Geography #9: Population
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Case Study: Pg 9-13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Define population.
The number of all the inhabitants living in an area.
What factors change population size?
Increases from births and immigration; losses from deaths and emigration.
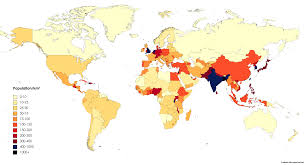
Define population density.
The amount of people living in an area of land.

What does densely populated mean?
Many people in a small area.

What does sparsely populated mean?
Few people in a large area.
What can the specified area of a population range from?
The size of a country to the entire Earth.
What is meant by under population?
The population cannot fully utilize the resources available.
What needs to be done when there is underpopulation?
There has to be an increase in population where the quality of life can only slowly be improved.
How can quality of life be improved in case of under population?
An increase in population would lead to an increase in quality of life.
How is population density calculated?
Population density = total population / total land area.
What is optimum population?
The population that maximizes benefits from available resources.
When is quality of life maximized in terms of population?
When the population is at optimum levels.
Define overpopulation.
When resources cannot sustain the current population.
What are the consequences of overpopulation?
Decline in quality of life through unemployment, pollution, and environmental degradation.
What are the three factors that cause changes in a country's population?
Births, deaths, and migration.
What is natural change?
A change in the population caused by births and deaths.
What is natural increase?
When the birth rate is higher than the death rate
Define natural decrease.
When the death rate is higher than the birth rate.
What does migration include?
Immigration and emigration.
What is immigration?
When people move into a country.
What is emigration?
When people move away from a country.
What is meant by population balance?
The balance achieved between the number of births and deaths within a population.
What is demography?
Study of population
What is the birth rate?
Number of live births per 1000 of the population
What is the fertility rate?
Average number of children per woman
What is the death rate?
Number of deaths per 1000 of the population
What is natural growth?
Birth rate minus death rate
What is the replacement rate?
A fertility rate of 2.1 children per woman
What is migration?
A permanent change of residence
What is net migration?
Number of Immigrants - Number of Emigrants
What is an immigrant?
A person moving into a country
What is an emigrant?
A person leaving a country
What is population density?
Number of people per km²
What is carrying capacity?
Number of people an area can support based on its resources and technology
What is Crude Birth Rate (CBR)?
The number of live births each year per 1000 of the population in an area
What is Crude Death Rate (CDR)?
The number of deaths each year per 1000 of the population in an area
What is natural change?
An imbalance between the CBR and CDR
What is a natural increase?
When there is a higher birth rate than death rate.
What is a natural decrease?
When there is a higher death rate than the birth rate.
What are the population growth characteristics of More Economically Developed Countries (MEDCs)?
Low population growth rates, with low death rates and low birth rates.
What are the population growth characteristics of Less Economically Developed Countries (LEDCs)?
High population growth rates with high birth rates and high death rates.
What impact does improving healthcare have in LEDCs?
Improving healthcare leads to death rates falling, while birth rates remain high.
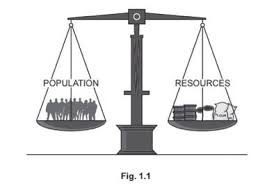
What is the result of the optimum population?
The highest standard of living.
What happens if there are too many people & too few resources?
The standard of living falls.
Why is an optimum population beneficial?
It provides enough people to develop the country's resources, resulting in the highest standard of living.
What is carrying capacity?
The number of people that an area can support.
What is overpopulation?
When there are too many people in an area that can be supported by its resources and technology to have a good standard of living.
What is underpopulation?
When there are more resources available than the population can use effectively.
What are the consequences of overpopulation?
Increased pollution & crime rates, unemployment & underemployment, food and water shortages, and pressure on services (healthcare & education).
What are some consequences of underpopulation?
A shortage of workers leading to lower levels of exports and production affecting the wealth of an area, underused resourced resulting in waste, food & water shortages, fewer people pay taxes leading to higher taxes, and fewer customers for good and services.
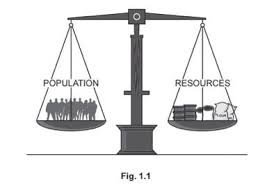
What is the optimum population?
The balance between the number of people and the resources available.
What factor contributes to high birth rates related to family planning?
Poor family planning, leading to unintended pregnancies & increased infant mortality.
What is a factor for high birth rates regarding contraception?
Limited access to contraception results in higher birth rates as couples cannot effectively plan the timing or number of children they desire.
Why are children required on land in high birth rate contexts?
Due to economic necessity. Families may depend on children's labor for agricultural tasks, contributing to household income and assisting with daily tasks.
How do children and their old parents relate in high birth rates?
Countries without good care services for the eldery, people have children to ensure they are taken of when older.
What is a common desire influencing high birth rates?
To have a son, leading to continued attempts until they have one.
What role do religious beliefs play in high birth rates?
Religions oppose any form of contraception and encourage families to have many children.
What factor relates to the emancipation of women in low birth rates?
Getting an education and increased career-mindedness, results in them having children later on in life.
How does access to contraception affect birth rates?
It results in low birth rates by allowing individuals to control fertility and plan family size.
What economic factor influences low birth rates?
High cost of raising children

What type of policies can result in low birth rates?
Anti-natal policies
How does the age of marriage influence birth rates?
Women who marry and have children later in life leads to low birth rates.
What demographic trend contributes to low birth rates?
Urbanisation - When people move from rural areas to cities, it leads to changes in lifestyle and societal values.
In urban settings, individuals often face higher living costs and prioritize career goals, education, and personal achievements over starting families.
Limited living space and access to education and healthcare in urban areas also discourage larger family sizes, resulting in lower birth rates.
What factors contribute to high death rates related to life expectancy?
Low life expectancy and high infant mortality
How does food scarcity relate to death rates?
Food scarcity results in starvation
What issue in the healthcare system contributes to high death rates?
Lack of medical infrastructure and doctors, leading to untreated disease
How does poor hygiene affect death rates?
Poor hygiene and sanitation allows diseases to spread easily, leading to higher death rates.
What type of diseases impact high death rates?
Sexually transmitted diseases such as HIV/AIDS
What contributes to low death rates regarding life expectancy?
Long life expectancy and low infant mortality rate
How does employment in factories affect family size?
Increased employment means fewer children are needed to work on the farmland.
What is the effect of lower infant mortality on birth rates?
More children survive, reducing the need to have many babies.
How does family planning impact birth rates?
Increased use of family planning methods leads to lower birth rates by enabling couples to control the timing and spacing of their pregnancies.
Why do birth rates decrease?
Increased family planning, access to contraception, lower infant mortality, and more employment opportunities.
What impact does improvement in food quality and security have on death rates?
Access to nutritious food promotes better health, thereby lowering death rates.
How does sanitation improvement affect death rates?
Better sanitation and water supplies lead to lower death rates. Access to clean water and proper waste disposal reduces the spread of disease, ultimately improving public health and life expectancy.
What medical improvements contribute to falling death rates?
Better facilities, vaccinations, treatments, scientific advancements, doctors, and new drugs.
How does sanitation influence death rates?
Good hygiene and sanitation contribute to low death rates, with programs like WaterAid, assisting these things.
What ensures there is no starvation in low death rate contexts?
Abundant food supply
How does access to healthcare affect death rates?
Good access to medicine/hospitals results in low death rates.
Why do birth rates remain high?
Due to high infant mortality, economic value of children, cultural traditions, and lack of contraception.
How does previous high infant mortality affect birth rates?
Parents keep having babies in the hope some will survive, leading to high birth rates.
In what way are children considered economic assets and how is that affecting the birth rate?
They work on family farms and help produce food for survival, resulting in high birth rates.
Why do death rates decrease?
Improvements in medical care, sanitation, and food quality.
What role does the lack of contraception play in birth rates?
Leads to higher birth rates. Access to contraception allows family planning, reducing unwanted pregnancies and lowering birth rates.
How does previous high infant mortality affect birth rates?
Parents keep having babies in the hope some will survive.
What are some reasons health wise, for high death rates?
Alcoholism and smoking in Russia lead to high rates of cancer. Obesity from fast food in the USA leads to high rates of heart disease.
How can awareness help death rates fall?
Increase spread of knowledge about a better diet and healthier lifestyle leads to decrease in death rates.
How does poly play into high birth rates?
In polygamous societies, a man many have one more than one wife, leading to more children.
Whats an example of poly situation?
Former King of Sobhuza of Swaziland, who had 70 wives and 210 children.
Population growth or fall is calculated by…
Natural Change + Net Migration
What are some probelms of rapid population growth?
Its slows down their development. Countries find it difficult to feed everyone, provide schooling, and basic healthcare. Resulting in millions going hungry, no education and skills to decrease poverty and develop, and millions suffering and dying of illness and disease.
Define sustainable development.
Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.

What are some examples of anti-natal policies?
Withdrawing tax allowance from people with large families.
Giving incentives through cash and priority for school places.
With the media and posters.
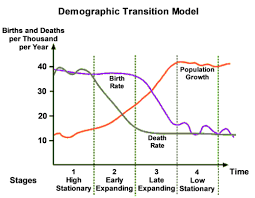
What are the characteristics of Stage 1 in a Demographic Transition Model?
High birth and death rates, total population is low but is balanced due to high birth rates (36/37 per 1000) and death rates (36/37 per 1000). Countries are undeveloped at this stage but there are none as of today.
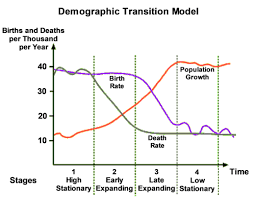
What are the reasons for the high birth and death rates in Stage 1?
High birth rates - Lack of access to contraception, women marry young, high infant mortality so more are born in the hopes they survive, needed for farming, no family planning, and religious and social encouragement.
High death rates - Poor healthcare, disease, famine, and many children die.
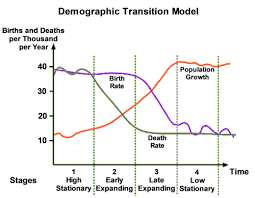
What are the characteristics of Stage 2 in a Demographic Transition Model?
The death rates falls rapidly while the birth rate remains high. Total population will start to rise as a result of the falling death rates (around 18/19 per 1,000).
What are the reasons for the high birth rates and falling death rates in Stage 2?
High birth rates - Lack of access to contraception, women marry young, high infant mortality so more are born in the hopes they survive, needed for farming, no family planning, and religious and social encouragement.
Falling Death Rates - Improved medical care, cleaner water, more and better food, improved sanitation, and a decrease in infant mortality.
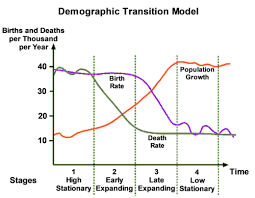
What are the characteristics of Stage 3 in a Demographic Transition Model?
The birth rate falls rapidly (down to around 18 per 1000). Death rate continues to fall but more slowly and steady (to 15 per 1000). Total population is rising rapidly. The gap between birth and death rates will narrow.
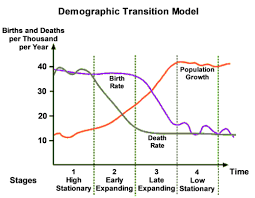
What are the reasons for the falling birth and death rates in Stage 3?
Birth rate - Fewer people are farmers who need children to work on the land, available birth control, decreased infant mortality, women are staying in education longer and marrying later, increased desire for material possessions than large families.
Death rate - Improved medical care, cleaner water, more and better food, improved sanitation, and a decrease in infant mortality.
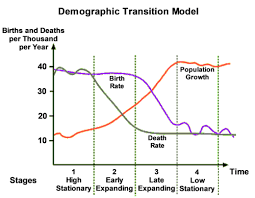
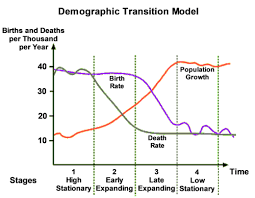
What are the characteristics of Stage 4 in a Demographic Transition Model?
Birth rates and death rates are both low and usually balanced. Total population is high and growing slowly. Its balanced by the low birth rate (15 per 1,000) and death rate (12 per 1,000). Contraception is widely available and there is a social desire to have smaller families.