Macroeconomics
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
GDP vs GNP/GNI
GDP: gross domestic product; measures the total value of goods and services within a countries borders
GNP: gross national product: GDP+outside a country’s borders, nationality+remittances
GDP types and pros of using it to measure economic growth
Nominal GDP: total economic output, without adjusting for inflation
Real GDP: adjusts for inflation-more accurate
real GDP=nominal GDP/price deflator times 100
PROS of using GDP to measure growth:
comparison of economic strengths
provides GDP per capita-avg. income
easy to track and manage
CONS
overestimates quality of life
GDP doesn’t equal happiness
does not show inequality
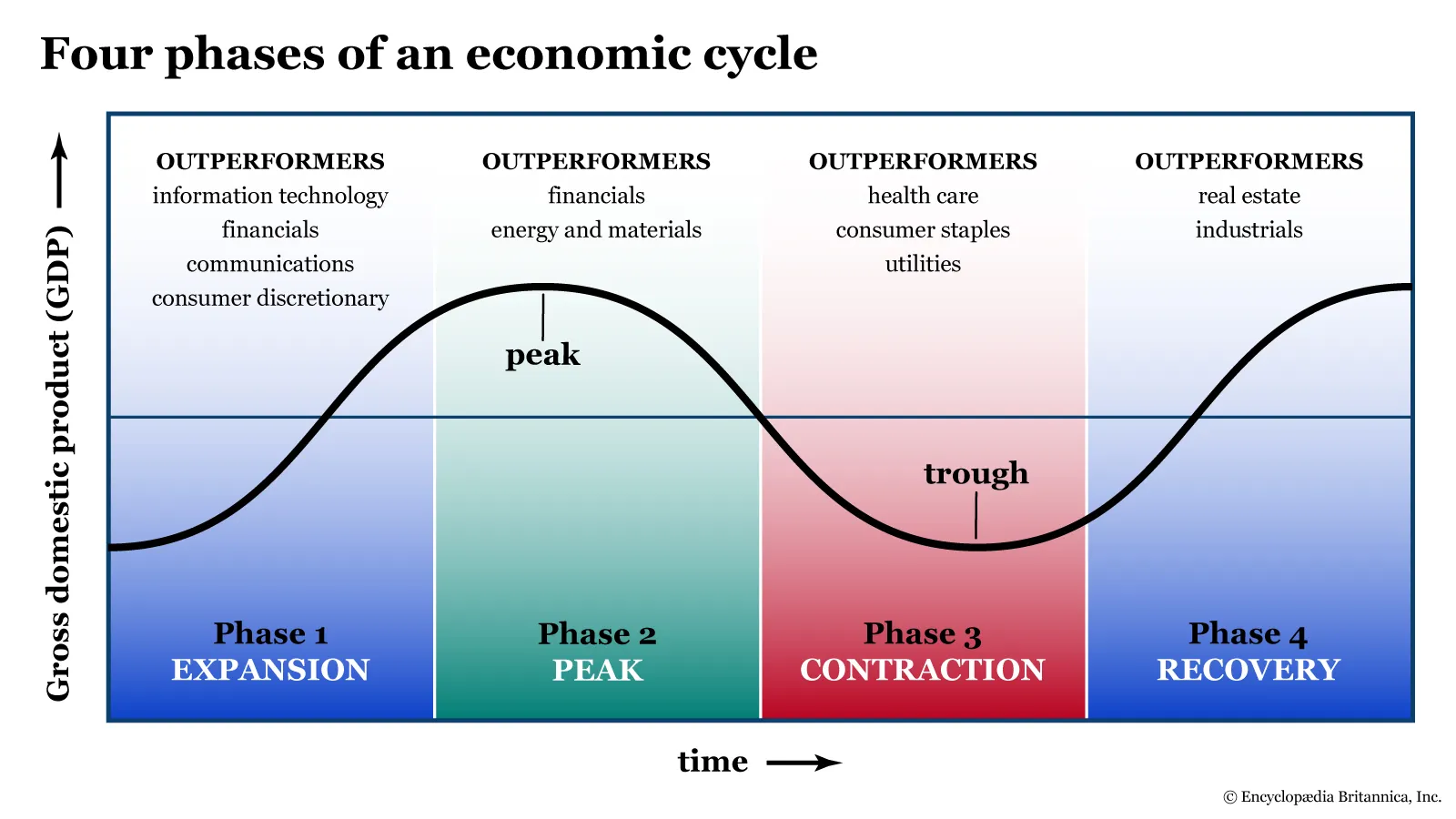
The business cycle
natural cycle of ups and downs in economic activity of a firm
Expansion: growth, employment rises, business expands
Peak: growth reaches a peak, slows down
Contraction: economic activity declines, possible recession
Trough: lowest point before recovery
alternative measures of well being
world happiness report
gross national happiness
OECD
green GDP
aggregate demand-AD and factors affecting it
total demand for goods and services in an economy
C+I+G(X-M)
factors affecting:
changes in consumption, investment, G, X, M
aggregate supply-AS, types and factors affecting them
total output of goods and services at every price level
short run(SRAS): period where prices remain the same
Long run(LRAS): maximum sustainable output
factors affecting:
SRAS: temporary; wage changes, taxes, subsidies
LRAS: permanent; labor force, education, technological improvements
new classical SRAS vs keynesian LRAS model
New classical: supply creates demand
supply side
efficiency of market forces-no gov. intervention
Keynesian: demand creates its own supply
demand side
gov. intervention needed
LRAS graph stages: in the short run an economy can produce more without raising prices-when at full capacity, output can’t increase without causing inflation
Flat section: room for growth, output is below potential
upward slope: closer to full employment-resources become more scarce
firms raise wages and prices
vertical section: full employment, can no longer increase output
say’s law
classical economic idea: supply creates its own demand
in the long run, there can’t be general overproduction or unemployment
argued against government intervention
economic growth in the short run vs long run
short run:
increased consumption
fiscal/monetary policy
excessive AD-causes inflation
Long run:
improvement in factors of production
capital: better technology
labor: population growth
natural resources
inflation vs deflation vs disinflation
inflation: persistent increase in the general price level
deflation: persistent fall in the general price
disinflation: a slowing down of inflation
types of inflation
formula: CPI1-CPI2/CPI1 times 100
demand pull: the good inflation
higher demand than supply, prices go up but GDP goes up
cost push inflation: the bad inflation
higher cost of producing, prices go up, GDP goes down
costs of government debt
debt servicing cost
credit ratings
impact on future taxation and spending
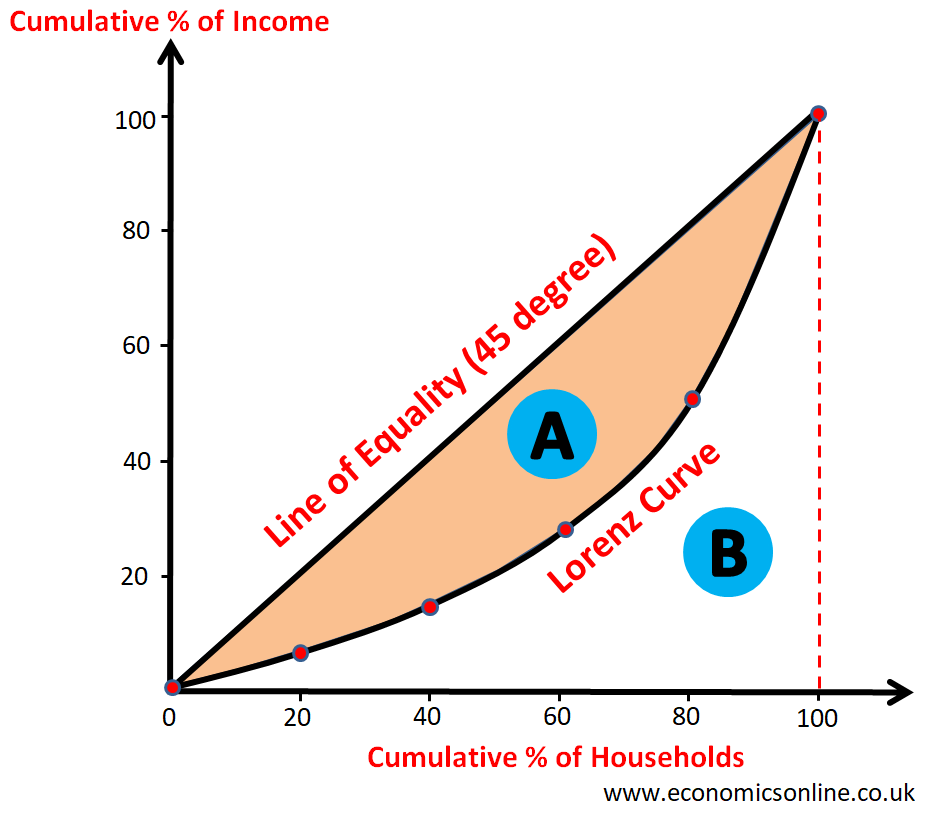
lorenz curve and gini coefficient
lorenz curve: visual indicator of distribution of wealth
gini coefficient: math indicator A/A+B
0-perfect equality 1-perfect inequality
types of poverty and inequality causes and fixes
absolute poverty: unable to access basic human needs (food, shelter)
Relative poverty: below 50% of a countri’s averge earnings
Inequality causes:
opportunity
discrimination
human capital levels (skills, knowledge, education)
Policies to reduce inequality:
direct, indirect taxes
minimum wage
UBI
policies reducing discriminations
5 types of unemployment
1. Frictional Unemployment
people are between jobs or looking for their first job, usually short-term
2. Structural Unemployment
Caused by a mismatch of skills or changes in the economy, often long-term
3. Cyclical Unemployment
Caused by a fall in demand during a recession
4. Seasonal Unemployment
Happens because of seasonal changes in demand for certain jobs
5. Real Wage Unemployment
Caused when wages are too high, above the market-clearing level
minimum wage laws or strong unions
government policies; Fiscal policy types and pros and cons
use of government spending
expansionary fiscal policy:
aim: close recessionary gaps, boosting the economy
cut taxes-more consumption and investment
increase government spending
contractionary FP:
aim: close inflationary gaps, slowing the economy
increasing taxes-decreasing consumption, investment
decrease government spending
ex. austerity
PROS:
can target specific economic sectors
effective in a recession-boosts confidence
CONS:
political pressure
time lags-bureaucracy takes time
government debt rises, crowding out possibilities
keynesian multiplier
government spending leads to a larger overall increase in income, GDP
more gov. spending=bigger impact on GDP, people spend even more money
formula=1/1-MPC
MPC: marginal prosperity to consume
government policies; Monetary policy types and pros and cons
Central bank's way to control economic factors
Expansionary MP: promote growth during times of trouble
decrease interest rates-increased spending
buy government bonds
decrease minimum reserve ratio
Contractionary MP: slowing down the economy during high inflation
increase minimum reserve ratio
sell government bonds
increase interest rates-decrease spending
PROS:
flexible, easily reversible
short time lags-policies implemented quickly
CONS:
low consumer and business confidence
lowering interest rates is ineffective when close to 0
money multiplier effect
process by which banks make money through lending
initial deposit of money leads to a larger increase in the money supply
government policies; supply side types and pros and cons
aim at improving the production side of the economy
Market based: reducing barriers for businesses
deregulation-removing rules, regulations
privatization: greater incentive to innovate
trade liberalization
PROS:
no burden on government budget
improved resource allocation-private entities are better are determining equilibrium
CONS:
equity issues (profit>equity), business self interest
time lags
environmental impact
Interventionist: government intervention needed
investment in infrastructure, education, training
PROS:
direct support for a specific industry
improvs long term growth, reducing inequality
CONS:
time lag
high costs
may cause inflation
crowding out
government borrowing pushes out private investment by raising interest rates