Chemistry - Grade 10
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
How an element’s location on the periodic table is related to its Bohr-Rutherford diagram and therefore its ionic charge
The position of an element in the periodic table indicates its number of valence electrons, which determines its Bohr-Rutherford diagram and helps predict the ionic charge an atom will acquire when it forms ions. Elements in the same group have similar ionic charges due to their similar electron configurations.
Which elements form cations and anions
Cations are typically formed by metals, which lose electrons and have a positive charge, while anions are formed by nonmetals, which gain electrons and have a negative charge.
Major characteristics of metals, non-metals, ionic compounds and molecular compounds
Metals: Conduct heat and electricity, are malleable (can be shaped) and ductile (can be stretched into wires), and have a shiny appearance.
Non-metals: Poor conductors of heat and electricity, brittle in solid form, and have a dull appearance.
Molecular Compounds: Formed between non-metals through electron sharing (covalent bonds). They have lower melting points and do not conduct electricity.
Ionic Compounds: Formed between metals and non-metals through electron transfer. They have high melting points and conduct electricity when dissolved in water.
How the formula for a molecular compound is different from an ionic compound
The formula for a molecular compound represents the actual number of atoms of each element present, using prefixes to indicate the quantity, while the formula for an ionic compound indicates the ratio of cations to anions without prefixes, reflecting the overall charge neutrality.
Lewis structures for ionic compounds
Example
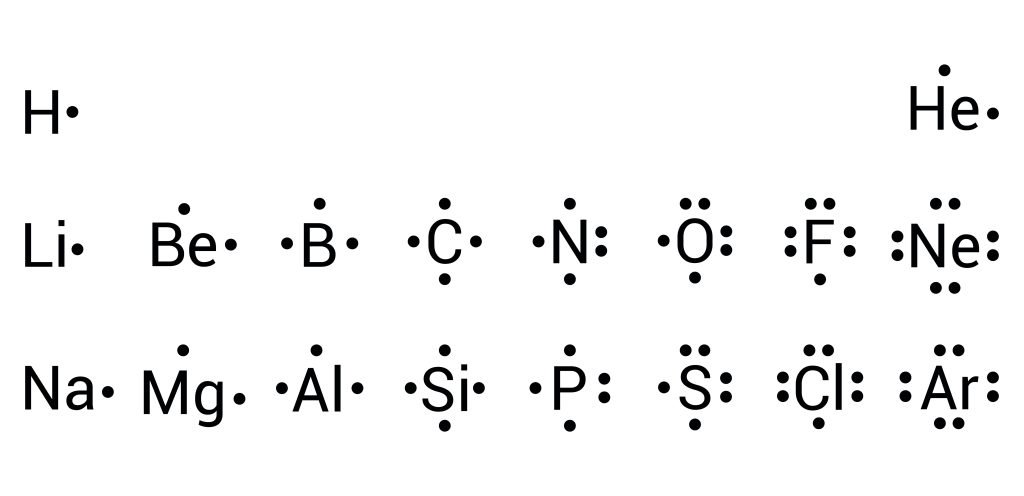
Diatomic elements
Molecules composed of two atoms, typically of the same element, such as H2, O2, and N2.(H O F Br I N Cl)
Difference between physical and chemical properties
Physical properties are observable characteristics, while chemical properties describe a substance's potential to undergo chemical change.
Appropriate vocabulary to describe physical and chemical properties
Terms like color, odor, melting point, reactivity, and flammability.
Identify the signs of a chemical change
Signs include color change, gas production, temperature change, and formation of a precipitate.
Name and write the formulas for acids and bases (Explanation on other side)
Acids are substances that donate protons (H+) in a solution, typically characterized by a sour taste. Examples include hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Bases are substances that accept protons or donate hydroxide ions (OH-), often having a bitter taste; examples include sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).