Surgical Skills - Study Tips 1
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
What are the special instruments used for an ovariohysterectomy (spay)?
Snook spay hook
What are the general instruments needed for a spay/castration?
Soft tissue surgical pack
What layers are closed on an OHE?
Linea Alba, Subcuticular layer, and Skin
What layers are closed on a Feline Castration?
There is no need
What layers are closed on a Canine Castration?
Subcuticular layer
How many layers are closed after an OHE?
3 layers
How many layers are closed after a Canine Castration?
1 layer
How many layers are closed after a Feline Castration?
No layers
What are the indications for OHE?
• Sterilization
• Neoplasia of reproductive tract
• Treatment of neoplasia elsewhere in the body influenced by reproductive hormones
• Trauma or injury to reproductive tract
• Dystocia
• Uterine torsion
• Abolition of heat cycle
• Stabilization of other systematic diseases
• Congenital abnormalities
What are the indications for a Feline Castration?
• Sterilization
• Prevent roaming
• Prevent aggressive behavior/fighting
• Prevent urine spraying/marking
• Correct congenital abnormalities
• Treat scrotal neoplasia
• Treat scrotal abscess, infection, or trauma
• Treat endocrine abnormalities
• Treat hormone-related disease elsewhere in the body
What are the indications for a Canine Castration?
• Sterilization
• Prevent roaming
• Prevent aggressive behavior/fighting
• Prevent urine marking
• Correct congenital abnormalities
• Treat scrotal or testicular neoplasia
• Treat scrotal abscess, infection, or trauma
• Treat hormone-related disease elsewhere in the body
What is your role during spay/castration surgeries?
• Maintaining sterile environment
• Monitoring patient
• Managing instrument table
• Passing proper instruments
• Maintaining tissues (retraction/moistened)
• Maintain hemostasis
What is the appropriate way to take the history of a patient?
Be concise and chronological. Get the signalment, reason for visit, specific history for presenting complaint (without asking leading questions & if any treatments for the current problem), and current medications/vitamins/supplements. While talking with the client, let the patient out (if aggressive, leave in cage/muzzle) and observe the temperament, attitude, body condition, and any anxiety while the patient gets familiar with the room/relaxes.
What are leading questions?
Questions that can influence the answers that the owners give. (Ex. Has it been there for a long time? Is Rex eating less or losing weight?)
What are open-ended questions?
Questions that get the owner to talk about the presenting complaint without influence. (Ex. When did you first notice it? Have you noticed any changes in Rex?)
What is included in signalment?
Age, breed, sex, reproductive status
Can the 18yo daughter of an owner sign a consent form?
No
Who must sign the consent form?
The owner of the animal
What information is on the consent form?
• Identifies the patient
• Specific procedures to be performed
• Potential risks
• Veterinarian’s name
• Signature of the owner of the patient
• Owner contact information
What are the sources of surgical infection?
• The operating room environment
• The operating team
• Surgical instruments and supplies
• The patient’s endogenous flora
What is the most common source of surgical infection?
The patient’s endogenous flora
What clothing should you wear as a surgical assistant?
Clean scrubs (tucked in shirts and drawstrings)
What PPE should you wear as a surgical assistant?
• Surgical cap (hair completely covered)
• Surgical mask/Beard cover
• Shoe covers (over surgery dedicated shoes)
What cannot come into the surgery room?
Cellphones, pagers, and shoe covers/shoes worn elsewhere in the clinic
What should a surgical assistant’s nails look like?
Kept shorter than the fingertips and polish free
What is open gloving?
A type of gloving when only the hands need to be sterile to perform a procedure.
What procedures can be performed with open gloving?
• Minor procedures
• Catherizations
• Bone marrow biopsy
What does closed gloving provide?
Provides assurance against contamination because bare skin is not exposed.
What is assisted gloving?
Gloving that requires two people
When is assisted gloving required?
When a glove is contaminated during surgery.
What is the preferred method of gloving for surgical procedures?
Closed gloving
How are instruments passed during surgery?
Instruments are placed firmly into the palm of the surgeon’s hand.
How are scalpels passed during surgery?
The cutting edge is away from the surgeon in a way that is ready to use.
How are ring instruments passed during surgery?
Rings are placed in the palm of hand, ready to use.
What does the surgical assistant manage the instrument table?
• Loading needles properly
• Instrument and sponge counts
• Having ring handles closest to the surgeon
• Knowing what the surgeon needs before the procedure
• Knowing what each instrument does
• Passing instruments properly
What are sponge and instrument counts?
A count of the items before and after the procedure
Why are sponge and instrument counts done?
To ensure nothing is left in the body cavity.
How much blood does a 3×3 sponge hold?
6 mls
How much blood does a 4×4 sponge hold?
10 mls
How much blood does a laparotomy sponge hold?
100 mls
How is blood loss quantified when using sponges?
By knowing how much blood each size can absorb and adding together the amounts. (Ex. Two 3×3s, five 4×4s, and one lap sponge = 162mls of blood loss)
What should you do before a surgery?
Eat a substantial meal, be adequately hydrated, and visit the restroom
What prep is done before a surgery?
• Changing into clean scrubs
• Turning on lights and heating devices
• Unwrapping sterile instruments
What type of cautery uses a ground plate that is placed under the patient so the current will pass through the patient towards the ground plate?
Monopolar
What type of cautery has no grounding plate, and the current goes from one tip to another?
Bipolar
What can you never use when using a cautery?
Alcohol
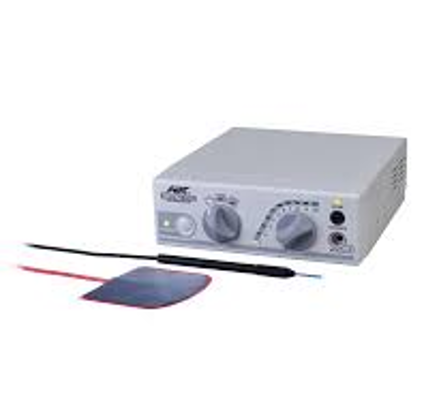

What is the image an example of?
Monopolar cautery

What is the image an example of?
Bipolar cautery
Which suction tip is used to remove large amounts of fluid from the body cavity?
Poole

What is the suction tip displayed in the image?
Poole
Which suction tip is generally used in ortho and neuro surgeries because of its small tip?
Frasier

What is the suction tip displayed in the image?
Frasier
Which suction tip is general-purpose in surgeries?
Yankauer
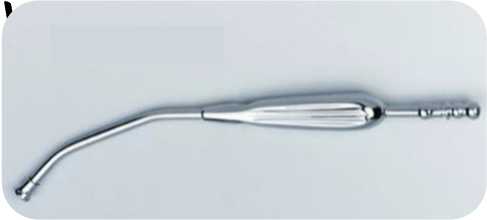
What is the suction tip displayed in the image?
Yankauer
What is the inherent capability of suture to return to, maintain, its original gross shape?
Memory
What is the amount of friction created as suture is pulled through the tissue?
Drag
What is the degree to which absorbed fluid is transferred along a suture?
Capillarity
What is the measurement of the ability of a material/tissue to resist deformation or breakage?
Tensile strength
What is the holding capacity of a suture?
Relative knot security
What is the degree to which suture will deform under stress or load and return to its original form when the load is removed?
Elasticity
What is the degree to which suture will deform without breaking and will maintain its shape after removal of the deforming force?
Plasticity
What is the ease of handling and the ability of the suture to change shape?
Pliability
What is tendency of a suture to slowly and permanently deform under constant stress?
Creep
What suture pattern is the easiest to learn and provides secure closing?
Simple interrupted
What suture pattern is tied off only on the ends and saves time and suture materials?
Simple continuous
What suture pattern forms an X pattern and is faster than simple interrupted, it is most commonly used on skin?
Cruciate
What suture pattern distributes the forces away from the incision and is typically used in cancer patients?
Horizontal mattress
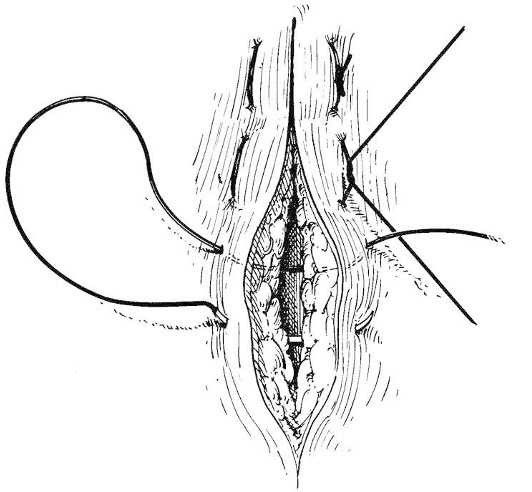
What suture pattern closes dead space and places the knot in the deepest layer?
Buried
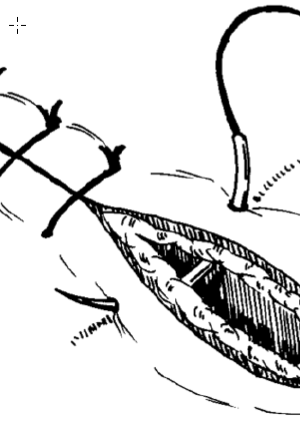
What suture pattern is shown in the image?
Simple interrupted
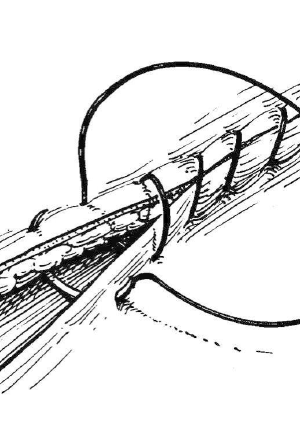
What suture pattern is shown in the image?
Simple continuous
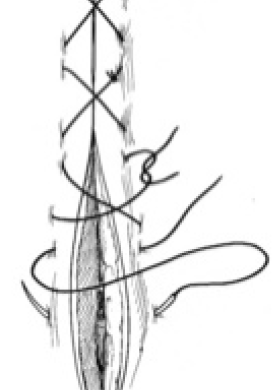
What suture pattern is shown in the image?
Cruciate
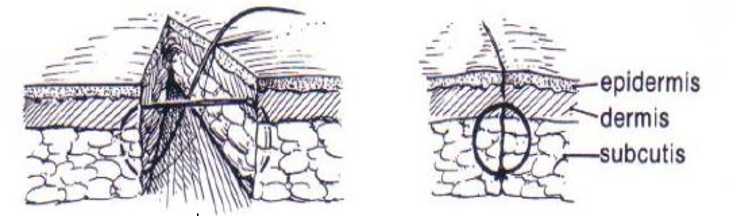
What suture pattern is shown in the image?
Horizontal mattress
What suture pattern is shown in the image?
Buried
What are cutting suture needles used for?
Tough fibrous material and some cardiovascular procedures
What are taper suture needles used for?
Soft tissue
What are reverse cutting suture needles used for?
Skin
What is a straight suture needle used for?
ET Tube placement
What is a micropoint suture needle used for?
Fine point
Do braided sutures have a degree of capillarity?
Yes
Which suture loses most of its tensile strength within 60-90 days in living mammalian tissue?
Absorbable
Which suture is manufactured from the small intestine submucosa of sheep?
Catgut
What are the most common suture needles?
• Cutting
• Taper
• Reverse cutting
What are examples of absorbable suture?
• Polyglycolic acid (Dexon)
• Polyglactin 910 (Vicryl)
• Poliglecaprone 25 (Monocryl)
• Polydiaxanone (PDS)
• Polyglyconate (Maxon)
What are examples of non-absorbable suture?
• Polyester (Nylon)
• Polypropylene (Prolene)
• Stainless steel
How do you properly hold thumb forceps?
Hold like a pencil
How do properly hold scissors and forceps?
With the tips of your thumb and ring finger in the rings while your index and middle finger support the instrument.
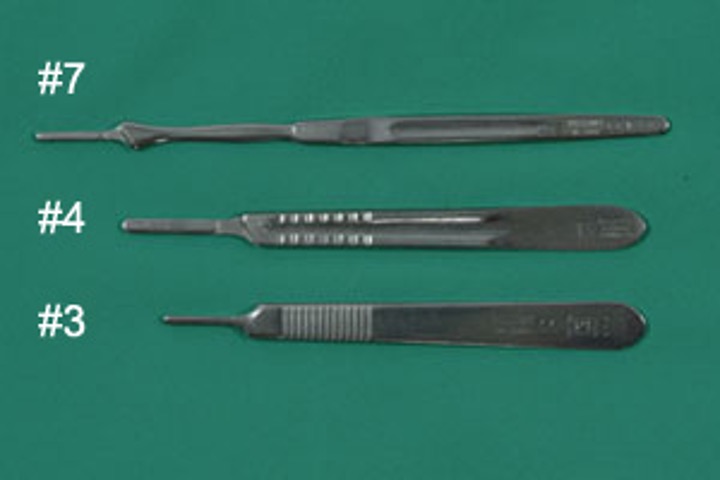
#3 is most commonly used in small animal surgery, #4 is commonly used in large animal, and #7 is used for neuro. What is this instrument?
Scalpel handle

What is the instrument in the image? It’s used to cut the patient.
Scalpel blade
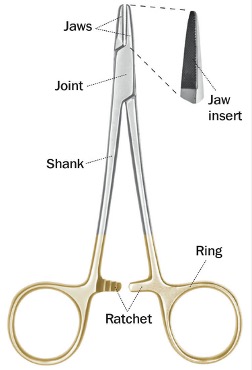
These are used to hold needles ONLY, what are they?
Needle holders
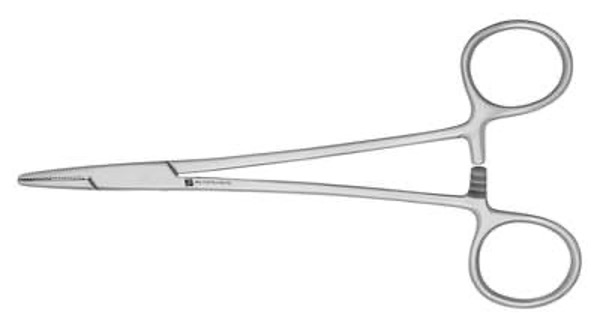
These don’t have scissors, what are they?
Mayo-Hegar needle holders
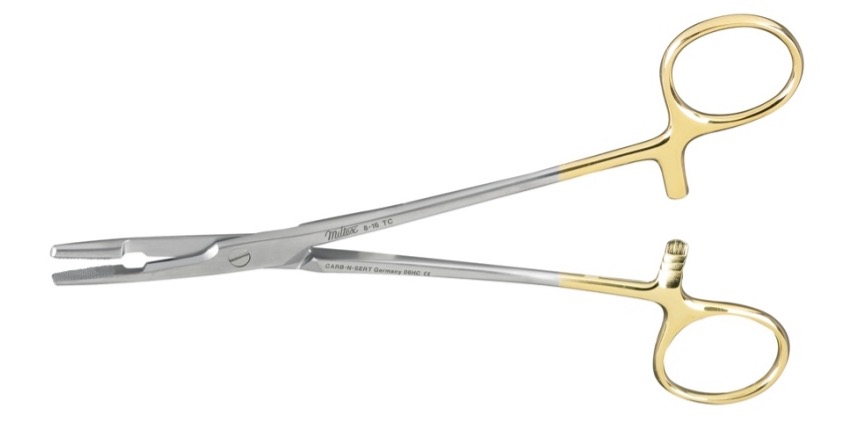
These have scissors, what are they?
Olsen-Hegar needle holders

General forceps used for tissue handling, suturing, and cautery; what are they?
Brow-Adson thumb forceps
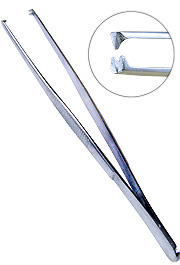
Rat-tooth tip, for suturing skin and fascial planes; what are they?
Adson (Rat-Tooth) thumb foreceps

Delicate forceps which minimize trauma to tissues; what are they?
DeBakey thumb foreceps
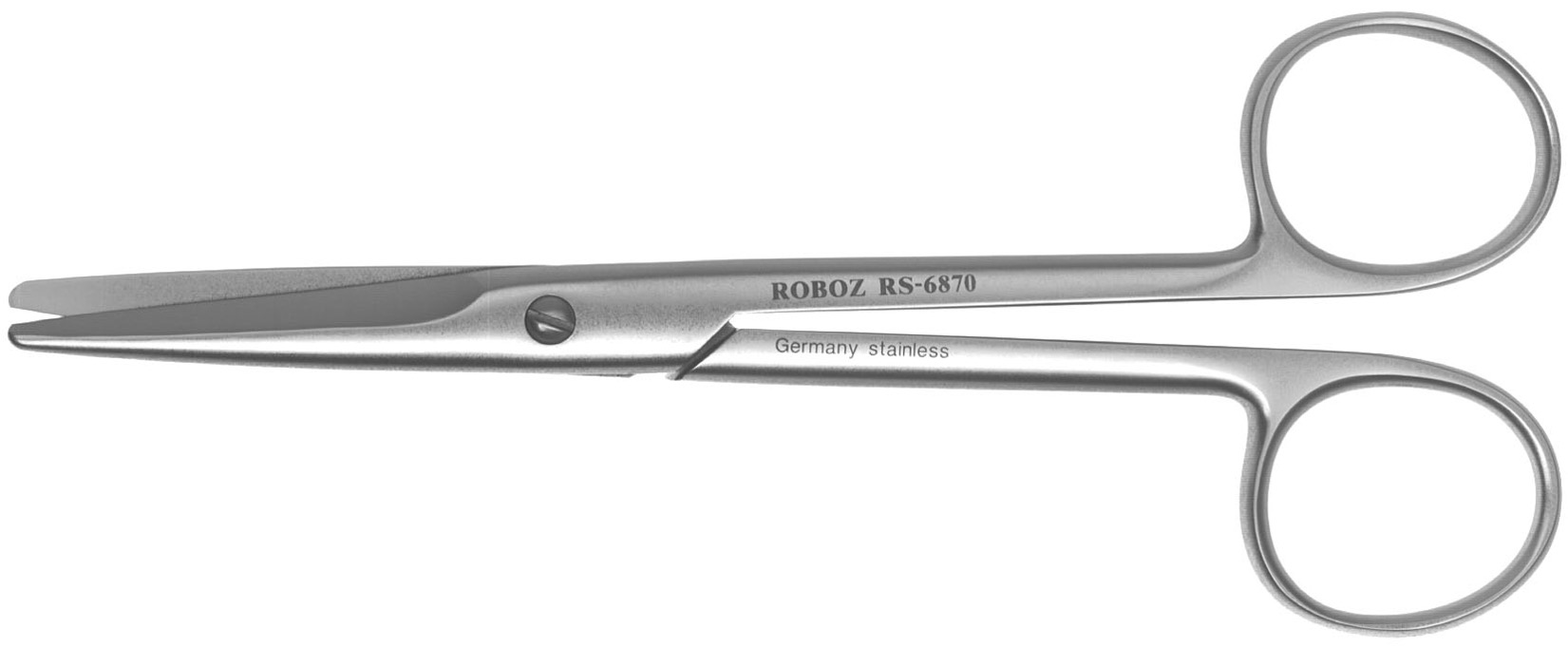

• Handle length similar to cutting blade length
• Used for tougher, thicker tissue; Fibrous tissue; & Joint capsule
What are they?
Mayo scissors
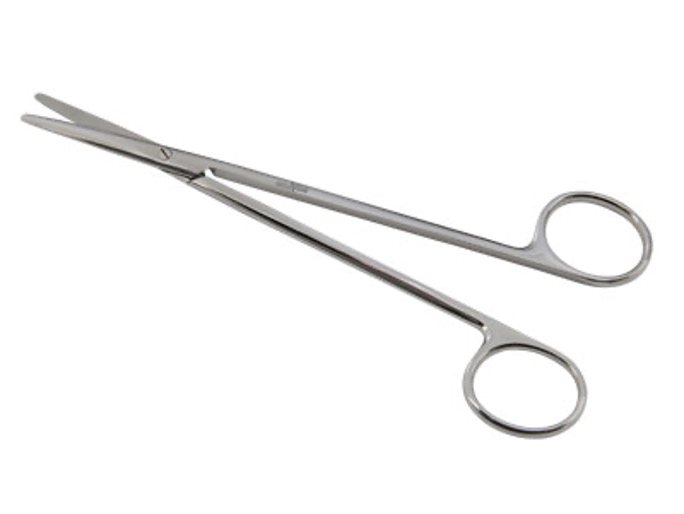
•Longer handle than cutting blade length
•Used for finer tissue dissection; Abdominal surgery; Cystotomy; & Gastrotomy
What are they?
Metzenbaum Scissors

What type of scissors are these?
Lister bandage scissors

What type of scissors are these?
Littauer suture scissors
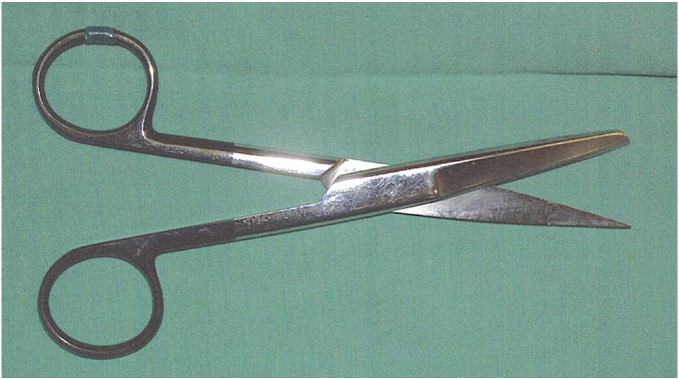
What type of scissors are these?
General operating scissors
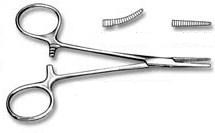
•Straight or curved jaws, used to control point bleeders
•Smallest hemostats
What type of forceps are these?
Halsted mosquito hemostatic forceps