Unit 4: Mod Chem Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Pure substance
A substance made of only one kind of matter and having definite properties

Element
A pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances
Atom
The basic particle from which all elements are made

Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
Heterogeneous mixture
A mixture in which you can see the different parts

Homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which you cannot see the different parts

Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another.
Colloid
A mixture containing small, undissolved particles that do not settle out.
Physical property
A characteristic of a pure substance that can be observed without changing it into another substance

Melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid
Boiling point
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas

Filtration
A process that separates materials based on the size of their particles.
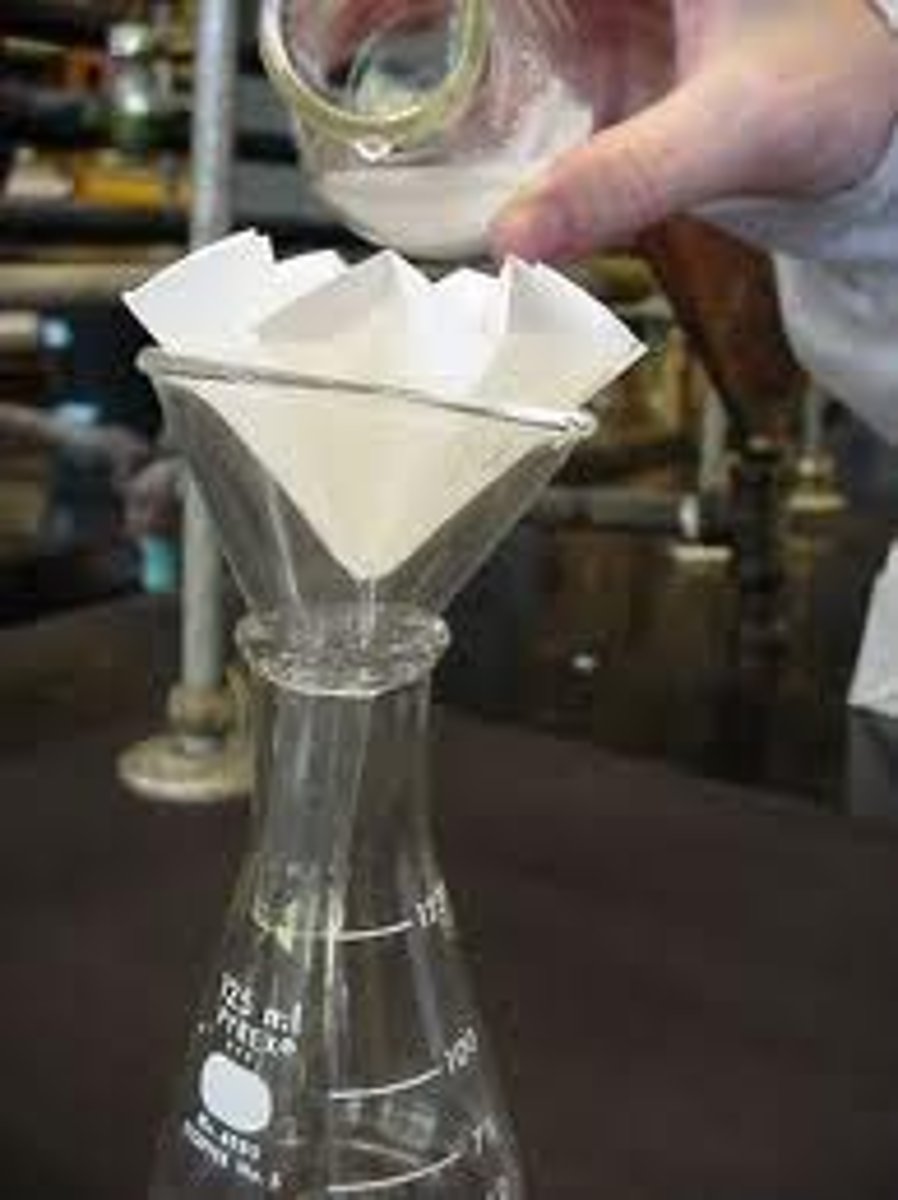

Distillation
The process of purifying a liquid by boiling it and condensing its vapors

Physical change
A change of matter from one form to another without a change in chemical properties

Chemical property
Describes its ability to change into different substances
Chemical change
A change in matter that produces one or more new substances

Precipitate
A solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction.

Law of Multiple Proportions
if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers
Law of Definite Proportions
a given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass
Avogadro's hypothesis
equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles
HONClBrIF
diatomic elements
Alloys
mixtures of two or more metals
Avogadro
Said gases of the same volume contain the same number of particles
Empedocles's
All matter was composed of four elements: fire, air, water, and earth.
Democritus
He suggested that atomos were eternal and could not be destroyed.
Torricelli
Showed that air has weight and was capable of pushing down on a column of liquid mercury
Priestley
His discovery revealed that substances could combine together or break apart to form new substances with different properties
Lavoisier
Established the law of conservation of mass
Dalton
When elements react to form compounds, they react in defined, whole-number ratios
Air
a solution of oxygen and other gases dissolved in nitrogen
1. a transfer of energy
2. a change in color
3. the production of a gas, or
4. the formation of a solid.
Possible clues to chemical change