Chapter 3: Bonding & Chemical Interactions (12%)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
less
More vs. Less
Elements with an incomplete octet are stable with ______ than 8 electrons
EX: H, He, Li, Be, and B
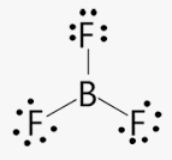
more
More vs. Less
Elements with an expanded octet are stable with ______ than 8 electrons
EX: all elements in period 3 or greater
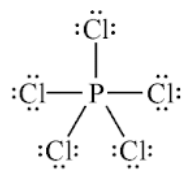
odd
Even vs. Odd
Compounds with an _____ number of electrons CANNOT have 8 electrons in each element
low, high
High vs. Low
Ionic bonds are formed via the transfer of one or more electrons from an element with a relatively _____ ionization energy to an element with a relatively _____ electron affinity

electronegativities, 1.7
Ionic bonds occur between elements with large differences in _______________ (> ___), usually between metals and nonmetals
crystalline lattices
Ionic compounds form ____________ _________ → large, organized arrays of ions
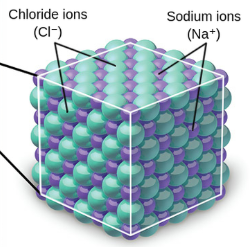
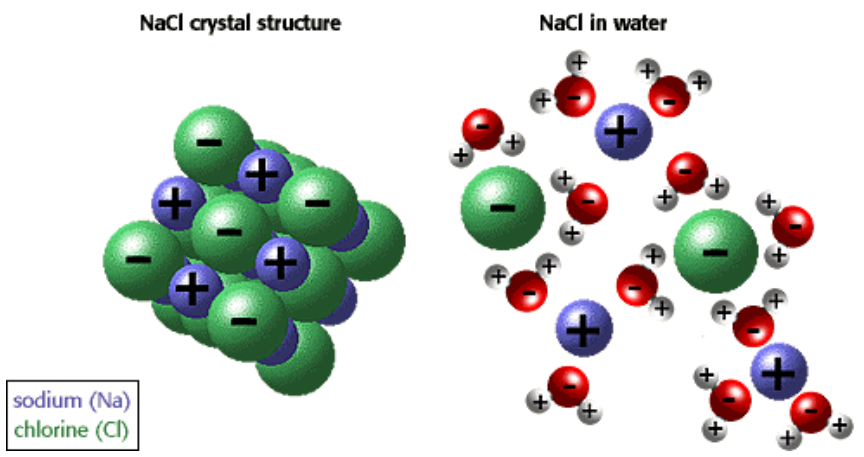
dissolve
Ionic compounds tend to _________ in water and other polar solvents
high
High vs. Low
Ionic solids tend to have ______ melting and boiling points
lose, cations
In ionic bonds, metals _____ electrons to become ________
gain, anions
In ionic bonds, nonmetals ______ electrons to become ________
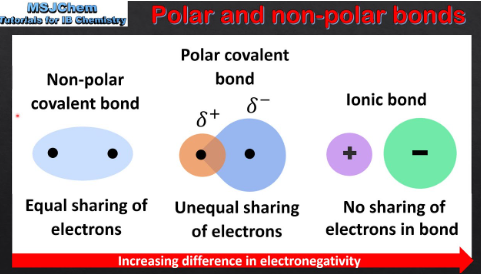
electronegativities
A covalent bond is formed via the sharing of electrons between two elements of similar __________________
bond order
Refers to whether a covalent bond is a single, double, or triple bond
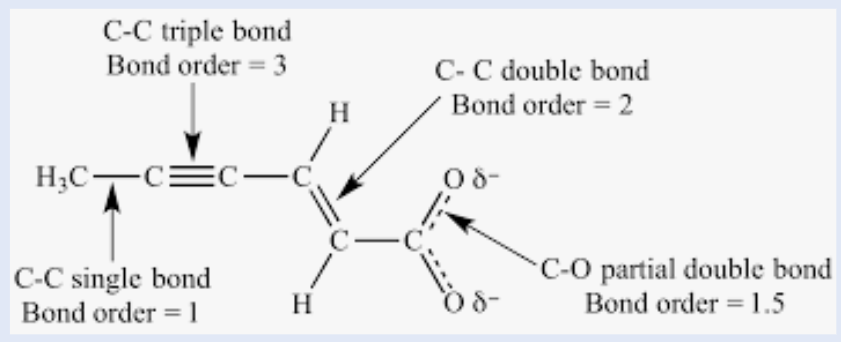
increases, increases, decreases
As bond order increases, bond strength __________, bond energy __________, and bond length ___________.
0.5, electronegativity
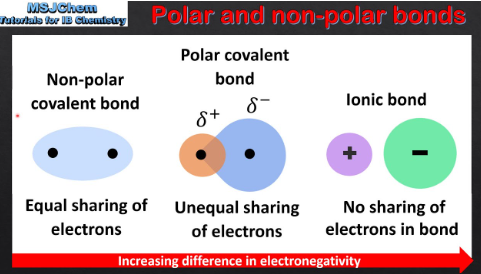
Nonpolar covalent bonds result in molecules in which both atoms have exactly the same (or <___ difference in) ________________
H, N, O, F, Cl, Br, I
Name the 7 naturally occurring diatomic elements that form nonpolar bonds with an atom of the same element (aka naturally in the “X2” form)
electronegativities, 0.5, 1.7, ionic
Polar covalent bonds form when there is a significant difference in ________________ (___ to ___), but NOT enough to transfer electrons and form an ______ bond.
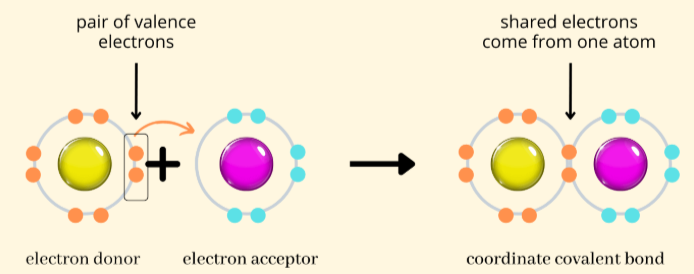
coordinate covalent bonds (or dative bonds)
Result when a single atom provides both bonding electrons while the other atom does not contribute any electrons
Most often found in Lewis acid-base chemistry
Lewis dot structures
A chemical representation of an atom’s valence electrons
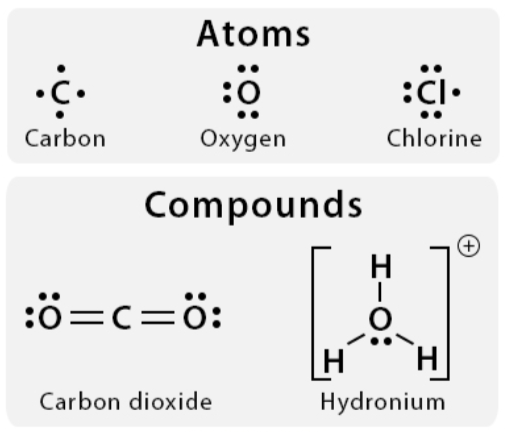
valence electrons
The number of dots in a Lewis structure = the number of ________ ________ for that element
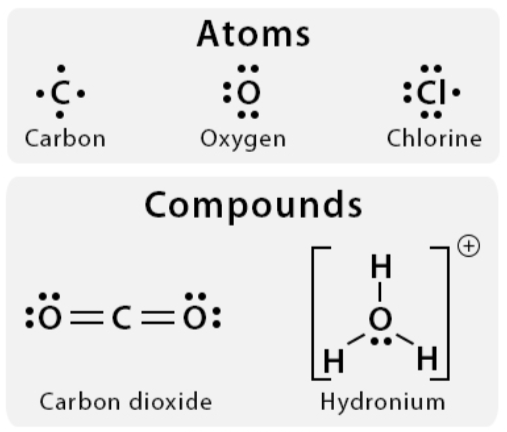
valence electrons
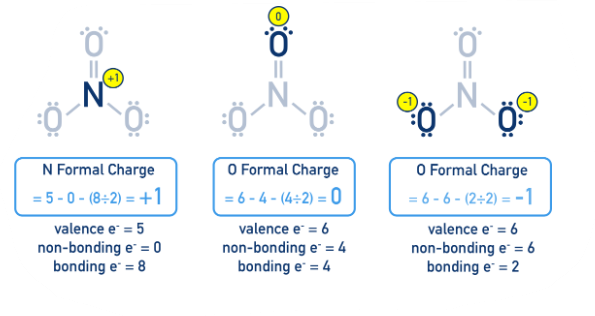
Formal charges exist when an atom is surrounded by more or fewer _________ _________ than it has in its neutral state
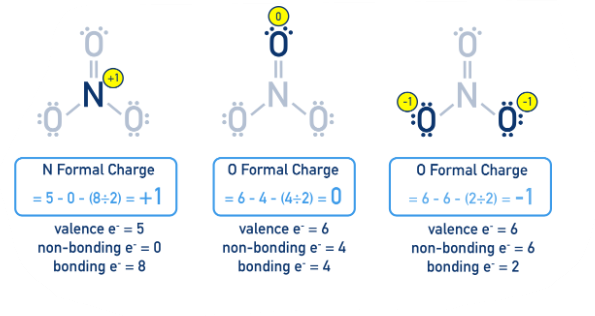
# of valence electrons - # of dots (lone electrons) - # of lines (covalent bonds)
Formula for calculating an atom’s formal charge
resonance structures
For any molecule with a pi system of electrons (aka double/triple bonds), _____________ ____________ exist
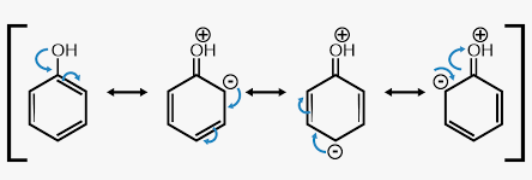
resonance structures
Represent all of the possible configurations of electrons (both stable and unstable) that contribute to the overall structure
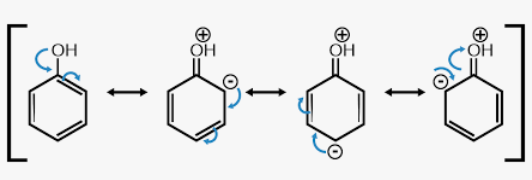
contributes, resonance hybrid
The more stable the resonance structure, the more it ___________ to the character of the ___________ _________
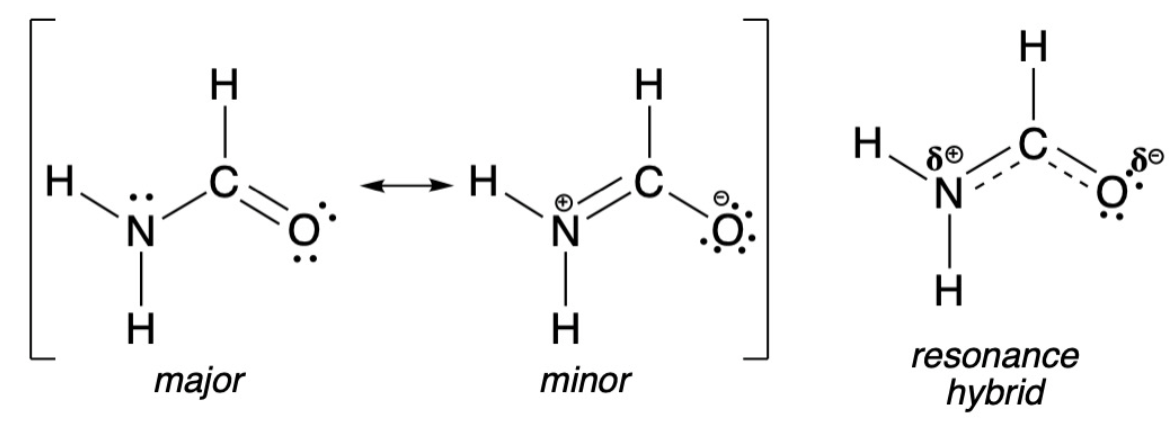
1, 0
A single bond consists of ___ sigma (σ) bond(s) and ___ pi (π) bond(s)
1, 1
A double bond consists of ___ sigma (σ) bond(s) and ___ pi (π) bond(s)
1, 2
A triple bond consists of ___ sigma (σ) bond(s) and ___ pi (π) bond(s)
VSEPR theory
Proposes that electrons, whether bonding or nonbonding, arrange themselves to be as far apart as possible from each other in 3D space, leading to characteristic geometries
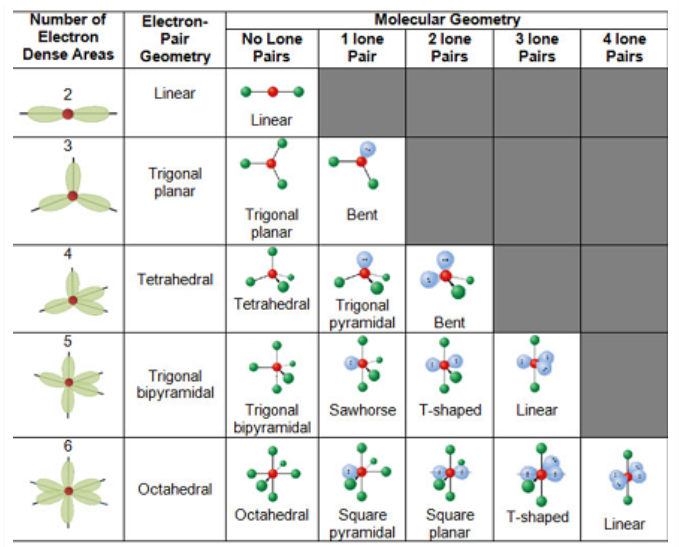
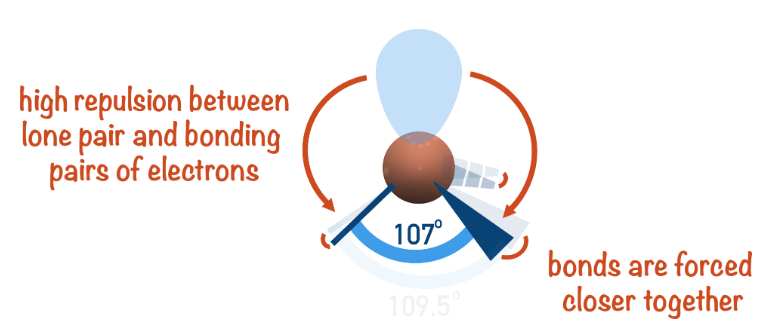
more
Less vs. More
According to the VSEPR theory, nonbonding electrons exert ______ repulsion than bonding electrons because they reside closer to the nucleus
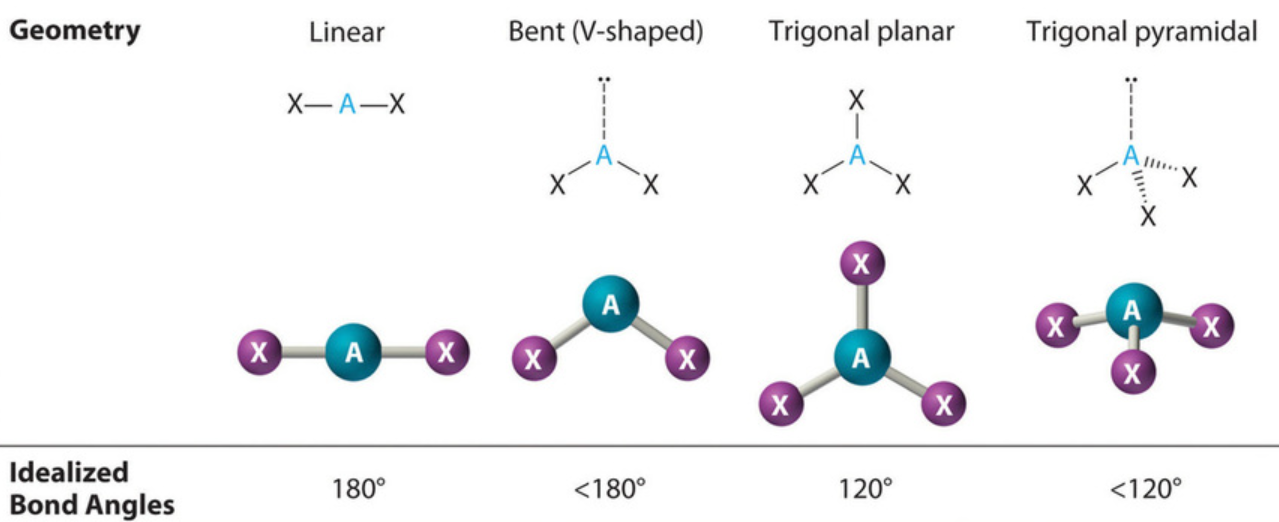
electronic geometry
Electronic Geometry vs. Molecular Geometry
Describes the spatial arrangement of all pairs of electrons around the central atom, including both the bonding and the lone pairs
Used in the determination of the ideal bond angle
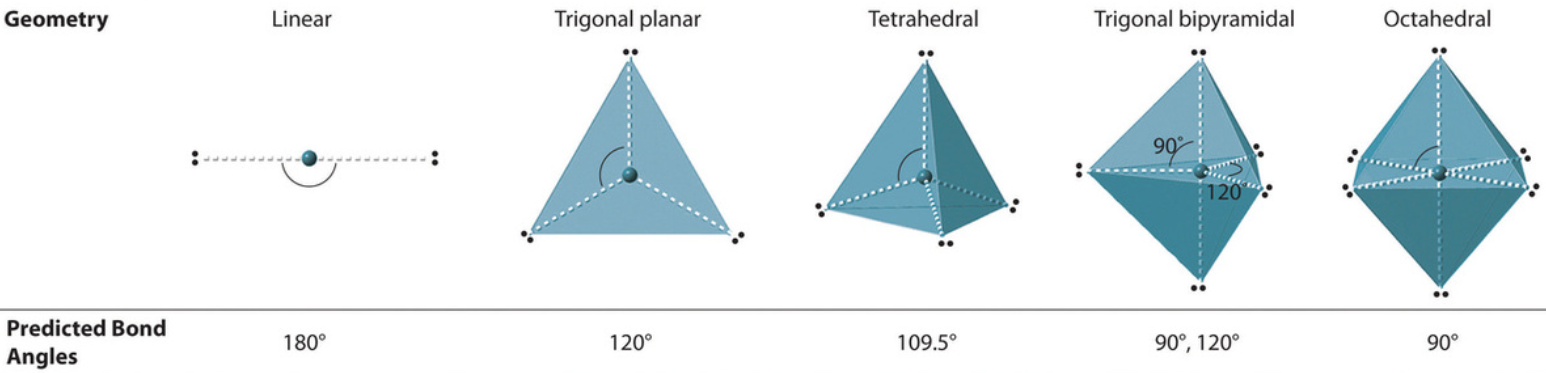
molecular geometry
Electronic Geometry vs. Molecular Geometry
Describes the spatial arrangement of ONLY the bonding pairs of electrons around the central atom
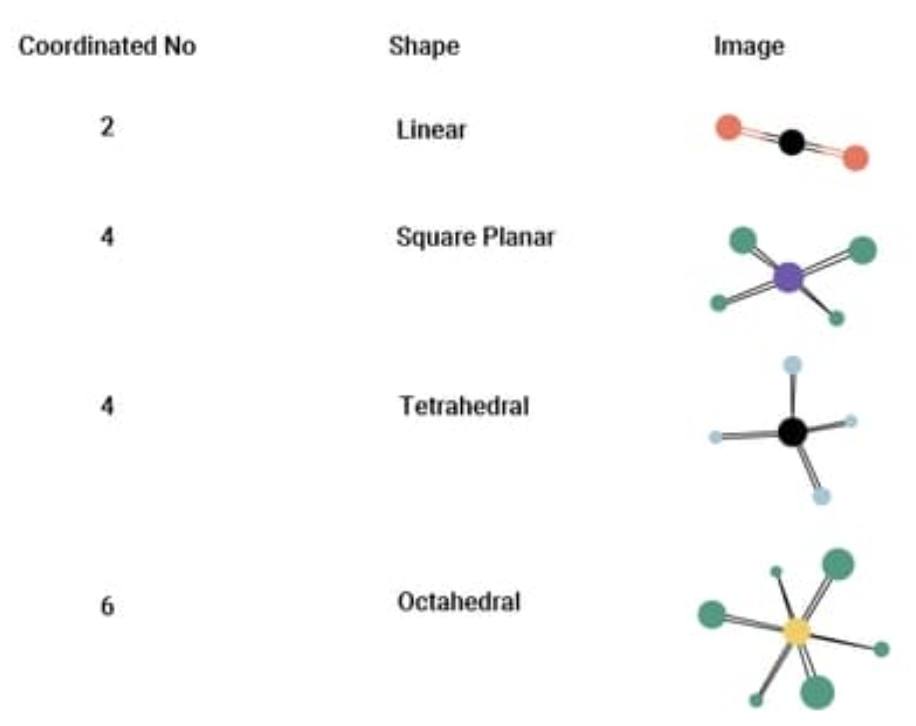
The coordination number is the relevant factor
coordination number
The total number of atoms, ions, or ligand atoms directly bonded to a central atom in a molecule or crystal
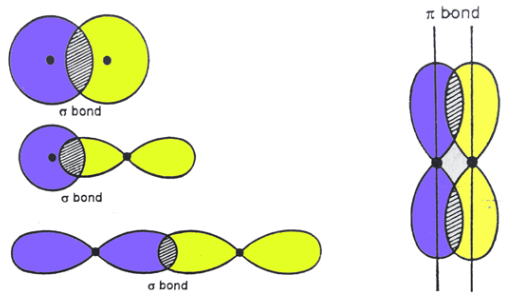
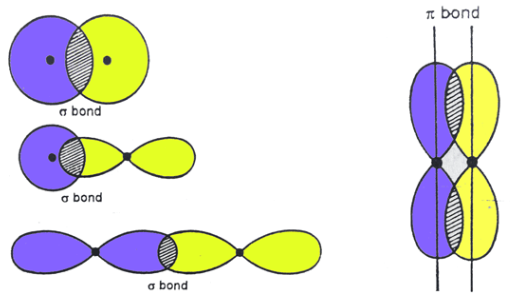
overlap
sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds describe the patterns of _________ observed when molecular bonds are formed
atomic, molecular
When two atoms bond to form a compound, the _______ orbitals interact to form a ____________ orbital which describes the probability of finding the bonding electrons in a given space
single atom, molecule
ATOMIC orbitals describe the probable location of electrons around a ________ ______, while MOLECULAR orbitals describe the probable location of electrons in a ____________.
sigma bonds
Sigma Bonds vs. Pi Bonds
The result of head-to-head overlap
Allow for free rotation about the axes
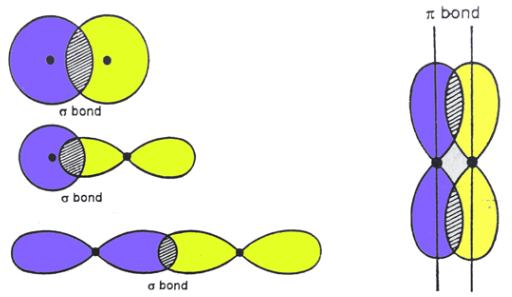
pi bonds
Sigma Bonds vs. Pi Bonds
The result of the overlap of two parallel electron cloud densities
Do NOT allow for free rotation about the axes
weaker
Are covalent bonds STRONGER or WEAKER than ionic bonds?
weaker
Are intermolecular forces STRONGER or WEAKER than covalent bonds?
London dispersion forces
London Dispersion Forces vs. Dipole-Dipole Interactions vs. Hydrogen Bonds
The weakest of the intermolecular interactions
The result of induced dipoles that change and shift moment to moment
Present in all atoms and molecules
A type of van der Waals force
Temporary
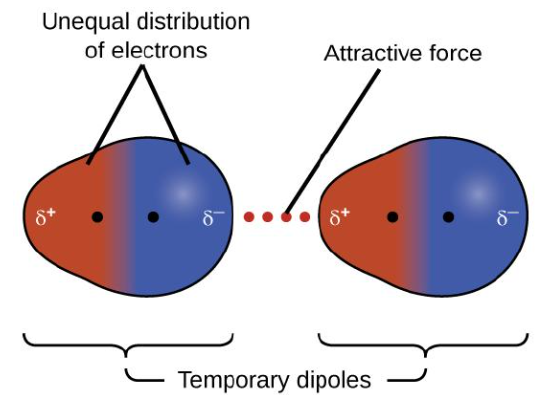
increase, large, polarizable
London dispersion forces __________ as the size of the atom or structure increases because ______ molecules are more easily _____________
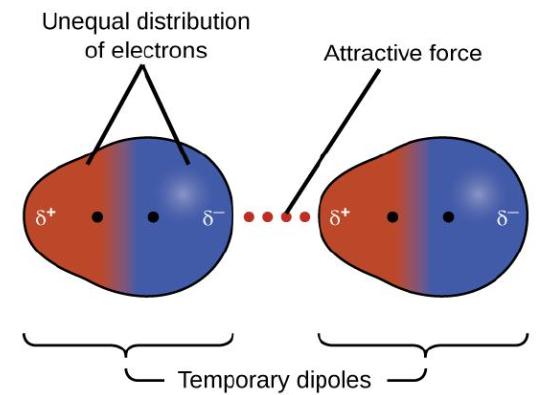
dipole-dipole interactions
London Dispersion Forces vs. Dipole-Dipole Interactions vs. Hydrogen Bonds
Occurs between the oppositely charged ends of polar molecules
Stronger than London forces
Evident in the solid and liquid phases
Negligible in the gas phase due to the distance between particles
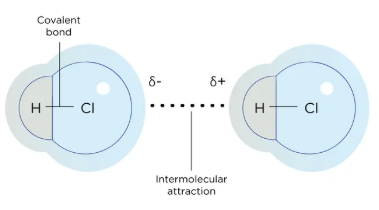
hydrogen bonds
London Dispersion Forces vs. Dipole-Dipole Interactions vs. Hydrogen Bonds
A specialized subset of dipole-dipole interactions
Occurs when hydrogen is bonded to 1 of 3 very electronegative atoms → F, O, or N
high
High vs. Low
Substances that display hydrogen bonding tend to have unusually _____ boiling points