Pargas Exam 2: Change and Adaptability
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Change requires...
Adaptability
Change Factors that Force Adaptability
-Technology
-Employment
-Aging
-Life itself
Change and Adaptability are Impossible Unless...
-we dismantle rigidity
-we recognize that discomfort is our ticket to meaning
-we drop the "should" in our mindset
Fluid Intelligence
Our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood
- global capacity to reason
- Ability to learn new things
- think abstractly and solve problems
Crystallized Intelligence
Our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age
- Prior learning and past experiences
- Based on facts
Growth Mindset
The idea that our abilities are malleable qualities that we can cultivate and grow
Fixed Mindset
The idea that we have a set amount of an ability that cannot change
First stage of Change: Status quo
A person's initial reaction is shock or denial
Second stage of change: Disruption
Anger and fear
Third Stage of Change: Exploration
Acceptance
Fourth Stage of Change: Rebuilding
Commitment
What We Need in Business Today?
- Organizations are becoming more and more global
- Those running these organizations lament the lack of skills that prepare students to succeed across cultures and comfort zones
- How do we extend the limits of our comfort zones?
- Change and innovation are moving us forward very fast
Reactive Change
Making changes in response to problems or opportunities as they arise
Proactive (planned) Change
Making carefully thought-out changes in anticipation of possible or expected problems or opportunities
White Water Metaphor
-When you can't count on stability or predictability, managers and organizations must constantly adapt and be comfortable and prepared for the next rapid
Lewin's Three-Step Process
The "Calm Waters" Metaphor
- Take it apart, rebuild, and settles
Managing Resistance to Change: Unfreezing
- Share reasons
- Empathize
- Communicate
Managing Resistance to Change: Change Intervention
- Benefits
- Champion
- Input
- Timing
- Training
- Pace
Managing Resistance to Change: Freezing
- Top Management Support
- Reinforce
Errors in Unfreezing
-Not establishing a great enough sense of urgency
-Not creating a powerful enough guiding coalition
Errors in Change
- Lacking a vision
- Under-communicating the vision by a factor of 10
- Not removing obstacles to the new vision
- Not systematically planning for and creating short-term wins
Errors in Refreezing
-Declaring victory too soon
-Not anchoring changes in the corporation's culture
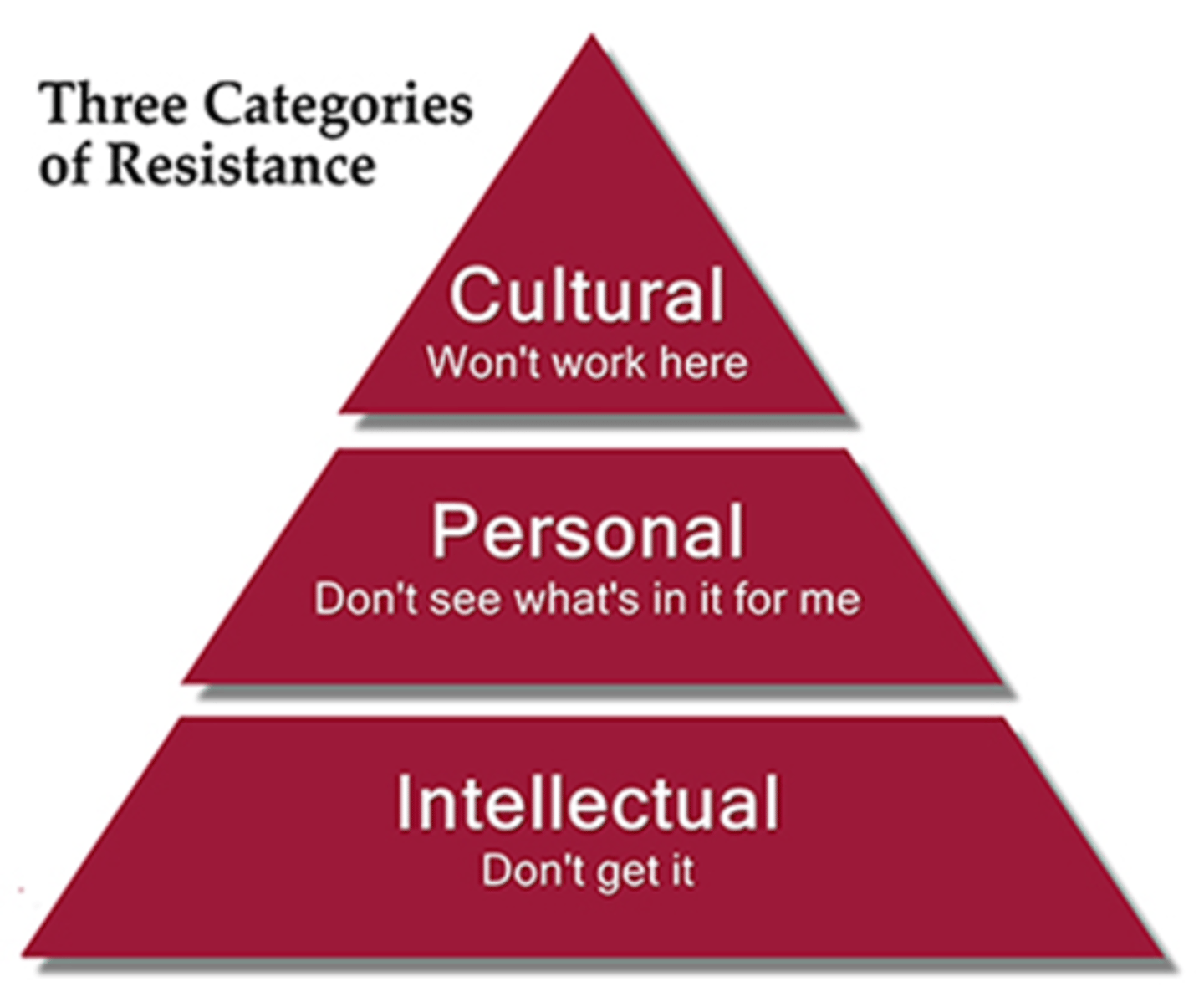
Understanding Resistance to Change
- Caused by self-interest, misunderstanding and distrust
- "The way we have always done it"
- Humans have a general intolerance to change
- Fear that changes will result in a loss of something
Kiss of Yes
some of the strongest resisters may support the changes in public, but then ignore them in private
Organizational Decline
occurs when companies don't anticipate, recognize, neutralize, or adapt to the internal or external pressures that threaten their survival
Organizational Decline: Blinded Stage
Decline begins because key managers don't recognize the internal or external changes that will harm their organizations
- Lack of awareness to changes
- inability to comprehend the significance of changes
- overconfidence
Organizational Decline: Inaction Stage
Organizational performance problems become more visible, management may recognize the need for change but still take no action
- managers may be waiting to see if problems will correct themselves
Organizational Decline: Faulty Action Stage
Management will announce belt-tightening plans designed to cut costs, increase efficiency, and restore profits
- managers assume that if they run a stricter organization, company performance will return to prior levels
Organizational Decline: Crisis Stage
Bankruptcy or dissolution is likely to occur unless company completely reorganizes the way they function
- at this stage, companies usually lack the resources needed to fully change how they run their business
Organizational Decline: Dissolution Stage
- After failing to make needed changes, organization is dissolved through bankruptcy proceedings or by selling assets to pay suppliers, bank, creditors
Jim Collins's Five Stages of Decline
- Arrogance
- Undisciplined Pursuit of More
- Denial of Risk and Peril
- Grasping for Salvation
- Capitulation, Irrelevance or Closing
What is Creativity?
Combining new ideas in unique ways or making unusual connections
What is Innovation
Process of taking a creative idea and making it into a useful product, service, or method of operation
Technology Cycle
A cycle that begins with the birth of a new technology and ends when that technology reaches its limits and is replaced by a newer, substantially better technology
Product Innovation
Create new products or improve existing versions of products
Process Innovation
A change in the way a product or service is conceived, manufactured, or disseminated
Incremental Innovation
A succession of very small upgrades or improvements that a company makes to its products
Radical Innovation
Creation of products, services, or technologies that replace existing ones