INTRO TO ENTOMOLOGY
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
meaning of anthro
joint
meaning of pod
foot
class of phylum arthropoda (4)
Crustacea
arachnida
insecta
myriapoda
body divided into segments
tagmatization
3 parts of tagmatization
Head
Thorax
Abdomen
Where is the deposition of chitin
exoskeleton
division of cuticle
schlerite
schlerite
tergum
sternum
pleuron
space full of hemolymph
hemocoele
heart
large dorsal artery
branches and ramifies with internal organs
trachea and tracheoles
digestion parts
foregut or stomodeum
midgut or mesenteron
hindgut or proctodeum
ingestion, passage, food disintergration
foregut or stomodeum
food storage and enzyme secretion
midgut or mesenteron
food absorption and fecal expulsion
hindgut or proctodeum
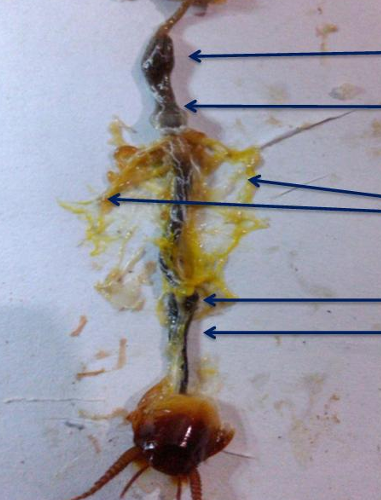
upmost
crop
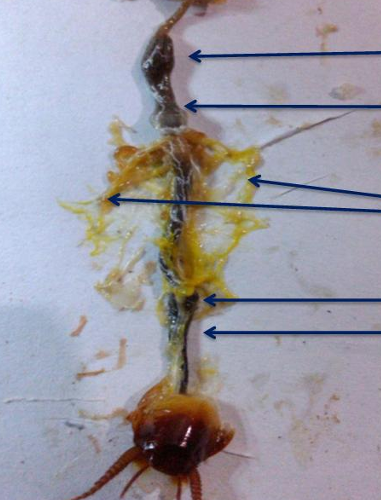
down to the upmost
gizzard
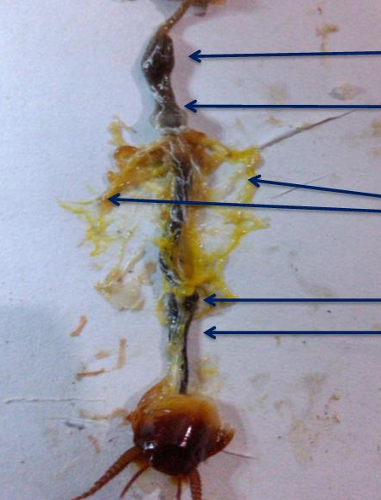
third to the upmost and middle
malphigian tubes
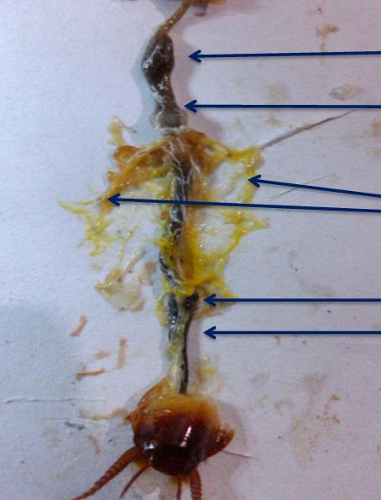
2nd to the lowest part
ileum
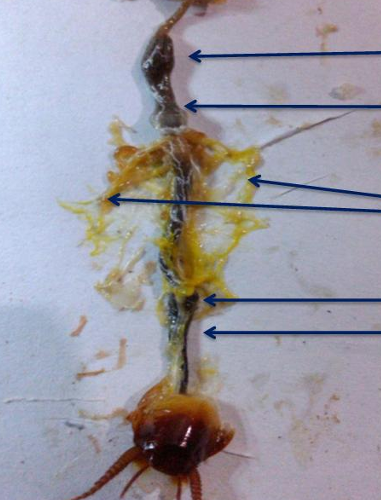
lowest part
colon
excretion in insects and mites
malpighian tubes
excretion in crustaceans
nephridia
excretion in arachnids
coxal gland
brain
supraesophageal center
parts of nervous system
supraesophageal center
ganglionated ventral nerve cord
parts of female reproduction
ovary
oviduct
uterus
vagina
spermatheca
parts of male reproduction
testes
vas deferens
seminal vesicle
penile organ
2 types of arthropod development
complete/ complex/ holometabolous life cycle
incomplete/ simple/ hemimetabolous
4 stages - egg, larva, pupa, adult
complete/ complex/ holometabolous life cycle
1 or 2 stages missing except the adult stage
incomplete/ simple/ hemimetabolous
stages in life cycle: unsegmented
egg
stages in life cycle: feeding stage
larva/ maggot/ grub/ caterpillar
stages in life cycle: quiescent
pupa
stages in life cycle: leaves the egg with similar morphology with adult
nymph
stages in life cycle: reproductive stage
adult
stages in life cycle: young adult
imago
periodic shedding or moulting of exoskeleton
ecdysis
term for immature insect between each ecdysis
instar
length of time spent between each ecdysis
stadium
types of larva
polypod
oligopod
apodous
complete leg
polypod
thoracic legs only
oligopod
no legs
apodous
caterpillar
polypod
beetle
oligopod
maggots
apodous
types of pupa
exarate
obtectate
coarctate
wing and legs free from body
exarate
wings and legs bound to body by moulting fluid
obtectate
last larval skin retained; hardened skin (puparium) encloses pupa
coarctate
ex of exarate
beetles
ex of obtectate
mosquito and tabanus
ex of coarctate
musca and oestrus
types of female
oviparous
ovoviviparous
viviparous/ larviparous
pupiparous
parthenogenetic
lays undeveloped eggs
oviparous
lays larvated eggs
ovoviviparous
lays larva such as oestrus and sarcopahaga
viviparous or larviparous
lays larva that immediately turns into pupa such as tse tse flies and hippoboscids
pupiparous
reproduce without fertilization
parthenogenetic
mouthparts are used for biting and grinding solid foods
mandibulate (chewing)
mouthparts are primarily used for sucking liquids with or without stylet
haustellate
mouthparts lacks stylets and are used to suck liquids
siphoning
mouthparts are used to sponge and suck liquids
sponging