Limbic System
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Cortical input to hippocampal formation is funneled via the _____ Cortex
entorhinal
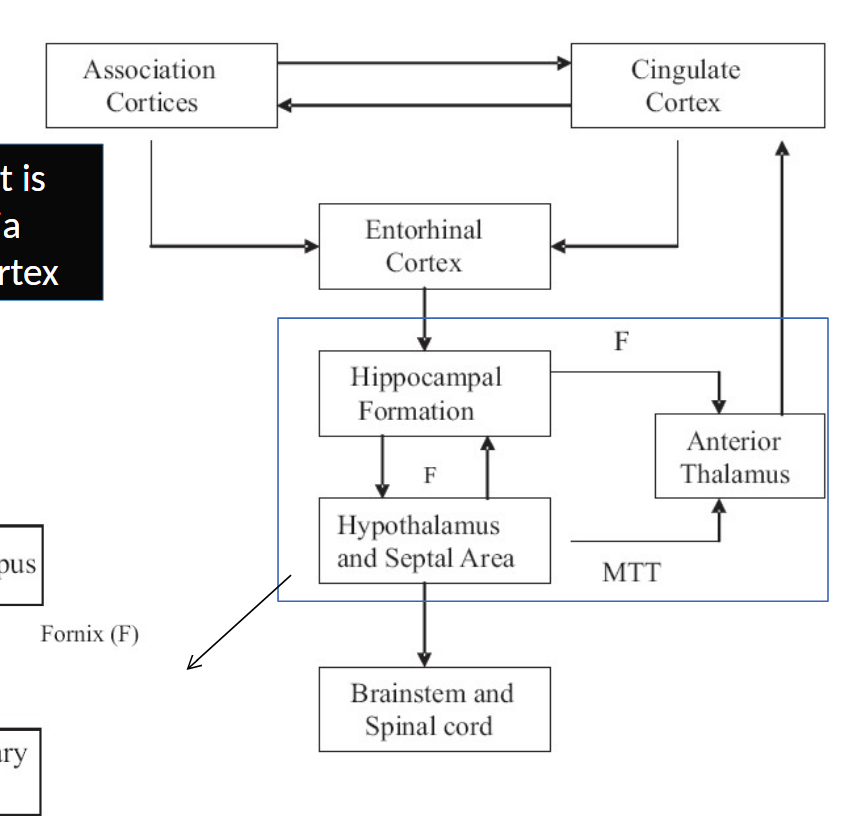
Papez Circuit: _______ communicates with mamillary body through _____, then they communicate with ______ ______ of ______ through _______ tract, then it communicates with cingulate Gyrus through ____ ______, then goes to ________ gyrus through the cingulum, which then goes to entorhinal cortex which then goes back to hippocampus through _____ pathway
hippocampus fornix anterior nucleus thalamus mamillothalamic internal capsule parahippocampal perforant
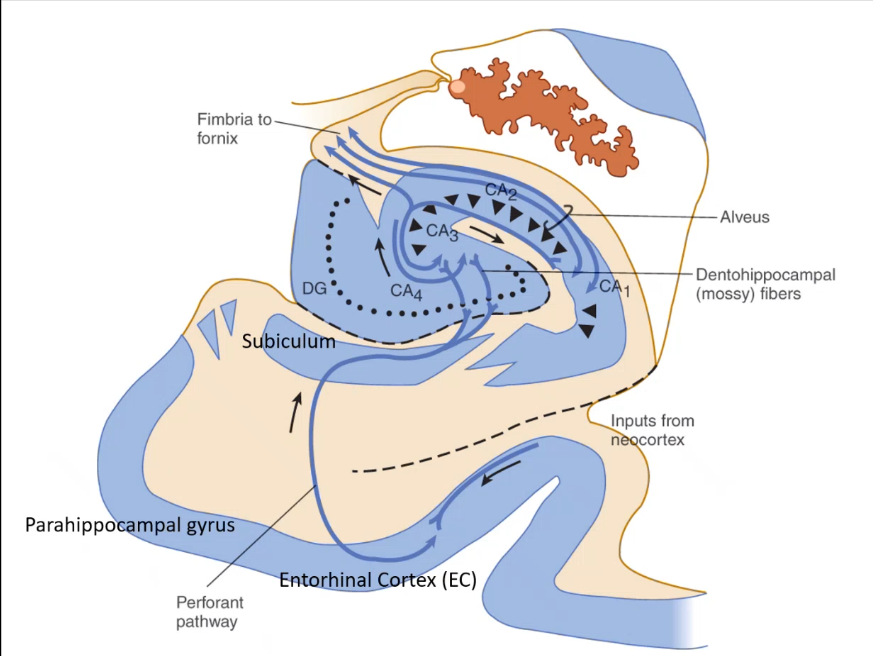
so information is brought in by the ______ ____ which travels to ____ using the _______, from CA3 info can either go to ____ then back to subiculum or fornix, or info can go directly to ______
entorhinal cortex CA3 subiculum CA1 fornix
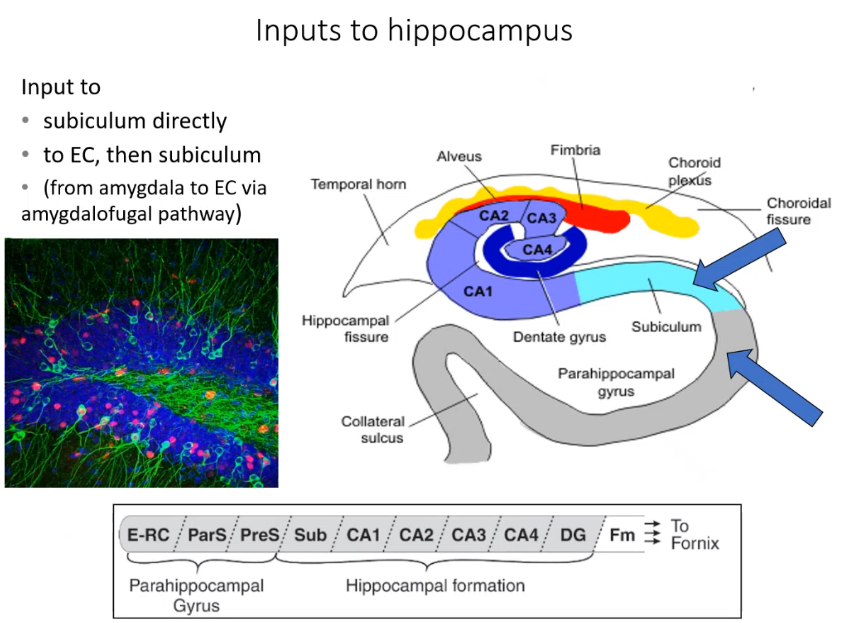
input to hippocampus can either go to _____ directly or through _____ ____ then subiculum,
subiculum entorhinal cortex
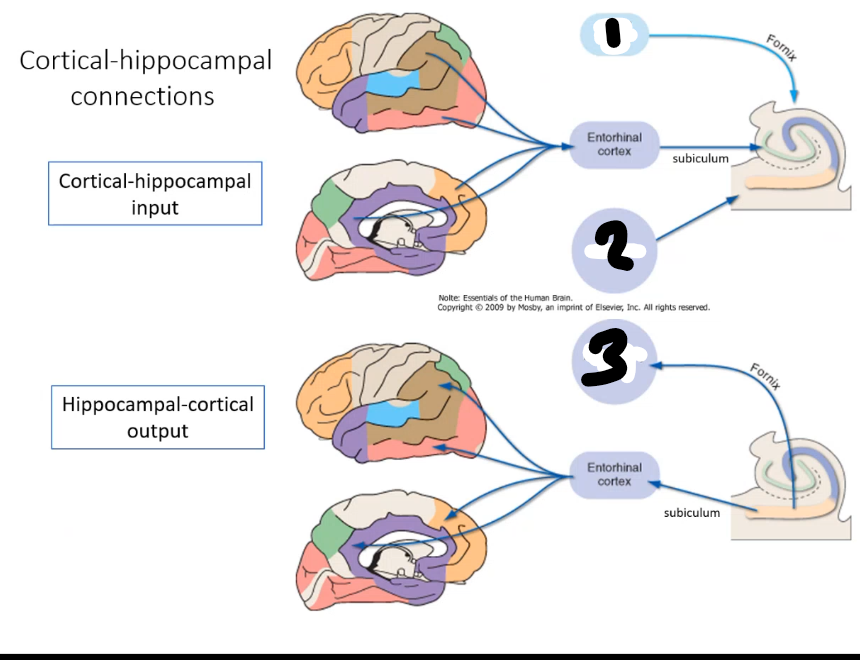
1 is a relay station between hippocampus and hypothalmus involved in emotional memory, reward and motivation
1 septal nuclei 2 Amygdala 3 mamillary body
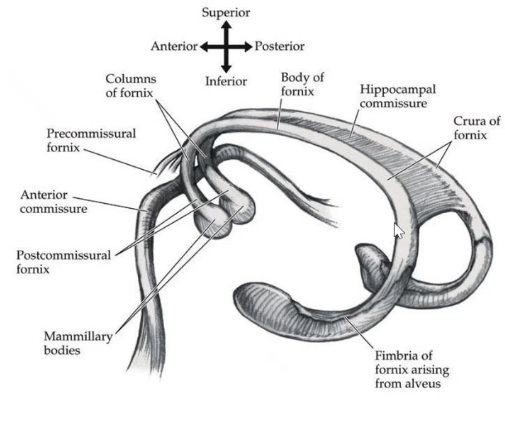
_____ converge in midline to become the fornix, it goes forward splitting into columns which goes to _____ ______ (postcommissural) and to the ______ (precommisural)
fimbria mamillary bodies septum
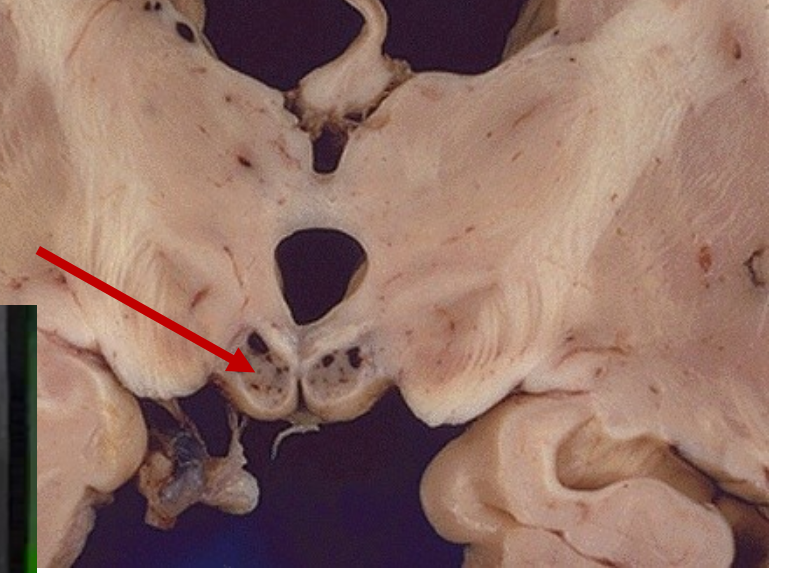
_____ syndrome results in memory loss caused by lack of ______ especially in chronic alcoholics, patietns may ______ or fill in gaps in memory with falsification, this can cause lesions to the _____ ______
korsakoff thiamine confabulate mamillary bodies
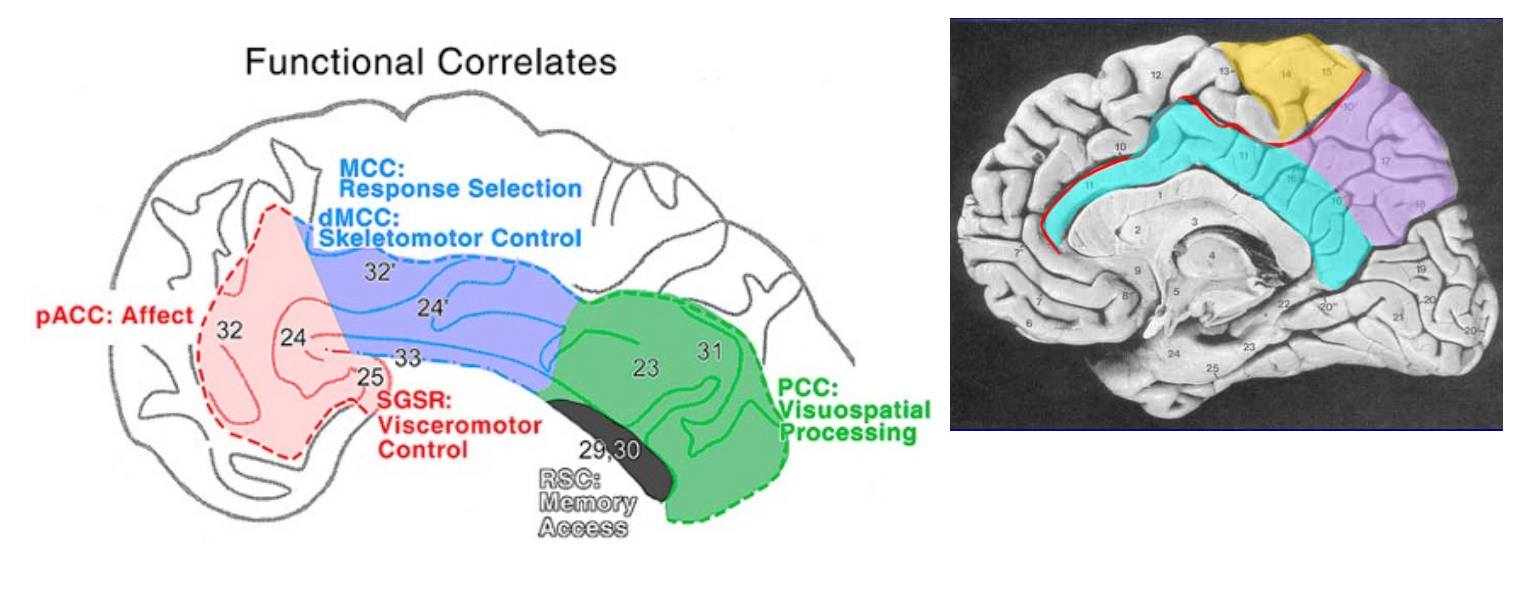
1 is the _____ _____, which receives input from ____ ____ of thalamus and _____, _____, and _____ visual cortex, connects to parahippocampal cortex through the _____ bundle
cingulate gyrus anterior nucleus frontal somatosensory anterior cingulum
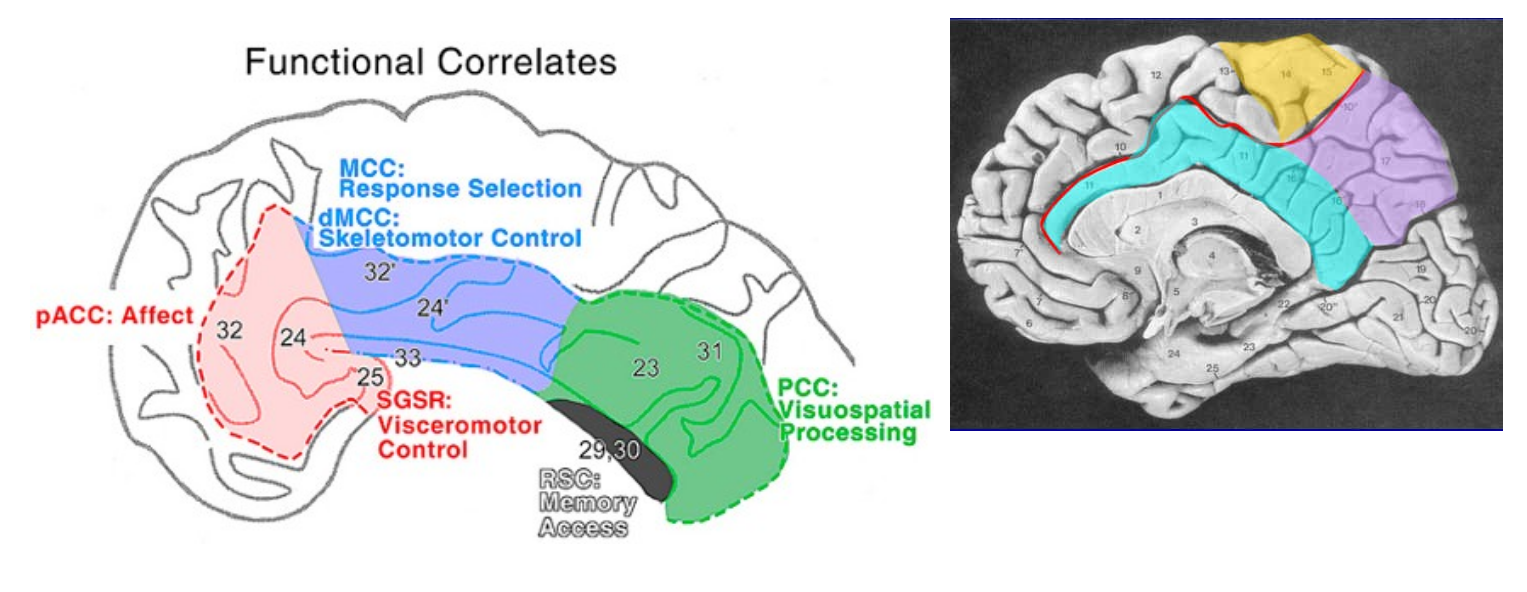
_____ ____ primary function is emotional processing, learning, and emotional memory. Attention flexibility (shifting attention, moving from idea to idea), empathy, there is an abnormal structure and function in _________. _____ region is involved in attention and emotional processing, ______ region is involved in motor planning and pain processing, _____ region is involved in memory retrieval and visual spaltial stuff
cingulate gyrus schizophrenics anterior medial posterior
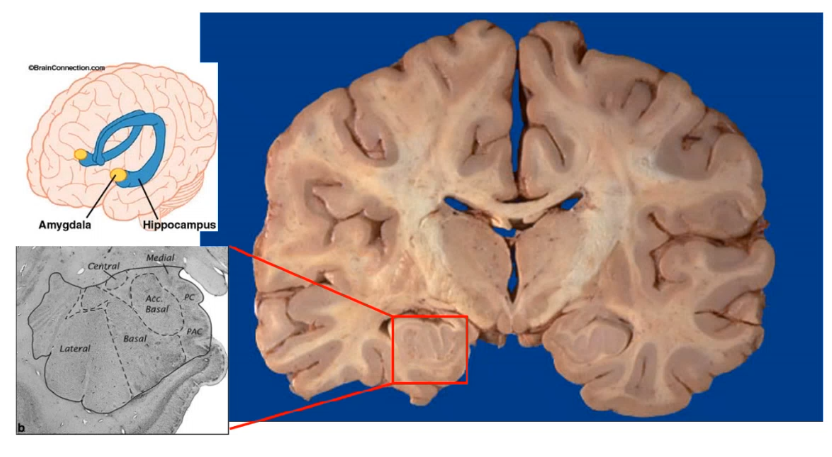
_____ receives preprocessed sensation (tacile, vsual, auditory , visceral) then projects to cerebral cortex and hypothalamus, involved in anger and fear recognition.
Position is similar to hypothalamus but is more anterior, hippo campus will have a c shape in coronal view
amygdala
there are two pathways from thalamus to Amygdala, the ____ road goes from thalamus to sensory cortex then Amygdala and is more accurate and slow (realizing that a shadow is just a coat), ____ road goes direcyl from thalamus to amygdala and is fast (jumping at a shadow)
high low
the ______ can inhibt control of ______ _____ in high stress situations for rapid decision making
Amygdala prefrontal cortex
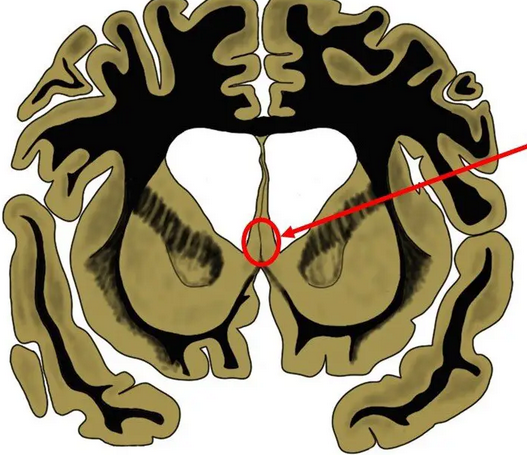
_____ ____ serve as relay of afferent cholinergics (acetylcholine) from ______ to hypothalamus, functions in ____ rage and _____ _____, also has efferent connections to _____ cortex
septal nuclei hippocampus septal emotional memory prefrontal
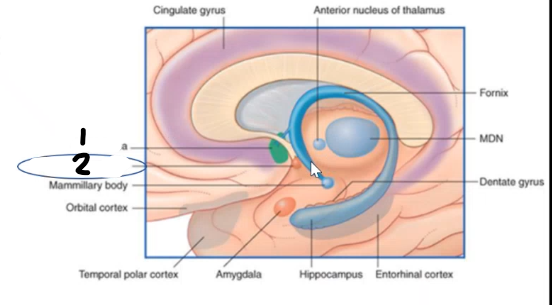
1 is the ______ _____, 2 is the _____ _____ aka the ventral striatum where the _____ and ____ meet, important for reward and pleasure, the ____ ____ _____ pass through both 1 and 2 and connects VTA and brain stem (electric stimulation of MFB = intense reward in animal studies)
septal nuclei nucleus accumbens caudate putamen medial forebrain bundle
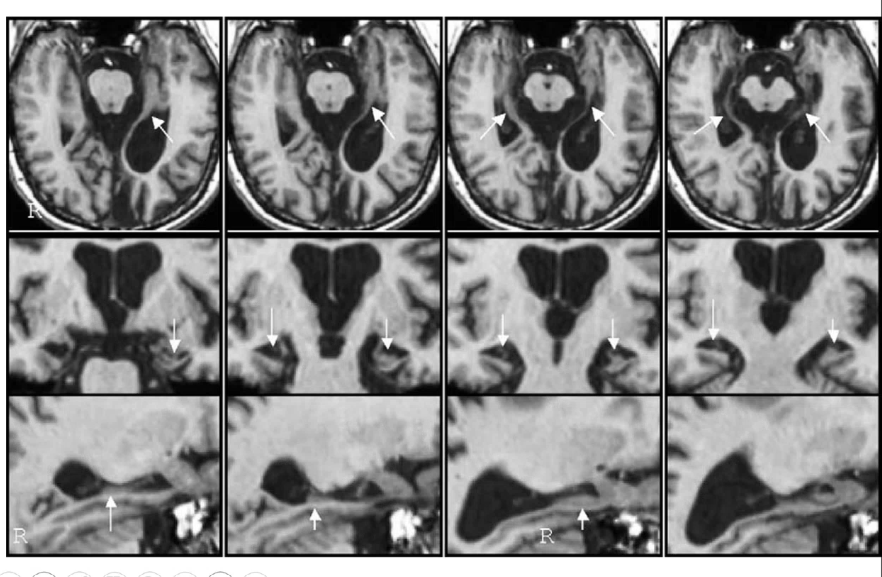
anterograde amnesia with retrograde amnesia is most likely lesion in _______ and sonicated structures in medial temporal lobe
hippocampus
alcohol abuse, with malnutrition and dehydration, presents with delusions hallucinations, unable to recall why hes in hospital and doesn’t know age, mostly likely diagnoses is ______ syndrome
korsakoff
_____ _____ is primarly involved in addiction
nucleus accumbens
a patient with anterograde amnesia would have a lesion in the _____, they have would have weak skilled memory but unable to make episodic or declarative memories
hippocampus
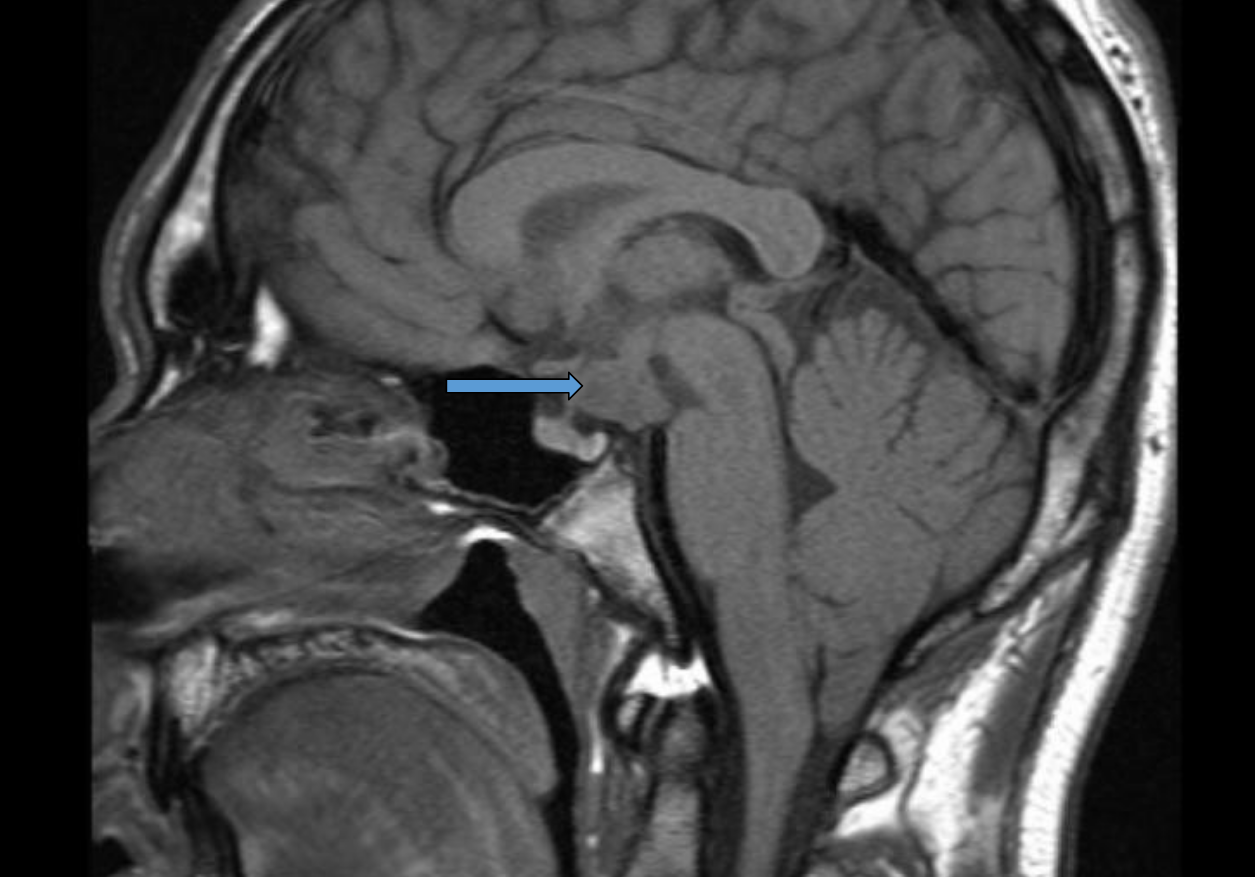
patient presents with auditory hallucinations, sexual aggressiveness, destructive behavior, hypersomnolence, most likely ____ _____ syndrome (sleeping beuty syndrome), MRI shows patietn with tumor where _______ should be
klein levens hypothalamus
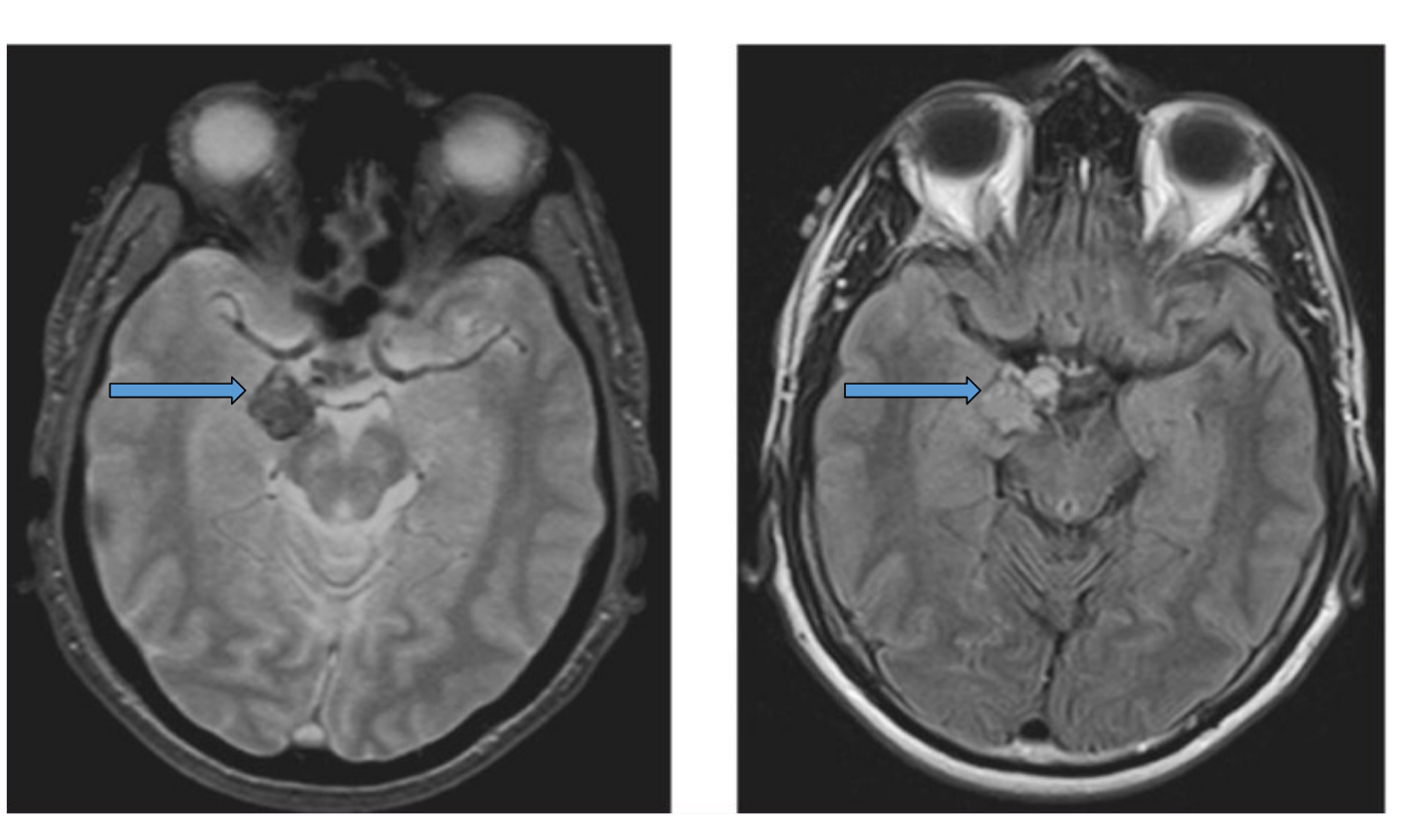
patients presents with difficulty findings words, hyper sexual behavior, flirtatious, patient most likely has damage to her _____ and ___ _____ syndrome, damage could be bilateral or unilateral
Amygdala kluver bucy
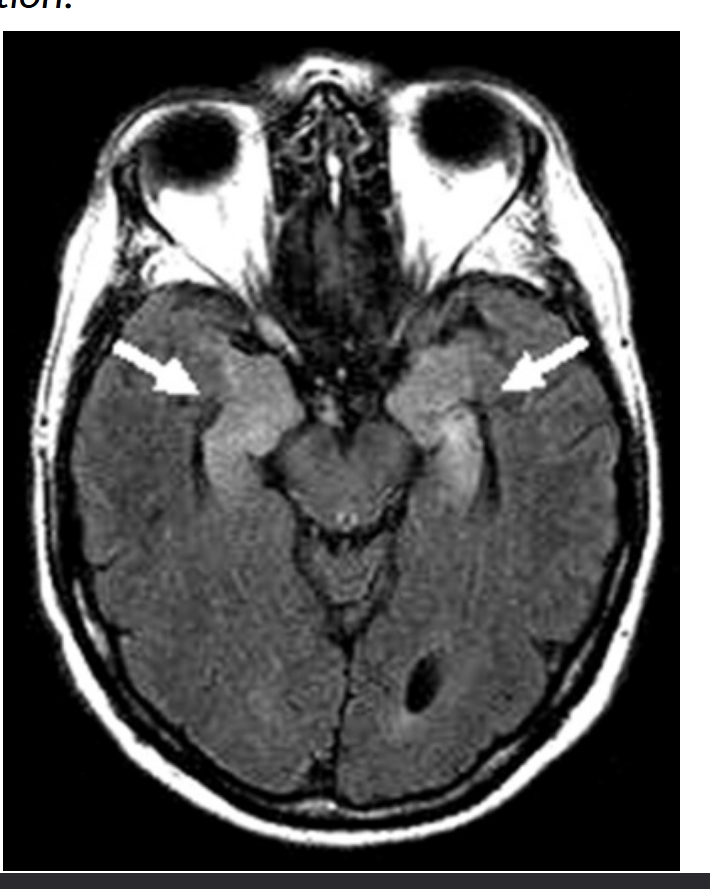
patient presents with apathy, confusion, memory difficulty, disorientation, sexual disinhibition, MRI shows white fattening in limbic system (amygala and hippocampus) , patient has _____ ______ where antibodies (gaba-b) target the limbic system, chest x ray showed lung masses which were cancerous
limbic encephalitis
Patient is unable to follow commands, and sometimes does not respond at all when asked questions. abscense of willpower and ability to act in decisive way. this is caused by problems with _____ _____
prefrontal cortex
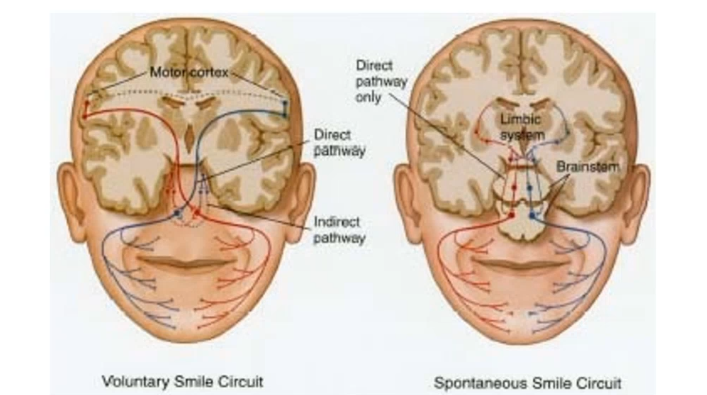
voluntary smile comes from motor cortex, but spontaneous smile comes from _____ system and more specifically the ____ _____
limbic basal ganglia