IMF's Chemistry
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
When is a molecule polar?
- Molecule is not symmetrical
- Unequal sharing of electrons in the bond
- Caused by a large difference between the atoms in the bond
- There are unbonded or lone pairs of electrons on the central atom of a molecule
Define Intermolecular Forces
The attractive forces between molecules
What is the strength difference between intra and intermolecular forces?
The chemical bonds between atoms (intra) is much stronger than the ones between molecules (inter)
define Van der Waals forces
The weak bond between two molecules
What are the 4 types of IMF's?
Ionic, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole forces, London dispersion forces
How to know the strength of Ionic
- It is the strongest IMF
- the larger the charge, the stronger the force
How to know the strength of London Dispersion Forces
- More electrons means a larger London dispersion force
- Larger Molar MASS means larger London dispersion forces
- Larger molecules have larger London dispersion forces
How to know the strength of Dipole-Dipole Forces
- Occur between polar molecules
- Larger electronegativity difference, larger force
- Larger molar MASS (MM), larger force
How to know the strength of Hydrogen Bonding
- Larger electron negativity difference, larger force
- Larger Molar Mass, larger force
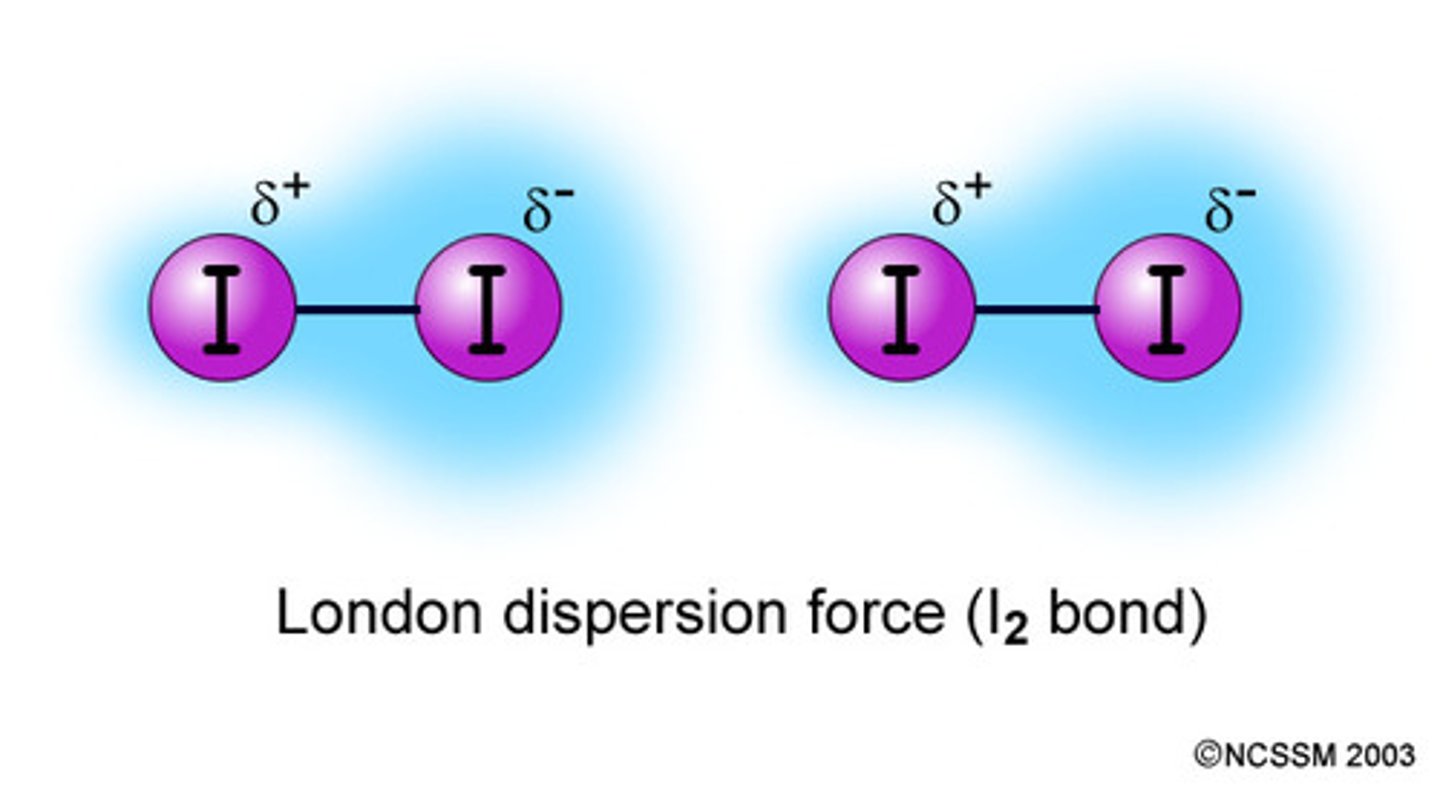
Define London Dispersion Forces
- Attraction between 2 instantaneous dipoles (charges)
- Asymmetrical electron distribution
- All atoms and molecules contain it
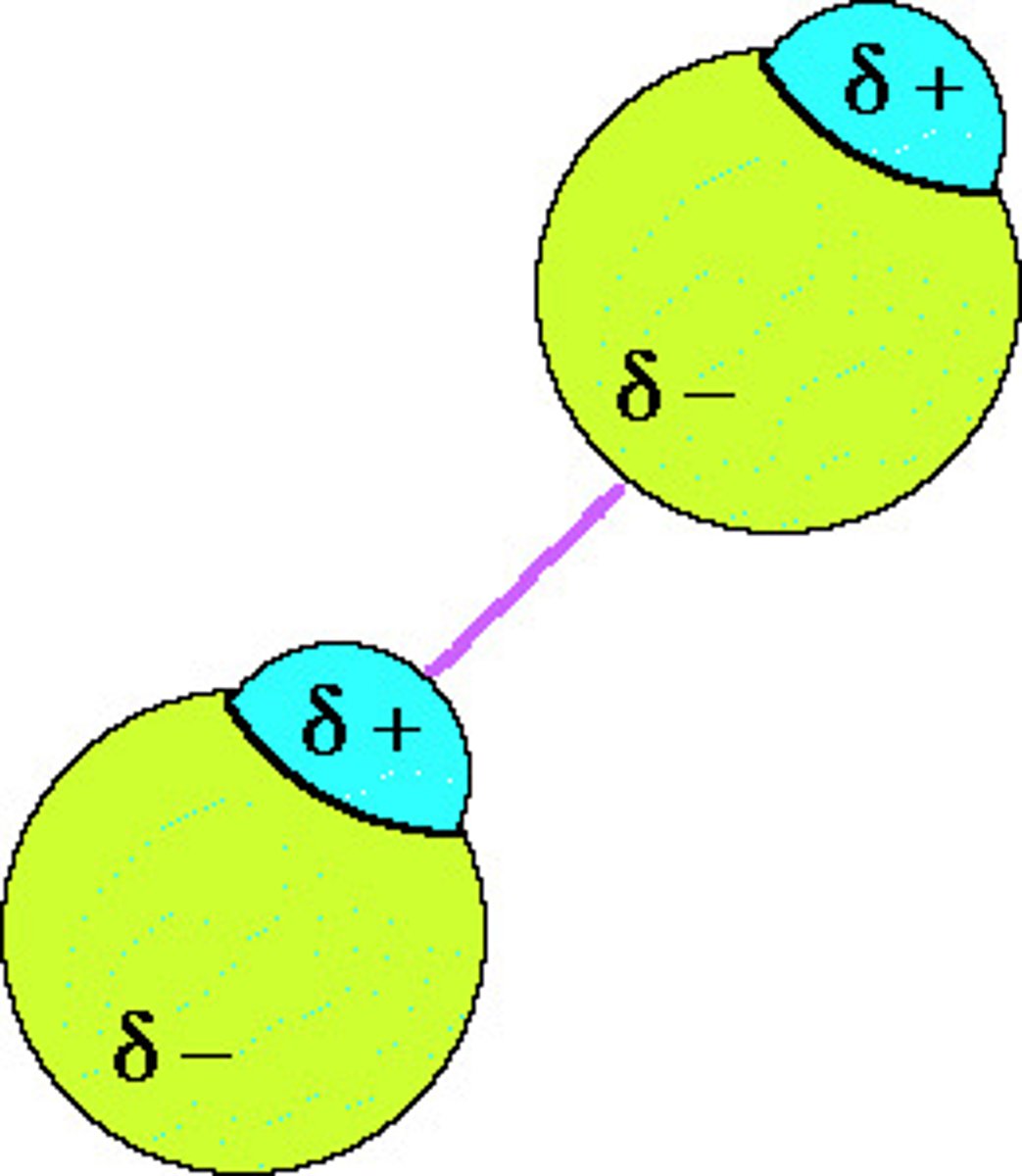
Define Dipole-Dipole forces
- Attraction between 2 permanent dipoles
- Polar molecules
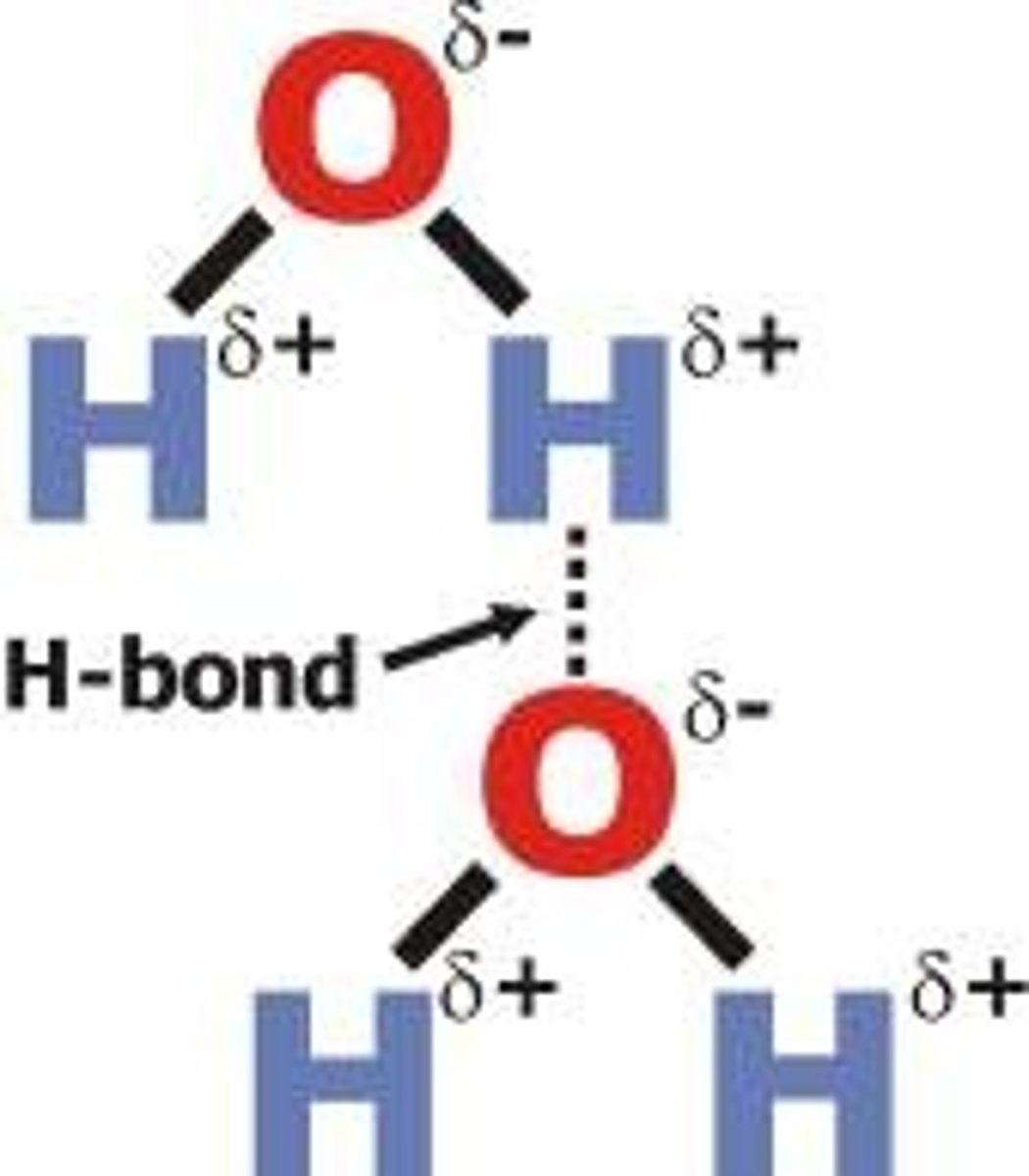
Define Hydrogen Bonding
- Attraction between hydrogen and F, N, or O (F-H, N-H, O-H bonds)
- Extremely polar bonds - very strong dipole-dipole force
Other information on London Dispersion Forces
- Increase in strength as molar mass increases (more electrons).
Other information on Dipole-Dipole Forces
- Increase in strength when molecules are closer together
Other information on Hydrogen Bonding
- NOT chemical Bonding
Put IMF's in order of strongest to weakest (bonds)
Ionic, Hydrogen bonding, Dipole-dipole, London dispersion
Put IMF's in order of highest boiling point to lowest boiling point
Ionic, Hydrogen bonding, Dipole-dipole, London dispersion
(The stronger the IMF's the more heat is needed to break the bonds)
What do phase changes deal with?
Making and breaking intermolecular forces, not bonds
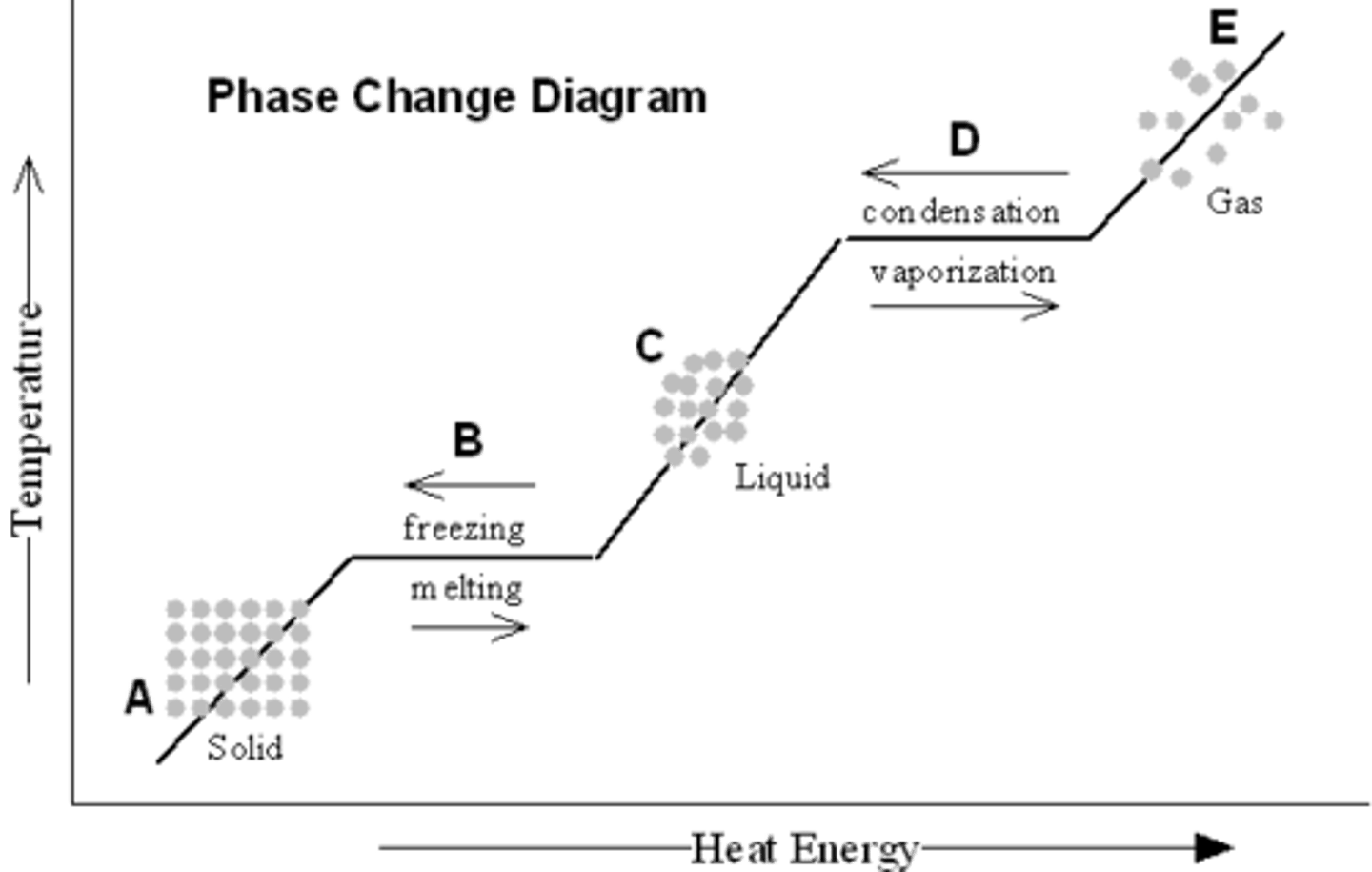
Phase change for water
Flat points are when the phase change occurs
- Axis are Temperature and Energy input