Life's Edge terms to know
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
organoids
three-dimensional structures that are derived from stem cells and mimic the structure and function of specific organs in the body. They are typically grown in a laboratory setting and can be used to study organ development, disease modeling, and drug testing. These have the potential to revolutionize medical research and personalized medicine.
2
New cards
neurons
specialized cells in the nervous system that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals. They are the basic building blocks of the nervous system and play a crucial role in processing and transmitting information in the brain and spinal cord. These consist of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon, which allows them to receive, process, and transmit signals to other neurons or target cells.
3
New cards
cryptobiosis
a biological state in which an organism's metabolic activities become extremely slowed down or completely halted, allowing it to survive in harsh environmental conditions. During this, organisms can withstand extreme temperatures, desiccation, high radiation, and lack of oxygen. Examples of organisms capable of cryptobiosis = tardigrades
4
New cards
hypothalamus
a small region in the brain that plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. It helps control body temperature, hunger and thirst, sleep patterns, hormone production, and the release of hormones from the pituitary gland. Additionally, it is involved in emotions and the autonomic nervous system.
5
New cards
ventilators
medical devices used to assist or replace the breathing function of patients who are unable to breathe on their own. They deliver oxygen to the lungs and remove carbon dioxide from the body. They are commonly used in hospitals, particularly in intensive care units, to support patients with respiratory failure or other breathing difficulties.
6
New cards
metabolic rate
the rate at which an organism uses energy. It represents the total energy expenditure of an individual, including both basal metabolic rate (energy required for basic bodily functions at rest) and additional energy used for physical activity and digestion. Metabolic rate can vary among individuals due to factors such as age, sex, body composition, and genetics.
7
New cards
ATP
energy in a form the body can use
8
New cards
pythons
grow their digestive system to digest their food then return to their normal state
9
New cards
slime mold
a type of organism that is not a true mold or fungus, but rather a unique group of organisms that exhibit characteristics of both animals and fungi. They are typically found in damp environments and are known for their ability to move and change shape.
10
New cards
carbohydrates
organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are one of the 4 macro-nutrients, along with proteins and fats, and serve as a primary source of energy for the body. Carbohydrates can be classified into three main types: sugars, starches, and fibers. Sugars are simple carbohydrates found in fruits, honey, and table sugar. Starches are complex carbohydrates found in grains, potatoes, and legumes. Fibers are also complex carbohydrates found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Carbohydrates provide energy, support brain function, and play a role in maintaining overall health.
11
New cards
proteins
Proteins are large, complex molecules composed of amino acids. They play crucial roles in the structure, function, and regulation of cells and tissues in living organisms. Proteins are involved in various biological processes, such as enzyme catalysis, cell signaling, immune response, and muscle contraction. They are essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids that fold into specific three-dimensional structures, which determine their function.
12
New cards
primary structure
non polar covalent bonds(strongest bonds) - poly peptides(proteins) connects amino acids in a chain
13
New cards
secondary structure
polypeptides from primary and hydrogen bonds connect amino acid chains
14
New cards
tertiary structure
Bonds: polypeptides(1st), hydrogen(2nd), and ionic.
Interactions: Vanderwaal and Hydrophobic
Covalent Bonds: Non-polar(peptides), Disulfide Bridges
Interactions: Vanderwaal and Hydrophobic
Covalent Bonds: Non-polar(peptides), Disulfide Bridges
15
New cards
Quaternary structure
no new bonds hydrogen bonds connect polypeptide units
16
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis
removes water and joins/forms macro molecules
17
New cards
hydrolysis
The use of water to break bonds. opposite of dehydration synthesis, hydrogen ions(+) attract molecules and break bonds (denaturing)
18
New cards
amino acid construction
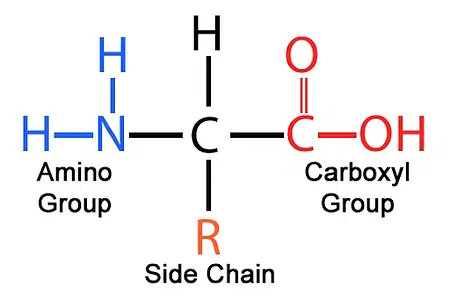
19
New cards
how could the membranes of cells being compromised affect the ability of proteins to function properly?
without the membrane the cell is more susceptible to bonds being broken and denaturing
20
New cards
Why is it beneficial to have the ability to sense death and how would that relate to proteins?
A. preservation: not eating things that will harm you
staying away from dangerous areas
knowing where food is (scavengers)
B. chemical receptors only made for 1 protein so that’s how death is sensed
staying away from dangerous areas
knowing where food is (scavengers)
B. chemical receptors only made for 1 protein so that’s how death is sensed
21
New cards
What can you conclude about the hypothalamus’s structure and why was it coded to be so fragile?
it was probably made with lots of hydrogen to be easily broken. it was coded to be fragile because its powerful and so it doesn’t negate all the salt in your body
22
New cards
How would proteins help facilitate the process of a python’s small intestines doubling in size?
proteins help build the muscles of the intestines
23
New cards
How would photons damage trees? Why is a layer of chlorophyll on maple leaves beneficial?
photons(light) as energy would break the bonds of the proteins. This is beneficial so the trees don’t die as easily.
24
New cards
Why is it important to understand proteins if you are going to create anitbiotics?
So you know what part of the protein/DNA sequence to attack/remove
25
New cards
What do you think the role of proteins are in the membrane? What are some similarities of proteins and lipids?
Similarities: hydrophobic on the outside hydrophilic on the inside. Non polar bonds on the inside covalent bonds on the outside. Proteins in the cell membrane move particles of the cell across the membrane and communicate between the cell and the outside environment
26
New cards
Why is it important to have something linked to the amino acids that make up a protein?
So they can connect/bond with other things that aren’t more amino acids
27
New cards
homeostasis
the ability of an organism or system to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. It involves various physiological processes that regulate temperature, pH, blood sugar levels, and other factors within narrow limits. This balance is crucial for the proper functioning of cells, tissues, and organs.
28
New cards
liposomes
small spherical vesicles composed of lipid bilayers. They are artificial structures that mimic cell membranes. They are commonly used in drug delivery systems due to their ability to encapsulate and transport drugs to specific targets in the body. They can also be used to deliver nutrients, vaccines, and genetic material. Liposomes have a wide range of applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and research.