Muscular System
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Apart of Physiology Essentials 100 at UniSA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Muscular System
Consists of skeletal muscles and tendons that gives us the ability to move, protect and support tissues, and generate heat when muscles contract.
What are the four types of tissues?
Epithelial tissues
Connective tissues
Nervous tissues
Skeletal tissues
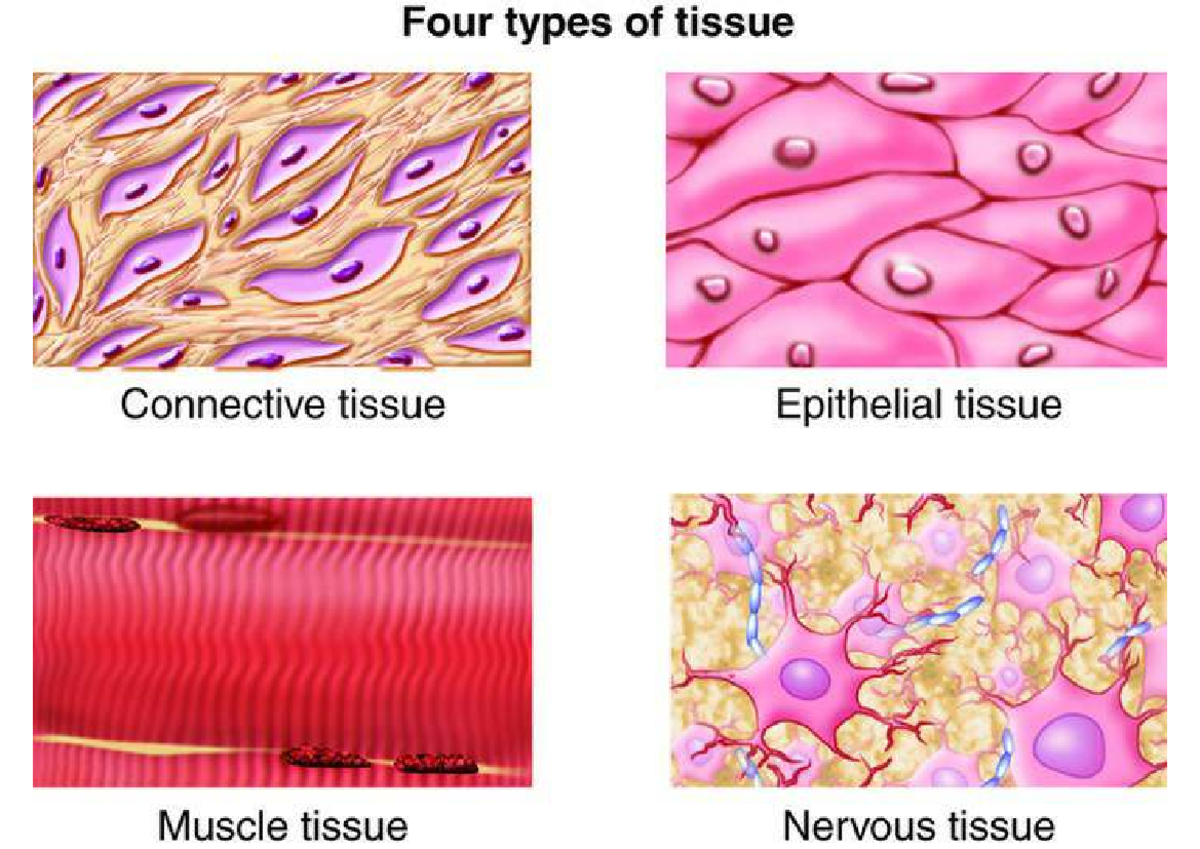
What is the difference between epithelial and connective tissues?
Connective tissues fill the internal space of the body whereas epithelial tissue covers exposed surfaces/organs.
Nervous tissue
A type of tissue found in the nervous system that are involved in interpretating and responding to stimuli, homeostatic control, and control of emotions, memory, and behaviour.
Skeletal tissues
A type of tissue that makes up the skeleton that is responsible for movement, storage of proteins and energy, maintain body heat, and guard body entrances/exits.
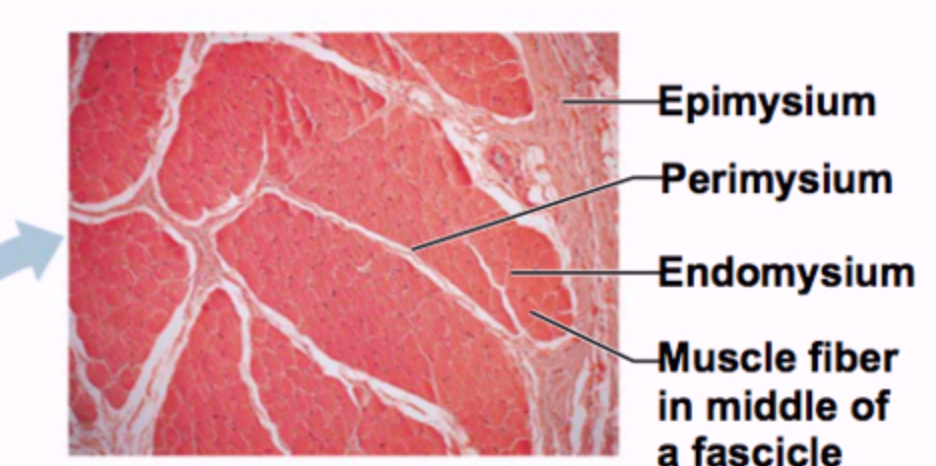
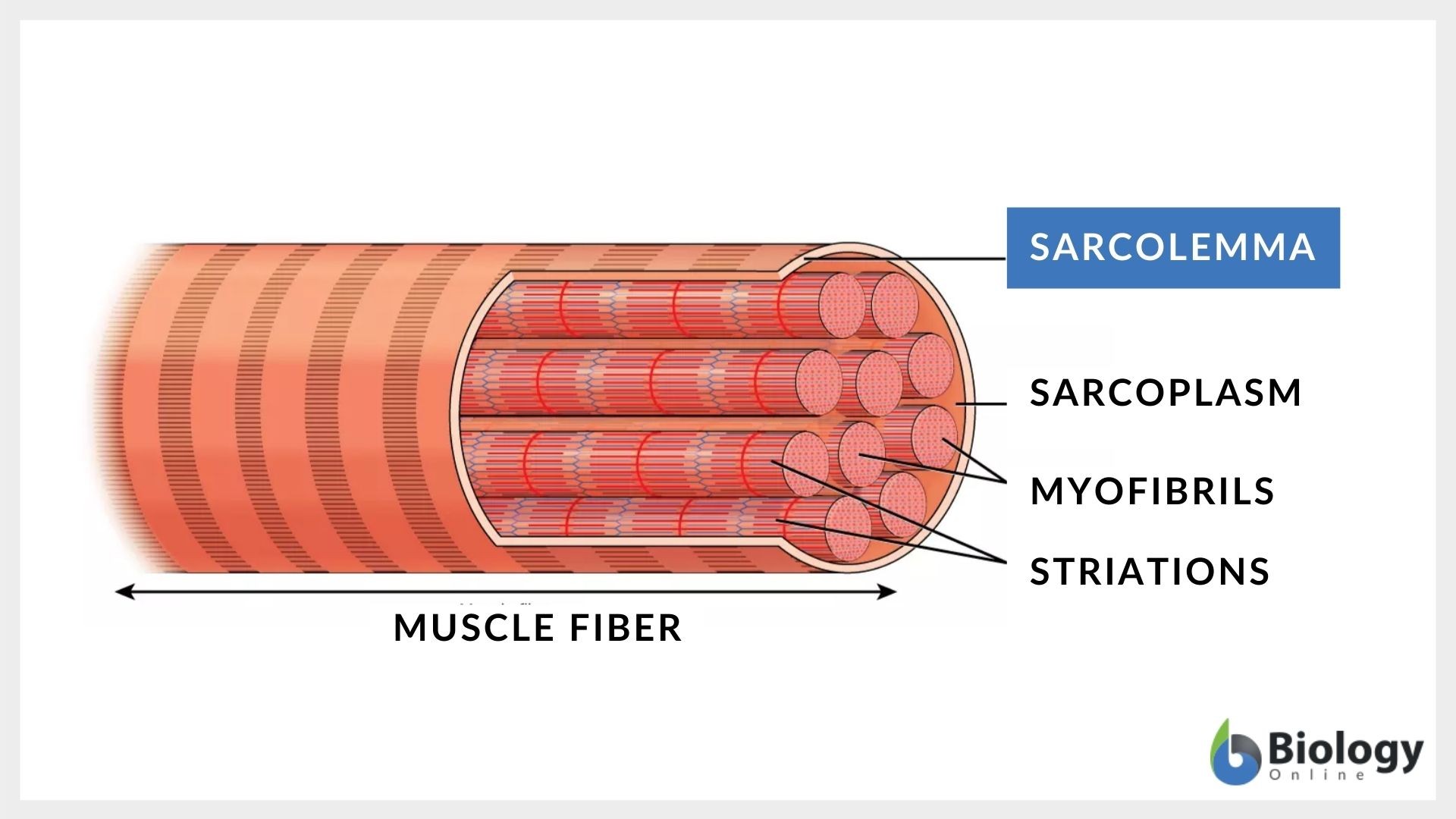
Muscle fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibres/cells.
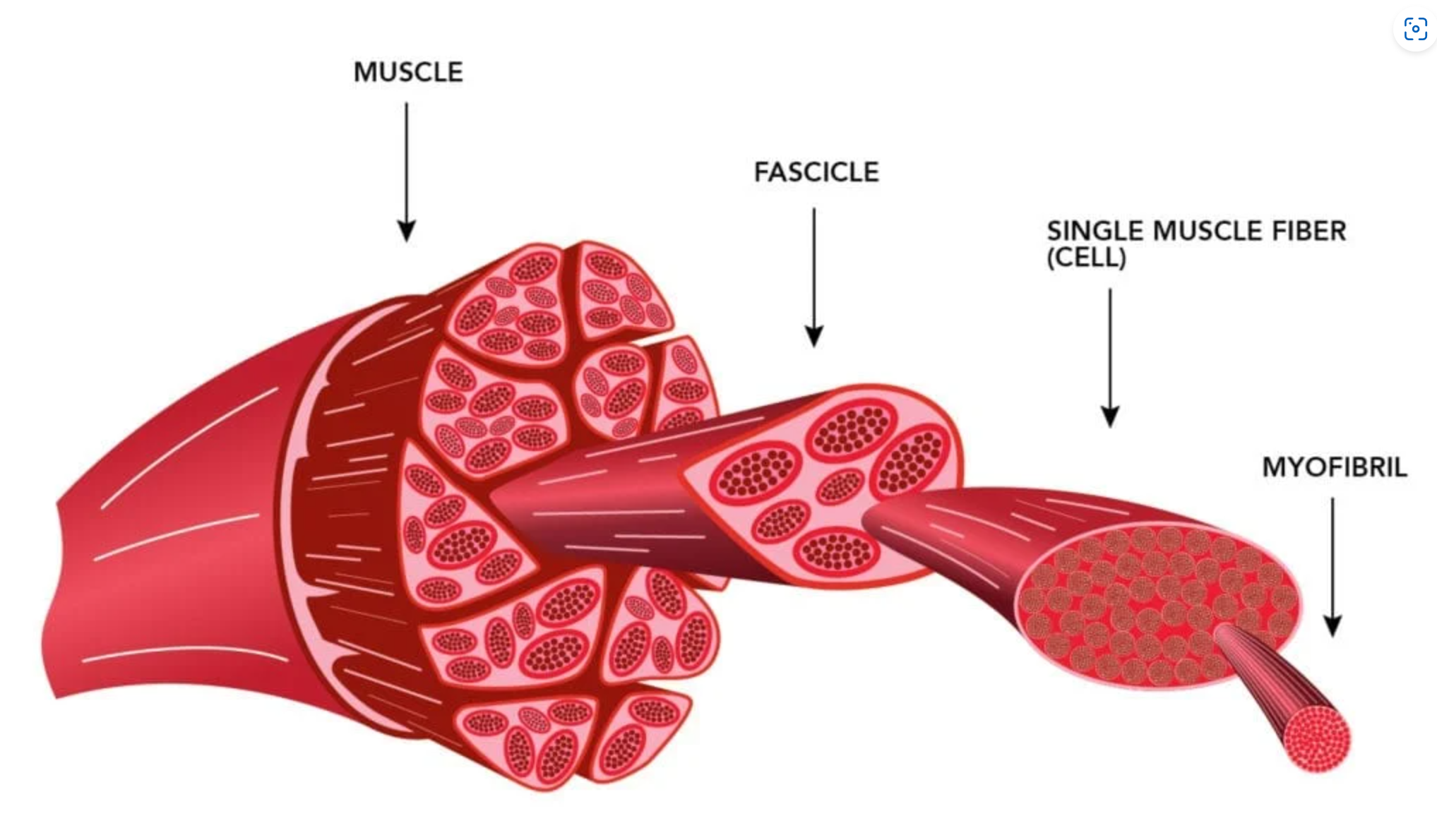
What are the three connective tissues found in the skeletal muscle and where it surrounds?
Epimysium (surrounds the skeletal muscle)
Perimysium (surrounds the muscle fascicles)
Endomysium (surrounds the muscle fibre/cell)
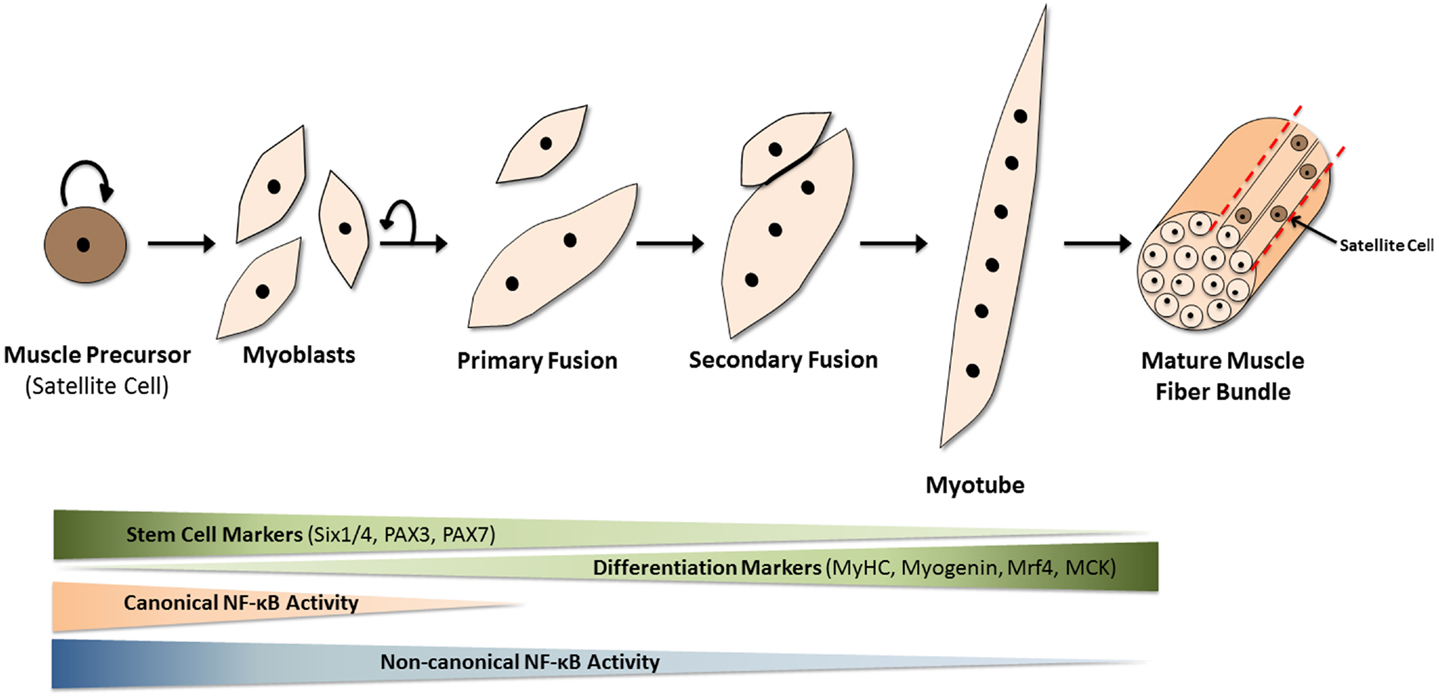
What is the difference between myoblasts and myosatellite cell?
Myoblasts are precursors cells that develop into muscle fibres whereas myosatellite cells are stem cells that are the result of not fusing with myoblasts.
What is the sarcoplasm and sarcolemma similar to?
Sarcoplasm is like the cytoplasm for the skeletal muscle whereas sarcolemma is like the plasma/cell membrane.
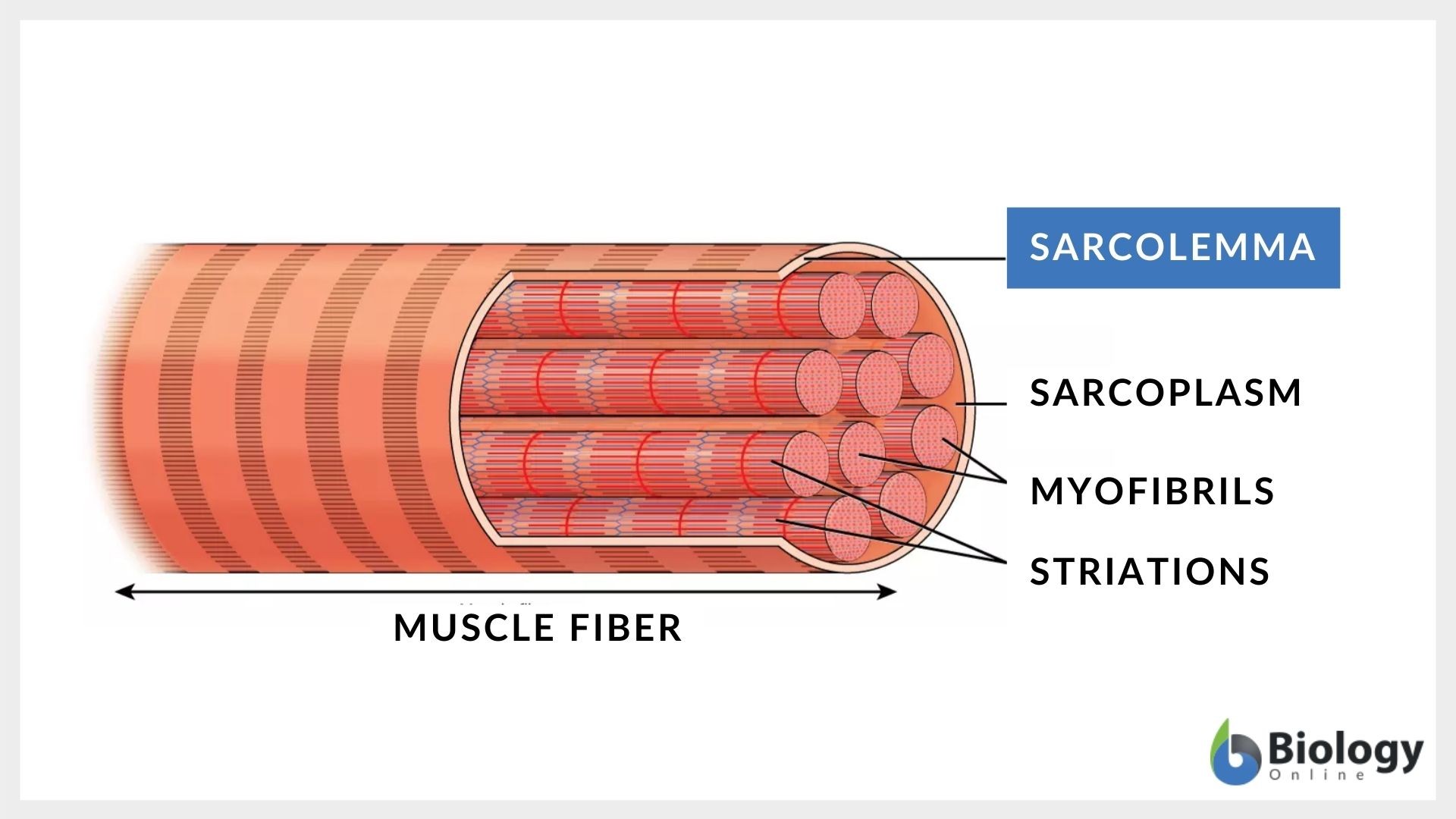
Myofibrils
Basic-rod like organelle in the skeletal muscle cell made up of myofilaments, sarcoplasmic reticulum, and Transverse-tubules.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
A tubular network around each myofibril where the terminal cisterna stores calcium, that initiates muscular contraction when released into the cytosol.
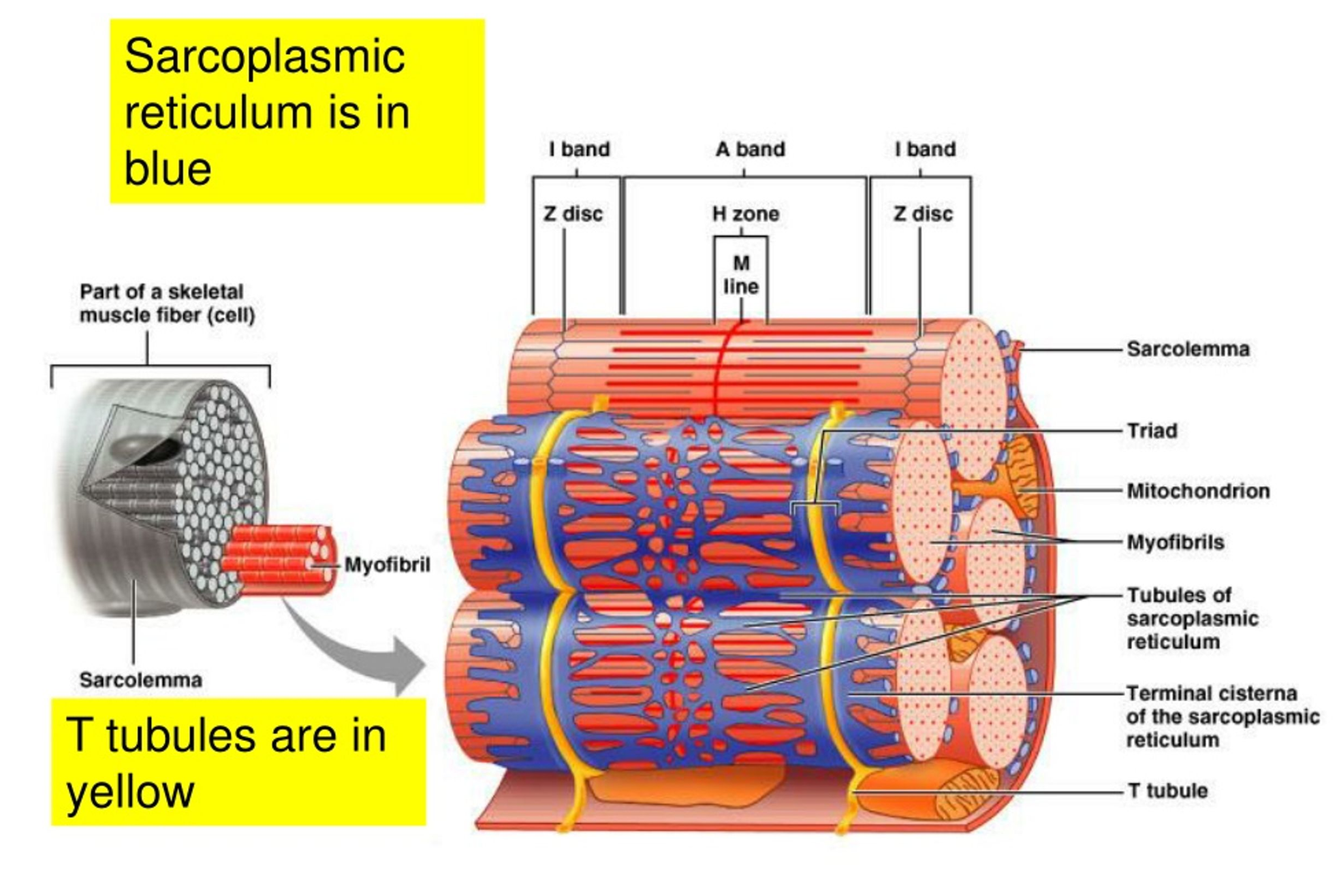
Transverse-tubules
Extensions of the sarcolemma that conducts action potential from the sarcolemma into the muscle fibre, causing all regions of the muscle fibre to contract at the same time.
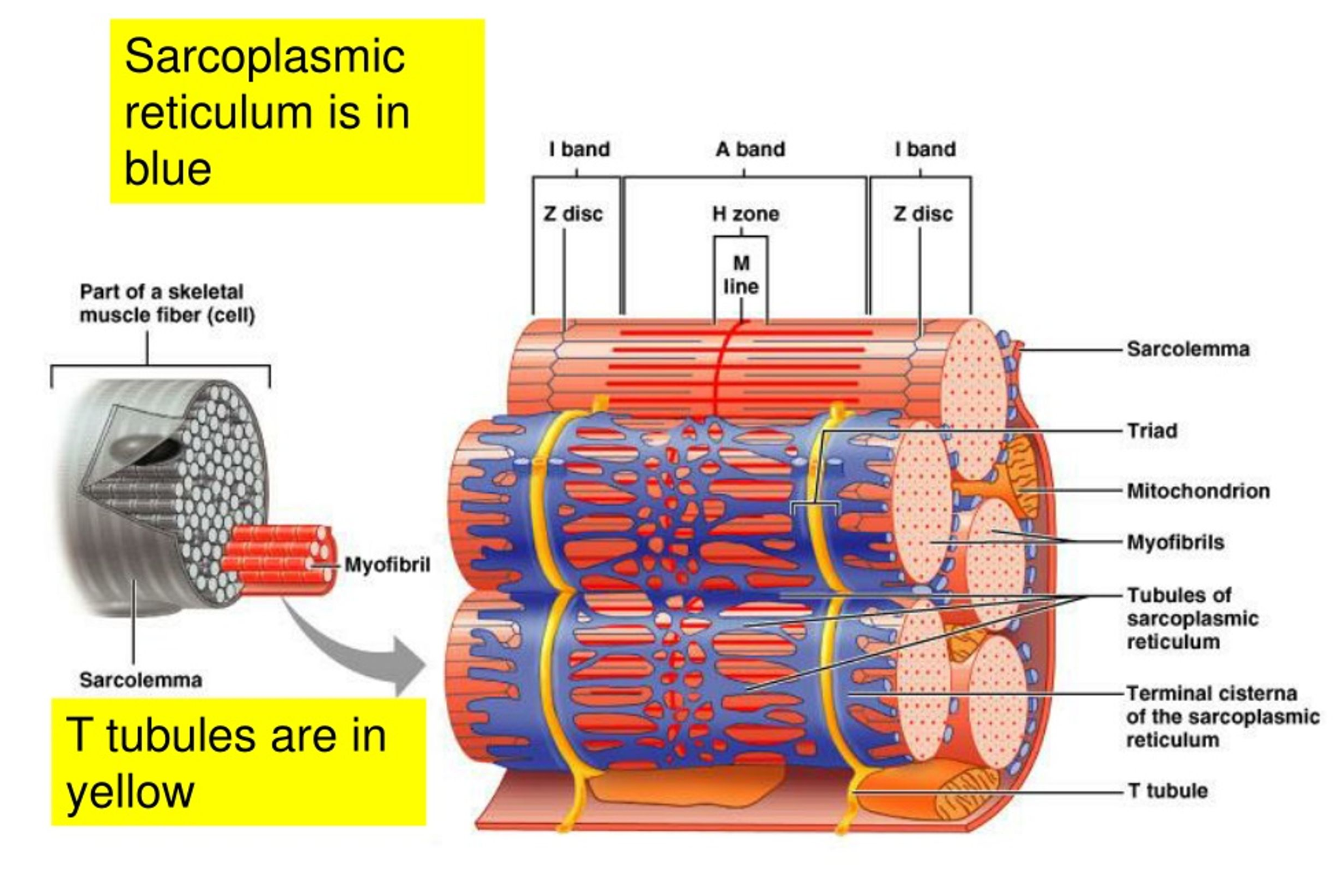
Sarcomere
Smallest functional units of a muscle fibre, consisting of myofilaments arranged in repeating functional units.
What are the thin and thick myofilaments?
Thin myofilaments are proteins actin, troponin, and tropomyosin whereas thick is primarily the protein myosin.
What is the sliding myofilament theory?
A theory that explains the mechanism of muscle contraction, where the thick and thin filaments slide past each other and move towards the centre of the sarcomere, shortening the muscle fibre.
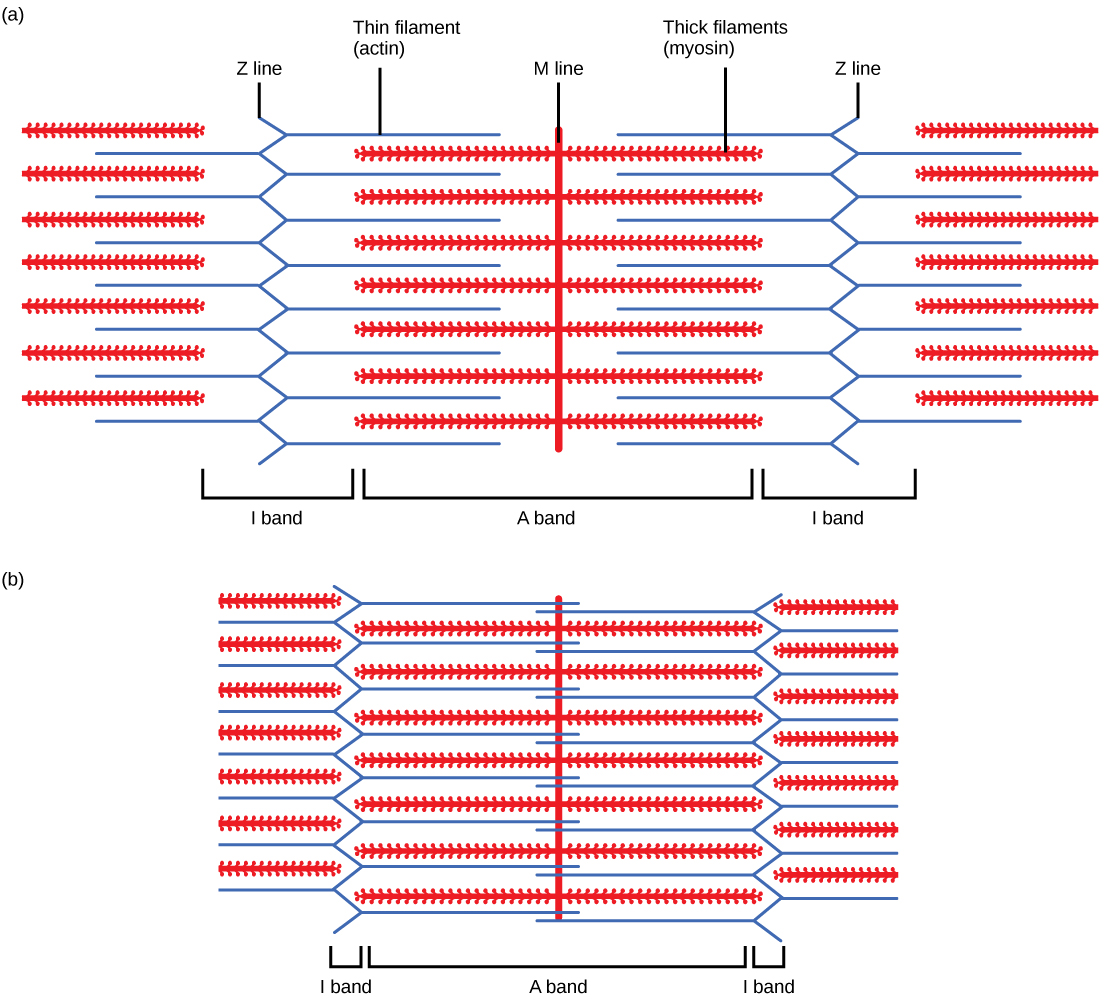
Cross-bridge
In the sliding myofilament theory, the cross-bridge is the molecular complex formed when thin and thick filaments interact.
Power stroke
In the sliding myofilament theory, the power-stroke is a phase where the myosin head propels the actin filament towards the centre of the sarcomere.
What are two factors that impact tension produced by single muscle fibres?
Sarcomere length and stimulation frequency of action potentials.
What are seven factors that impact tension by the whole muscle?
Number of motor units active during a task
Type of muscle fibres
Type of contraction being performed
Speed of muscle contraction & relaxation
Duration & intensity of muscle contraction
Joint angle
Availability of energy sources
Muscle twitch
The result of an action potential travelling down a motor neuron to innervate a muscle fibre(s).
How does the length-tension relationship affect muscle contraction?
The length of the sarcomere impacts the amount of tension produced to stimulate muscle contraction, where it’s ideal to reach maximum tension when the thick and thin filaments overlap but do not extend across the sarcomere’s centre.
What is the result of exercise-induced muscle fatigue?
A decline in voluntary muscle force power.
What is the main energy source for muscle contraction?
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).
What protein can assist in the production of ATP?
Creatine.
How much ATP molecules are produced between anaerobic and aerobic metabolism
In anaerobic metabolism, 2 ATP molecules are produced whereas aerobic produces between 34 to 38 ATP molecules.
When we age, what happens to our skeletal muscle mass?
It decreases, which leads to a decrease in capacity to generate tension. This will lead into a increase of connective tissue, which will decrease muscle stretch.
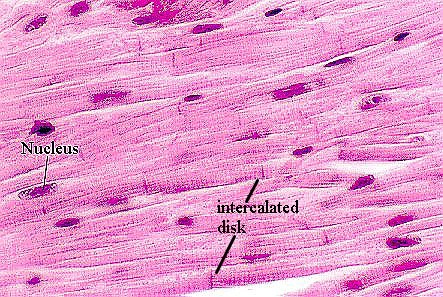
What are some characteristics of cardiac muscle (4 points)?
Single nucleus.
Straited appearance.
Almost totally dependent on aerobic metabolism for energy.
Can connect to other cardiac muscle cells at specialised sites (intercalated disks).
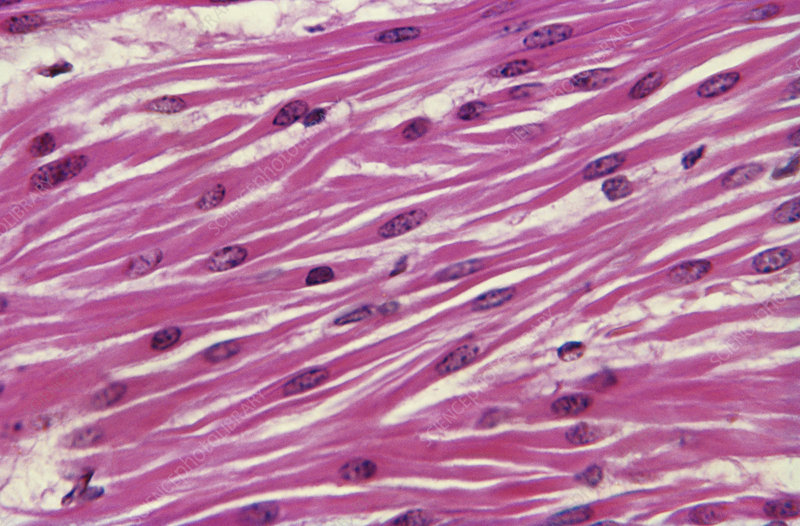
What some characteristics of smooth muscle (4 points)?
Single-centrally located nucleus.
Lack of t-tubules, myofibrils, and sarcomeres.
Non-straited appearance.
Thin and thick filaments scattered throughout the sarcoplasm joined together by dense bodies.