chapter 1-3 macro
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Why do economics exist?
To deal with the scarcity of resources and human wants.
study of how countries use resources to satisfy their unlimited needs or the individual want/
scarcity
imbalance of unlimited human wants and limited resources
Opportunity cost
cost of making a choice. it’s the next best alternative, subjective.
marginal analysis
the way desicions are made (based on current knowledge, hence marginal.) about deciding costs and benefits. The outcome benefits will be higher than the opportunity cost. MB >>MC
Incentive
something that encourages a change of behavior. The raised price of chocolate is an incentive not to buy chocolate.
three fundamental questions of market capital system
what to produce — decided by costumer behavior
how to produce— firm decision
for whom to produce— aka income, quantity and market value of resources owned. dollar votes.
economics interactions
gains of trade
market move through equilbrium
resources used up efficiently
markets lead to equilibrium
government involvement
Trade
done when marginal benefits for both parties is greater than their marginal costs. This happens b/c of specilizations.
markets move toward equilbirum
equilibrium is state where there’s no change. markets stop moving when they can’t be better off than they already are.
resources
using resources as efficiently and every opportunity to better oneself. Operating efficiently means someone has to to be worse off.
equity
hard to measure. To have equity, we sacifice efficiency
as long as gains exist,
people will exploite them/
governments involvement to make markets competeitive
welfare of society
level of consumption and good people enjoy
standard of living
cost of living
dollar amount of goods and services for a standard of living
economics flutations
rise of fall of production in the economy. the business cycle.
recession and expansion + unemployment and inflation
another person’s spending is another person’s income
a person spending on a good causes income of the reproducing the good increases
trade off
comparison of costs and benefits.
Positive economics
objective statements that can be proven right or wrong
normative economics
determining desirabilities of outcome based on valued judgement. Ex: should taxes be lowered to raise consumer spending to get out of a resession?
slope of ppc
= the oppertunity cost of horizontial axes.
rise/ run = a/b = opportunity cost of b
allocative economy
prioritize goods that consumers want in correct quanity. market capital economy may not achieve this.
differing abilities in producing various goods & services in that country.
specialization
Types of resources
Land is the bounty of the Earth: includes natural resources such as oil, coal, minerals, etc.
Labor includes both physical and mental human effort
Capital are the tools, equipment, and factories
Human capital is the educational achievements and skills of the labor force (which increase labor productivity).
Entreprenurship is the ability to organize resources & take risks to develop new ways of production and new products.
Technology
knowledge of how to poduce goods and services
When resources are specialized..
the opportunity cost becomes bigger.
why is a country ppc curved?
Because of the oppertunity cost is bigger due to specialization
a ppc curve going outward right?
means increases in resources and tech improved standard of living, The position is depedent on the country’s resources and tech
If technology only improves for one good (a new fishing technique increases the catch with same amount of ships) then the PPF will shift out from that axis only.
this does not mean we can only produce more of that good. it frees up more resources to put into other goods
Comparative advantage
refers to an ability to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another
Absolute Advantage
is the ability to produce more than another, given the same resources.
law of increasing opportunity cost
resources are not equally suited for all types of production
Markets
Are a mechanism that brings buyers and sellers together to exchange goods, services, and resources. It is a device for allocating and rationizing goods
two types of markets
Product market: where consumer goods are bought and sold. Business firms are the seller, consumers are the buyers
Resource market: where the resource services are bought and sold. Resource owners(consumers) are the sellers and business firms are the buyers
demand
relationship between the price and the quantity demanded of a good
quanity demanded
amount of an item that buyers are willing and able to purchase over a certain time period, at a specific price, ceteris paribus.
normal good
Buy more of a good when income increases
Inferior good
Buy less of that good when income increases
Subsitute
Two goods that perform the same function (interchangeable)
complements
Two goods that perform the same function (interchangeable)
Law of demand
price and quanity demanded of a good are inversely related
demand schedule
A list of possible prices with the corresponding quantity demanded at that price
demand curve
As the price of a good decreases, buyers are willing and able
to purchase more of this good, all other variables constant
relative price
price of the one you want/ other good= relative price of what you want
$4 for unit of blackberry/ 2$ for unit of strawberry= 2 strawberry for blackberry
what causes demand to change
taste and preference, expectation, price, market consumers availablity
profit equation
Profit = Revenue – Cost = (Price x Quantity) - Cost
what influences supply
1. Price of the good
2. Price of inputs (resources)
3. Technology
4. Prices of other goods that can be produced by the firm (for multi-good firms)
5. Expectations of future price
6. Number of Firms
7. Taxes and Subsidies on the good
law of supply
The price and quantity supplied of a good are directly related
supply schedule
A list of possible prices with the corresponding quantity supplied at that price
Equilibrium
At rest, no tendency to change, forces in balance.
Market equilbrium
−the price, once reached, when there will be no tendency to change.
Also the price the market comes to rest at and where there are forces in balance.
There are no more unexploited opportunities
quanity demanded = quanity supplied
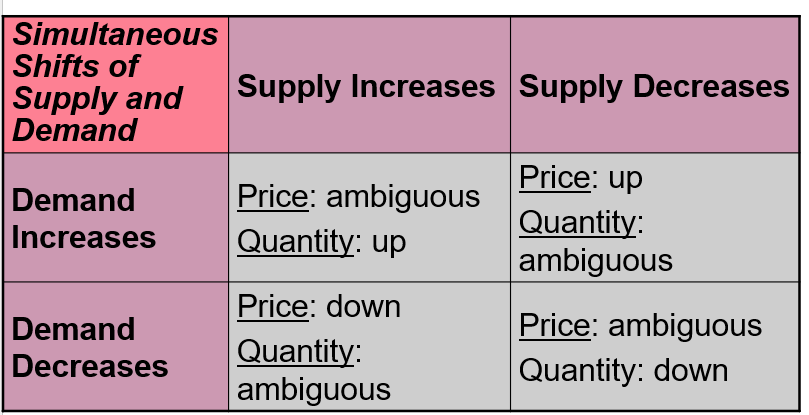
demand supply expectations