Year 10 Biology - Our Journey to Now
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Fossil
Any remains or trace of a formerly living organism preserved by a natural process.

Trace fossil
Any indirect evidence of life preserved as an impression in rock; trails, footprints, tracks, burrows, and bite marks.

Extinction
A term that typically describes a species that no longer has any known living individuals.
Fossil record
Chronological collection of life's remains in sedimentary rock layers.
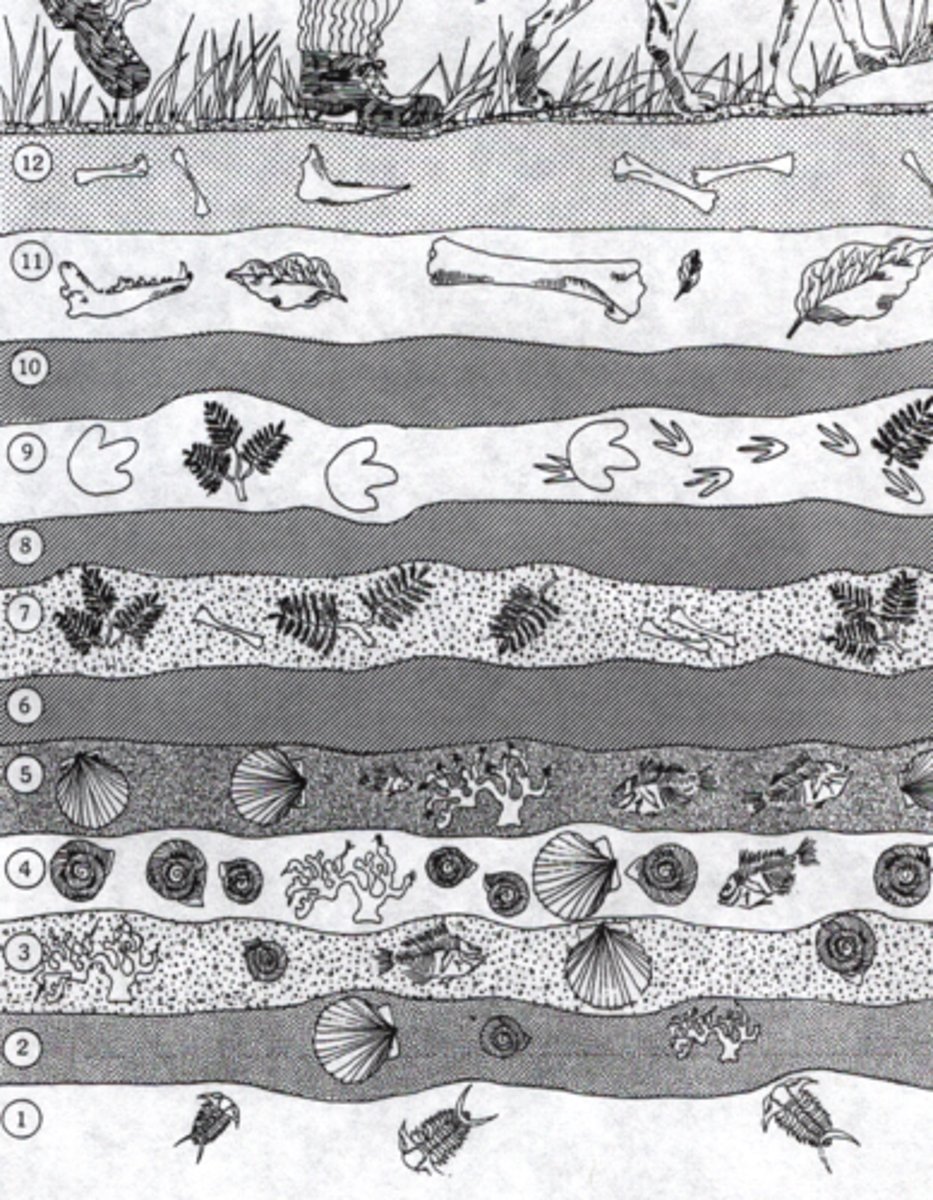
Index fossil
A fossil known to have lived in a particular geologic age that can be used to date the rock layer in which it is found.

Law of Superposition
In a sequence of layered rocks, the older rocks will be under the younger (newer) rocks.
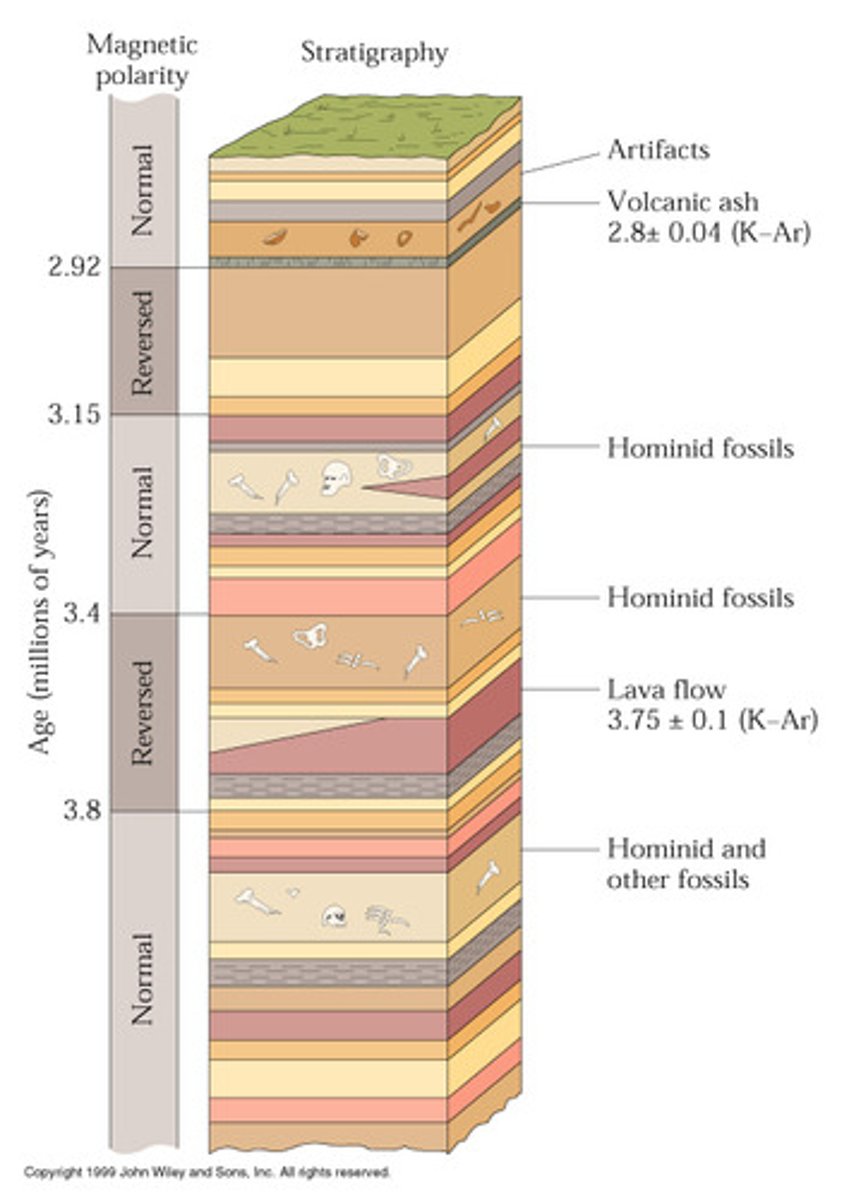
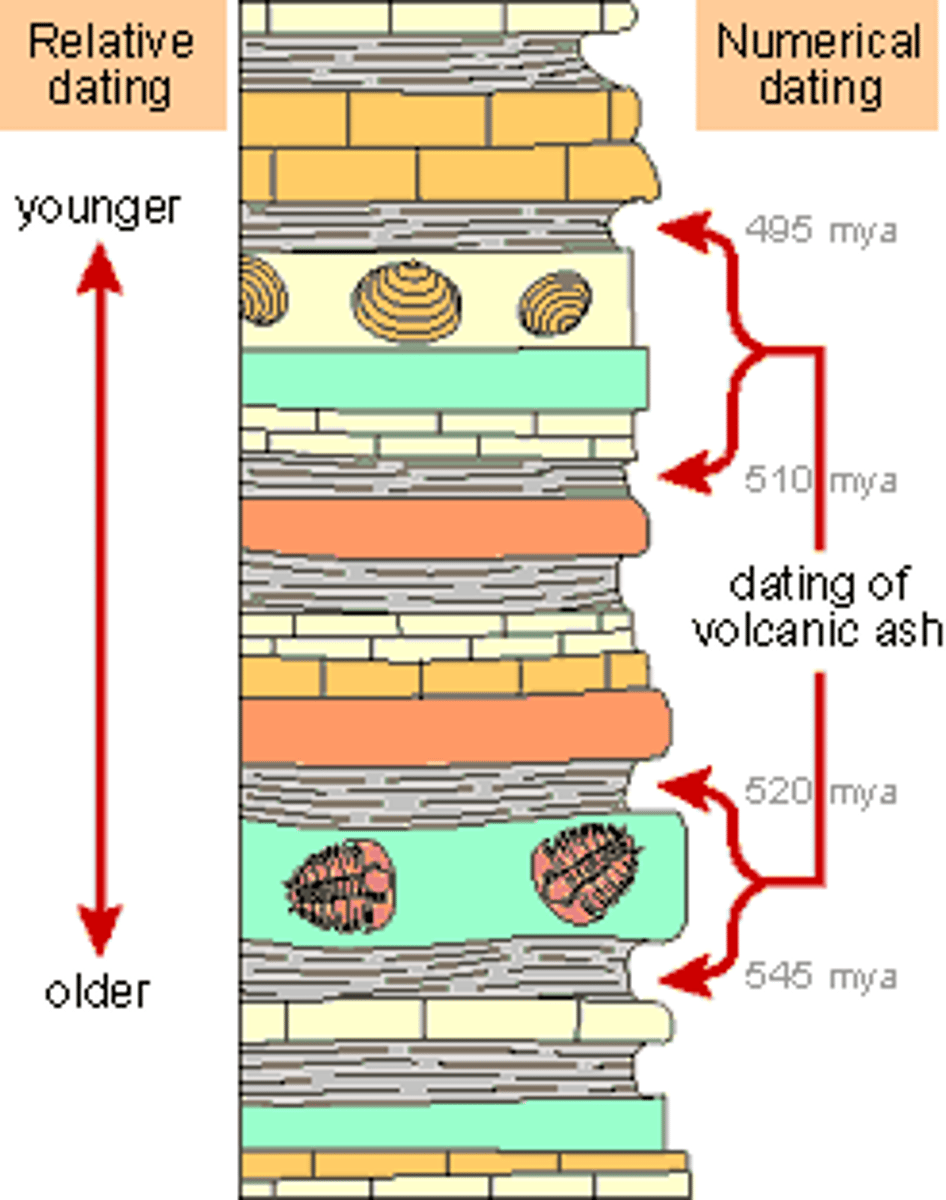
Relative dating
Method of determining the age of a fossil by comparing its placement with that of fossils in other layers of rock.
Amber
Small animals, mostly insects, get stuck in tree resin. Resin is a sticky substance the comes from a tree. The resin hardens and becomes a fossil.

Petrified fossil
The soft parts of a once living thing is replaced by minerals.

How animal fossils form
-Animal dies
-Soft parts rot or decompose
-Bone and teeth remains are buried under sediment
-The remains are replaced with minerals and turn into rock
-The earth slowly moves and cracks.
-Wind/Weather (rain, snow, ice) expose the fossil
What does it mean if Paleontologist find fossils in the same place?
-They lived together if found in the same rock
-They are the same age if found in the same layer
What does the layers of rock (sediment) in the earth tell Paleontologists?
It tells how old the fossil is
-Older fossils are in deeper layers of earth
-Younger fossils are in a higher layers of earth
Where are fossils usually found?
Sedimentary rock
What are the different kinds of fossils?
petrified fossils, molds, casts, carbon films, trace fossils, and preserved organisms
absolute dating
A technique used to determine the actual age of a fossil eg carbon dating
Fossil Evidence for Evolution
looking at historical organisms for change and similarities to present day organisms
Describe Lamarck's Theory of Transmutation
An organism can acquired changes within their lifetime. These changes are passed to their offspring.
Describe the Theory of Creation
All living organisms were created in their present form by God. No new species arise and no species become extinct.
Describe Darwin's Theory of Evolution
All organisms are descended from a common ancestor, with species changing over time due to the mechanism of natural selection.
Provide an example of comparative anatomy, used to support the theory of evolution.
Pentadactyl limb - human, whale, bat, cat
Provide an example of comparative embryology, used to support the theory of evolution.
21 day old embryo with similar morphology - chicken, pig, human
Provide an example of biochemical molecules, used to support the theory of evolution.
DNA has a similar chemical structure across all living organisms. The greater the similarity in code, the more closely related. Humans and chimpanzees have a DNA similarity of 98.8%.
Provide an example of fossil evidence, used to support the theory of evolution.
Trilobite fossils in the fossil record, show gradual change in diversity over time.
Provide an example of biogeographical evidence, used to support the theory of evolution.
Fossils of the Nothofagus pine can be found throughout Australia, New Zealand and Antarctica during a period of time when all land masses were connected.
Australian marsupials are an example of speciation due to geographic isolation.
Speciation
Two populations, after a period of isolation and different selection pressures, become genetically distinct and are no longer able to reproduce to form fertile offspring.
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
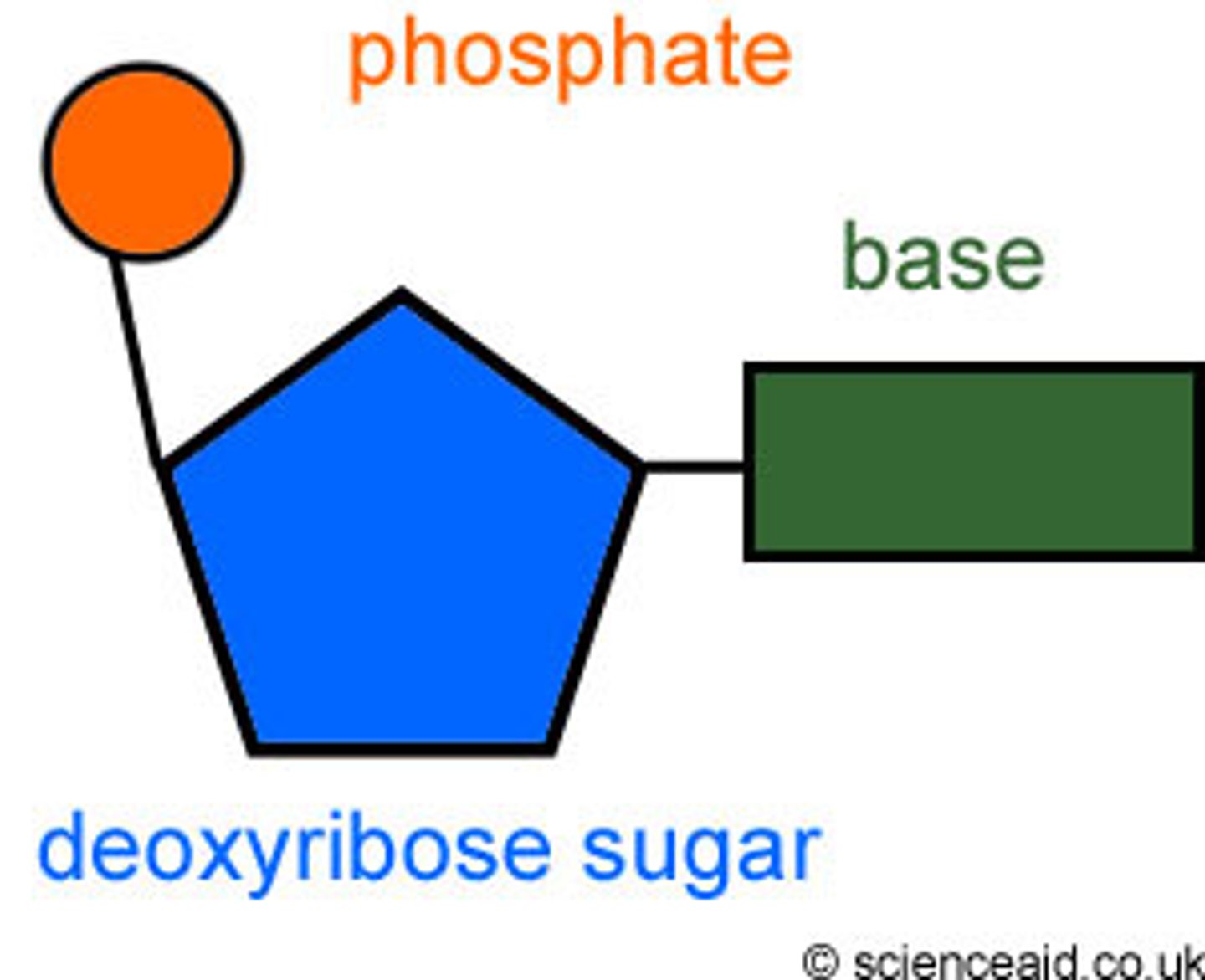
Describe the basic structure of a nucleotide.
Phosphate molecule; deoxyribose molecule; nitrogenous base
Describe the complimentary base pairing observed in DNA.
Adenine (A) - Thymine (T)
Guanine (G) - Cytosine (T)
Who developed the first accepted model of the DNA structure?
Watson and Crick
Describe the DNA molecule
- A double stranded helix.
- Each strand is composed of a polymer of nucleotides.
- The strands run in opposite directions. (antiparallel).
- The strands are bonded by weak hydrogen bonds between complimentary pairs.
Describe a gene.
- A section of DNA that codes for a particular trait.
- Most genes have a fixed location on a chromosome.
- Only 1% of human DNA codes for a trait.
Describe the chromosome.
- Chromosomes are long, twisted double strands of DNA.
- DNA is coiled around specialised proteins called histones.
- Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes.
Describe the structure of a chromosome
Two sister chromatids connected by a centromere.
Genome
- All the genetic information held within a cell.
- All cells within a organism have an identical copy of the genome.
Number of chromosomes in a human skin cell.
46 (23 pairs)
Chromosomes are assigned a number based on...
- size (autosomal chromosomes)
- the last pair define the gender. (sex chromosomes)
haploid
one copy of each chromosome
diploid
two copies of each chromosome
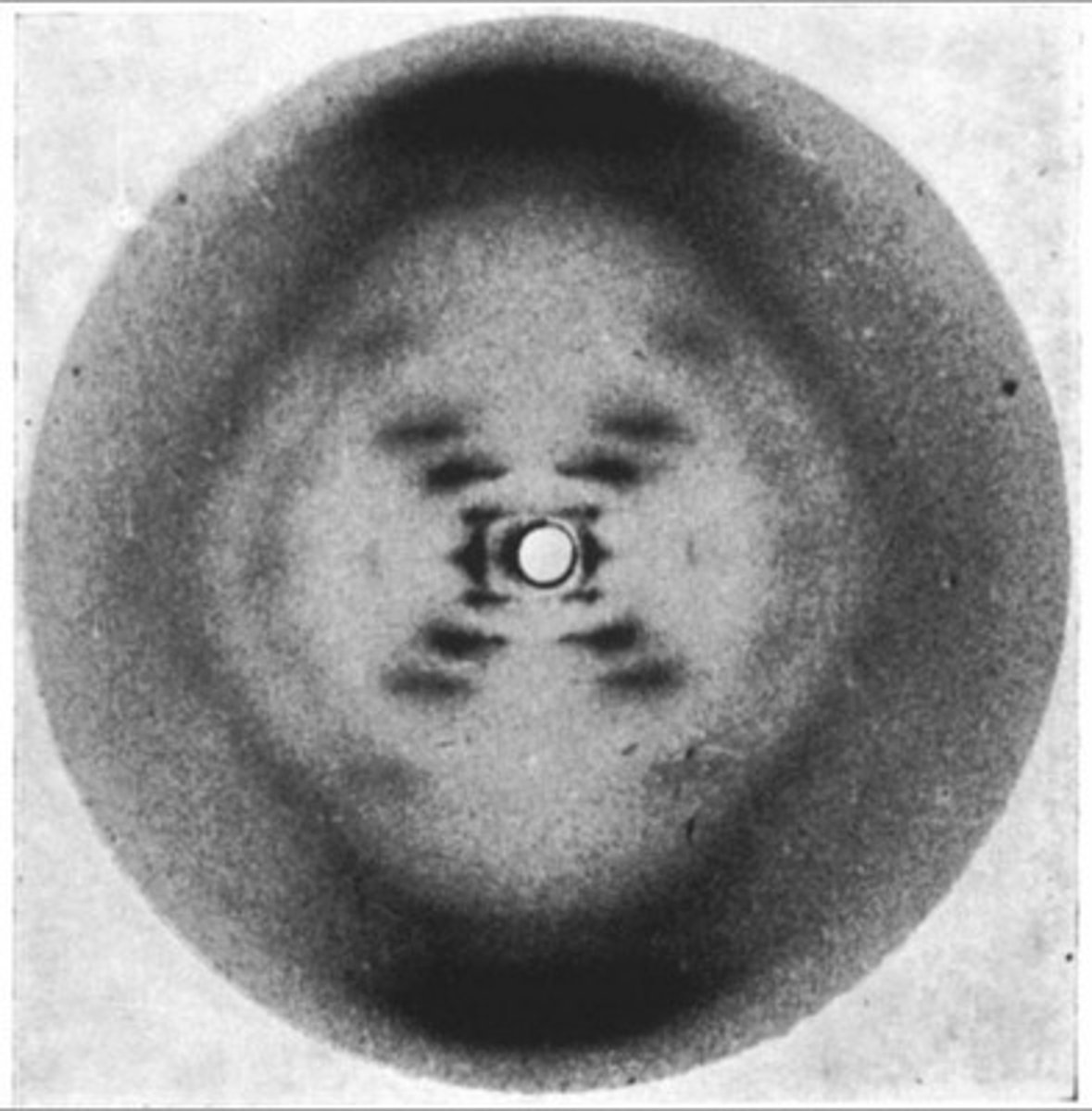
What was Rosalind Franklin's contribution to understanding the structure of DNA.
Franklin used her X-Ray Crystallography image of wet DNA to outline the double strand, helical shape of DNA and the number of nucleotides per turn.