fluid and electrolyte balance
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Net secretion
clearanceX > GFR
Net reabsorbed
clearanceX < GFR
1o regulated by renal-related hormones:
Aldosterone (ANG II), ADH, ANP
MEMORIZE FLOWCHART
Aldosterone
Diffuses across membrane because of cholesterol backbone and increases/modulates activity of sodium and potassium channels and atpase pump
More sodium absorbed
More potassium secreted
Binds to intracellular receptor
Membrane Recycling
Vasopressin binds to membrane receptor.
Receptor activates CAMP second messenger system.
Cell inserts AQP2 water pores into apical membrane. AQP2 increase or decrease depending on how much ADH there is
Water is absorbed by osmosis into the blood.
Drinking large amount of water | |||
Vol inc
Osm dec
Ingestion of isotonic saline | |||
Vol inc
Osm no change
Ingestion of hypertonic saline |
Vol inc
Osm inc
Replacement of sweat loss with plain water | |||
Vol no change
Osm dec
Normal volume and osmolarity | |||
No changes to vol and Osm
Eating salt without drinking water |
Vol no change
Osm inc
Incomplete compensation for dehydration | |||
Vol and Osm dec
Hemorrhage | |||
Vol Dec
Osm no change
Dehydration (e.g., sweat loss or diarrhea) |
Vol Dec
Osm inc
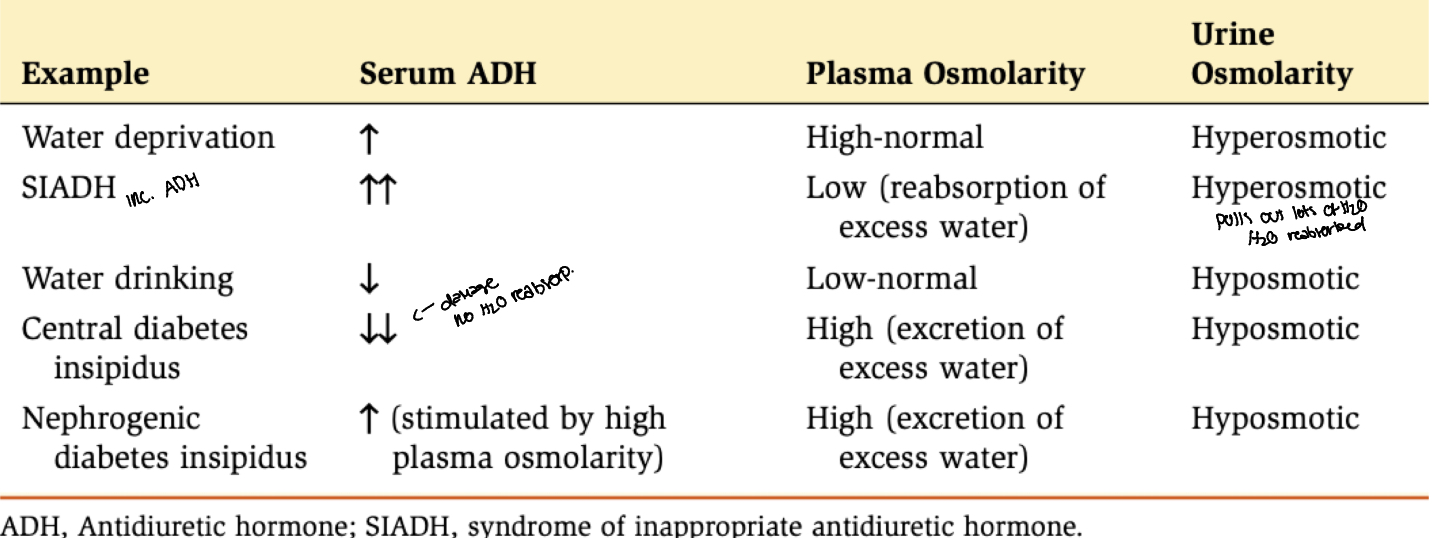
osmoregulation
Body fluid osmolarity is maintained at a value of about 290mOsm/L (for simplicity, 300mOsm/L)
It occurs in late distal tubule and collecting duct.
Water reabsorption is responsible for maintaining constant body fluid osmolarity.
Normal urine
50 to 1200 mOsM
isosomatic urine
urine osmolarity =blood osmolarity
Hyperosmotic urine
urine osmolarity > blood osmolarity
Hypoosmotic urine
urine osmolarity < blood osmolarity
ADH is main determinant to osmolarity of urine
MEMORIZE
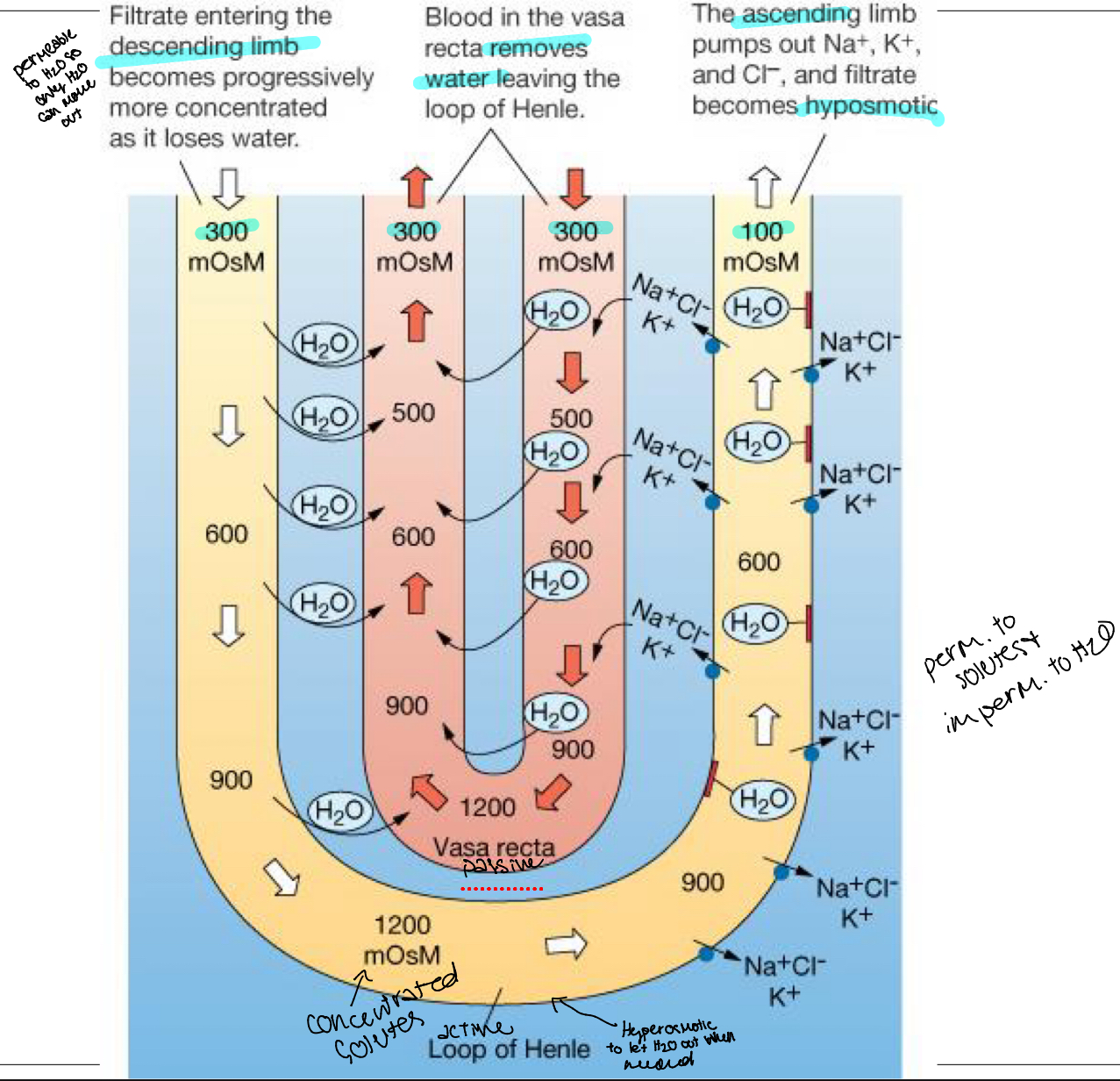
loop of Henle
Functions: Site of production of dilute urine, Create/maintain osmotic gradient in medulla
Mechanisms: Countercurrent multiplication (loop of Henle), Countercurrent exchange (vasa recta)
Countercurrent: flow is parallel, opposite directions
establishes the medullary concentration gradient
Countercurrent multiplication (loop of henle)
active process that establishes the medullary osmotic gradient.
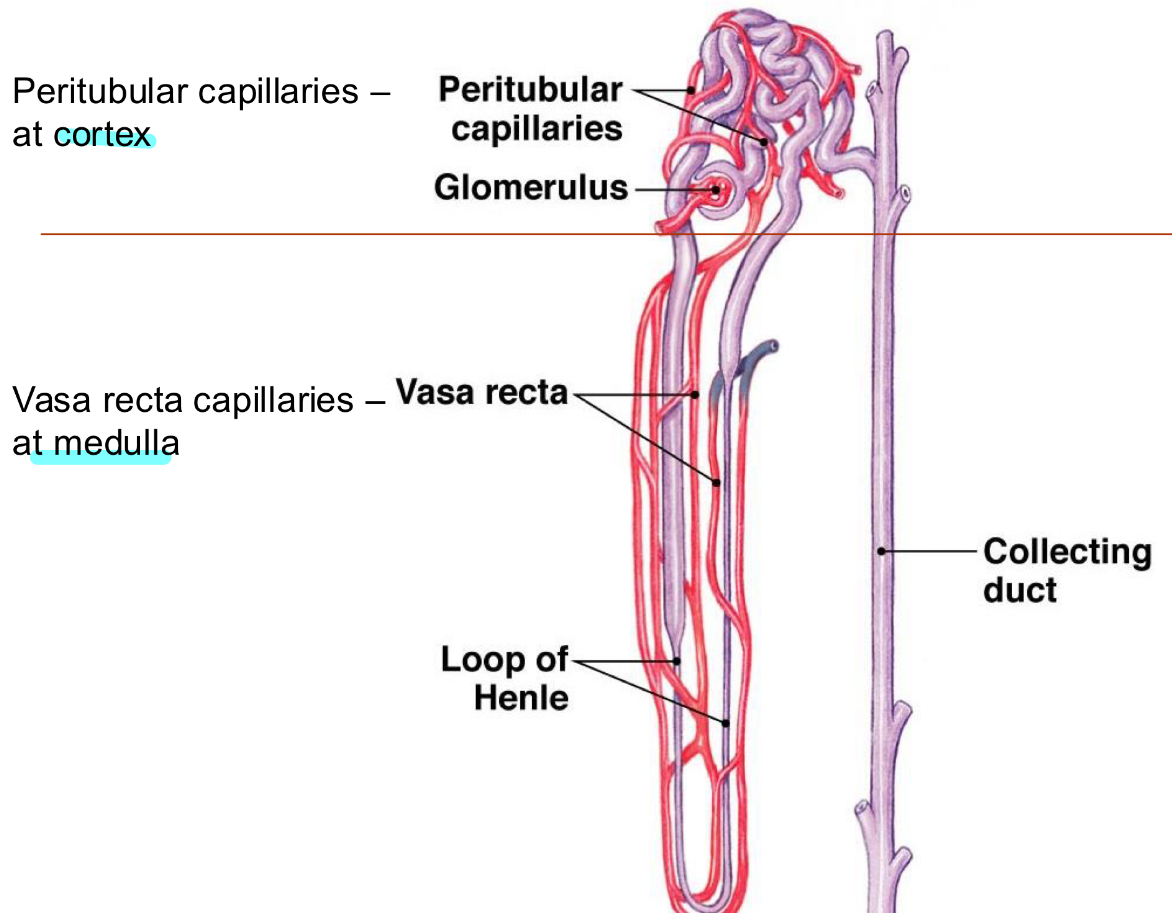
Countercurrent exchange (vasa recta)
passive process that helps maintain the gradient. The passive properties of the vasa recta are the same as for other capillaries: They are freely permeable to small solutes and water. Blood flow through the vasa recta is slow, and solutes and water can move in and out, allowing for efficient countercurrent exchange.
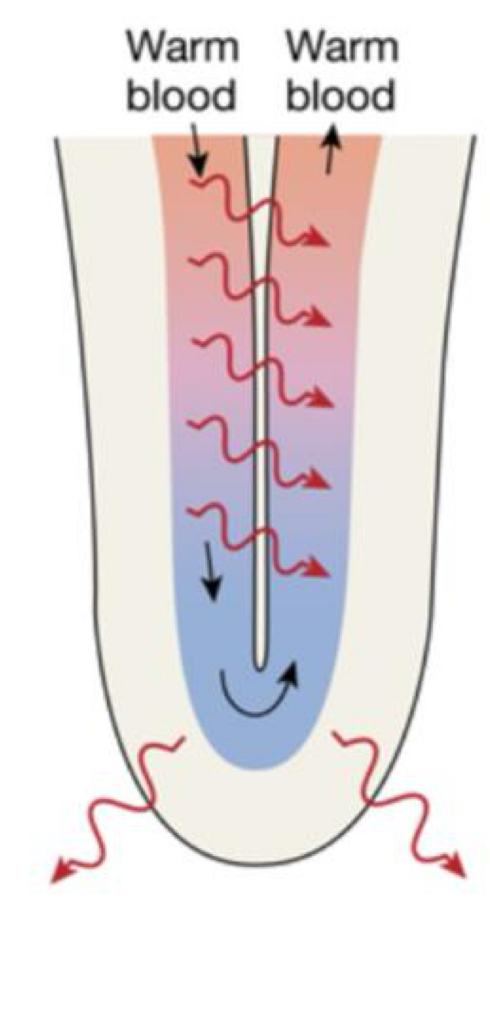
Countercurrent heat exchanger
allows warm blood entering the limb to transfer heat directly to blood flowing back into the body.
Proximal tubule
Isoosmotic fluid
300 mOsm
Loop of henle
Hyperosmotic fluid
Higher osmolarity
Distal tubule
Hyposomotic fluid
~100mOsm
Loop of henle and vasa recta