Clinical Skills - Foot - Distal
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Handbook 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
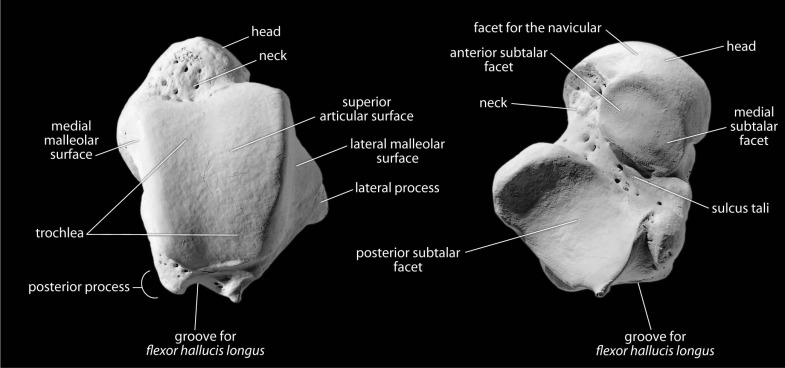
Skeletal Anatomy:
Talus:
Trochlea
Head
Neck
Articular surfaces for: Medial malleolus + Lateral malleolus
Posterior process and groove for FHL
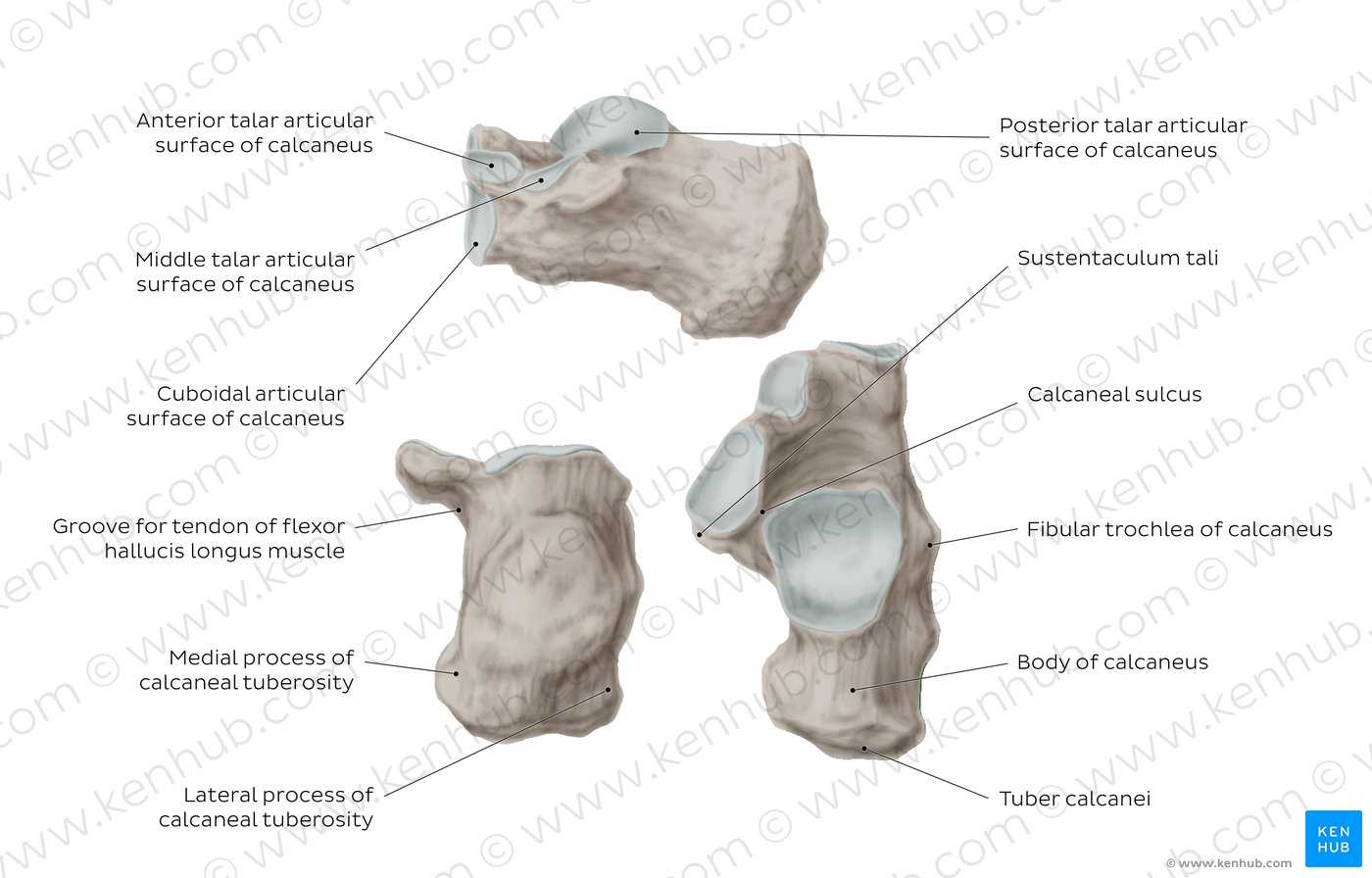
Calcaneus:
Calcaneal tuberosity – medial and lateral process
Articular surface for talus
Sustentaculum tali
Surface for cuboid
Groove for FHL and PL
Fibular trochlea
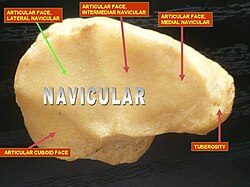
Navicular:
Tuberosity
Groove for talus and cuneiforms
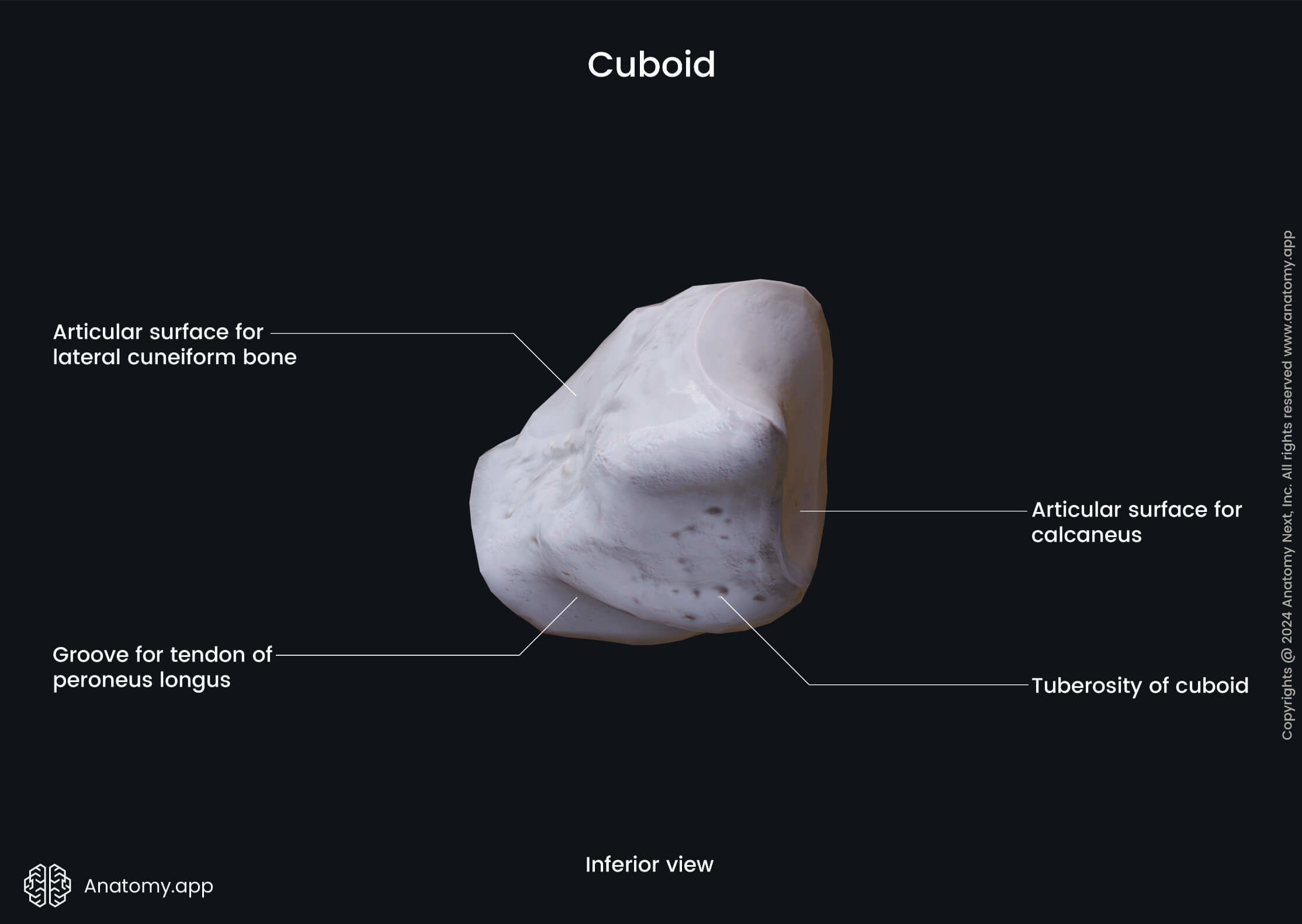
Cuboid:
Tuberosity
Groove for per. long.
Articular surfaces for talus and cuneiforms
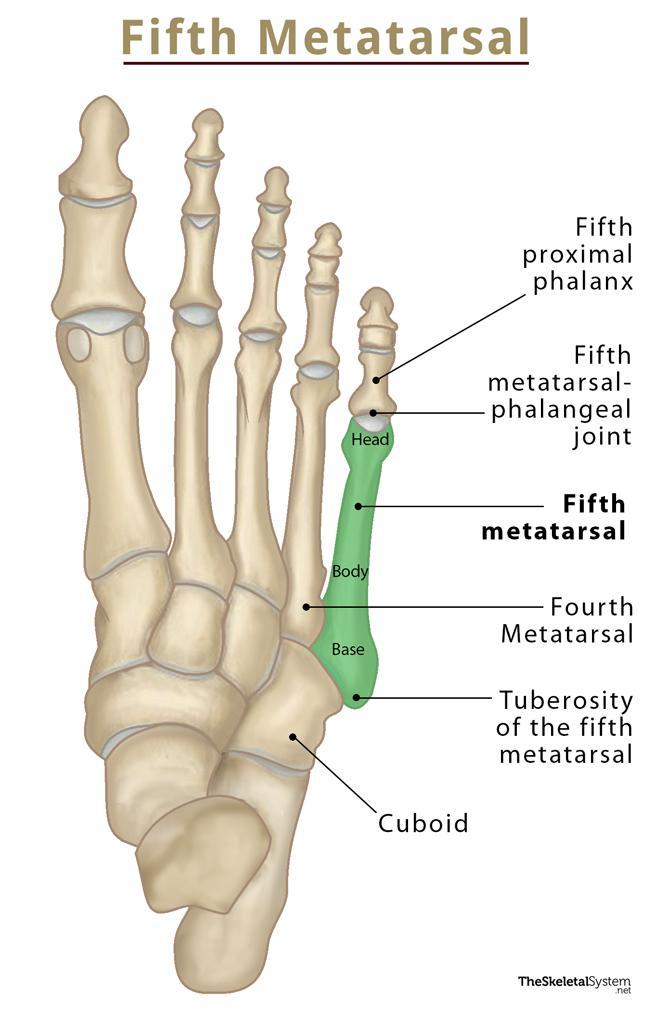
Metatarsals:
Base, shaft and head
Tuberosity of 5th MT
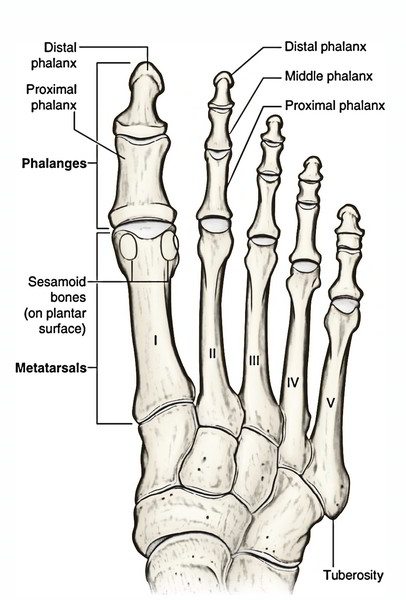
Phalanges:
Base, shaft, head
Proximal, middle and distal
Palpate the prominent bony landmarks at the level of the ankle.
Surface Anatomy:
Medial and lateral malleoli:
Palpate the medial and lateral malleoli with thumb and index finger. Move your fingers inferior and anterior in relation to the malleoli until they move into a depression behind the anterior compartment tendons. Your fingers should be on either side of the neck of talus. The head is the most anterior point, articulating with the navicular.
Head/Neck of talus and talocrural joint
With your thumb and index finger in position, move the ankle into full plantarflexion. The trochlea should roll forwards from underneath the tibia, so that you can now palpate over the anterior aspect of the trochlea.
Trochlea of talus
With the ankle in plantargrade (neutral), palpate the medial malleolus, and then move your fingers inferior until you palpate a small prominence (like a bony ledge). Inferior to the ledge, you will feel soft tissue only – this is how you know you are on the sustentaculum tali. Superior to the ledge, you are on the medial joint line of the subtalar joint.
Sustentaculum tali
Find the sustentaculum tali (calcaneus) and the navicular. Try to palpate where the bones meet on the medial foot.
Discuss the joint structure.
Talocalcaneonavicular joint
From the sustentaculum tali move your fingers anteriorly, the next bony prominence you feel on the medial aspect is the navicular tuberosity. Remember that the head of the talus should articulate with the navicular. Check that everything lines up.
Navicular tuberosity
Palpate between the sustentaculum tali and the navicular tuberosity.
Spring ligament (Talocalcaneonavicular ligament )
First palpate the 5th metatarsal until you find the tuberosity on the proximal aspect. Move off the 5th metatarsal onto the cuboid bone just proximal to it.
The cuboid is also located anterior/distal to the sinus tarsi.
Cuboid:
Try to palpate where the cuboid meets the calcaneus on the lateral foot and discuss the joint structure.
Calcaneocuboid joint
Like the cuboid, these are easiest to find by starting distally on the adjoining metatarsals and moving proximally from there:
· Medial cuneiform sits proximally to the 1st metatarsal
· Intermediate cuneiform – second metatarsal
Lateral cuneiform – third metatarsal
Cuneiforms:
Draw a line along the bases of the metatarsals (Tarsometatarsal Joints)– note how the first metatarsal is shorter than the others.
The metatarsal heads are best found on the plantar surface and become visible in toe extension (metatarsophalangeal joints).
Metatarsals (Draw lines)
Identify the proximal, middle and distal phalanges by moving distally across each joint. The first toe has only proximal and distal phalanges (interphalangeal joints).
Phalanges:
Extend the toes and observe a small circular muscle belly on the dorsum of the foot, just anterior to the sinus tarsi.
Extensor digitorum and extensor hallucis brevis
Palpate the Achilles tendon of the gastrocnemius, soleus +/- plantaris
Achilles Tendon:
Palpate the attachment of the Achilles tendon to the posterior aspect of the calcaneus.
Calcaneal Tuberosity:
Palpate the strong fascia on the sole of the foot.
Note how the fascia becomes more taught when the toes extend at the metatarsophalangeal joints (Windlass mechanism).
Plantar fascia (including plantar aponeurosis)
Draw a line over the various arches. Observe the arches in non-weightbearing and weightbearing. Visualise the structures that support the arches.
Medial Longitudinal, lateral longitudinal and transverse arches
Extend the toes at the metatarsophalangeal joints and observe the prominent metatarsal heads on the plantar surface of the foot.
Metatarsal heads

Abduct the big toe (+/- resistance)
Origin:
Medial tubercle of calcaneal tuberosity
Insertion:
Medial side of base of proximal phalanx 1st digit
Nerve Supply:
Medial Plantar Nerve (S2,S3)
Muscle Identification:
Abductor Hallucis:
how to test +
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
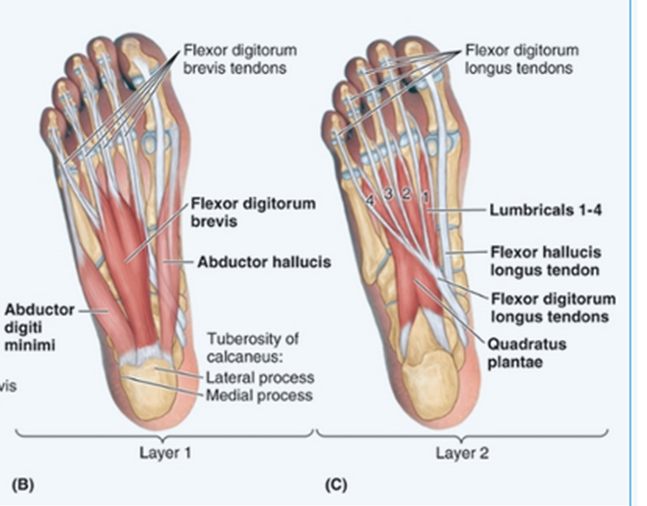
Flex proximal interphalangeal joints.
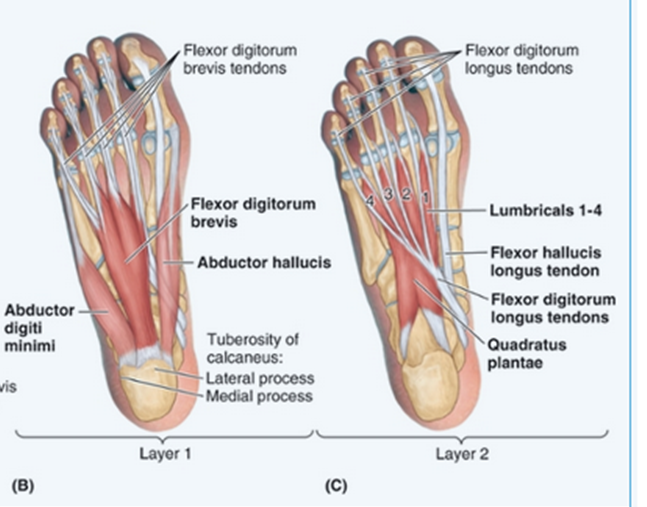
Origin:
Medial tubercle of calcaneal tuberosity
Insertion:
Both sides of middle phalanges of lateral 4 digits
Nerve Supply:
Medial Plantar Nerve (S2,S3)
Flexor Digitorum Brevis
How to resist/activate
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
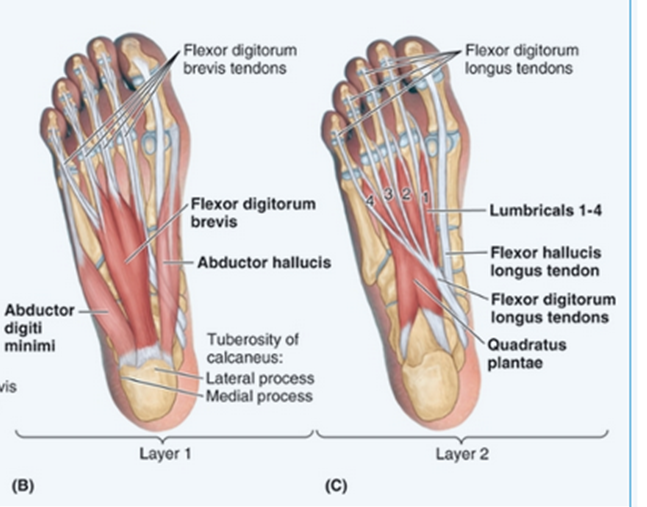
Abduct the little toe
Origin:
Lateral tubercle of calcaneal tuberosity
Insertion:
Base of proximal phalanx of 5th digit
Nerve Supply:
Lateral plantar nerve (S2,3)
Function:
Abduction + flexion of little toe at MTPJ
Abductor Digiti Minimi:
How to activate/test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
Flex the distal interphalangeal joints – working through FDL
+
Origin:
Plantar surfaces of calcaneus (Medial + Lateral tubercles)
Insertion:
Posterolateral margin of tendon of FDL
Nerve Supply:
Lateral Plantar Nerve (S2,3)
Function:
Flexion of lateral 4 toes (through attachment to FDL)
Assists in propulsion
Quadratus Plantae:
How to activate/ test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
Flexion at the metatarsophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints.
From Flexor to Extensor Compartment
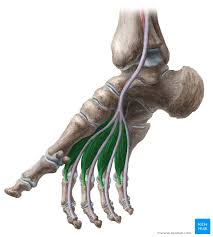
Origin:
Tendon of FDL
Insertion:
Base of proximal phalanx and extensor hood
Nerve Supply:
Medial (1st lumbrical) and lateral (Lateral 3 lumbricals) plantar nerves
Function:
MTP Flexion + IP extension
Lumbricals:
How to activate/ test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
Flex the little toe at PIP
Origin:
Base of 5th MT
Insertion:
Base of proximal phalanx of 5th digit
Nerve:
Lateral Plantar Nerve
Function:
Little toe flexion @ MTPJ
Flexor digiti minimi
How to activate/ test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function

Adduct big toe. Hold against resistance.
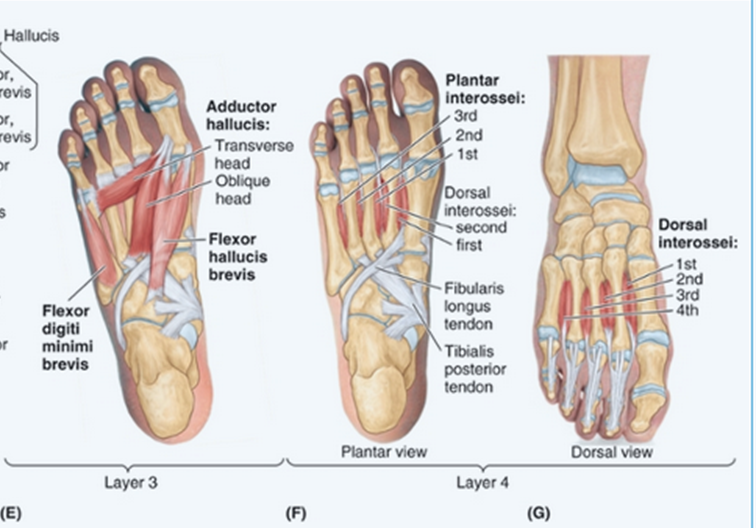
Origins:
Oblique head MT’s 2-4
Transverse head - MTP’s (plantar ligaments)
Insertion:
Lateral side of base of proximal phalanx
Nerve Supply:
Lateral Plantar Nerve
Function:
Adduction of great toe
Support of transverse arch
Adductor Hallucis:
How to activate/ test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
Flex big toe at PIP.
Origin:
Plantar surface of cuboid and lateral cuneiform
Insertions (2 heads):
Base of proximal phalanx (Medial - abductor hallucis) (Lateral - adducotr hallucis - check)
Nerve:
Medial Plantar Nerve
Function:
Great toe flexion at MTPJ
Aids in push off phase of gait.
Flexor hallucis brevis:
How to activate/ test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
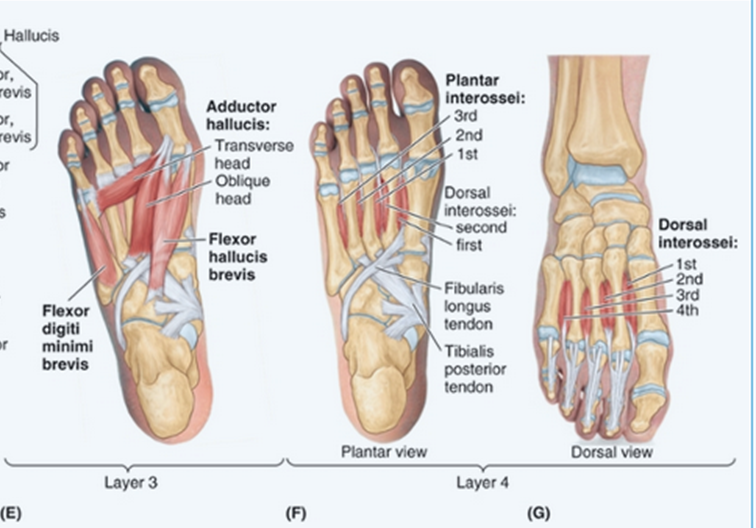
Adduct lateral toes
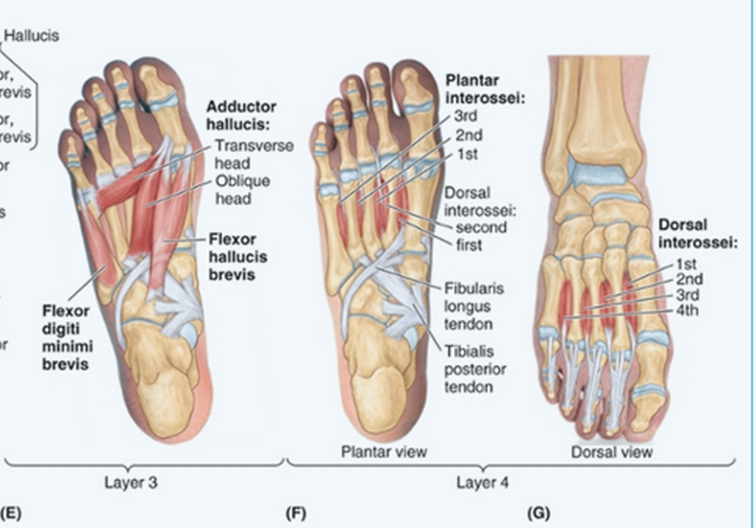
Origin:
Medial side of plantar surface of proximal MT’s 3-5
Insertion:
Medial side of base of proximal phalanx 3-5
Nerve Supply:
Lateral Plantar Nerve
Function:
Adduction of MTPJ’s 3-5 (PAD)
Control during push off
Plantar Interossei:
How to activate/ test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
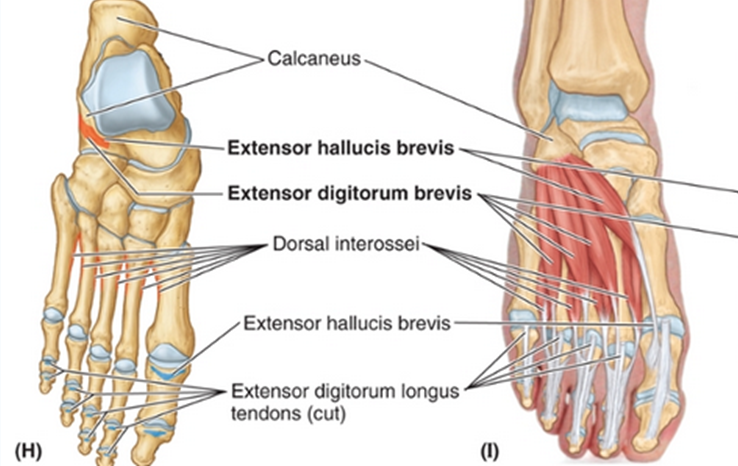
Extend big toe at PIP
Origin:
Calcaneus - floor of sinus tarsi
Insertion:
Dorsal aspect of base of proximal phalanx of great toe
Nerve Supply:
Deep peroneal nerves (L5, S1)
Function:
Great toe extension at the MTP
Extensor Hallucis Brevis:
How to activate/ test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
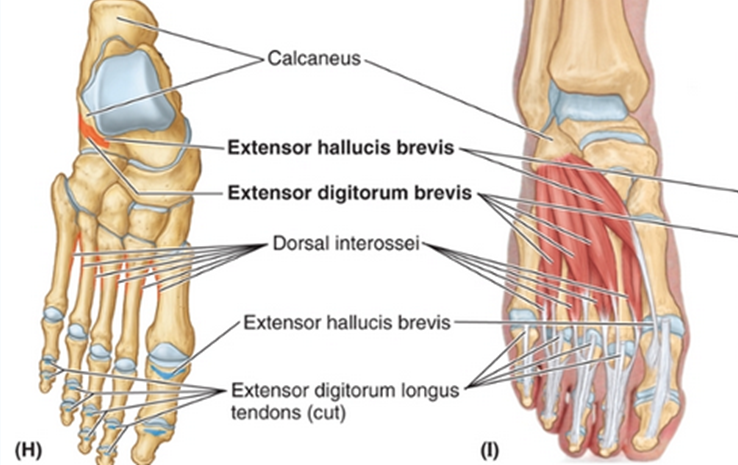
Extend big toe at PIP
Origin:
Calcaneus - Floor of sinus tarsi
Insertion:
extensor hoods of toes 2-4
Nerve Supply:
Deep peroneal nerve
Function:
Extension of toes 2-4
Extensor Digitorum Brevis:
How to activate/ test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function
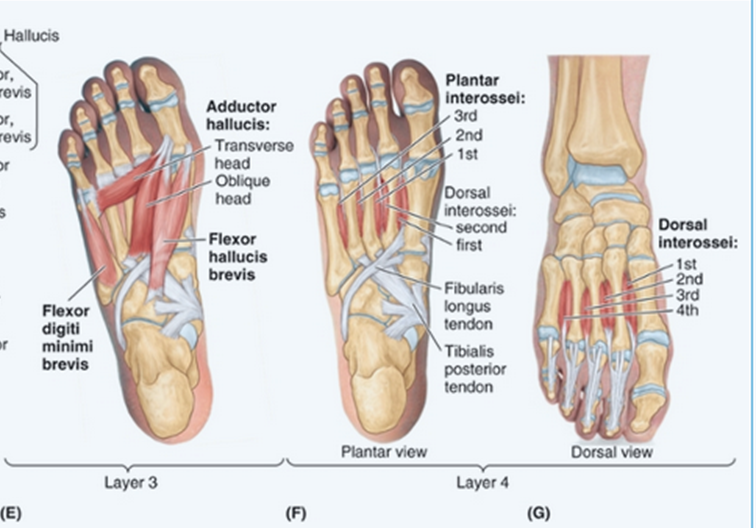
Abduct lateral toes
Origin:
Dorsal surface of proximal metatarsals (medial and lateral sides)
Insertion:
Bases of proximal phalanges 2-4
Nerve Supply:
Lateral Plantar Nerves
Function:
Abduction of MTPJ’s 2-4 (DAB - dorsal interossei ABductor)
Control of forefoot during pushoff
Dorsal Interossei:
How to activate/ test
+
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Function