Chapter 46 - Nursing Care of Patients with Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Strain
-A soft tissue injury that occurs when a MUSCLE or TENDON is excessively stretched
-Use RICE
Sprain
-Excessive stretching of LIGAMENTS from twisting movements
-RICE and NSAIDs
Dislocation
Common injury in which the ends of the bones (joints) are moved out of their normal position, usually caused by trauma or a disease
RICE
Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation used to treat soft tissue injuries like strains and sprains.
Bursitis
inflammation of a bursa
Bursae
fluid filled sacs that cushions tendons during movement to prevent friction between bone and tendon
S/S of Bursitis
achy pain, stiffness, swelling, redness, or burning pain
Rotator cuff injury
Muscle contraction causes these tendons to tighten and move or rotate the shoulder
Be Safe! Be Vigilant!
-Use lifting devices.
•Draw sheets
•Mechanical moving devices
-Avoid pulling up on patient's arms to avoid patient injury.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
-Median nerve compression in wrist's carpal tunnel
-Occurs with swelling in tunnel
§Finger, hand, arm pain/numbness
-Relieve inflammation and rest wrist.
•Splint
•Anti-inflammatory
•Surgery
-Teach prevention.
Fractures
break in a bone
Cause of Fractures
Trauma
Pathological
Closed fracture
does not break the skin
Open fracture
breaks the skin - infection risk
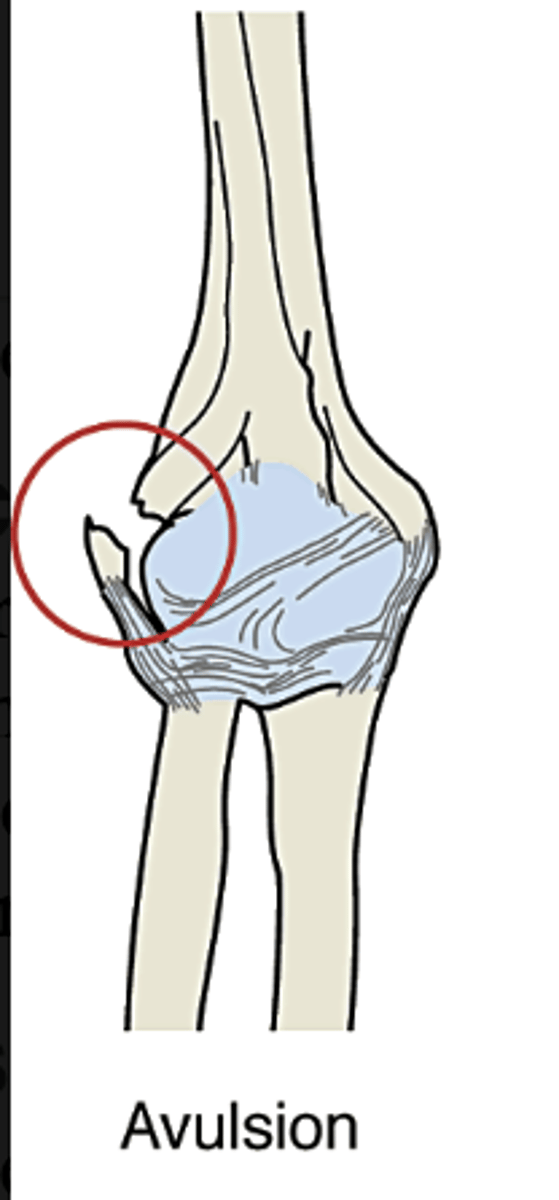
Avulsion
a piece of bone is torn away from the main bone while still attached to a ligament or tendon
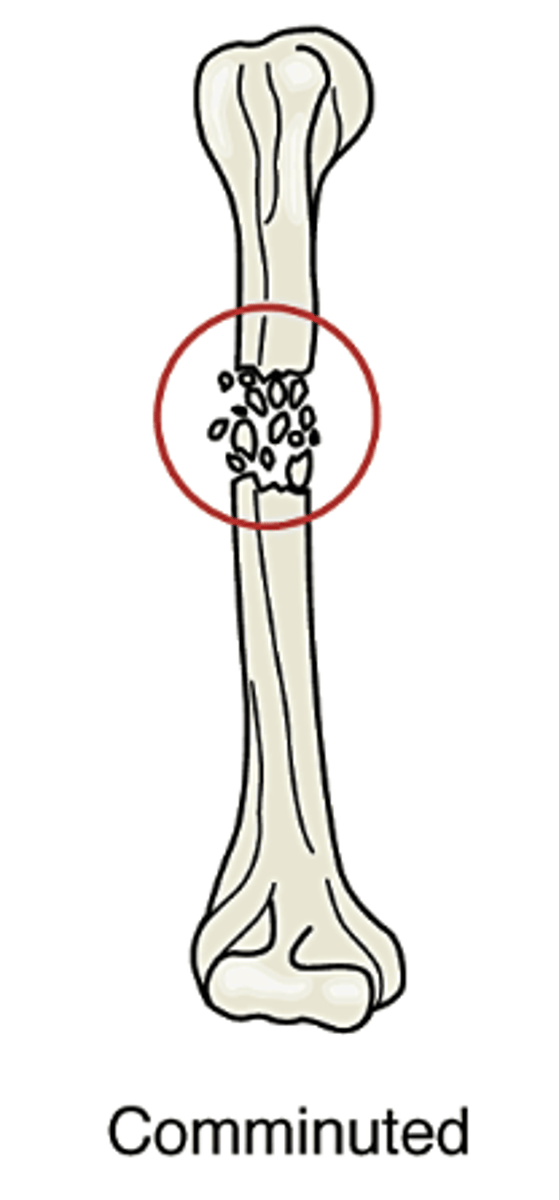
Comminuted
Bone is splintered or shattered into numerous fragments. often occurs in crushing injuries.
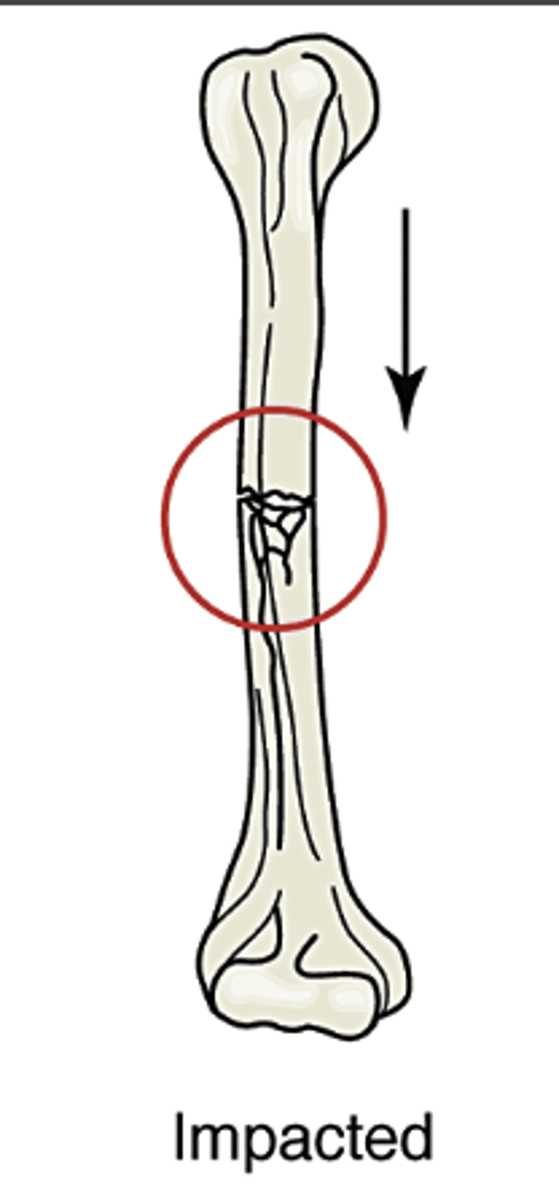
Impacted
bone is forcibly pushed together, resulting in bone being pushed into bone
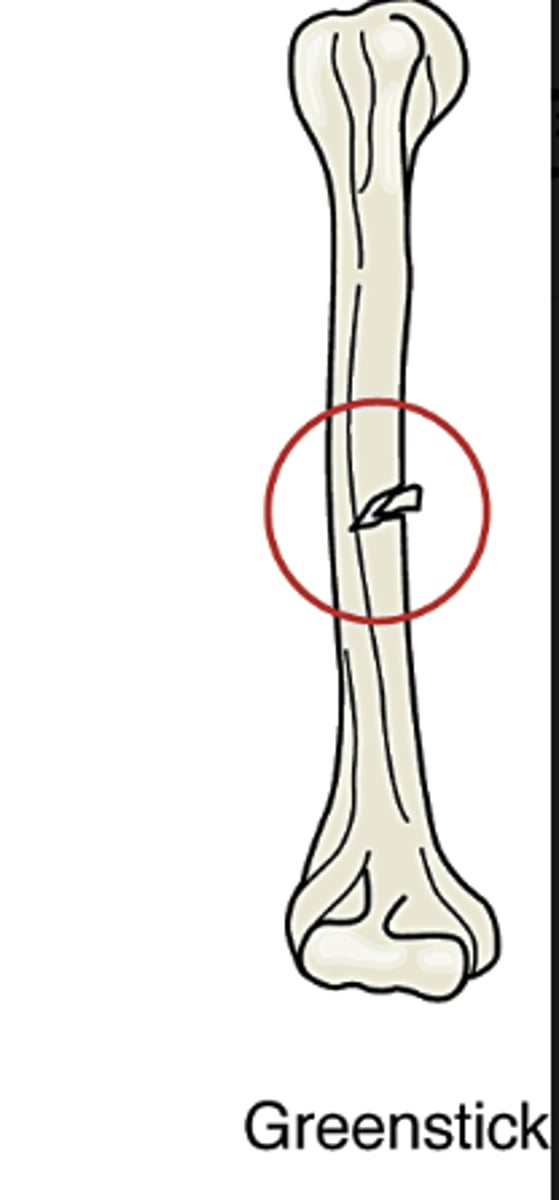
Greenstick
Bone is bent and fractures on the outer arc of the bend. Often seen in children.
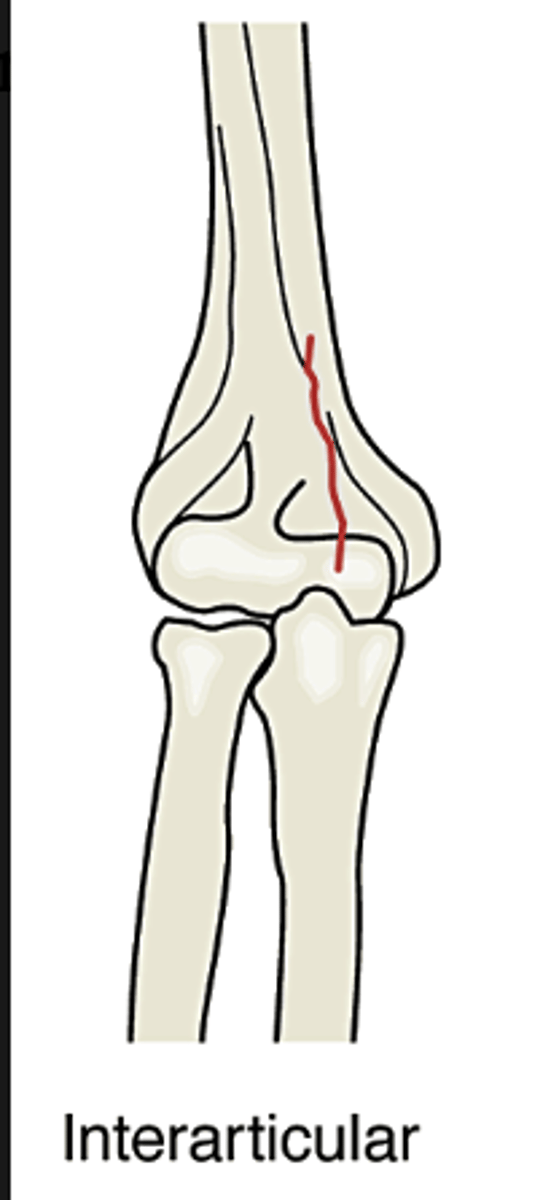
Interarticular
fracture involves bones within a joint
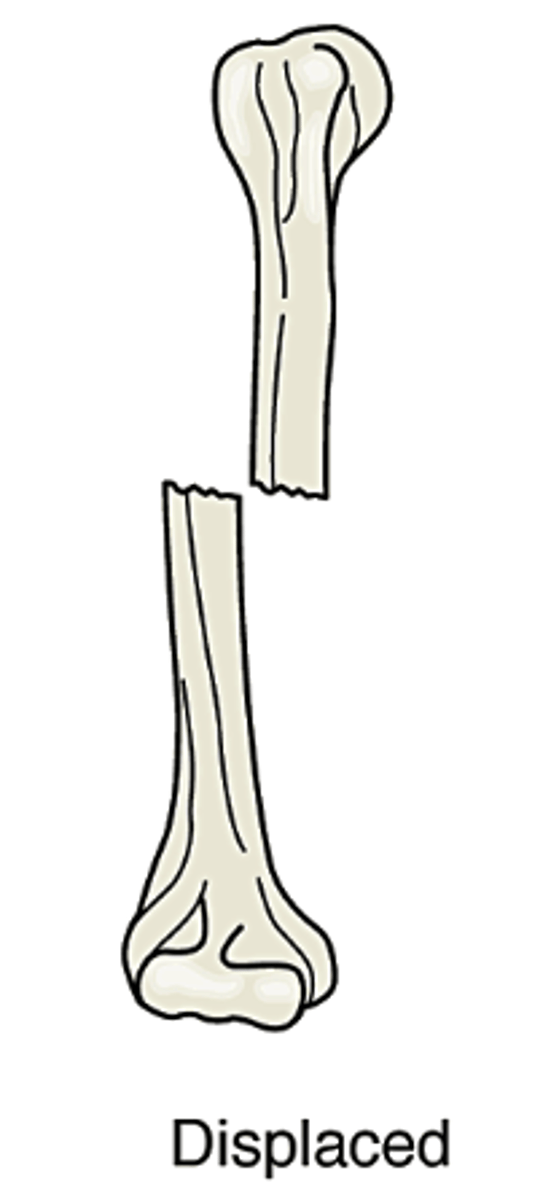
Displaced
Bone pieces are out of normal alignment. One or more pieces may be out of alignment
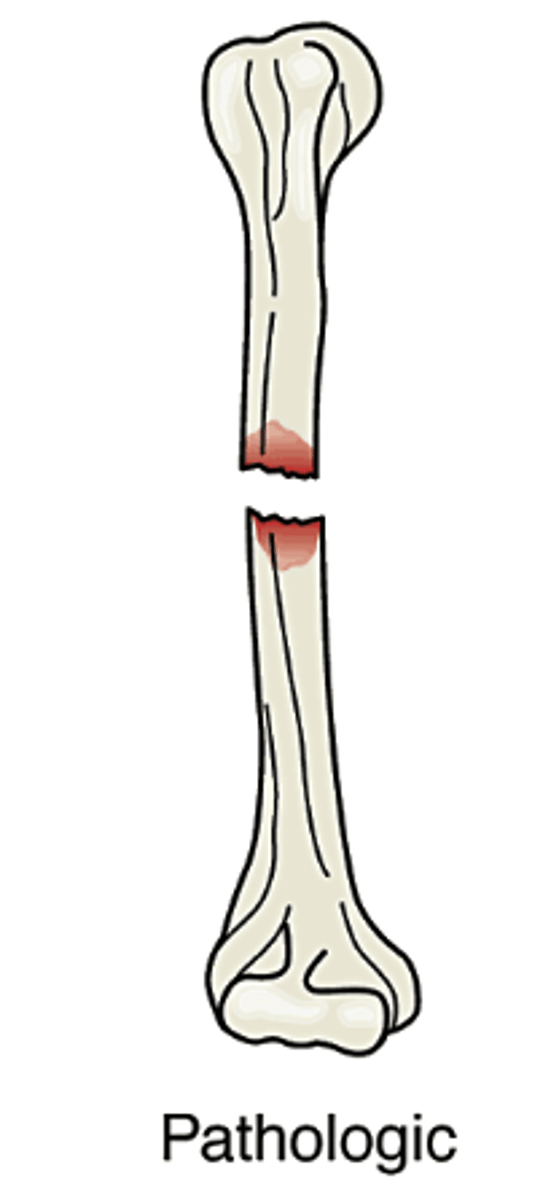
Pathological
Caused when bone is weakened either by pressure from a tumor or an actual tumor within the bone
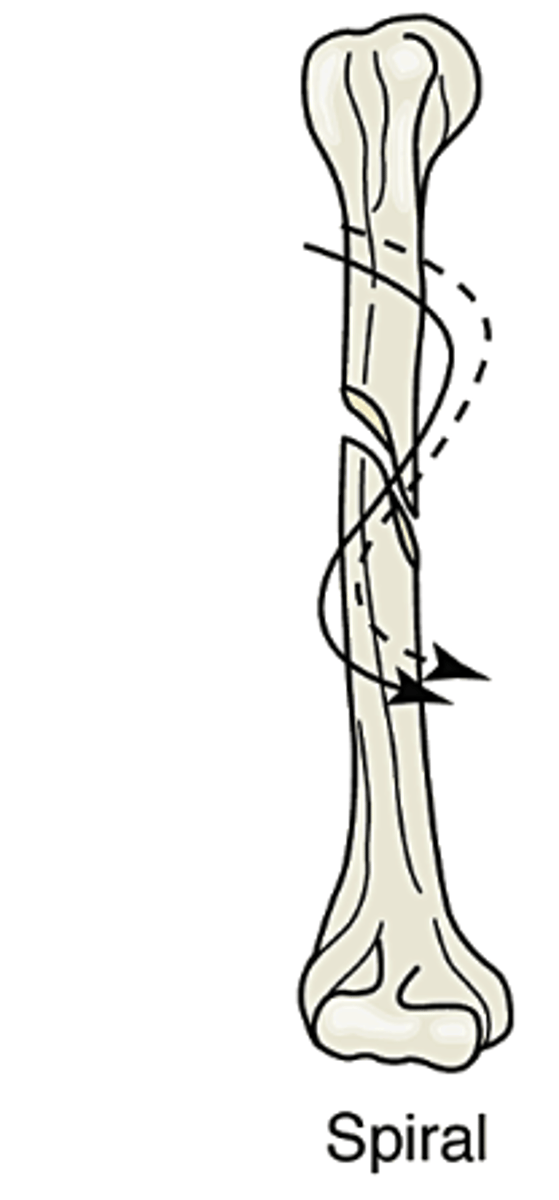
Spiral
fracture curves around the shaft of the bone; from a twisting motion
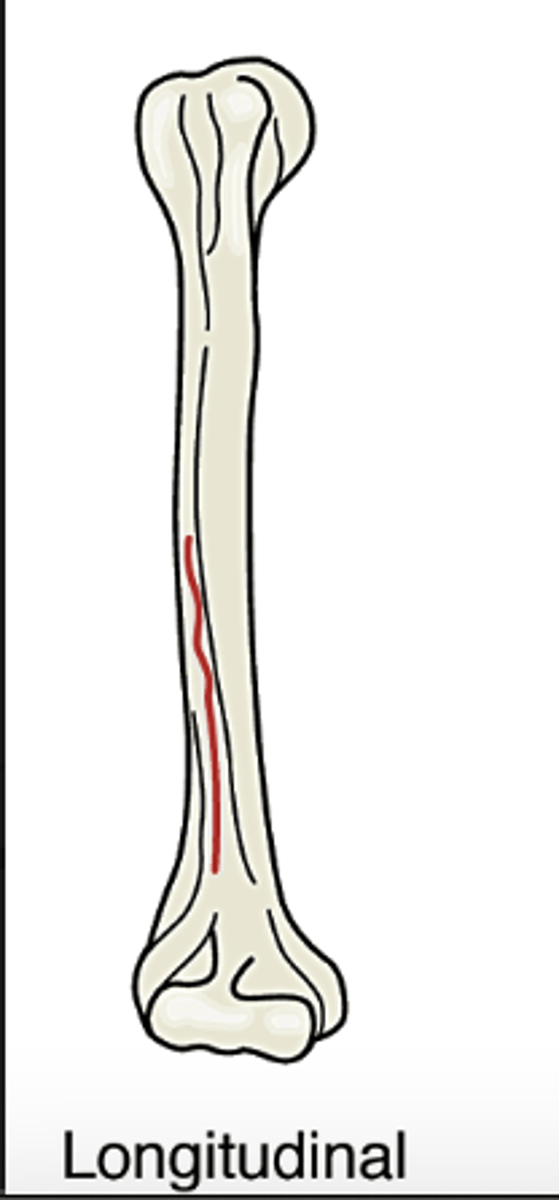
Longitudinal
fracture occurs along the length of the bone
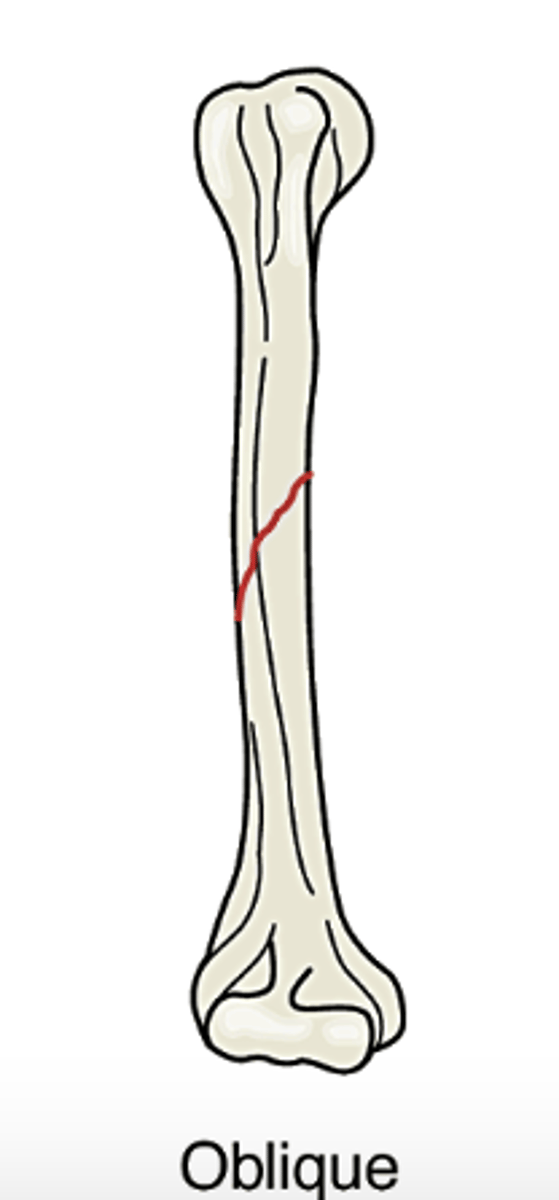
Oblique
fracture occurs diagonally or at an oblique angle across th ebone
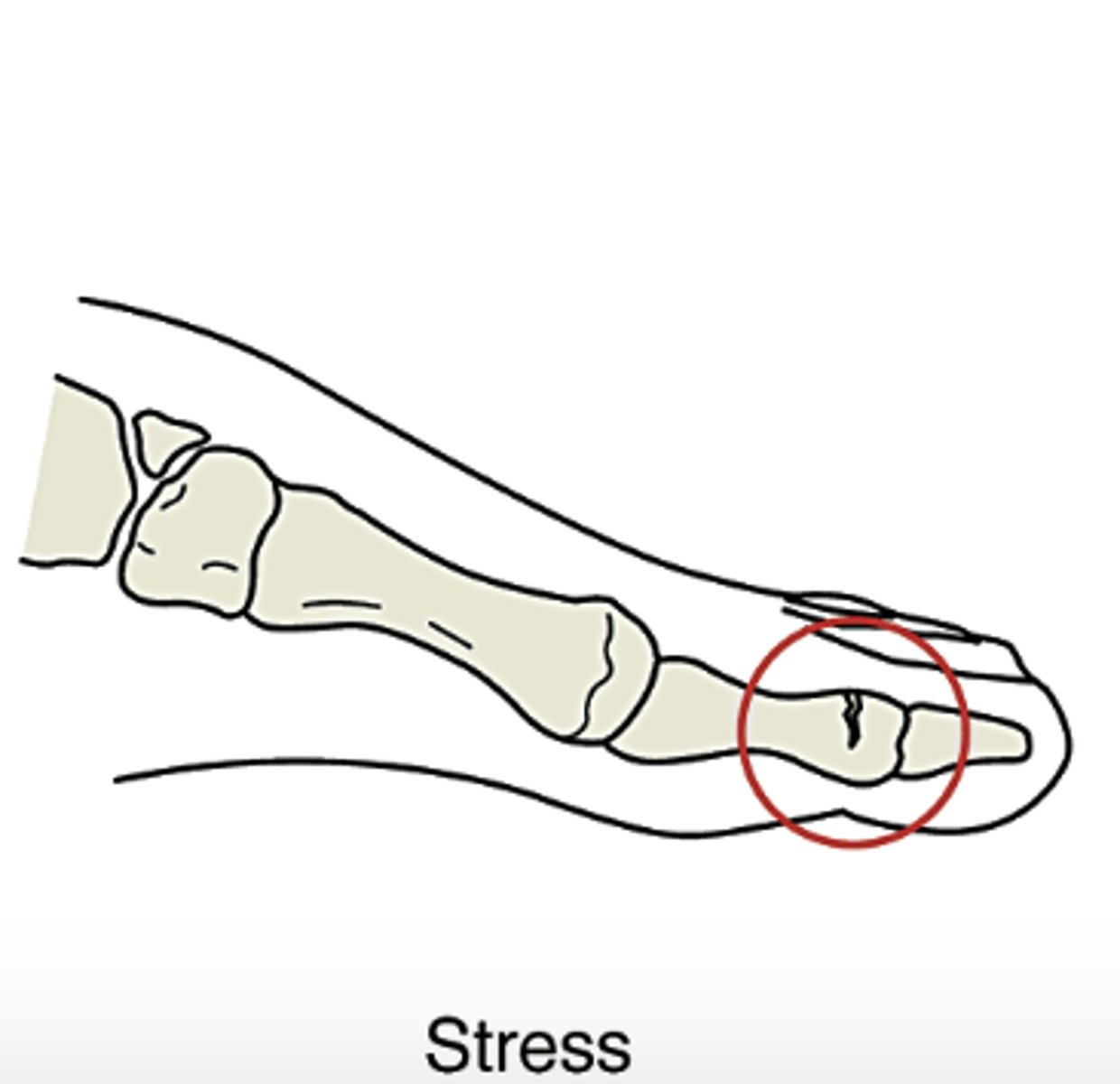
Stress
results in the bone being fractured across one cortex. this is an incomplete fracture.
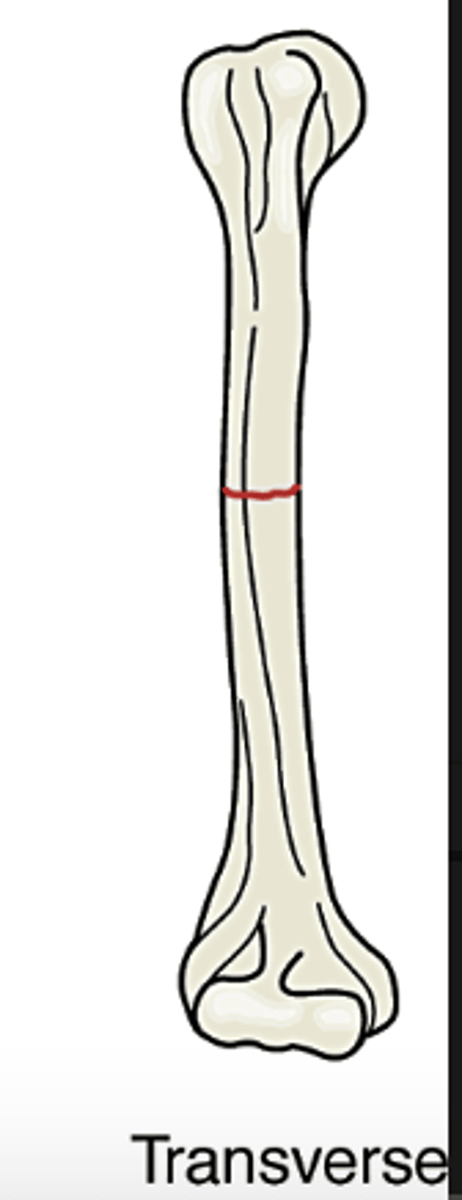
Transverse
bone is fractured horizontally
Depressed
bone is pushed inward. often seen with skull and facial fractures.
S/S of Fractures
-Pain
-Decreased ROM
-Limb rotation
-Deformity, shortening of limb
-Swelling
-Bruising
Diagnostic tests of Fractures
X-ray
CT scan
Emergency treatment of Fractures
-splint it as it lies
-seek medical treatment
Therapeutic goals of Fractures
-Realignment of bone ends
-Immobilization
Fracture Healing Phases
inflammation, repair, remodeling
Management - Closed Reduction
-Manual realignment
-Elastic wraps/splints
-Casts
-Traction
*Skin
*Skeletal
Management - Open Reduction with Internal Fixation
Metal plates, screws
Prosthesis
Management - External fixaton
Pins, metal frame
Allows care of wounds
Internal Fixation
A. Intertrochanteric fracture of the hip with fracture fixation via a side plate and screw combination device
B. Side plate and screw fixation of radial fracture
Complications of Fractures
•Hemorrhage
•Acute compartment syndrome
•Neurovascular compromise
•Infection
•Nonunion
•Thromboembolic complications
•Fat embolism syndrome
Compartment Syndrome
Acute compartment syndrome is a limb-threatening condition in which pressure in limb compartments increases. This causes reduced circulation to the compartment's muscles and nerves.
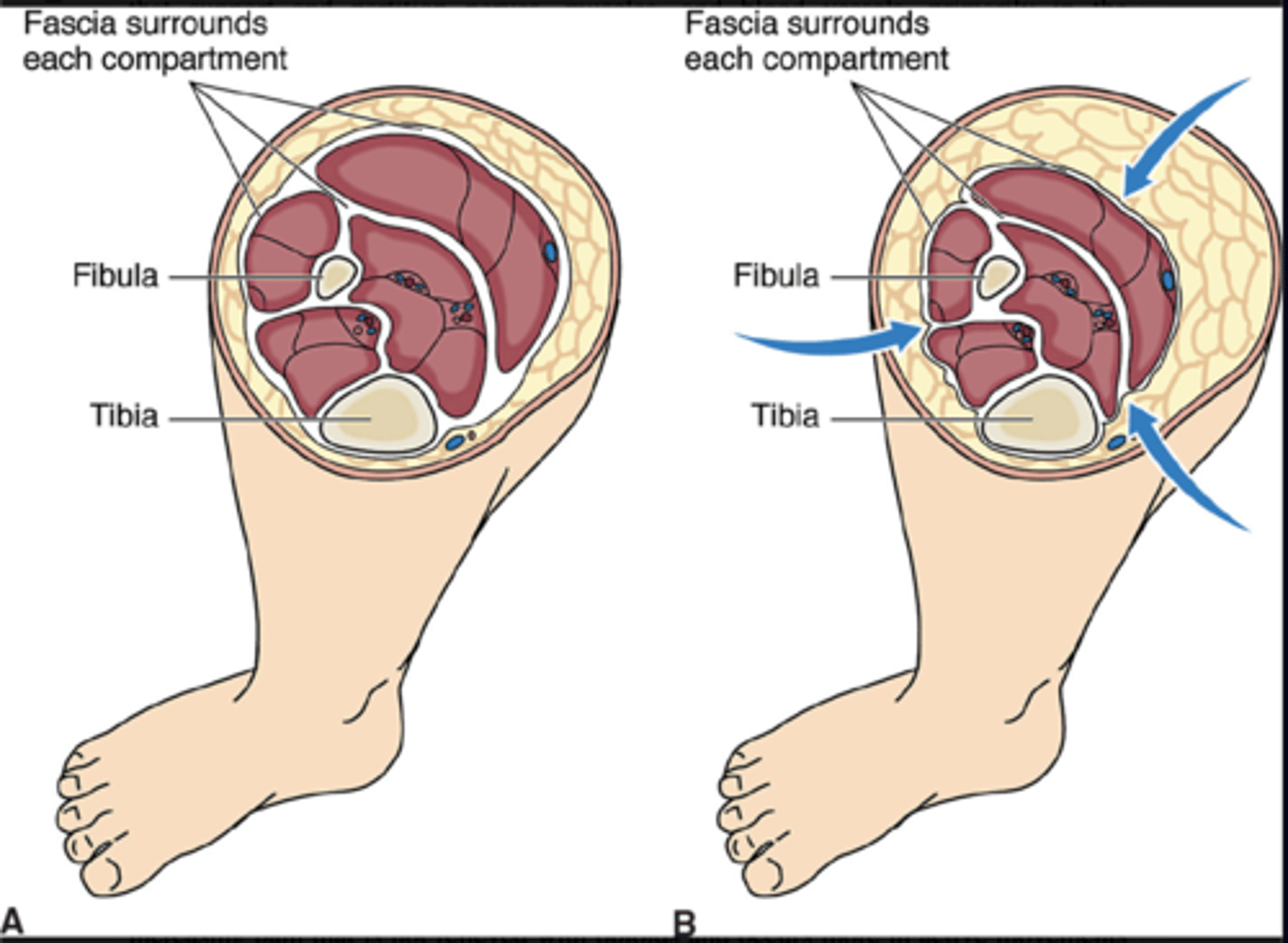
6 P's of Compartment Syndrome
-Pain
-Paresthesia
-Pallor
-Paralysis
-Pulselessness
-Poikilothermia
Severe pain that is not relieved with opioids and occurs more in active movements than passive movements
Acute compartment syndrome
Pain
severe, unrelenting, and increased with passive stretching
Paresthesia
painful tingling or burning
Pallor
but there may be warmth or redness over the area
Paralysis
late symptom
Pulselessness
late and ominous sign
Poikilothermia
temperature matches environment; i.e. the extremity is cool to touch
Fat embolism S/S
-Respiratory failure, cerebral involvement, and skin petechiae.
-Tachypnea, dyspnea, and cyanosis
Fat embolism Causes
Long-bone fractures; surgical fracture repair; multiple fractures
Hip fracture
Nursing care for Fractures
•Neurovascular checks
•Pain management
•Cast, traction, pin care
‒Palming wet cast
•Skin care
•Nutrition
•Self-care deficits
Psychosocial
Patient Education of Fractures
-Cast care
-Pin care
-Nutrition
Osteomyelitis
Infection of bone
Site pain, redness, warmth, swelling, fever
True or False: Use sterile technique for all dressing changes with osteomyelitis
True
Osteomyelitis - Curative Therapy
debridement, reconstruction, antibiotic
Osteomyelitis - Palliative Therapy
chronic suppressive antibiotic therapy
Osteomyelitis - Nonresponsive
Amputation
Nursing Care - Osteomyelitis
Prevention is key!
Hand hygiene
Sterile dressing changes
Medication teaching
Osteoporosis
-Metabolic disorder of low bone mass
-Prone to fractures
-Most common: Spine, wrist, hip
-All bones affected
-Imbalanced remodeling process
Prevalence - Osteoporosis
•54 million people
•Women at greatest risk
•Healthy People 2030 objective: To increase the proportion of older adults who get screened for osteoporosis.
hip/vertebral fractures (osteoporosis)
Reduced quality of life
Increased disability
Risk of death (during year after fracture)
Osteoporosis - Nonmodifiable risk factors
•Aging
•Female gender
•Family history of osteoporosis or fractures
•History of fractures
•Postmenopausal status
•Small boned, petite body build
•Low testosterone and estrogen in men
•White or Asian
Osteoporosis - Modifiable risk factors
•Excessive alcohol use
•Low calcium and vitamin D intake
•Excessive caffeine, protein, sodium
•Sedentary lifestyle
•Smoking
Prevention of Osteoporosis
•Build adequate bone before age 30.
•Ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake.
•Perform weight-bearing exercise (especially in childhood).
•Avoid alcohol and smoking.
S/S of Osteoporosis
-Back pain
-Height decreases
-Fracture
-Kyphosis
Effects of Osteoporosis
•Deformities
•Functional effects
•Emotional effects
•Socialize less due to body image
Diagnostic tests of Osteoporosis
•Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
•Serum calcium, vitamin D is decreased.
•Serum phosphorus is increased.
•Serum alkaline phosphatase is increased.
Therapeutic interventions of Osteoporosis
•Reduce risk factors
•Calcium supplements
•Vitamin D supplements
•Medications
Antiresorptive medications
Bisphosphonates
Calcitonin
Monoclonal antibody
Selective estrogen receptor modulator
Bisphosphonates
bind to bone and suppress osteoclast activity to prevent or reduce bone breakdown in osteoporosis
Examples of Bisphosphonates
-Alendronate (Fosamax)
-Ibandronate (Boniva)
-Risedronate (Actonel)
-Zoledronic Acid (Reclast)
Calcitonin
treats osteoporosis by decreasing bone loss
Examples of calcitonin
Fortical, Miacalcin
Monoclonal antibody
inhibits the protein that signals bone removal
Examples of Monoclonal antibody
Denosumab (Prolia)
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
-Increases bone mass by 2% to 3% each year.
-Designed to mimic estrogen in some parts of the body while blocking its effects elsewhere.
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) Medication
Raloxifene (Evista)
Anabolic (bone forming) medications
Teriparatide (Forteo)
Nursing Care of Osteoporosis
•Pain relief
•Symptom management
•Education
‒Prevention
‒Diet: Increase calcium, vitamin D
‒Exercise
‒Medication
•Fall prevention
Paget Disease
-Rare noncurable metabolic bone disease
-Abnormal weak bones
-Painful
-Diagnostic test: X-ray
-Bisphosphonates, calcitonin
-Relieve pain, teaching, promote life quality
Primary malignant tumors
•Osteosarcoma
‒Most common
•Ewing sarcoma
‒Most malignant
•Both mainly in children and young adults
S/S of Bone Cancer
Site pain and swelling
Tender, palpable mass
Therapeutic interventions of Bone Cancer
Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation
Nursing Care of Bone Cancer
•Postoperative care
•Supportive care
Metastatic Bone Disease
-Bone-seeking cancers
•Prostate, breast, lung, thyroid
-Pathological fractures
-Severe pain
-Therapeutic interventions
•Radiation
-Nursing care
•Supportive care, as with other cancers
Gout Pathophysiology
•Systemic connective tissue disorder
•Uric acid build-up
•Urate crystals deposited in joints/ connective tissues
•Severe joint inflammation
Causes and types of Gout
•Primary
‒Inherited problem with purine metabolism
•Secondary
‒Another health issue
‒Medications
S/S of AcuteGout
-Swollen, red, hot, painful inflamed joints
-Great toe
S/S of Chronic Gout
- Urate deposits under skin
- Renal stones
Diagnostic tests for Gout
-Serum uric acid
-Joint fluid: Uric acid crystals
Medication for Acute Gout
Colchicine (Colcrys) and NSAIDs
Medication for Prevention of Gout
-Febuxostat (Uloric)
-Allopurinol (Zyloprim)
-Probenecid (Benemid)
Nursing Care of Gout
•Patient education
‒Avoid foods high in purines.
‒Eating cherries/cherry juice may be helpful.
‒Avoid aspirin, diuretics, alcohol, stress.
‒Increase fluids to avoid kidney stones.
Osteoarthritis
-Affects more than 32 million people
-Common
-Degenerative joint disease
-Increases with age
Osteoarthritis Pathophysiology
•Affects entire joint
•Articular cartilage/joints bone ends deteriorate
•Joint space narrows, bone spurs develop, joint inflamed
•Joint deformities, pain, immobility
•Weight-bearing joints
Risk factors of Osteoarthritis
-Heredity
-Aging
-Obesity
-Excessive "wear and tear" on synovial joints
S/S of Osteoarthritis
•Joint pain
‒Intensifies after physical activity
•Stiffness
•Heberden and Bouchard nodes
‒Bony nodes on joints of fingers
Diagnostic Tests of Osteoarthritis
-X-rays
-MRI
-Synovial fluid analysis
Therapeutic interventions of Osteoarthritis
•No cure
•Exercise
•Weight control
•Medication
‒NSAIDs
‒Synvisc-One
•Heat or cold therapy
•Complementary therapies
‒Imagery, music therapy, acupressure, acupuncture
•Surgery
Total joint replacement
Patient Education of Osteoarthritis
-Protect joints
-Conserve energy
Rheumatoid Arthritis
-Chronic, progressive, systemic inflammatory disease
-Destroys synovial joints and other connective tissues
-Includes major organs
Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
•Synovitis
•Synovium thickens, fluid accumulates
•Destructive pannus erodes joint cartilage, destroys joint bone
•Pannus converted to bony tissue
•Joint deformity
•Other connective tissue affected