WSU Biology 315 Lecture Exam #2
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
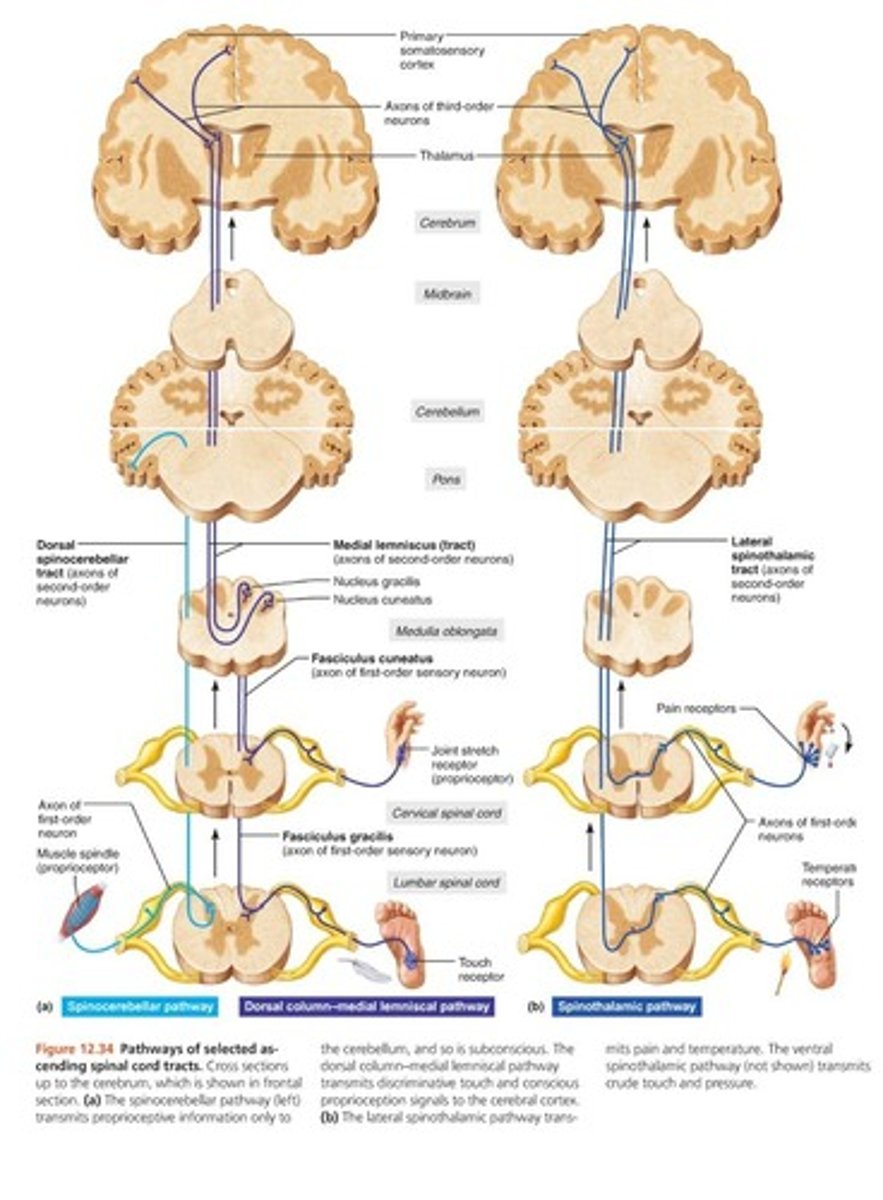
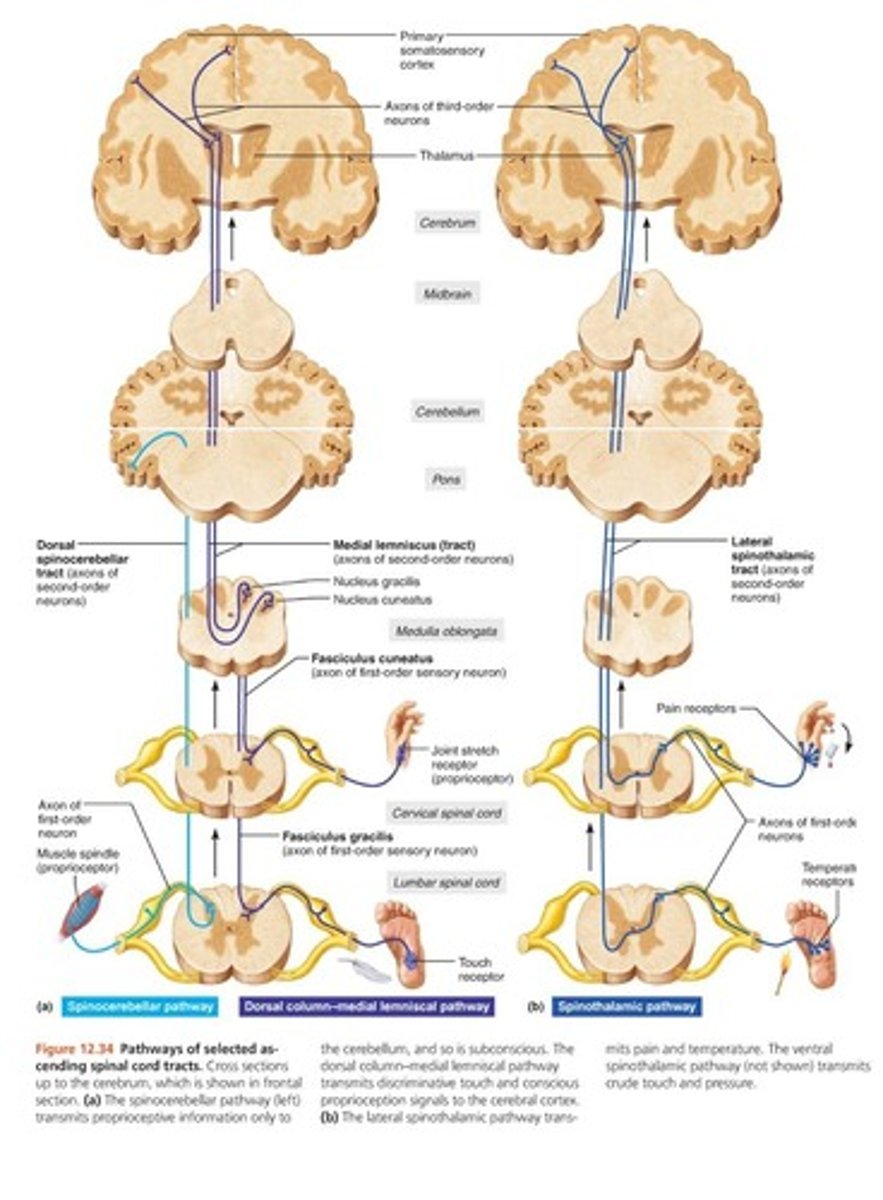
In ascending order, where do the synapses occur along the spinothalamic pathway?
spinal cord, thalamus, cerebral cortex
In ascending order, where do the synapses occur along the spinocerebellar pathway?
dorsal horns of spinal cord (travels through pons to cerebellum)
In ascending order, where do the synapses occur along the dorsal column pathway?
medulla, decussate toward thalamus, primary somatosensory area
autonomic ganglia
groups of autonomic nerve cells located outside the central nervous system, motor
cell body
biosynthetic center and receptive region
What are the components of the peripheral nervous systems?
consists of nerve extending from brain and spinal cord (cranial and spinal nerves)
interneurons
neurons located totally within CNS
An example of an afferent neuron is...
Touch, pain, pressure, vibration neurons
Two examples of efferent neurons are...
skeletal muscle neuron, smooth muscle neuron
What are the general somatic senses? (6 terms)
touch, pain, vibration, pressure, temperature, proprioceptive senses
What are the special somatic senses? (4 terms)
hearing, vision, smell, equilibrium
What are the general visceral senses?
stretch, pain, temperature, chemical changes, nausea, hunger
What is the only special visceral sense?
taste
What does the somatic motor system control?
skeletal muscle
What does the visceral motor system control?
regulates the contraction of smooth and cardiac muscle, secretion by glands
multipolar neuron
a neuron with more than two processes, usually many dendrites and one axon
An example of a multipolar neuron is...
interneuron (association neuron)
Bipolar neuron
two processes that extend from opposite sides of cell body
An example of a bipolar neuron is...
bipolar neuron of retina of eye
Unipolar neuron
one process that emerges from cell body and divides like an inverted letter T
An example of an unipolar neuron is...
sensory neuron
What are synapses in the nervous system?
sites of communication between cells
What are the different places on a neuron where synapses can occur?
axodendritic synapse, axosomatic synapse, axoaxonic synapse
What are action potentials?
specialized cells that conduct electrical impulses along the plasma membrane
What are the supportive cells of nerve tissue?
neuroglia (astrocyte, microglia, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, satellite cells, schwann cells)
Neuroglia function
support and protect neurons
microglia function
part of CNS defense, phagocytosis
ependymal cells function
help produce CSF, bear cilia that help circulate cerebrospinal fluid
oligodendrocyte function
wrap their cell processes around axons in CNS, produce myelin sheaths in Central Nervous System
satellite cell function
surround sensory neuron cell bodies within ganglia of PNS
schwann cell function
surround axons in the PNS, form myelin sheaths around axons of Peripheral Nervous System
How is myelin formed in the peripheral nervous system?
formed by schwann cells, one myelin sheath per schwann cell
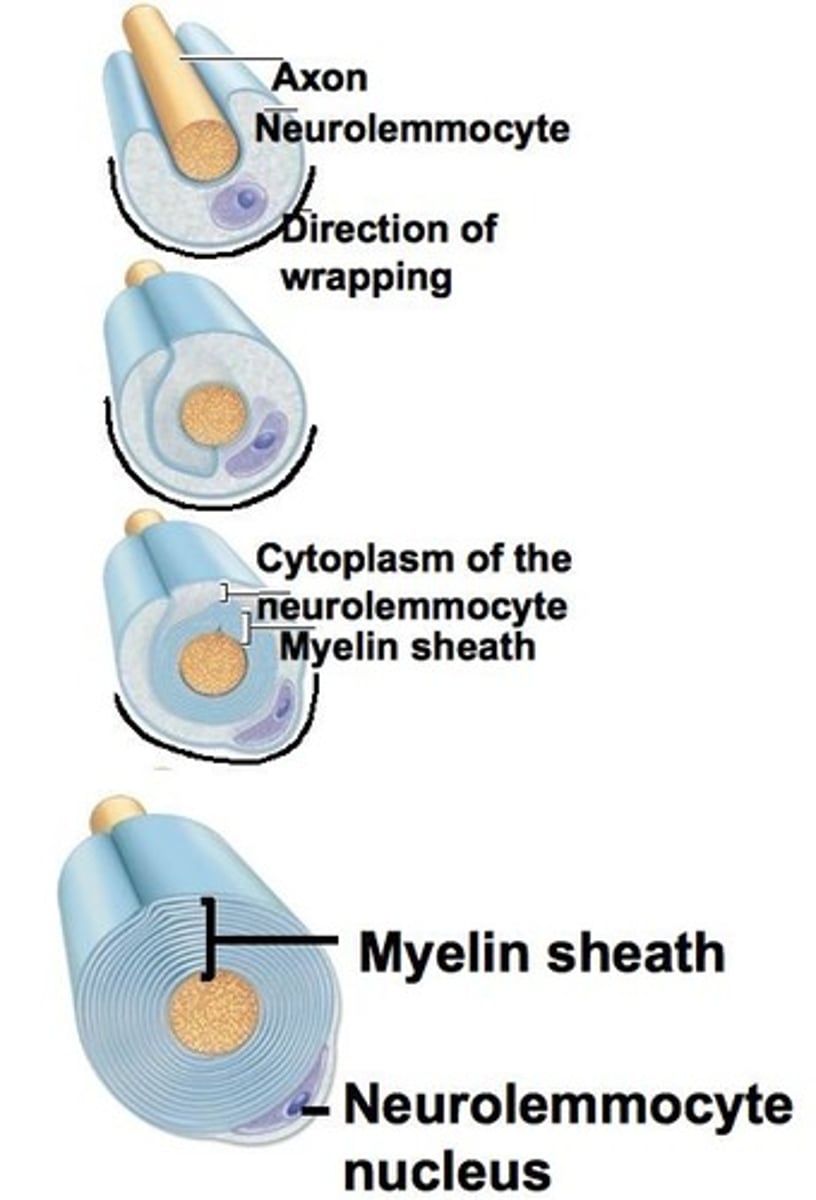
How is myelin formed in the central nervous system?
oligodendrocytes coil around many different axons and produce myelin
What type of tissue makes up the epineurium?
dense irregular connective tissue (E)
What type of tissue makes up the perineurium?
dense irregular connective tissue (P)
What type of tissue makes up the endoneurium?
loose connective tissue
What is gray matter? (3 terms)
cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals
What is white matter?
myelinated axons
What are the different ways that gray matter is organized in the central nervous system? (3 terms)
nuclei, cortex, and columns
nuclei
clusters of neuron cell bodies in CNS
columns
rows of neuron cell bodies
What are tracts in the central nervous system made of? (what are the tracts? 3 terms)
white matter (dorsal tracts, lateral tracts, ventral tracts)
What are the primary vesicles that form during brain development?
prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon
prosencephalon
the forebrain
mesencephalon
the midbrain
rhombencephalon
the hindbrain
What are the secondary vesicles that form during brain development?
telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, myelencephalon
Prosencephalon divides to form which secondary vesicles?
telencephalon, diencephalon
Rhombencephalon divides to form which secondary vesicles?
metencephalon, myelencephalon
What are the adult brain regions that develop from secondary vesicles? (8 terms)
the cerebral hemispheres, thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, midbrain, pons, cerebellum, medulla
The telencephalon develops into the...
cerebral hemispheres
The diencephalon develops into the...
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
The mesencephalon develops into the...
midbrain
The metencephalon develops into the... (2 terms)
pons, cerebellum
The myelencephalon develops into the...
medulla
Meninges
fibrous layer that covers the brain and spinal cord
What type of tissue is the Dura Mater comprised of?
dense irregular connective tissue
How is the Dura Mater organized?
periosteal layer against the skull and a meningeal layer outside of that, which also covers the spinal cord
What type of tissue is the Arachnoid Mater comprised of?
connective tissue
What type of tissue is the Pia Mater comprised of?
delicate loose connective tissue
How is the Pia Mater organized?
one thin layer clings tightly to the surface of the brain, follows convolutions of cortex
What is name of the fluid found in the subarachnoid spaces?
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
What other structures are present in the subarachnoid space?
blood vessels that supply the brain
In the spinal cord, ascending tracts carry what type of information?
sensory information
In the spinal cord, descending tracts carry what type of information?
motor information
What type of sensory information is carried by the dorsal column pathway?
touch, pressure, conscious proprioception
What type of sensory information is carried by spinothalamic pathway?
pain, temperature, non-discriminative touch
What type of sensory information is carried by the spinocerebellar pathway?
unconscious proprioception to cerebellum
How many synapses occur along the dorsal column pathway?
three synapses (D)
How many synapses occur along the spinothalamic pathway?
three synapses (S)
How many synapses occur along the spinocerebellar pathway?
two synapses
What are the final destinations in the brain for the dorsal column pathway?
primary somatosensory area of cerebral cortex (D)
What are the final destinations in the brain for the spinocerebellar pathway?
pons to cerebellum
What are the final destinations in the brain for spinothalamic pathway?
primary somatosensory area of cerebral cortex (S)
function of precentral gyrus (Bromann's 4)
primary motor cortex
function of postcentral gyrus (Brodmann's 1-3)
primary somatosensory cortex
function of Brodmann's 5 & 7
integrates different sensory inputs
function of pyramidal cells
motor, specific ones control specific areas of the body
function of pyramidal tracts in cerebral hemispheres
control skilled movement
function of limbic system
emotions and memory
primary function of the thalamus
acts as a relay station for incoming sensory messages
lateral geniculate nucleus function of thalamus
receive input from retina, relay signals via optic tracts to primary visual centers
medial geniculate nucleus function of the thalamus
relays auditory information to cerebral hemispheres
function of the hypothalamus
main visceral control center of the body (control of ANS, regulation of body temperature, regulation of hunger and thirst sensations, controls secretion of pituitary gland and hormones, controls emotional response)
functions of the pineal gland
secretes melatonin
function of superior colliculi
visual reflexes
function of inferior colliculi
auditory reflexes
function of cerebral peduncles
contain pyramidal tracts, contain red nucleus and substantia nigra
function of superior cerebellar peduncles
output tracts, carry axons FROM cerebellum to primary motor cortex
function of periaqueductal gray matter
fright-and-flight reaction; panic behaviors (together with amygdala), mediates response to visceral pain (cold sweat, etc.), analgesia
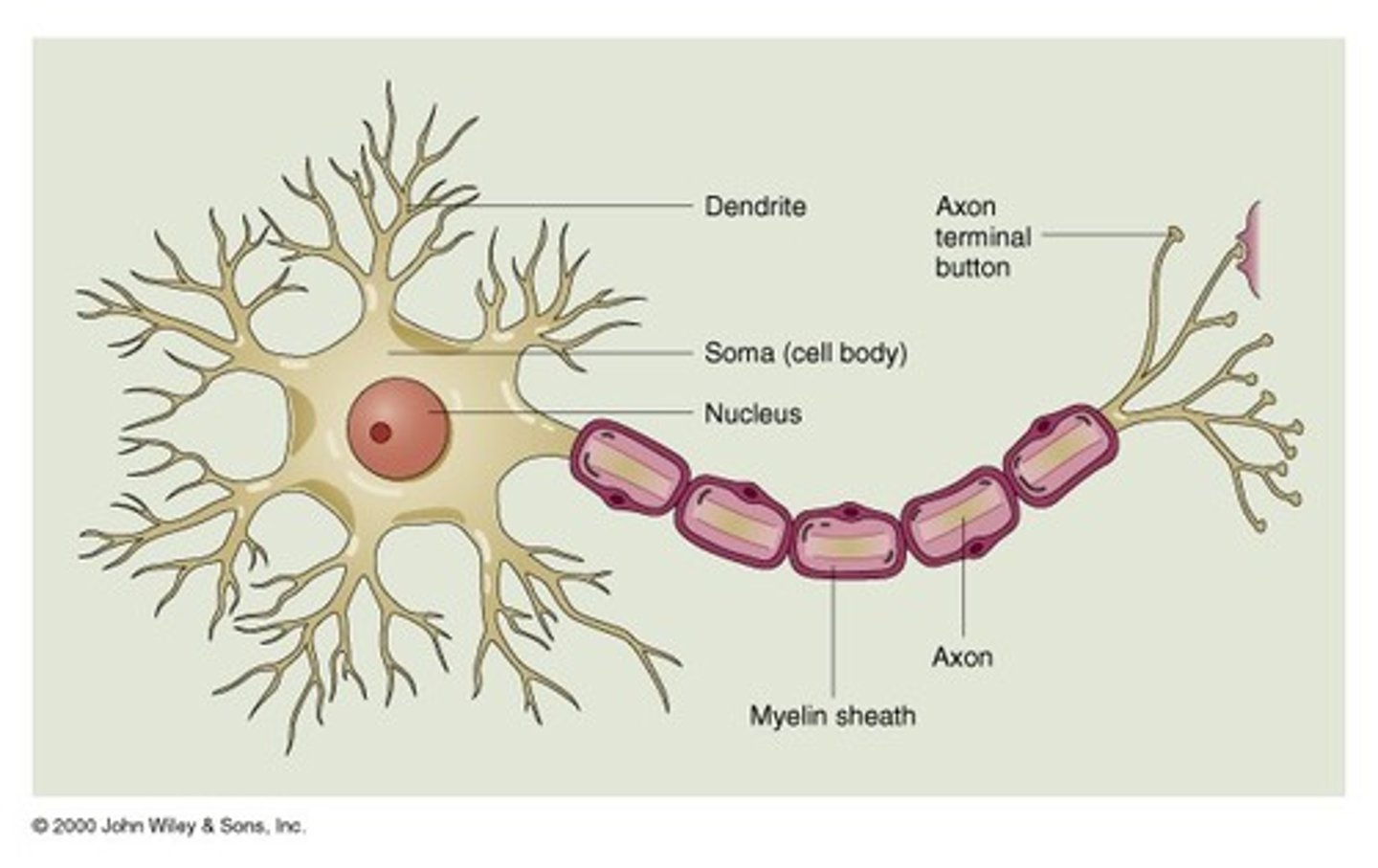
different parts of neurons (outside to inside)
axon terminals, dendrites, cell body, axon hillock
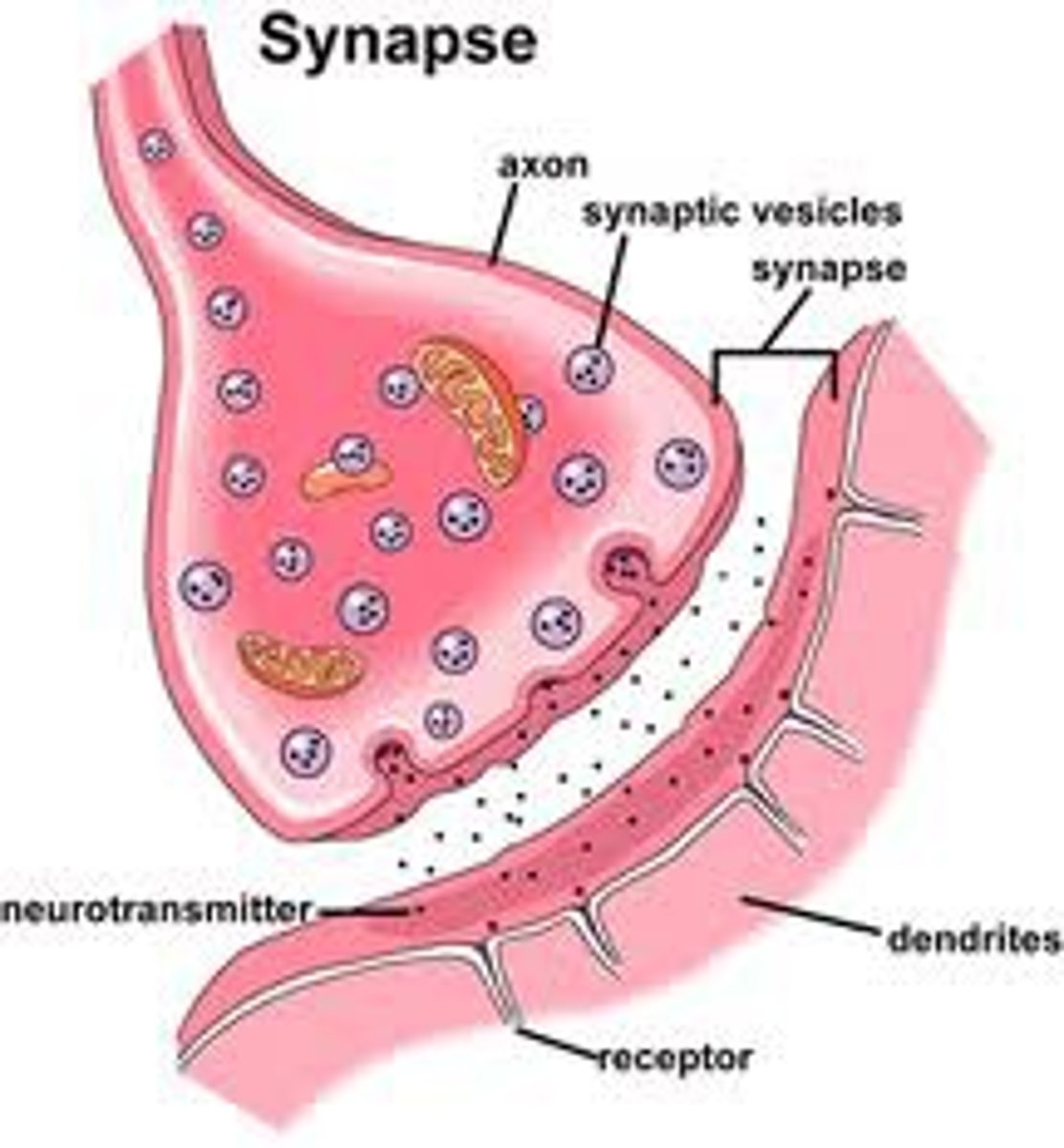
synapse anatomical structure approaching synapse (3 terms)
axon terminal, synaptic vesicles, synaptic cleft
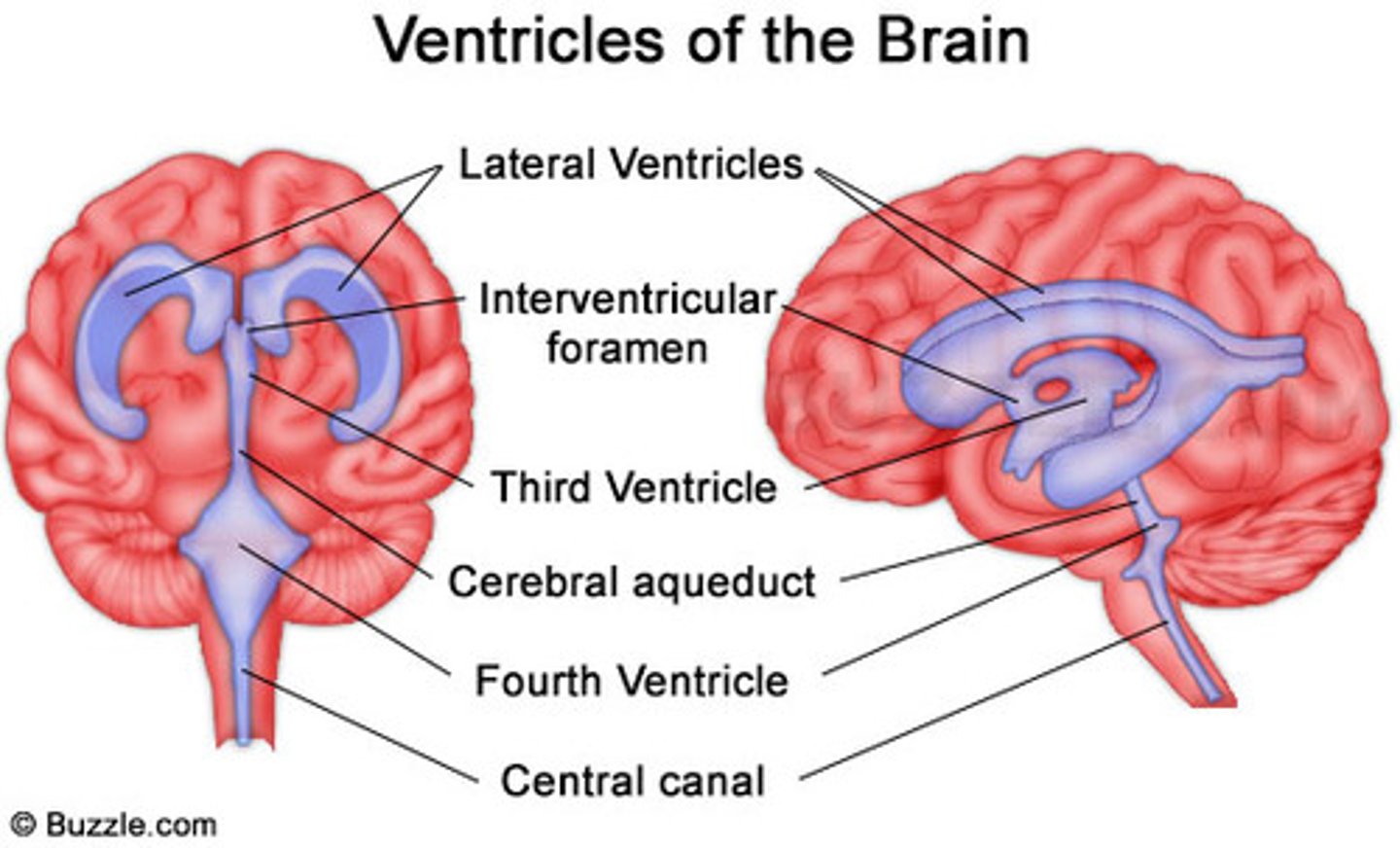
ventricles superior to inferior
lateral ventricles, third ventricle, fourth ventricle
cerebrospinal fluid pathway (5 terms)
choroid plexus, ventricles, lateral & medial apertures, subarachnoid space, dural sinuses
Where is cerebrospinal fluid produced?
choroid plexus
Where does the cerebrospinal fluid return to blood?
dural sinuses
dorsal column pathway (image)
dark blue left image
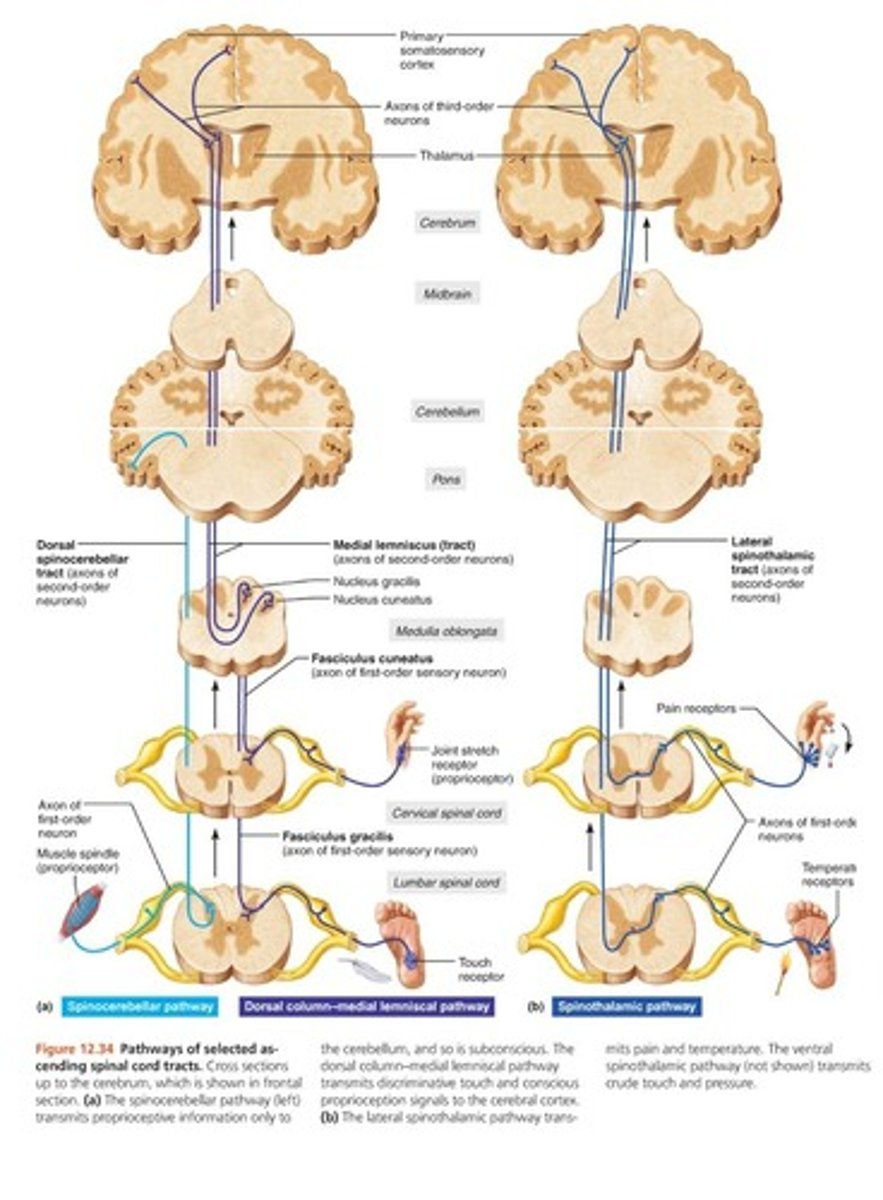
spinocerebellar pathway (image)
light blue left image
spinothalamic pathway (image)
right image
Inflow and outflow of information from cerebellum
superior cerebellar peduncles (outflow), middle cerebellar peduncles (inflow), inferior cerebellar peduncles (input to cerebellum)