CompTIA A+ 1102 Windows Networking
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Shared Resources
- make a folder or printer available on the network
- share by mapping a drive letter to a share
- shares ending with a $ are hidden
- view shares in Administrative Tools/Computer Management
Mapping Drives
- needed to access a share on a remote device
- associates a drive letter with a share name
- view network shares in "This PC"
- create using "map network drive"
- or by using "net use [drive letter]: \\[server]\[name]" in command prompt
- disconnect a share in the toolbar or by right-clicking the drive
Sharing a Printer
- access the share function in printer properties, file explorer, or the settings application
- manage printer access under the security tab
Accessing a Shared Printer
add the printer to your system from file explorer or from the settings application
Proxy Settings
- a proxy seperates users from the internet
- access from settings > network and internet
- or control panel > internet options > connections > LAN settings
Network Locations
- determined automatically, but changeable in the network status menu
locations:
- private
- home or work network
- shares your device and allows for connections
- public
- provides no sharing or connectivity features
Network Paths
- viewable in file explorer, using the server name and the share name
Metered Connections
- managed under Network Settings
- set a data limit
- can modify application communication
Windows Defender Firewall
- integrated into Windows
- should always be turned on
- but, can temporarily disable from the main screen
- requires elevated permissions
- has different settings for each network type (public and private)
Windows Firewall Configuration Options (list)
- block all incoming connections
- ignores your exceptions
- the most secure option
- modify notifications
- app blocking
Firewall Options for an application
- block or allow by port number
- use predefined exceptions
- set custom rules
How Windows Systems get IP
With the DHCP, Windows can:
- provide automatic IP addressing, by default
- provides an APIPA if there's no static address assigned, and no DHCP server available
Automatic Private IP Addressing (acronym)
APIPA
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
- allows for local communication only, hence the name, link-local address
- provides no internet connectivity
(APIPA) Range
169.254.1.0 to 169.254.254.255
TCP/IP Host Addresses are made of:
- IP address (unique identifier)
- subnet mask (identifies the subnet)
- gateway (the route off the subnet to the rest of the world)
What is the IPv4 loopback IP address?
127.0.0.1
IPv4 DHCP configuration location
- control panel > network and sharing center > change adapter settings
- then, right click an adapter and click the properties option
- lastly, left click the IPv4 settings and choose properties
Network Setup
- control panel > network and sharing center
- a step-by-step wizard to set up a new connection or a new network
- many different connection options
VPN Concentrators
- used to securely connect to private, corporate devices from a remote site
- utilizes a private tunnel from your device, to the VPN concentrator, and vice versa
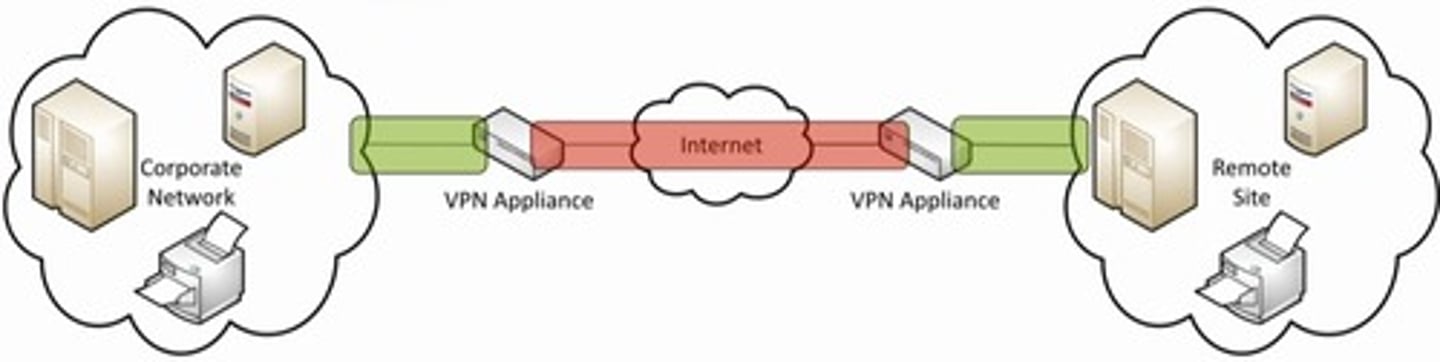
VPN Connections
- Windows includes a built-in VPN client
- can integrate a smart card for MFA
- once set up, use the network status icon on the taskbar to enable or disable the VPN
Wireless Network Setup
provide (to the wizard):
- network name (SSID)
- security type (encryption method)
- encryption type
- TKIP, AES
- security key
SSID (acronym)
service set identifier
Wired Connections
- plug and play, direct connections
- the fastest connection is the default
- modify this in properties
- can also configure alternate connection, here
WWAN Connections
- built-in mobile technology
- USB connected or 802.11 wireless technology
- tethering/hotspots
- usually requires a hardware adapter and antenna connections
- as well as third-party software