalves seen in the class asteroidea (sea stars)
Two stomachs, one can be everted through their mouths or secreted as digestive juices into or onto their prey before ingestion; they can digest bivalves while still alive and inside their own shells
Aristotle’s lantern
Found in class echinoidea (urchins); used for feeding on algae
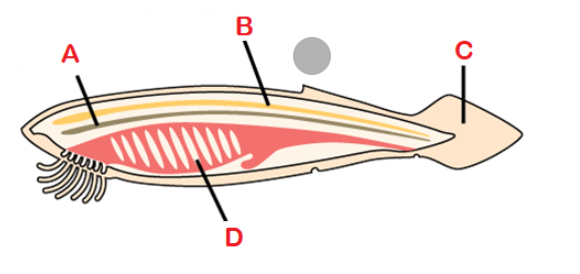
A
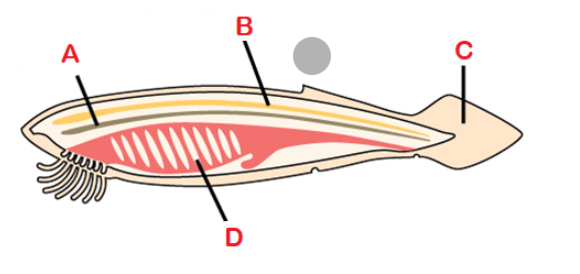
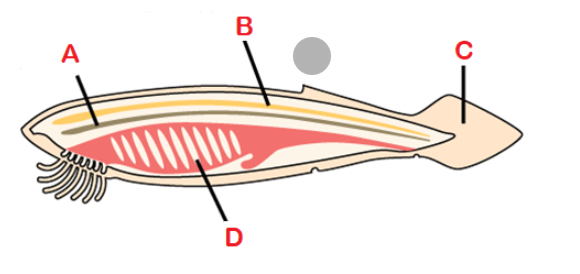
Notochord
Notochord
A flexible, rod-shaped mesodermal strucutre that is found in the embryonic stage of all chordates and in the adult stage of some Chlorate species
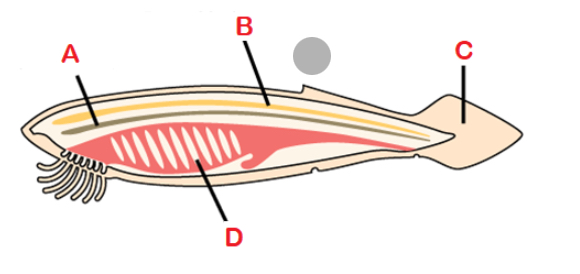
B
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
Dorsal to notochord, developed into the brain and spinal cord
C
Post anal tail
Post anal tail
Posterior elongation of the body, extending beyond anus; contains skeletal elements and muscles; locomotion, balance, courting, and signaling
D
Pharyngeal gill slits
Paryngeal gill slits
Openings behind the mouth that extend to outside world; develop into gill and jaw supports in fishes; ears, tonsils, thymus, hyoid and jaw supports in tetrapods
Which group of invertebrate chordates have an adult body plan that closely resembles the ancestral condition of all chordates
Cephalochordata (lancelets)
Which group of invertebrate chordates has a larval stage with a body plan that closely represents the ancestral condition of all chordata, that is lost in the adult stage
Urochordata (tunicates, sea squirts, salps)
What are two characteristics of Agnathans that distinguish them from Gnathostomes
Lack of jaws and lack of paired lateral appendages (fins)
Why are hagfishes (myxini) considered part of the Craniata but not part of the Vertebrata?
They have a cranium but no vertebral column (notochord fully developed instead)
Lamprey lifecycle
Eggs are fertilized externally and the larvae (ammocoetes) differ greatly from the adult form, closely resembling the adult cephalocordates; after spending 3 to 15 years as suspension feeders in the substrate of rivers and streams, they eventually attain sexual maturity; shortly afterward, the adults swim upstream, reproduce, and die within days
Heterocercal
Caudal fin has unequally sized fin lobes, with the tail vertebrae extending into the larger upper lobe
Homocercal
Caudal fin has equally sized upper and lower fin lobes, with numerous fine bones radiating out from terminal vertebra
Two specialized sensory systems that first evolved in members of the class Chondrichthyes
ampullae of Lorenzini; lateral line system
Ampullae of Lorenzini
Detects electromagnetic fields of living things
Lateral line system
Detects movement and vibrations in water
Four ways that chimaeras and ratfishes differ from other members of the class Chondrichthyes
Diphycercal tail (equally sized fin lobes with the tail vertebrae located between them), lack scales (lost secondarily in evolution), teeth modified as grinding plates (used to feed on mollusks and other invertebrates); gill slits not exposed (covered with operculum)
Three groups of ray finned fishes
Acipenseriformes, Holostei, teleostei
Acipenseriformes
Sturgeons (27 species) and paddlefishes (2 species); have heterocercal tails, primitive jaws
Holostei
Gars (7 species) and bowfins (1 species, can breath air); have homocercal tails, primitive jaws
Teleostei
Over 26,000 species in 448 families; homocercal tails, advanced jaws (“deadly pucker”)
Importance of lobe-finned fishes (sarcopterygii) in the evolution of tetrapods
Lungfish have complex lung structures homologous to the lungs of modern tetrapods; tiktaalik fossil is a link between lobe finned fish and 4-legged amphibians
Difference between amphibian life cycle and other tetrapods life cycles
Amphibians go through metamorphosis from an aquatic larva to a terrestrial adult; no other tetrapods undergo metamorphosis in the environment
Three orders of amphibians
Anura, Urodela, Apoda
Anura
Frogs and toads; continuous bodies, no ribs, no teeth on lower jaw, tailless adults, 7,400 species
Urodela
Salamanders; head distinct from body, ribs present, teeth on lower jaw, adults with tails, 765+ species
Apoda
Caecillans, legless, cylindrical bodies, vestigial eyes, retractable sensory tentacles, 215+ species
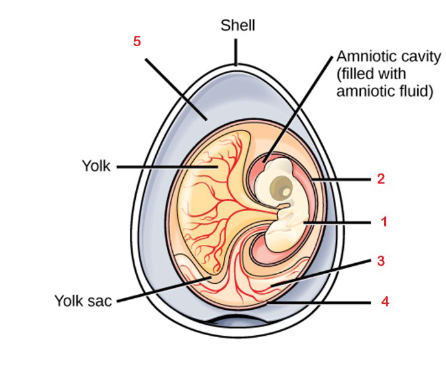
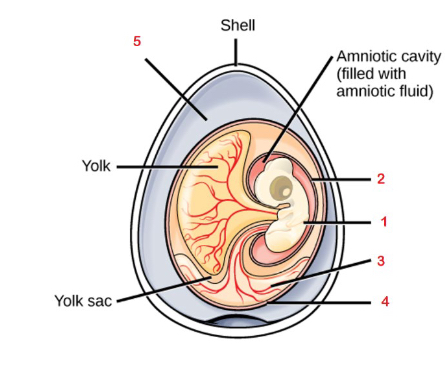
Why is the amniotic egg such an important evolutionary innovation
Key adaptation for the colonization of land, making reproduction independent from aquatic habitants allowing amniotes to adapt to all terrestrial habitats
5
Albumen
4
Chorion
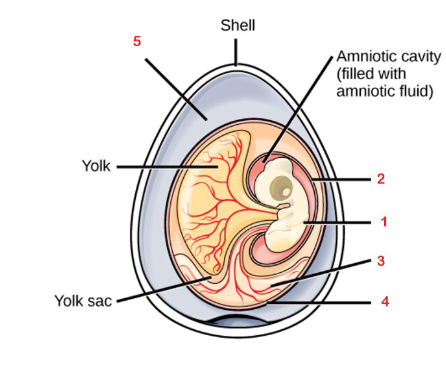
3
Allantois
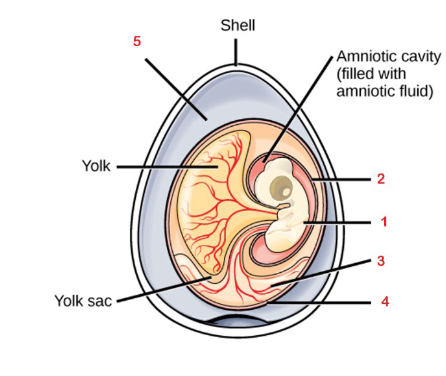
2
Amnion
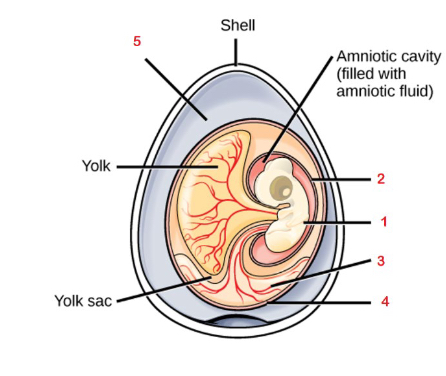
1
Embryo
Amnion
Fluid filled cavity that provides the embryo with its own internal aquatic environment; protects the embryo from mechanical shock and supports hyrdation
Allantois
Stores nitrogenous wastes produced by the embryo and facilitates respiration
Chorion
Facilitates exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the embryo and the egg’s external environment
Albumin
Egg white, outside of the chorion provides the embryo with water and protein
Yolk
Contained in the yolk sac and provides nutrients for the embryo
Three major lineages of Amniota
Anapsids, synapsids, diapsids
Anapsids
No temporal fenestra (extinct parareptiles)
Synapsids
Have a single temporal fenestra (modern mammals)
Diapsids
Have two temporal fenestra (turtles, Lepidosauria, archosaurs)
4 key characteristics shared between crododilians and birds that reflect both are descended from a common ancestor in archosauria
Four chambered hearts, nest building and brooding, prolonged parental care of hatchlings, use of vocalizations for communication
Six characteristics that birds evolved that are linked to their ability to fly
Endothermic and homeothermic (generate and maintain a constant elevated body temperature), high metabolic rate (due to flight), pneumatic (hollow) bones, feathers (modified scales, also used for insulation), sternum in shape of keel (large surface for flight muscle attachment), efficient respiration
Arboreal hypothesis
Tree dwelling ancestors to modern birds jumped from branch to branch using their feathers for gliding before becoming fully capable of flapping flight
Terrestrial hypothesis
Running (perhaps pursuing active prey such as small animals) was the stimulus for flight; wings could be used to capture prey and were pre adapted for balance and flapping flight
Palaeognathae
Ratites (ostriches, emus, rheas, cassowaries, tinamous, kiwis); precocial hatchlings (capable of feeding and moving on their own almost immediately)
Neognathae
All other birds; with altricial hatchlings (born in underdeveloped state that requires feeding and care from parents); some are semi-precocial or semi-alticial)
Pleurodira
“Side neck”; retract their neck horizontally, folding their neck to the side
Cryptodira
“Hidden neck”; retract their neck backward in a vertical S-curve
Hemipenes
Paired reproductive organs
Jacobson’s organ
Secondary olfactory sense organ (aka vomeronasal organ)
Pedicellate teeth
The root and crown are calcified, separated by a zone of non calcified tissue
Respiratory trees
Class holothuroidea; pair of gill-like structures that branch from the posterior gut; muscles around the cloaca pump water in and out of these
Class holothuroidea
Deeds on detritus, some are suspension feeders; unique echinoderms in having circulatory cells containing hemoglobin