Botany of modern medicine- Plant/Human biology, the skin, head, and face
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
plant/human interactions
respiratory, gastrointestinal, topical, olfactory, intravenous
natural substances
substances used in medicine that are unaltered
semi synthetic
laboratory substitutions to a natural substance
synthetic
compound made in a lab
homeopathic medicine
incredibly diluted natural substances that are basically ineffective
flowers
produce pollen or ovules that become seeds in the fruit
fruit
anything that houses seeds
primary metabolites
basic cell structures like DNA, RNA or organelles
secondary metabolites
non essential plant structures
terpenes (IMAGINE ONE)
multiple fused non aromatic carbon rings, use isoprene as a monomer
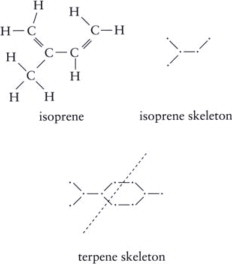
phenylpropanoids
composed of benzene rings
alkaloids
secondary metabolite containing nitrogen
polyketides
three carbon ring units like THC or CBD, tend to be toxic
flavonoids
a phenylpropanoid combined with a polyketide, 2 rings that branch to another ring, known for antioxidant properties
glycosides
a sugar and a non sugar connected by oxygen atoms
vehicle
treatment that replicates drug delivery
sham
completes all procedure except for the experimental one
endogenous
a substance that is produced within the body
exogenous
a substance that cannot be produced inside the body
amphipathic molecules
have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties
exogenous interactions
molecules that may disrupt enzymes, amphipathic molecules, GPCRs, ion channels, and DNA/cell membranes
antioxidants
prevent the change of molecular structure by reducing free radicals
reactive oxygen species
highly reactive forms of oxygen that are harmful to the body
inflammation
the body's reaction to fix something that involves the delivery of platelets and white blood cells
viruses
the largest population of prokaryotes on the skin
collagen
one of the most abundant proteins in animals that uses vitamin C in its pathway
fibrils
structures made of collagen that are vital to multicellularity and the extracellular matrix
epidermis
outermost layer of skin
dermis
middle layer of skin
atopic dermatitis
inflammation of the skin where skin cells are help together loosely, which leads to penetration of allergens and inflammation
SCORAD
Scoring of Atopic Dermatitis Index that involves extent and intensity of disease as well as pruritis and sleep loss- the higher the number, the worse the condition
transepidermal water loss
Abbreviated TEWL; water loss caused by evaporation on the skin's surface.
coconut oil
seed oil rich in lauric and myristic acid, good treatment for atopic dermatitis, saturated fat
olive oil
oil from oily fruits high in oleic acid and phenylpropanoids, unsaturated fat, can act as an antioxidant
honey
used to treat wounds, produces hydrogen peroxide and contains flavonoids and vitamins
eicosanoids
compounds such as prostaglandins and thromboxane that are synthesized by COX1 and aid in wound healing (signaling molecules), produced from omega-3 or omega-6 fatty acids
aspirin
acetylates COX enzymes and inhibits COX1 and the inflammatory response, can slow wound healing, based on a willow tree molecule
acne
clogged duct in your skin, often involves strains of cutibacterium acne
tea tree oil
contains mostly terpene structures like terpinen-4-ol and terpinene
citronella grass
citronellal from leaves can be used as a repellant, terpene molecule
beautyberry
callicarpenal harvested from leaves as a repellant, terpene molecule, highly effective
anacardiacae
plants that tend to be toxic or harmful to humans
poison ivy
contains a urushiol compound that causes an adverse reaction in humans, polyketide molecules
mango
fruit that contains resorcinol, may cause the same reaction as poison ivy in some
manchineel
contains huratoxin, toxic tree in Florida that produces sweet fruit
furocoumarin
phototoxic agent produced by apiaceae, rutaceae, and moraceae, polyketides
apiaceae
carrot/celery family
rutaceae
Citrus family
moraceae
fig family
bloodroot
promoted as a topical cancer treatment, is escharotic, contains sanguinarine
escharotic
causes tissue death (necrotic and apoptotic)
nettles
stinging hairs that contain acetylcholine and serotonin, depolarize neurons
prickly pear
mechanical dermatitis, contain barbed glochids and crystallized cellulose
dandruff
flaky scalp, uses tea tree oil as treatment
sclera
white protective layer of the eye
inner retina
location of photoreceptive sensory cells, continuous with optic nerve
choroid
middle, vascular layer of the eye, between the retina and the sclera
iris sphincter
constricts pupil
ciliary body
Structure surrounding the lens that connects the choroid and iris. It contains ciliary muscles, which control the shape of the lens, and it secretes aqueous humor.
aqueous humor
fluid in the eye, found between the cornea and the lens
acetylcholine
causes contraction of ciliary body and iris sphincter
pilocarpus sp.
agonist of muscarinic antagonist
atropine
muscarinic agonist, historically used to dilate pupils
tropicamide
synthetic muscarinic antagonist
glaucoma
collapsed eye canal
pilocarpine
potential treatment for glaucoma, will cause aqueous humor to contract and flow
cannabis
has been used in the treatment of glaucoma, contains polyketides, inhibitory to muscarinic GPCR and will hyper polarize neurons
diabetic retinopathy
hyperglycemia in the eye, leads to cellular damage of the retina and blood vessels, excess fructose damages proteins
pericyte death
cells wrap around vessels, can be a side effect of diabetic retinopathy
onion
releases syn-propanethial-s-oxide which causes eyes to burn
headaches and migraines
can be caused by inflammation, activates pain sensing nerves through TRPA1 agonists, high CGRP1 activity, low 5-HT activity
CGRP1
calcitonin gene-related peptide activity
headache tree
agonist of TRPA1 channel which leads to CGRP1 release and inflammation/pain signal
caffeine
antagonizes adenosine receptors
salivary a-amylase
breaks down starch, multiple copies in humans, inactivated by stomach pH
lipase
breaks down lipids
hydroxyapatite
mineral compound that makes up teeth
acidification
demineralization of the teeth caused by low pH found in sugary compounds
caries
cavities
plaque
microorganism films on teeth
stevioside
glycoside sweetener extracted from South American plant
m3 muscarinic receptors
increase saliva flow when agonized
cocaine
inhibits muscarinic receptors, linked to caries
sweet receptors
T1R2/T1R3 receptors activated by sugars, acid, and miraculin
gymnemic acid
antagonist of sweet receptors
miracle fruit
contains miraculin
umami receptors
T1R1/T1R3, activated by glutamate and aspartate amino acids
bitter receptors
T2Rs, around 25 different receptors in humans
multiple-ring structures
tend to agonize bitter receptors
periodontitis
inflammation of the gums that is negatively correlated with fruit and vegetable intake
sesame seed oil
good oil for oil pulling and oral health
araceae
plants that contain calcium oxalate crystals that cause stinging and edema
ethanol
obtained from drinking alcohol, increases cancer risk due to presence of acetaldehyde
tobacco
poses oral/lung cancer risk due to the formation of nitrosamines that bind to DNA