Physics and Measurement: Dimensions, Units, and Precision vs. Accuracy
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
[m]
The dimension for mass
[T]
The dimension for temperature
[I]
The dimension for current
[L]
The dimension for distance or displacement
[L]/[t]
The dimension for speed or velocity
[L]/[t]²
The dimension for acceleration
[m][L]/[t]²
The dimension for force
m/s
A unit for speed or velocity
m/s²
A unit for acceleration
m
A unit for distance or displacement
mi/hr
A unit for speed or velocity
km/hr
A unit for speed or velocity
mi/hr/sec
A unit for acceleration
t
The variable for time
Δx
The variable for horizontal displacement
Δy
The variable for vertical displacement
a
The variable for acceleration
v
The variable for velocity
Precision
The extent to which a given set of measurements of the same sample agree with their average.
Accuracy
The extent to which a given measurement agrees with the standard value for that measurement.
Low accuracy, low precision
A scenario where measurements are neither accurate nor precise.
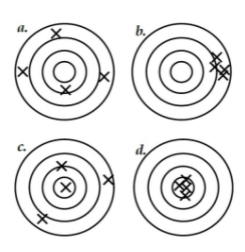
Low accuracy, high precision
A scenario where measurements are precise but not accurate.
High accuracy, low precision
A scenario where measurements are accurate but not precise.
High accuracy, high precision
A scenario where measurements are both accurate and precise.
While we ultimately strive for ?
Precision reflects our certainty of reliably achieving it.
While we ultimately strive for accuracy, ?
Precision reflects our certainty of reliably achieving it.
what's a?
Low accuracy, low precision
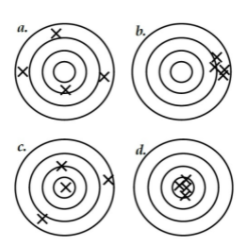
what's b?
Low accuracy, high precision
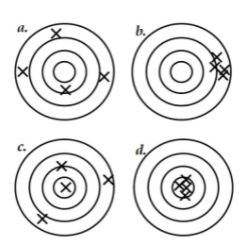
what's c?
High accuracy, low precision
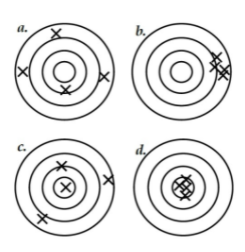
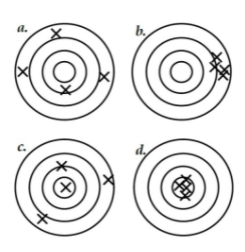
what's d?
High accuracy, high precision