Roman Art and Archaeology
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Who were the Villanovans?
were an ancient people of central Italy, known for their role in the early Iron Age. Laid the foundation for Etruscan culture.
What was the order of government in Rome?
Monarchy - Republic - Principate - Empire
Who was the first emperor ?
Octavian (Augustus)
What was the Via Sacra?
was the main street of ancient Rome, leading through the Forum and used for processions and religious ceremonies.
What was the Fasti Antiales Mairoes?
Early Roman Calendar
What was Varro’s significance?
was a Roman scholar and author, known for his chronologies on the history of Rome
What are the three theories regarding the origins of the Etruscans?
1) came from Lydia (Herodotus)
2) are Pelasgians (Pre-Greek inhabitants)
3) are native to Italy
Who were the ProtoVillanovans?
an early Iron Age culture in Italy, known for their distinctive burial practices and metalwork which preceded the Etruscan civilization.
What does the term Urnfield Culture mean in reference to the Villanovans?
refers to a burial practice where cremated remains were placed in urns and buried in fields
What were hut urns? (reference to Villanovans)
1000-700 BCE: mimicked real huts - wattle and daub, used for ashes, had animal and human forms on the roofs
When was the Orientalizing period?
720-580 BCE
Where has the vast majority of Attic Pottery found?
In Etruscan tombs
What was Bucchero?
A fine, dark clay that mimicked metal as it would have a sheen, but was cheaper to produce
what was the Aristonothos krater?
A large Ancient Greek vessel used for mixing wine, notable for its depiction of funerary scenes and mythological imagery.
What was Haruspicy?
A form of divination from the Etruscans involving the examination of the entrails of sacrificed animals to predict the future or gain insight.
What was the Liver of Piacenza?
An ancient Etruscan artifact, is a model of a sheep's liver used for haruspicy, containing inscriptions that guide divination practices, map of the cosmos
What was unique about Etruscan’s views on women?
1) not shameful for women to be naked
2) sharing women is common
3) can witness sexual experiences
What were tumuli?
Burial mounds built by the Etruscans and other ancient cultures, often containing graves and grave goods.
What were stelai?
Stone slabs or columns used as grave markers in Etruscan culture, often inscribed or adorned with reliefs.
What was the significance of Tarquinia in regards to Etruscan tombs?
1) over 200 tombs
2) mythological depictions
What was a keystone?
The central stone at the summit of an arch, crucial for its structural stability.
What was the Romanization of Etruria?
loss of Etruscan culture, institutions, and language
What was ager publicus?
Public land
What was significant about the Etruscan Warriors sculptures?
They were large sculptures that showed the influence of the Greeks on the Etruscans, however they were forged
Who were Romulus and Remus and what is their significance to Rome?
Mythical twins, raised by a she-wolf, Romulus kills Remus and becomes the founder of Rome and first king
what was the Rape of the Sabines?
Early Romans abducted women from the Sabine people to populate their city, leading to a conflict.
What was the Casa Romuli?
Alleged residence of Romulus, an iron age hut made of wattle and daub
What was the Forum Boarium?
a cattle market
What was the Cloaca Maxima or Great Drain?
an aqueduct that is still used and aided in helping with the flooding of the Tiber
What was the Shrine of Cloacina?
An open-air shrine dedicated to the Etruscan goddess Cloacina, located on the Via Sacra
what was the Curator Aquarum?
A Roman official responsible for overseeing the water supply and aqueducts in the city of Rome.
what was an arcade in reference to aqueducts?
A series of arches supporting the structure of an aqueduct, allowing it to span valleys and terrain.
What was the Forum Romanum?
The central public space in ancient Rome, used for various activities such as politics, commerce, and social gatherings.
What was the Comitium?
An open-air meeting space in the Forum Romanum designated for public assemblies and the electoral process, where citizens gathered to vote and discuss political matters.
what was the Curia Hostilia?
an original Etruscan temple where the senate would gather and was incorporated into the Comitium
What was a rostra?
a platform used for public speaking
What was a Tabularium?
records office on the Capitoline Hill
Who lived in the Regia and what was there role?
Head office of the ponifex maximus which was the head priest of the state
What is sacra publica?
public cult
What were the three orders of temples?
Doric, Ionic and Corinthian
What shape is a structure in a tholos formation?
circular
What was the Temple of Vesta for?
round as the cosmos (tholos), dedicated to Vesta, Vestal virgins, no cult statue; sacred flame instead, Vestalia festival (June 7-15)
What was Saturnalia?
A festival honoring Saturn, marked by feasting, gift-giving, and social reversals, celebrated in December. Similar to Christmas, salves and their owners would swap roles for the day (social norms flipped)
Who was Castor and Pollux?
mortal/immortal twins
what was significant about the Temple of Castor and Pollux?
a large podium and small rooms that were most likely offices including dentist offices
What was Magna Mater?
An ancient Roman deity associated with fertility and nature, often linked to the Great Mother goddess. Magna Mater was worshipped with elaborate festivals, including rites and ceremonies.
What were the Sibylline Books?
Prophetic writings containing oracles and prophecies that guided Roman state decisions and religious practices.
Who were the Galli?
self castrated, eunuch priests of Magna Marta who also cross dressed provide evidence of a third, less defined gender
What was significant about the Temple of Venus and Rome?
double temple (two cellae) and Venus and Roma depicted with weapons
Who was the Temple of Divus Antoninus and Diva Faustina dedicated to?
Antoninus Pius and his wife Faustina
What is significant about the Pantheon?
significant for its massive domed roof and oculus, showcasing innovative Roman engineering and architecture, contained 7 niches (planetary gods?), and had a rotunda (round structure in the back)
What was Mithraism and what was the significance?
mystery cult dedicated to Mithras, they had long initiation ritual and had secret handshakes, met underground and slaughtered bulls
What is a groma?
a measuring tool used by architects
what was castrum?
a military fort used by the Romans, designed for defense and organization of troops.
What was a manubial monuments?
triumphal’ architecture, built form the spoils of war
What was Circus Flaminius?
A Greek stadion, Etrsucan athletic areas, now gone
What was spolia?
The reuse of architectural elements and decorative materials from earlier buildings in new constructions, often as a form of tribute or reappropriation.
What were the five imperial fora?
Caesar, Augustus, Vespasian, Domitian/ Nerva, Trajan

Image ID
→ Sarcophagus of the Spouses
→ 6th century BCE
→ banqueting scene?
→ Funerary monument
→ shows both male and female lying together (not typical)

Image ID
→ Denarius depicting The Rape of the Sabines
→ 89 BCE
→ importance of the event since its on coinage
→ shows the myth of the rape of the sabines which occured when the early Romans abducted women from the Sabine tribe to secure wives for themselves, symbolizing the foundation of Rome's future expansion.
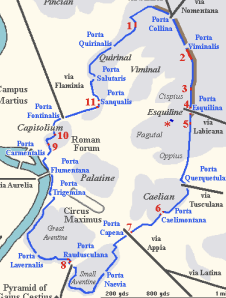
Image ID
→ Servian Wall
→ 4th century BCE
→ fortification
→ very tall
→ invasions became too much that these walls were not enough
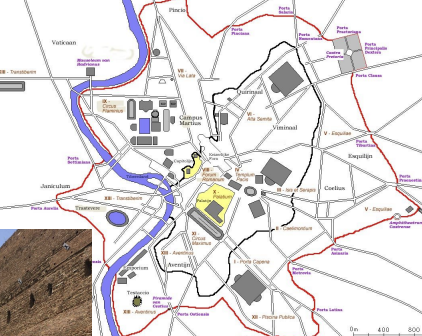
Image ID
→ Aurelian wall
→ 3rd century CE
→ civil wars
→ enhanced defenses
→ included all 7 hills and Campus Martius
→ incorporated previously built structures like the aqueducts
→ meant to fight off hit and run sieges

Image ID
→ Lapis Niger
→ 6th century
→ Cippus (grave marker) for Romulus’ grave?
→ some of the earliest latin depictions
→ Rex => king
→ boustrophedon (writing style that mimics a bull’s track)
→ sacred

Image ID
→ Forma Urbis Romae
→ 3rd century ce
→ one the wall of peace
→ many fragments
→ ancient map of the city
→ has helped us figure out where things once stood

Image ID
→ Curia Iulia
→ 44 BCE
→ great bronze doors
→ altar of victory
→ doors moved to Basilica of St. John Lateran in Rome.

Image ID
→ Temple of Iupiter Optimus Maximus
→ 6th century BCE
→ center of state religion
→ triple cella
→ represents the Olympic triad (Jupiter, Juno, Minerva)
→ terracotta cult sculpture scultped by an Etrsucan
→ housed the Sibylline Books - ‘prophetic’ texts consulted in times of crisis
→ altar outside
→ end of the Roman Triumph

Image ID
→ Temple of Concordia
→ 2nd century CE
→ peripteral temple
→ steps flanked by Hercules/Mercury
→ acroteria (ornamental sculptures or pedestals placed at the apex (top) and/or corners of a pediment)
→ patera and cornucopia
→ dedicated to Concord

Image ID
→ Ara Pacis
→ 1st century (9 BCE)
→ Altar of Augustan Peace
→ couldn’t dedicate it to himself so he dedicated it to state
→ horologium (pendulum clock)
→ Goddess Roma
→ many mythological depictions
→ peace, equality, family, divine approval

Image ID
→ Circus Maximus
→ 7th century BCE
→ largest circus in ancient Rome → venue for chariot races → could hold up to 250,000 spectators → symbol of Roman entertainment and public life
→ had 12 gates to represent the 12 months of the year
→ had an obelisk there (represents the exploitation of Egypt as a Roman province)

Image ID
→ Flavian amphitheatre
→ 1st century ce
→ 80 entrances
→ capacity 50,000-87,000
→ Ludi (gladiatorial games)
→ Naumachia (flooded theater with naval battles)
→ Velarium (awning)
→ seating by status
→ hypogeum (system to raise animals into the area for dramatic affect)
→ symbolizes public spectacle
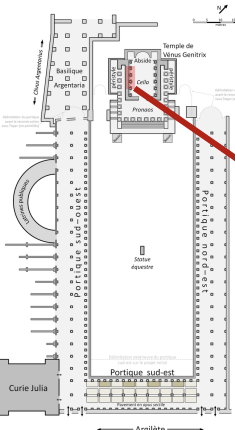
Image ID
→ Forum of Caesar
→ 46 BCE
→ first imperial forum (blueprint for the others)
→ attached to the curia Iulia
→ tabernae
→ double colonnade
→ equestrian statue of Caesar
→ Temple of Venus Genetrix
→ cult statue of Venus
→ Corinthian style
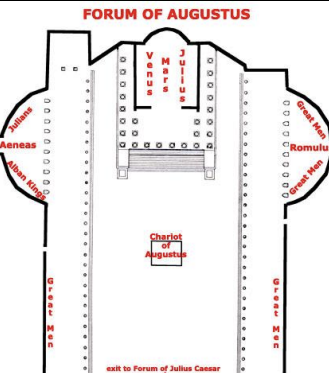
Image ID
→ Forum of Augustus
→ 1st century BCE
→ shares ‘wall’ with Caesar’s forum
→ 2 exhedra (open ‘recess’) - niches for bronze statuary
→ chariot statue (quadriga)
→ Temple of Mars Ultor
→ Ultor = avenger
→ against father’s killer

Image ID
→ Forum of Domitian/Nerva
→ 97 CE
→ ‘transitorium’ (passageway) into the forum
→ smallest of imperial fora
→ temple of Minerva
→ frieze of Arachne

Image ID
→ Forum of Trajan
→ 112 CE
→ largest imperial forum
→ market complex (markets of Trajan)
→ Trajan's Column (very tall, debates over how the friezes of it were supposed to be viewed)
→ 185 steps
→ libraries
→ Basilica Ulpia