Chemistry – GSCE/ exam formed questions (PAPER 1)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Explain why Copper oxide (CuO) has a high melting point. [3]
a lot of enrrgy required to break bonds
which are between the opposietly charged ions
Explain why water (H²O) has a low boiling point? [3]
little energy is required to break bonds
weak intermolecular forces
small molecules
why does solid sodium chloride not conduct electricity?
ions are not free to move
which ion makes a solution acidic?
H+
![<p>The student investigated the volume of CO² produced with different masses of calcium carbonate react with hydrochloride acid.<strong> describe a method he could use. </strong>[6]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c39d204e-de06-4f72-81b9-d3ec0bdbf7a4.png)
The student investigated the volume of CO² produced with different masses of calcium carbonate react with hydrochloride acid. describe a method he could use. [6]
measure certain mass of calcium carbonate using a balance
transfer mass of calcium carbonate to flask
measure certain volume of hydrochloric acid using a cylinder
add acid to flask and attach bung
record volume of gas produced in a specific amount of time
repeat investigation with different mass of calcium carbonate to calculate a mean
IV = mass of calcium carbonate
DV = volume of gas
CV = volume of acid
Explain what happens to sodium atoms and to oxygen atoms when sodium reacts with oxygen to produce sodium oxide (NA²O) [4]
sodium atoms lose one electron
oxygen atom gains two electrons
two sodium atoms form an ionic bond with one oxygen atom
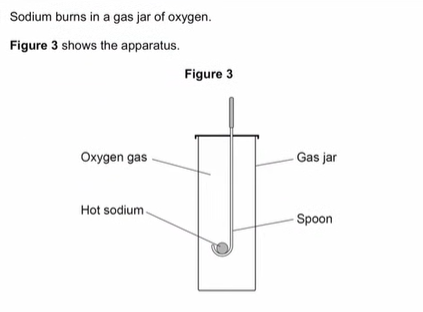
give two observations seen during a reaction.
yellow flame
white smoke