Histology Quiz 7
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
1
New cards
spleen
Only lymphoid organ that specifically filters blood
2
New cards
spleen
abdominal organ with both immune andnon-immune functions
3
New cards
Lymph nodes
encapsulated immune organs distributed along lymphatic vessels
4
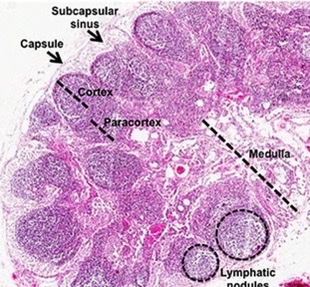
New cards
lymph node
what secondary lymphoid tissue?
5
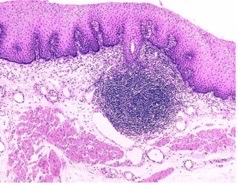
New cards
transient MALT
what secondary lymphoid tissue?
6
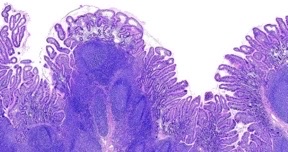
New cards
peyer’s patches
what secondary lymphoid tissue?
7
New cards
MALT
immune cells diffusely distributed throughout linings \n (mucosa) of digestive, respiratory, and urogenital tracts
8
New cards
recycling of old RBCs
additional non-immune function of spleen
9
New cards
intermingled red and white pulp
interior of spleen
10
New cards
capsule
outer region of spleen
11
New cards
RBC recycling
function of red pulp
12
New cards
immune fuction
fuction of white pulp
13
New cards
stave cells
specialized cells that line sinuses in the spleen to create gaps
14
New cards
healthy
what type of rbcs are inside sinusoids?
15
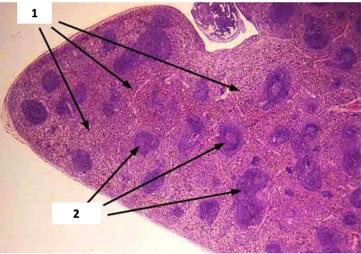
New cards
red pulp, white pulp
1 and 2
16
New cards
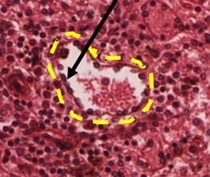
sinusoid, stave cells
identify the outlined spleen structure and the cells in it
17
New cards
digestion and nutrient absorption
fuctions of digestive system
18
New cards
GI tract
long, continuous, compartmentalized tube \\n through which food moves
19
New cards
oral mucosa
– Tissues lining the inside of the mouth (inner lips, \n cheeks, palates) \n – Consists of epithelium and underlying CT
20
New cards
stratified squamous non-keratinized
what type of epithelium in the oral mucosa?
21
New cards
loose ct then dense irregular ct w/ structures
underlies epitheium in oral mucosa
22
New cards
mechanical breakdown of food and sense of taste
fuction of tongue
23
New cards
skeletal
internal muscle in tounge
24
New cards
papillae
line dorsal surface of tounge to assist w/ food breakdown and taste
25
New cards
alternating perpendicular layers
how are the fascicles of the tongue arranged to allow movement in multiple directions?
26
New cards
lingual tonsils
occupies posterior third of toungue
27
New cards
filliform
\-papillae that are pointed for friction during chewing; most abundant
– No taste buds
– No taste buds
28
New cards
fungiform
Abundant papillae, rounded tops, with taste buds
29
New cards
Vallate
– Large, only 8-12, at back of tongue \n – Abundant taste buds and salivary glands
30
New cards
foliate
* papillae on sides of tongue \n – Rounded; with tastebuds
31
New cards
filiform
what type of papillae have partially keratinized epithelium?
32
New cards
fungiform have taste buds on top, foliate have them on the sides
how do foliate and fungiform papillae differ structurally?
33
New cards
vallate
what type of papillae have moats along their sides?
34
New cards
taste receptor cells
taste bud cells that sense flavor through microvilli and generate signal; larger nuclei
35
New cards
basal cells
act as stem cells; smaller and located at bottom of taste bud
36
New cards
pore
opening that allows taste receptor cells access tofood
37
New cards
nerve
transmits info from taste bud to brain
38
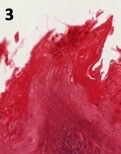
New cards
filiform
what type of papillae?
39
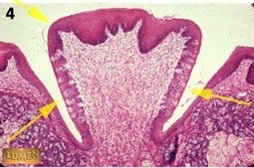
New cards
vallate
what type of papillae?
40
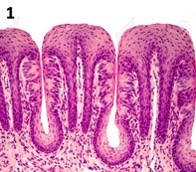
New cards
foliate
what type of papillae?
41
New cards
fungiform
what type of papillae?
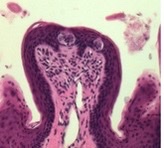
42
New cards
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa
four layers always present in GI tract (inner to outer)
43
New cards
epithelium, lamina propria (loose ct), muscularis mucosum
what makes up the mucosa layer of GI tract
44
New cards
thin layer of smooth muscle in mucosa
what is the muscularis mucosum?
45
New cards
dense irregular CT and embedded strusctures
components of submucosa
46
New cards
smooth muscle layers
what makes up the muscularis externa
47
New cards
outer mesothelium, connects to hold organs in place
what is the serosa
48
New cards
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
layers of GI tract
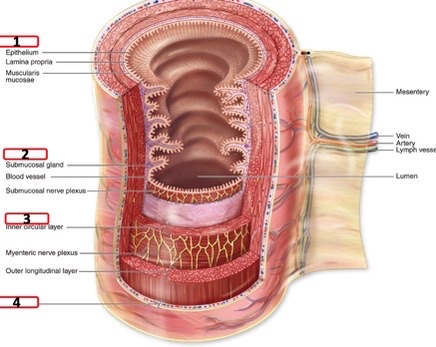
49
New cards
carry food from oral cavity to stomach
primary function of esophagus
50
New cards
non-keratinized stratified squamous
epithelium found in esophagus mucosa
51
New cards
mucous glands
glands embedded in esophagus submucosa
52
New cards
mucous glands
– Lined with simple columnar or cuboidal epithelium with pale staining secretions, ducts connect to lumen \n –helps lubricate food and protect epithelium
53
New cards
top of esophagus muscularis
where might you find skeletal muscle in the GI tract?
54
New cards
2
how many layers typically present in esophageal muscularis
55
New cards
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa
name the esophageal layers (inside to outside)
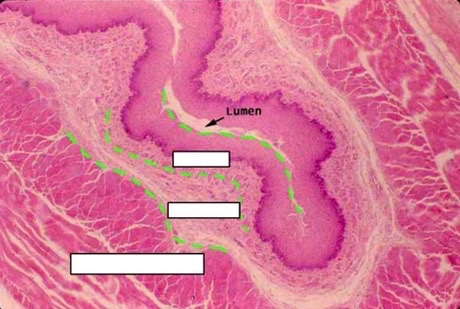
56
New cards
chemical and mechanical digestion, storage of food
stomach functions
57
New cards
cardiac, fundic, body, pyloric
4 regions of stomach
58
New cards
thick, layered smooth muscle for mechanical digestion
characteristics of stomach muscularis, why?
59
New cards
rugae
folds in stomach submucosa that can stretch to increase stomach size
60
New cards
gastric pits
glands in stomach mucosa
61
New cards
chemical digestion
function of stomach mucosa glands/ secretory cells
62
New cards
pits, glands
Stomach epithelium is flat on top, but has invaginations called gastric _________ that lead to g______
63
New cards
cardiac and pyloric stomachs, they don’t contribute to chemical digestion, only produce mucous
which stomach regions have less extensive pits and glands? why?
64
New cards
surface mucous cells
\-Line the gastric pits \n – Pronounced columnar shape \n – Mucous secretions will result in lightly staining cytoplasm
65
New cards
mucous neck cells
\-Located in isthmus/neck, and less columnar than surface cells
\-light staining cytoplasm form mucous secretion
\-light staining cytoplasm form mucous secretion
66
New cards
parietal cells
\-Located in neck and gastric glands \n – Secrete HCl into lumen for chemical digestion, and bicarbonate ions into submucosa to neutralize pH
67
New cards
acidophilic due to lots of mitochondria
staining of parietal cell and why
68
New cards
acidophilic and non-polarized with central nuclei
Appearance of parietal cells
69
New cards
secrete digestive enzymes for chemical digestion
function of chief cells
70
New cards
Basophilic and polarized
Appearance of chief cells
71
New cards
surface mucous cells, parietal cells, chief cells
1, arrows, 2
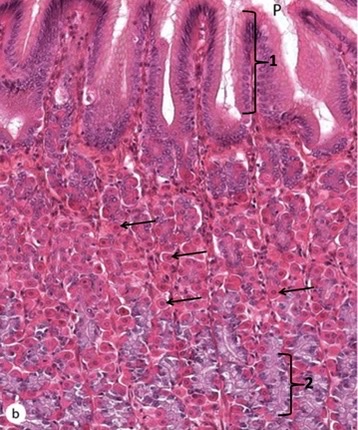
72
New cards
chemical digestion, nutrient absorption
small intestine functions
73
New cards
plica
permenant folds in walls of small intestine that increase surface area
74
New cards
villi
intestine projections towards lumen to increase SA with internal structure formed by lamina propria
75
New cards
microvillae
projections from apical surface of epithelial cells to increase surface area
76
New cards
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, plicae, villae
1,2,3,4,5
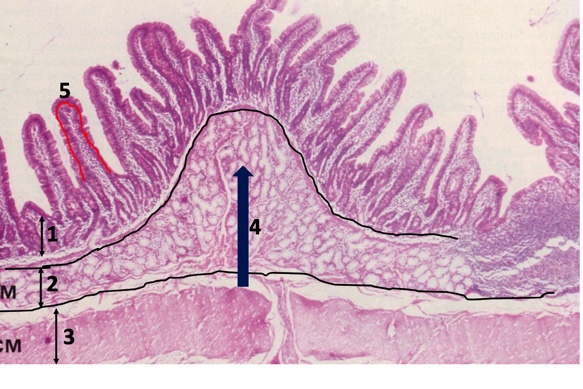
77
New cards
crypts
invaginations at bases of villi