(M) Week 7 - 8 Introduction to Arduino and Electronic Components
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Arduino
An open-source hardware, software, and content platform that is freely available to anyone who wants to use or modify it.
Its Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is free and users can change the software to meet their needs.
It has a worldwide community of more than 30 million active users.
It has powered thousands of projects over the years, from everyday objects to complex scientific instruments.
Electrical Safety
NEVER try to short-circuit the (+ and –) terminals to yourself.
Currents as low as 100mA can electrocute you! and can cause death.
Do not connect the circuit to a power source while troubleshooting
Do not plug a lot of devices into one outlet or extension cord.
Make sure that all electric cords are tucked away, and tidy.
Do not handle or operate electrical tools when your hands are wet or when you are standing on wet floors.
Water contains charged ions that make current easily flow.
Do not unplug cords using the cord wire, use the cord handle.
Board Handling
Do not leave the circuit board on a conductive surface as it may cause a short circuit and destroy the board.
As much as possible hold the board on the side and edges.
Prevent unnecessary pins from connecting to each other as it may short circuit and destroy the board.
Multimeter Usage
Always make sure that the range is appropriate for the value being measured.
Improper range will destroy the measuring instrument
Safety Rule
If you are unsure of what to do, always ask questions.
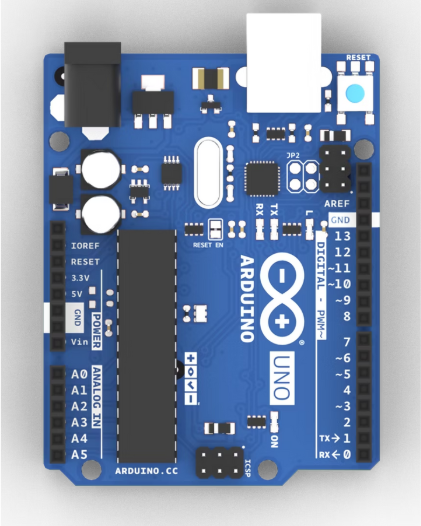
Arduino UNO R3
The microcontroller development board that will control your circuits. It is used to build interfaces and controls that allow the microcontroller to interact with other components.
Battery Snap
Used to connect a 9V battery to power leads. It can be easily plugged into a breadboard or your Arduino.
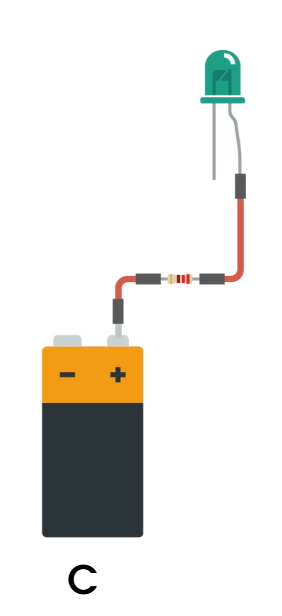
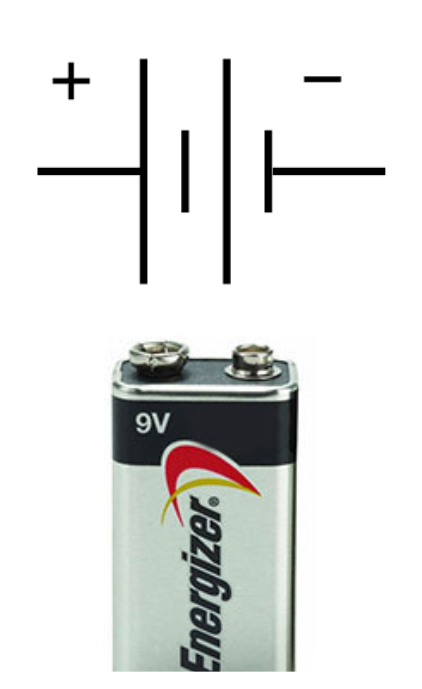
Battery
A device consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections provided to power electrical devices such as flashlights, smartphones, and electric cars.

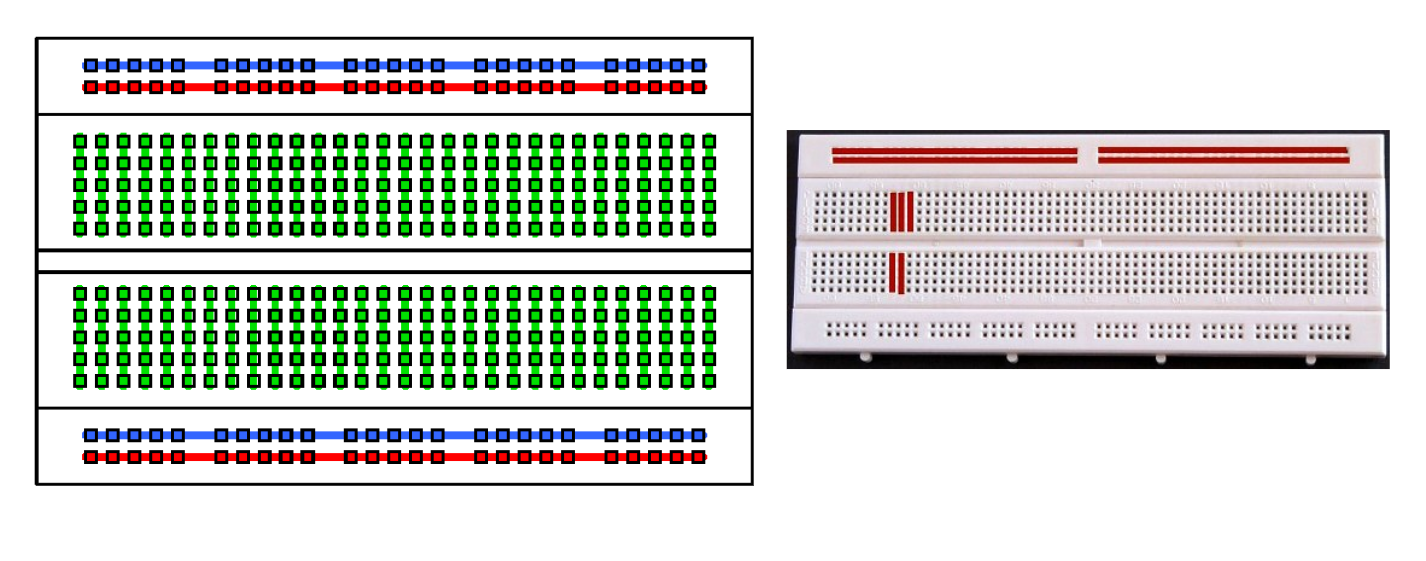
Breadboard
A board that allows you to easily build electronic circuits. It has rows of holes that let you connect wires and components. This specific type of board is a solderless breadboard.
A construction base for the prototyping of electronics.
Because the solderless breadboard does not require soldering, it is reusable.
Easy to use for creating temporary prototypes and experimenting with circuit design.
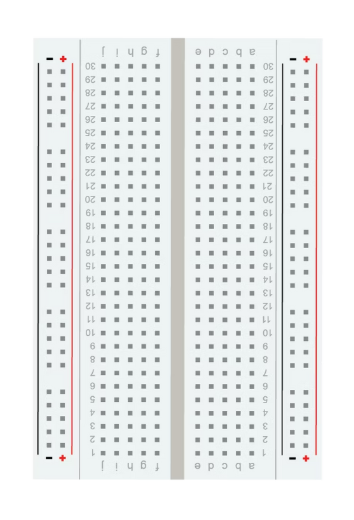
Breadboard Connections
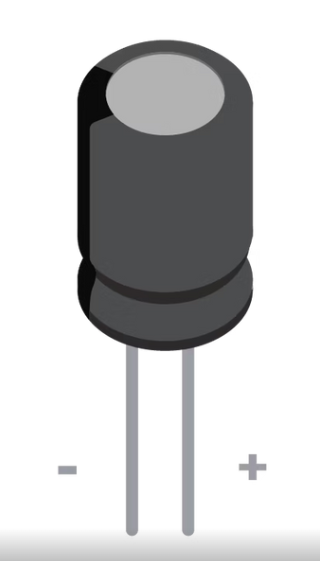
Capacitor
A component that stores and releases electrical energy in a circuit. When the circuit’s voltage is higher than what is stored in this component, it allows current to flow in, giving the component a charge. When the circuit’s voltage is lower, the stored charge is released
A passive two-terminal electrical component that stores potential energy in an electric field.
The effect of a component is known as capacitance.
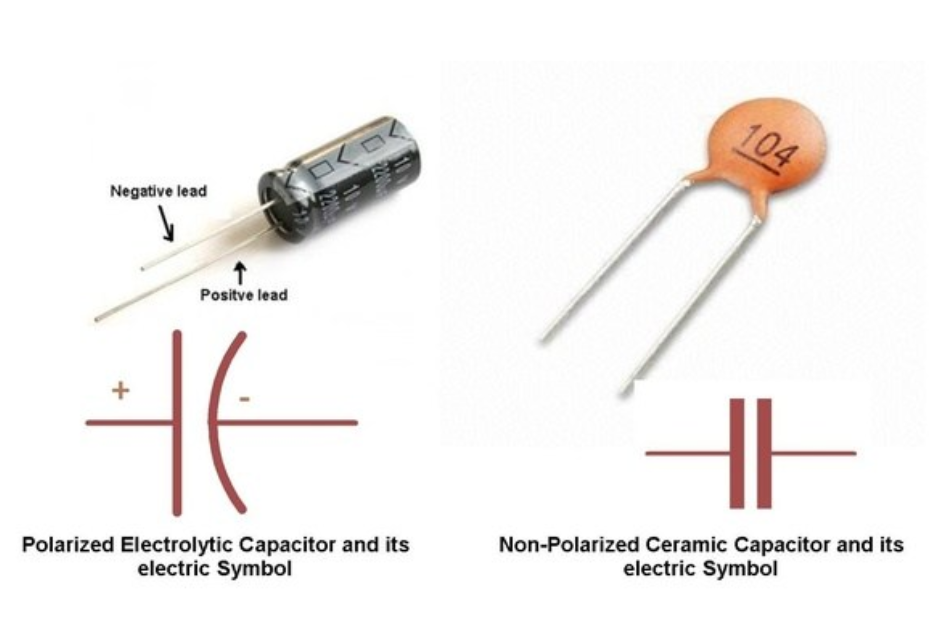
Determine Polarity in Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are often marked with a stripe. That stripe indicates the NEGATIVE lead. If it's an axial leaded capacitor (leads come out of opposite ends of the capacitor), the stripe may be accompanied by an arrow that points to the negative lead.
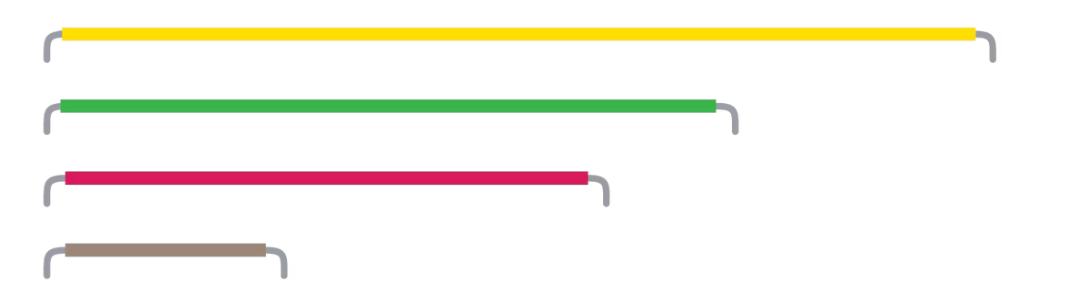
Jumper Wire
Used to connect components to each other on the breadboard and to the Arduino board.
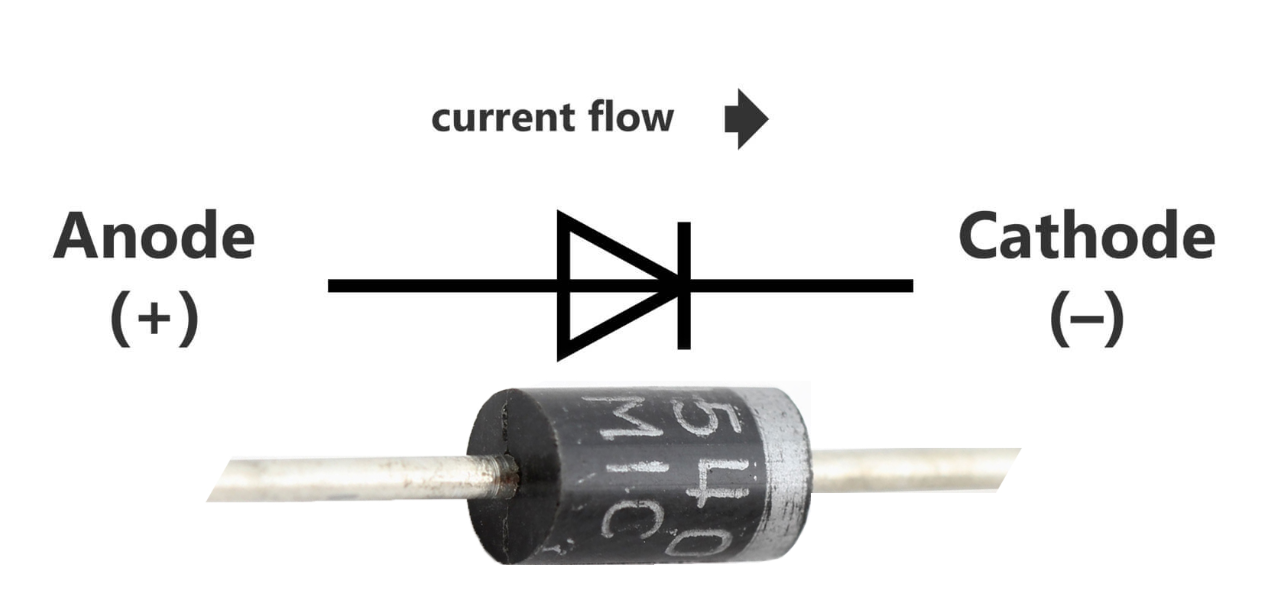
Diode
A semiconductor device with two terminals, typically allowing the flow of current in one direction only.
The most common function of this component is to allow an electric current to pass in one direction (called the diode's forward direction), while blocking it in the opposite direction (the reverse direction).
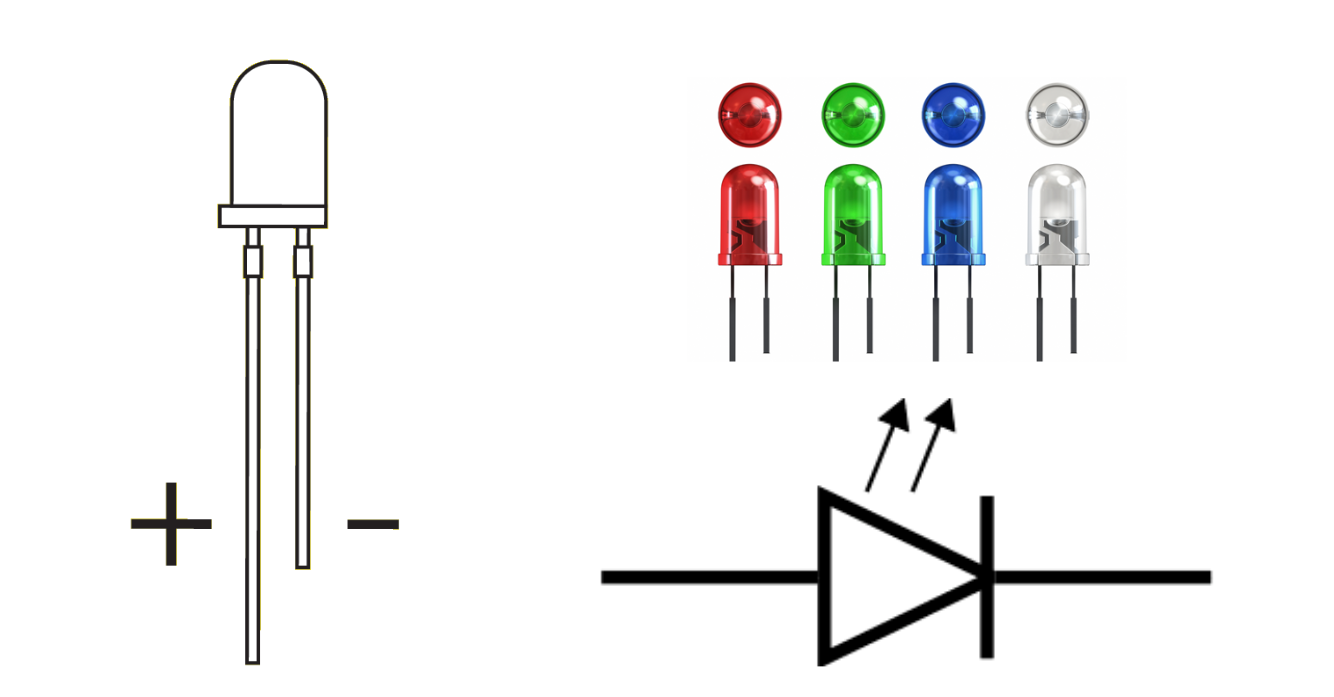
Light-Emitting Diode (LED)
A type of diode that lights up when electricity passes through it. Often used as indicators on electronic devices, inside TVs to display vivid colors, and as energy-efficient lighting in buildings.
Two-lead semiconductor light source.
Lasts longer and uses less energy than other types of lighting.
Has two terminals. The positive side is called the anode, and the negative one is called the cathode.
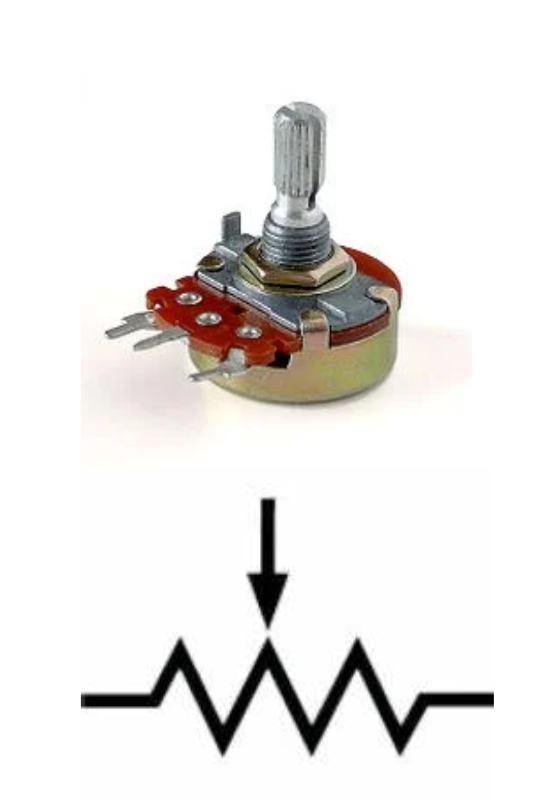
Potentiometer
A variable resistor with three pins. Two of the pins are connected to the ends of a fixed resistor. The middle pin is connected to a wiper that moves across the resistor.
A three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider.
It is a three-terminal resistor in which the resistance is manually varied to control the flow of electric current.
Power Lead
Longer jumper wire that is usually used to provide power and ground from the Arduino board to the breadboard.

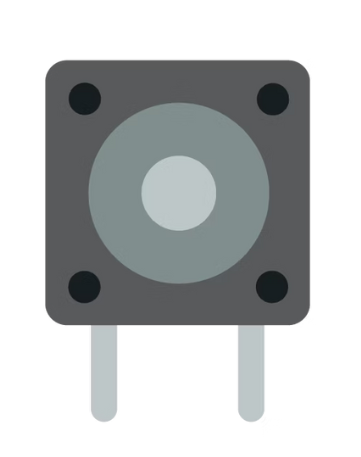
Push Button
A switch that closes the circuit when pressed. When released, the circuit becomes open again. Used as input devices and allow the Arduino board to detect on/off signals.
Switch
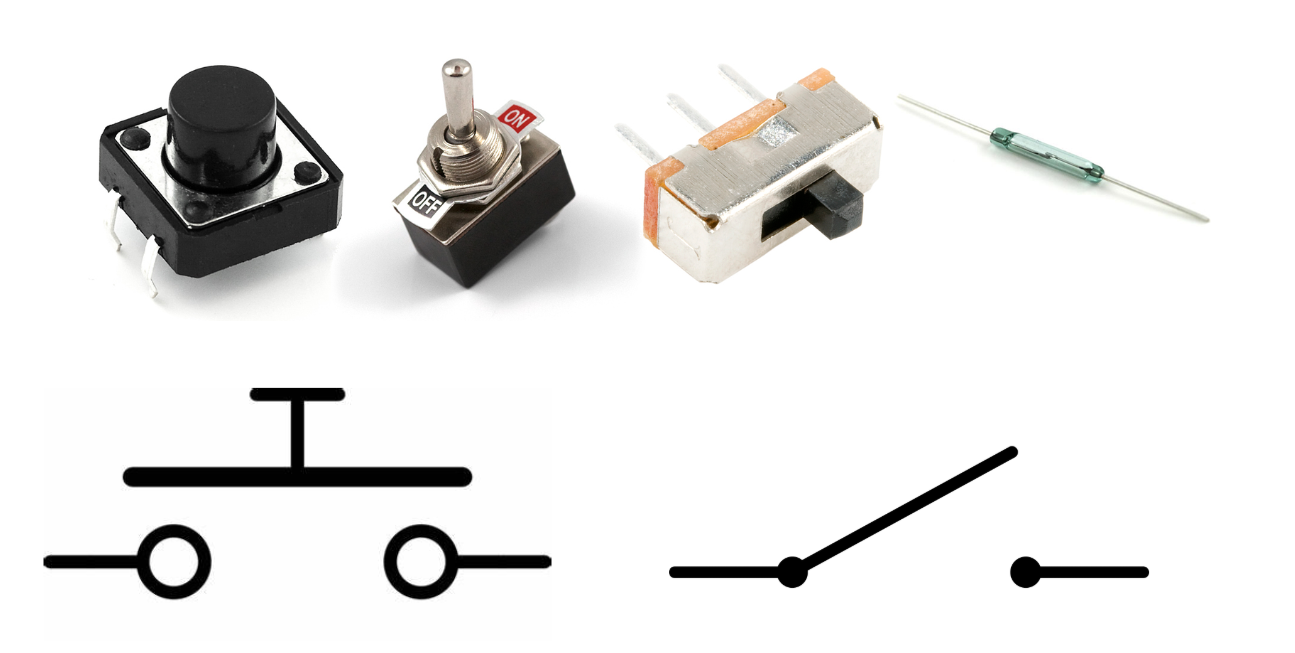
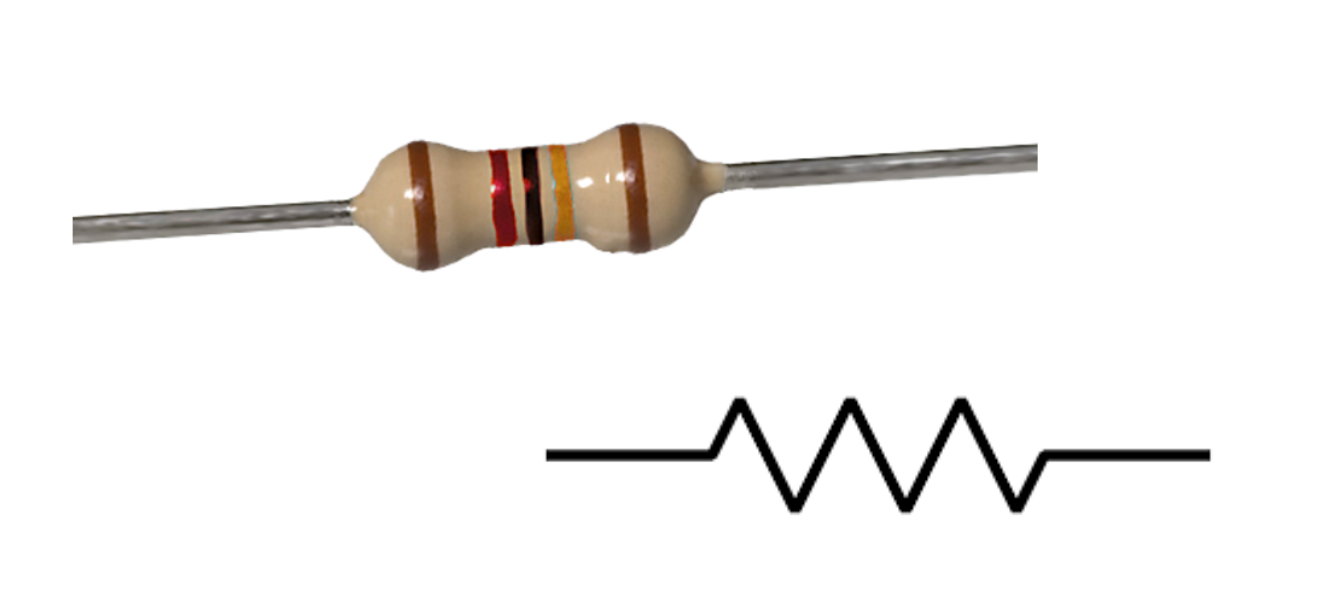
Resistor
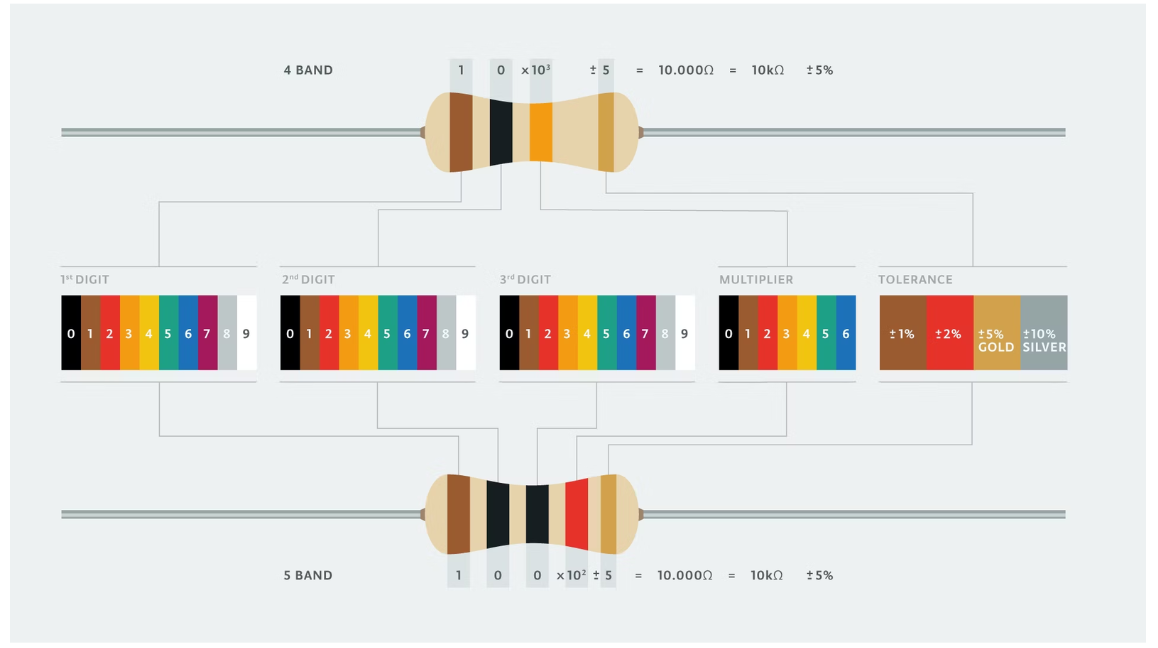
A component that resists the flow of electrical energy. It changes the voltage and current in the circuit. It is measured in ohms (Ω). The colored stripes on the resistor indicate its resistance value and tolerance.
A passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
In electronic circuits, these are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses.
Reversible, in the sense that they can be connected to the circuit in either direction.
They do not have a polarity.
Resistance Value
Piezo Buzzer
An electrical component that can be used to detect vibrations and create sounds. It can even produce melodies.
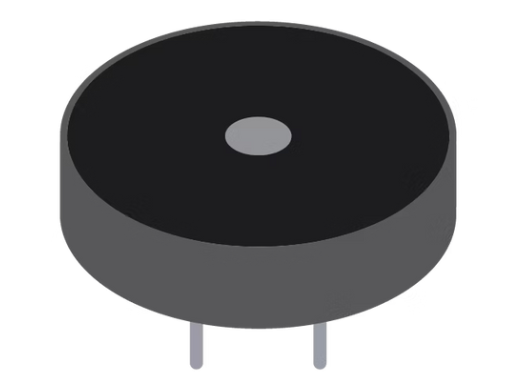
Buzzer
An electronic device that produces sound or melodies.

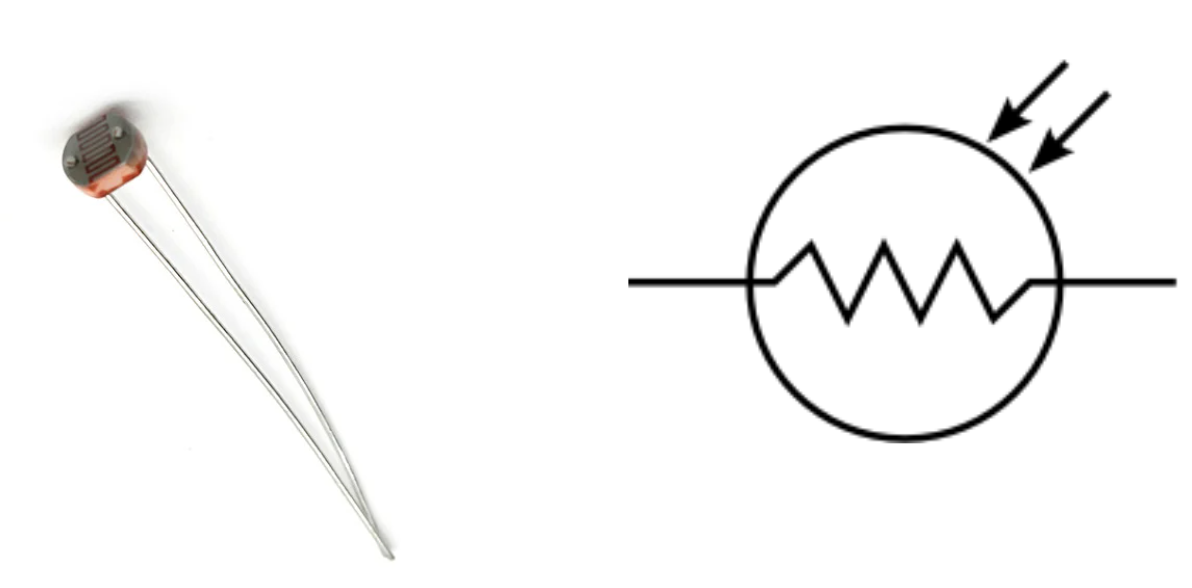
Photoresistor
A component that generates a current based on the amount of light it sees.
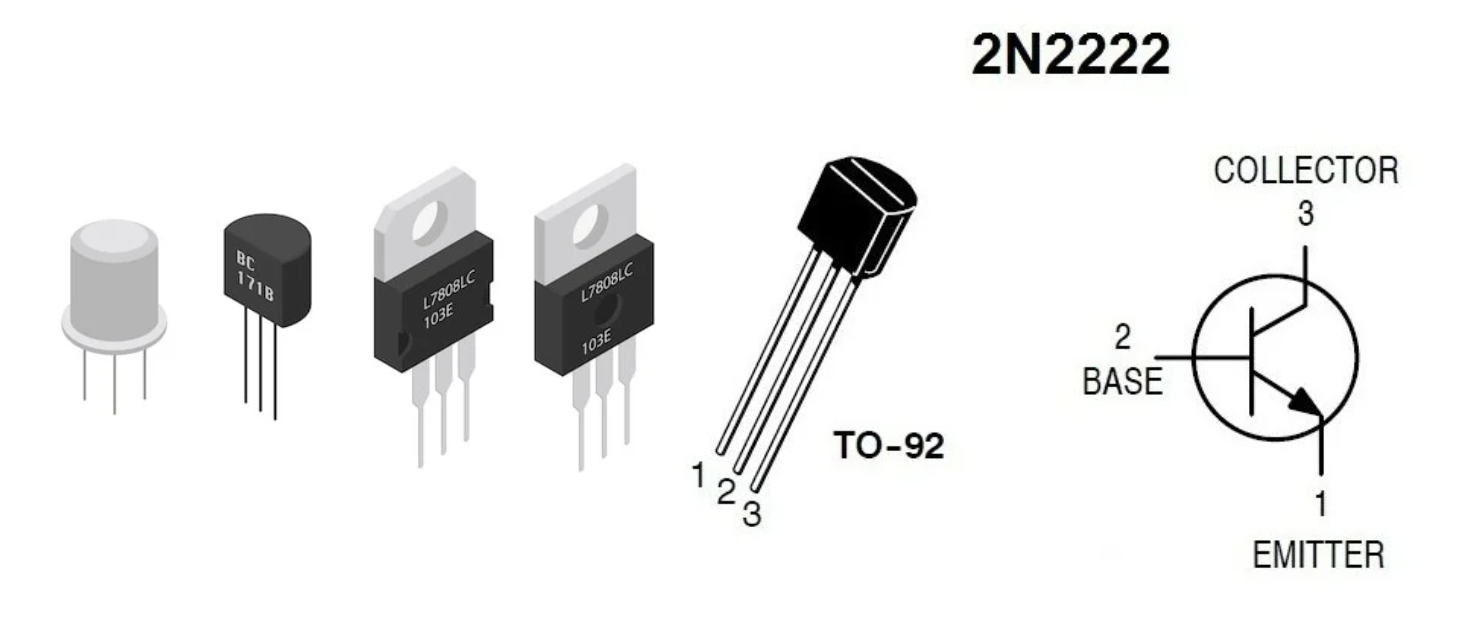
Transistor
A semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power.
It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit.
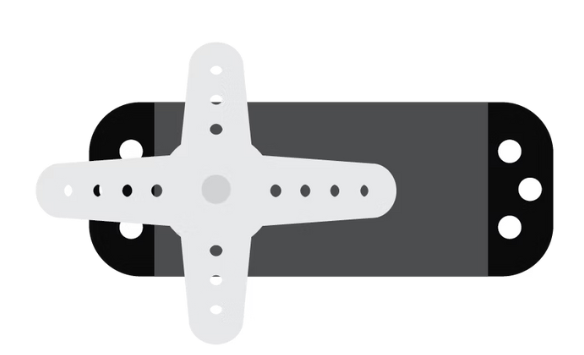
Servo Motor
A type of geared motor that can only rotate up to 180 degrees. It is controlled by electrical pulses sent from the Arduino board. The pulses tell the motor what position to move to.
USB Cable
Allows you to connect your Arduino board to a computer. This allows you to write, compile, and transfer programs to the Arduino board. Also provides power to the Arduino board.

Electronics
The branch of Physics and Technology concerned with the design of circuits using transistors and microchips and with the behavior and movement of electrons in a semiconductor, conductor, vacuum or gas.
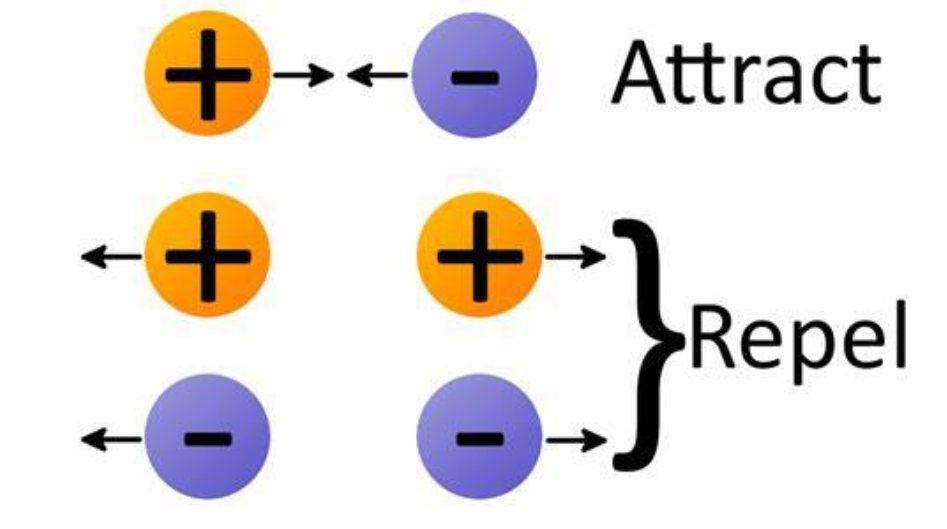
Electrical Charges
Opposite charges attract, same charges repel.
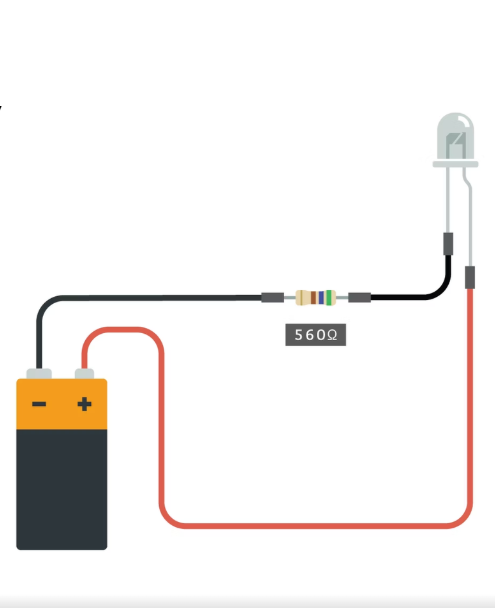
Circuit
A looped path that allows electricity to continously flow.
It has components such as a power source, switches, lights, motors, speakers, and other devices that use electricity to do something.
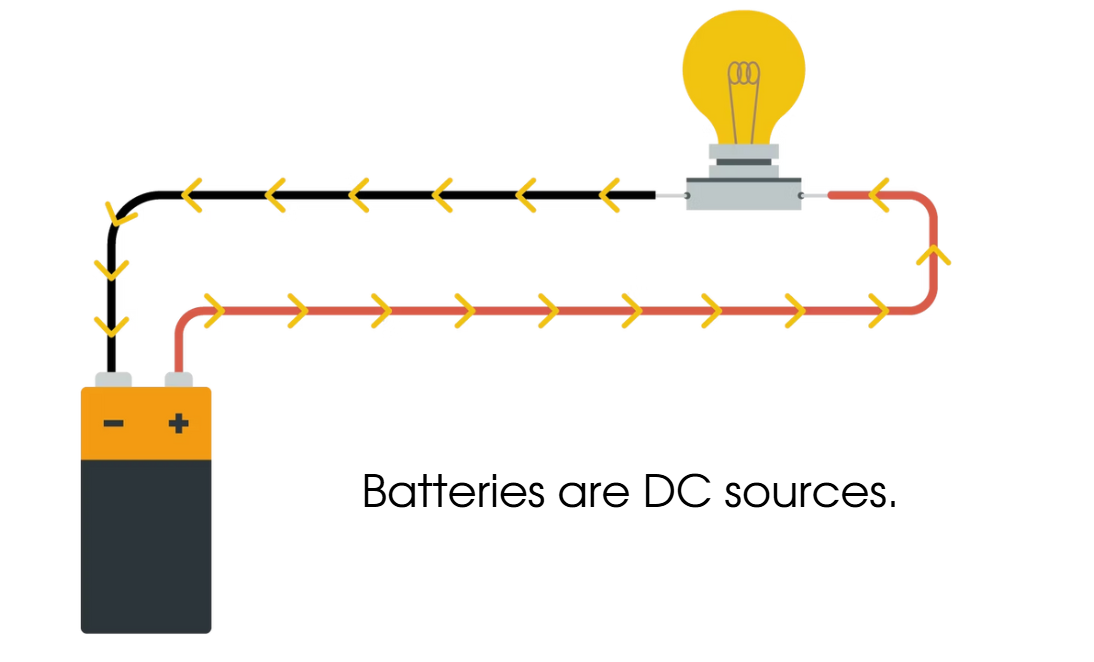
Direct Current
The current flows in one direction: positive (power) to negative (ground)
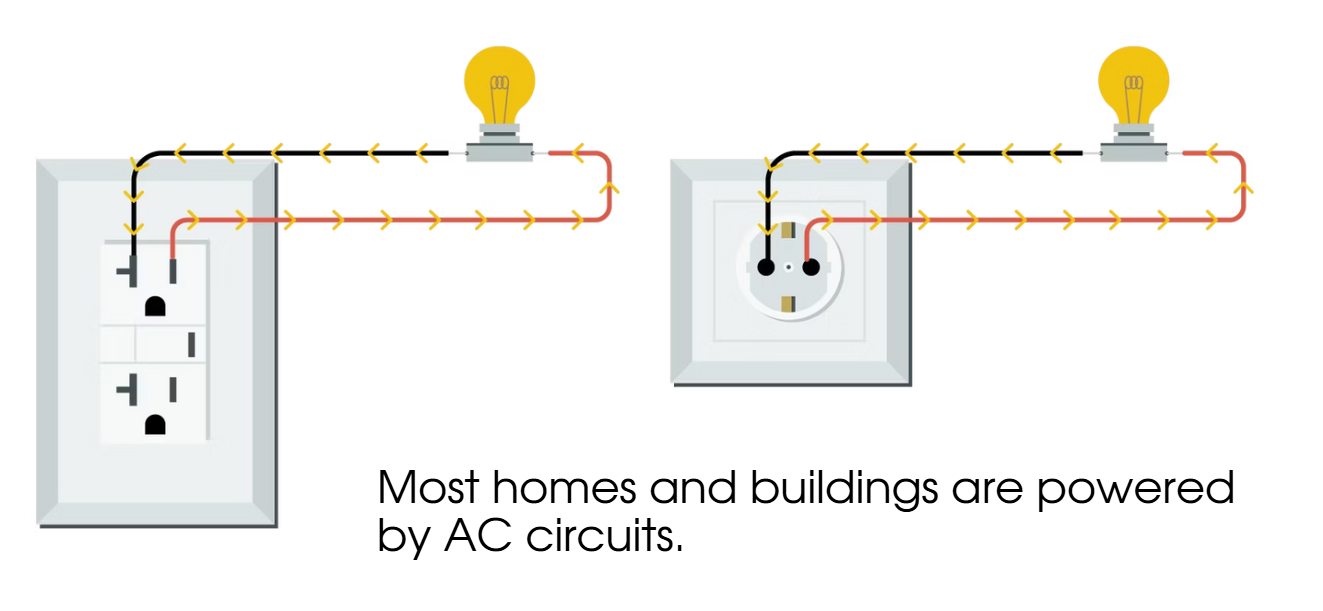
Alternating Current
The direction of current flow changes back and forth. As the current changes direction, the voltage circuit reverses forcing the current to flow the other home.
Closed Circuit
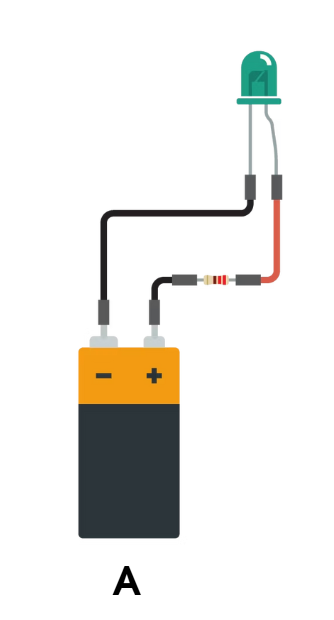
Short Circuit
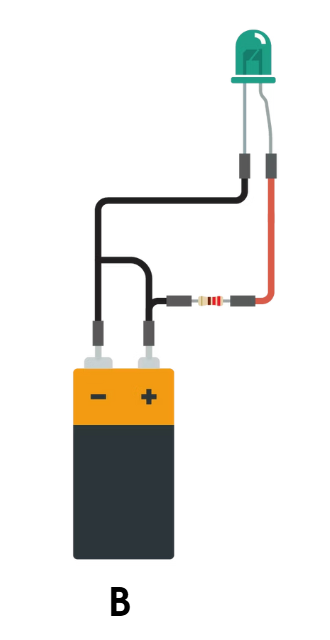
Open Circuit