APUSH: Period 5
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Manifest Destiny
A term coined by John L. O'Sullivan in 1845 to express the idea that Euro-Americans were fated by God to settle the North American continent from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean.

"Fifty-Four Forty or Fight"
slogan used in the 1844 presidential election as a call for us annexation of the Oregon territory
Wilmot Proviso
1846 proposal that outlawed slavery in any territory gained from the War with Mexico
free-soil movement
A political movement that opposed the expansion of slavery. In 1848 the free-soilers organized the Free-Soil Party, which depicted slavery as a threat to republicanism and to the Jeffersonian ideal of a freeholder society, arguments that won broad support among aspiring white farmers.

forty-niners
People who went to California looking for Gold (They left in 1849)

"slavery follows the flag"
The assertion by John C. Calhoun that planters could by right take their slave property into newly opened territories.

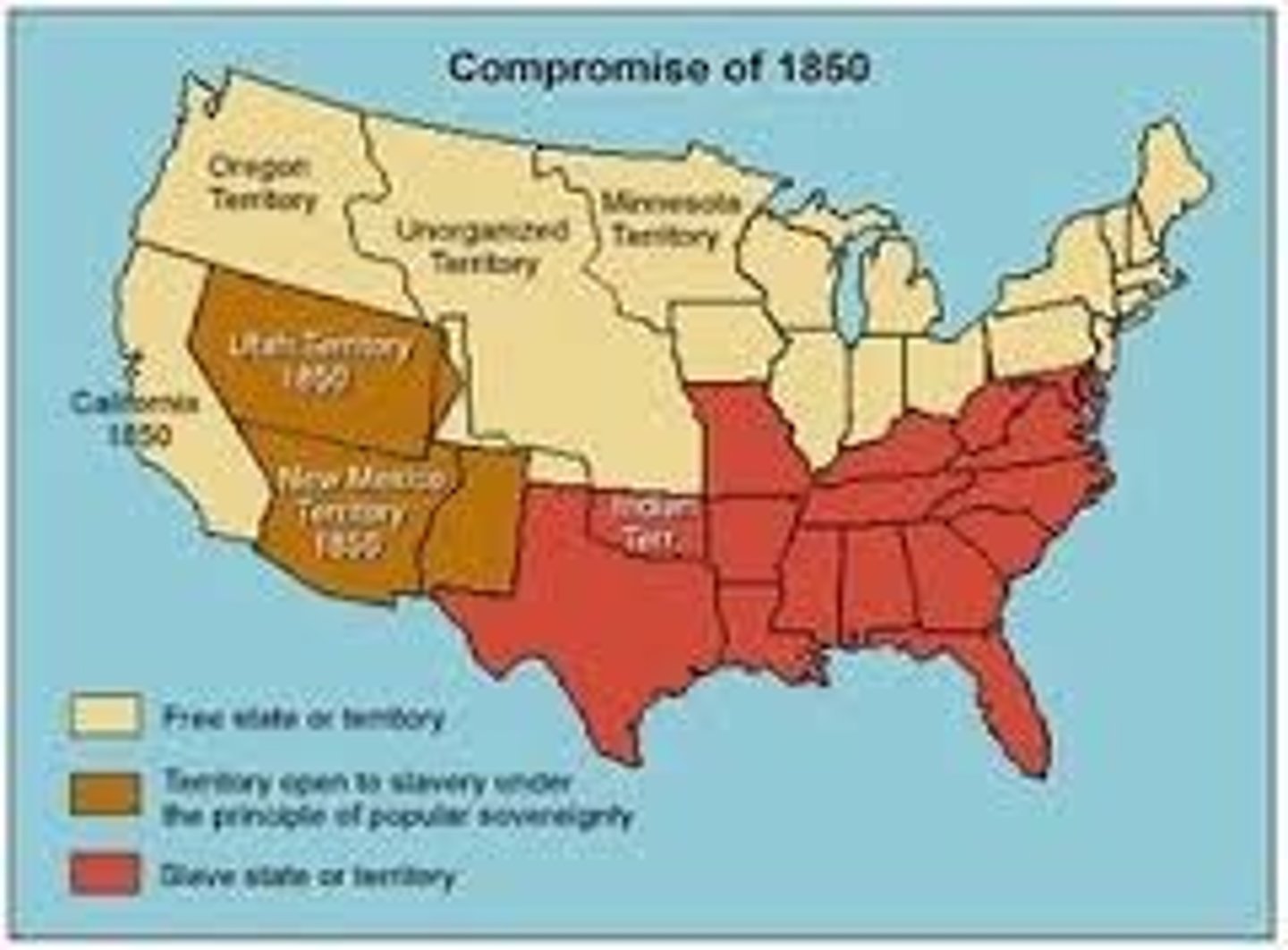
Compromise of 1850
(1) California admitted as free state, (2) territorial status and popular sovereignty of Utah and New Mexico, (3) resolution of Texas-New Mexico boundaries, (4) federal assumption of Texas debt, (5) slave trade abolished in DC, and (6) new fugitive slave law; advocated by Henry Clay and Stephen A. Douglas
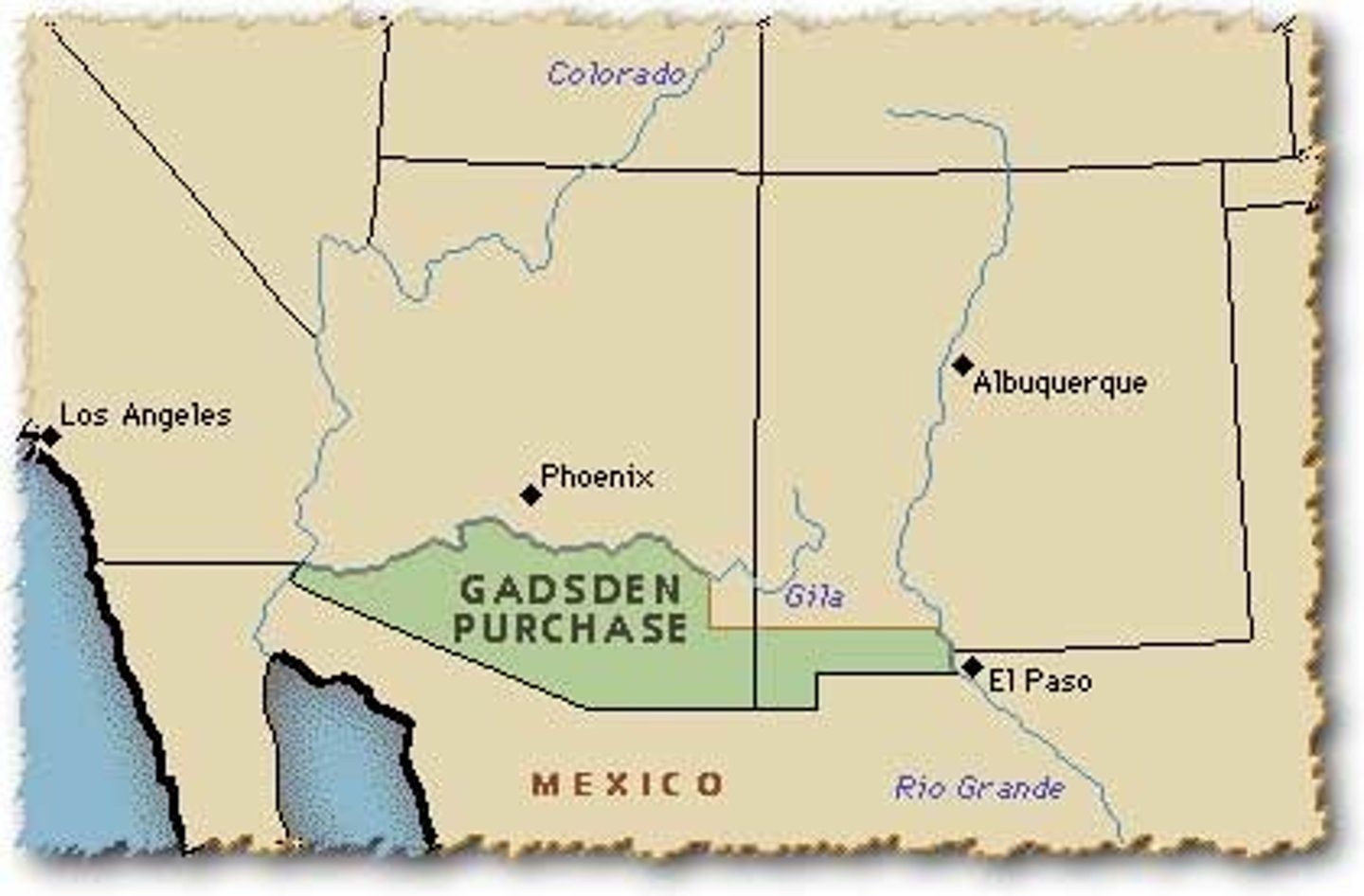
Gadsden Purchase
Agreement w/ Mexico that gave the US parts of present-day New Mexico & Arizona in exchange for $10 million; all but completed the continental expansion envisioned by those who believed in Manifest Destiny.
Ostend Manifesto
A declaration (1854) issued from Ostend, Belgium, by the U.S. ministers to England, France, and Spain, stating that the U.S. would be justified in seizing Cuba if Spain did not sell it to the U.S.
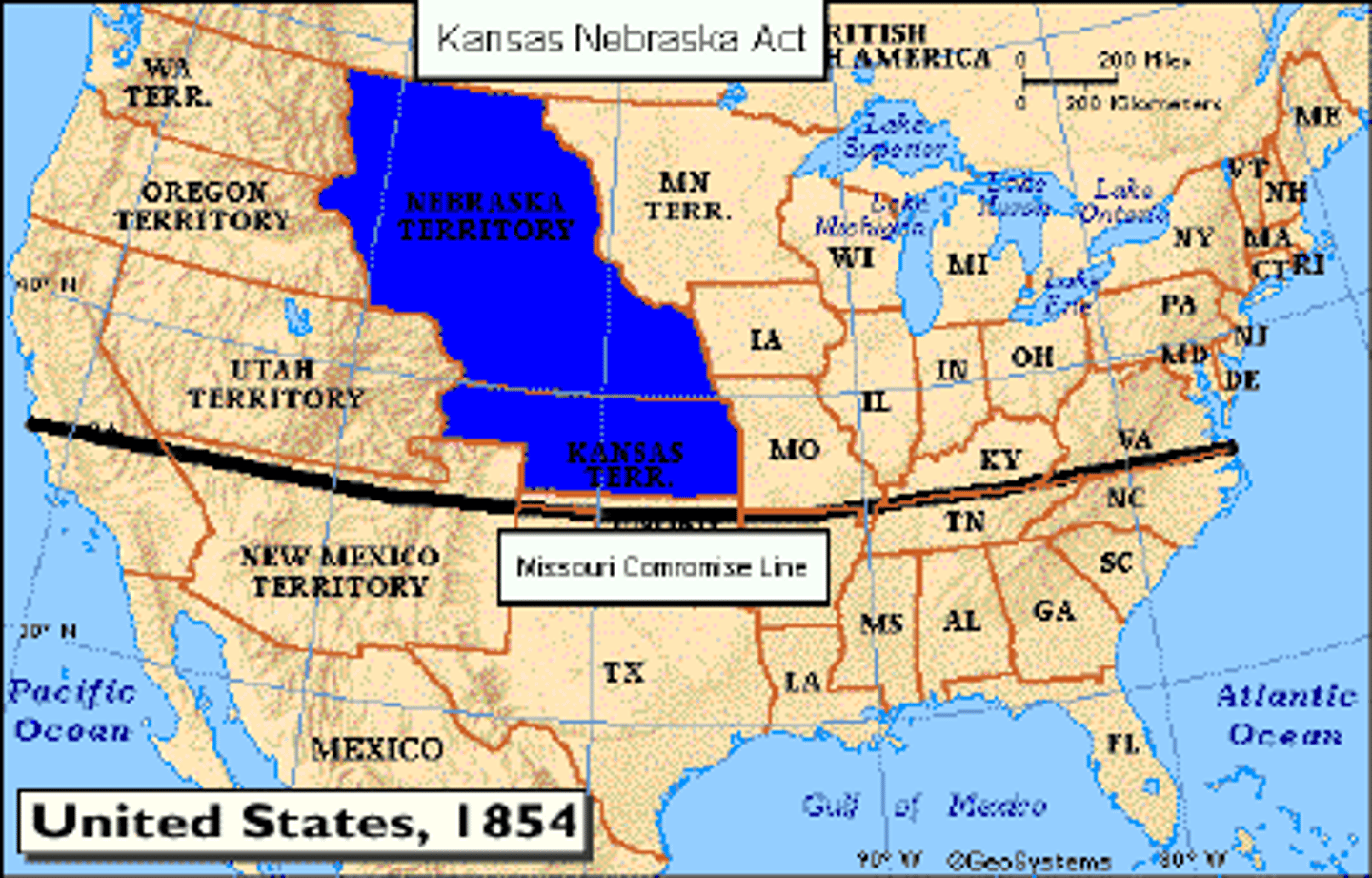
Kansas-Nebraska Act
1854 - Created Nebraska and Kansas as states and gave the people in those territories the right to chose to be a free or slave state through popular sovereignty.
Bleeding Kansas
A sequence of violent events involving abolitionists and pro-Slavery elements that took place in Kansas-Nebraska Territory. The dispute further strained the relations of the North and South, making civil war imminent.

Dred Scott v. Sandford
1857 Supreme Court decision that stated that slaves were not citizens; that living in a free state or territory, even for many years, did not free slaves; and declared the Missouri Compromise unconstitutional

James K. Polk
president in March 1845. wanted to settle Oregon boundary dispute with Britain. wanted to acquire California. wanted to incorporate Texas into union.

Frederick Douglass
(1817-1895) American abolitionist and writer, he escaped slavery and became a leading African American spokesman and writer. He published his biography, The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, and founded the abolitionist newspaper, the North Star.

Zachary Taylor
(1849-1850), Whig president who was a Southern slave holder, and war hero (Mexican-American War). Won the 1848 election. Surprisingly did not address the issue of slavery at all on his platform. He died during his term and his Vice President was Millard Fillmore.

Stephen Douglas
A moderate, who introduced the Kansas-Nebraska Act in 1854 and popularized the idea of popular sovereignty.
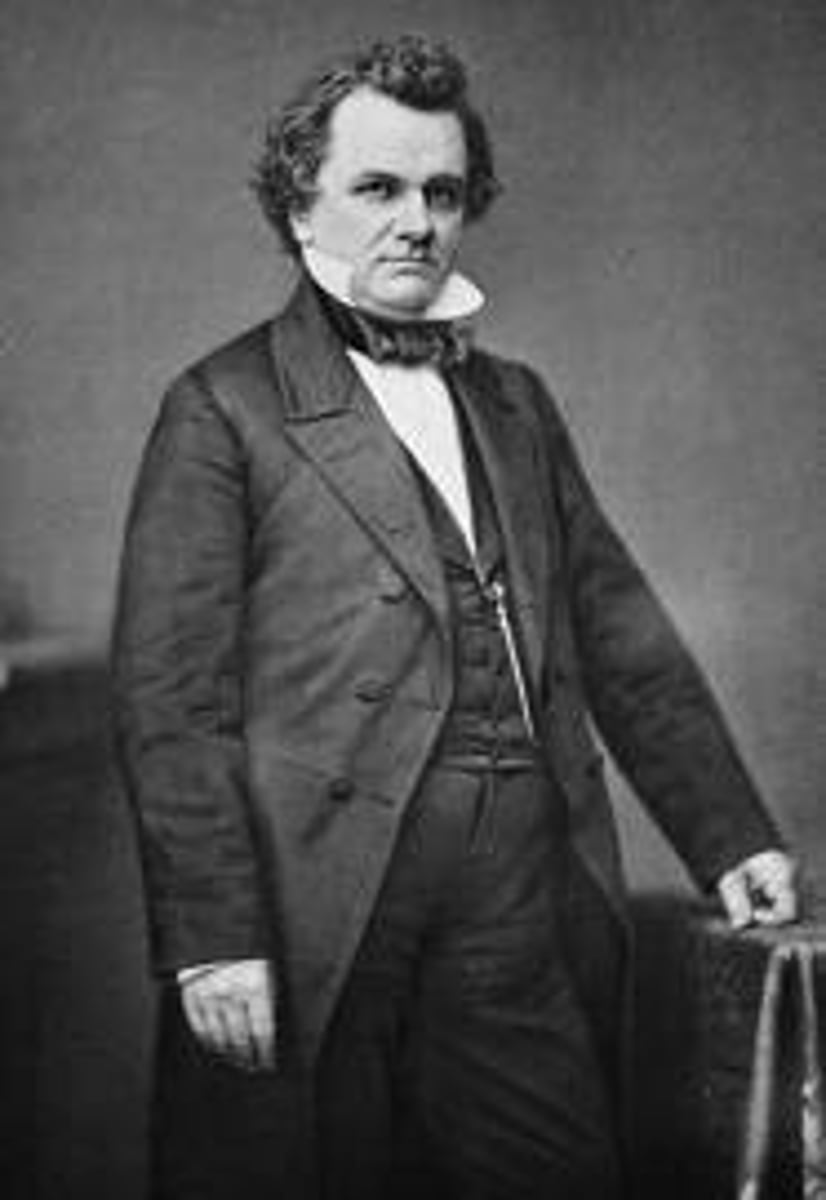

Harriet Beecher Stowe
Author of Uncle Tom's Cabin
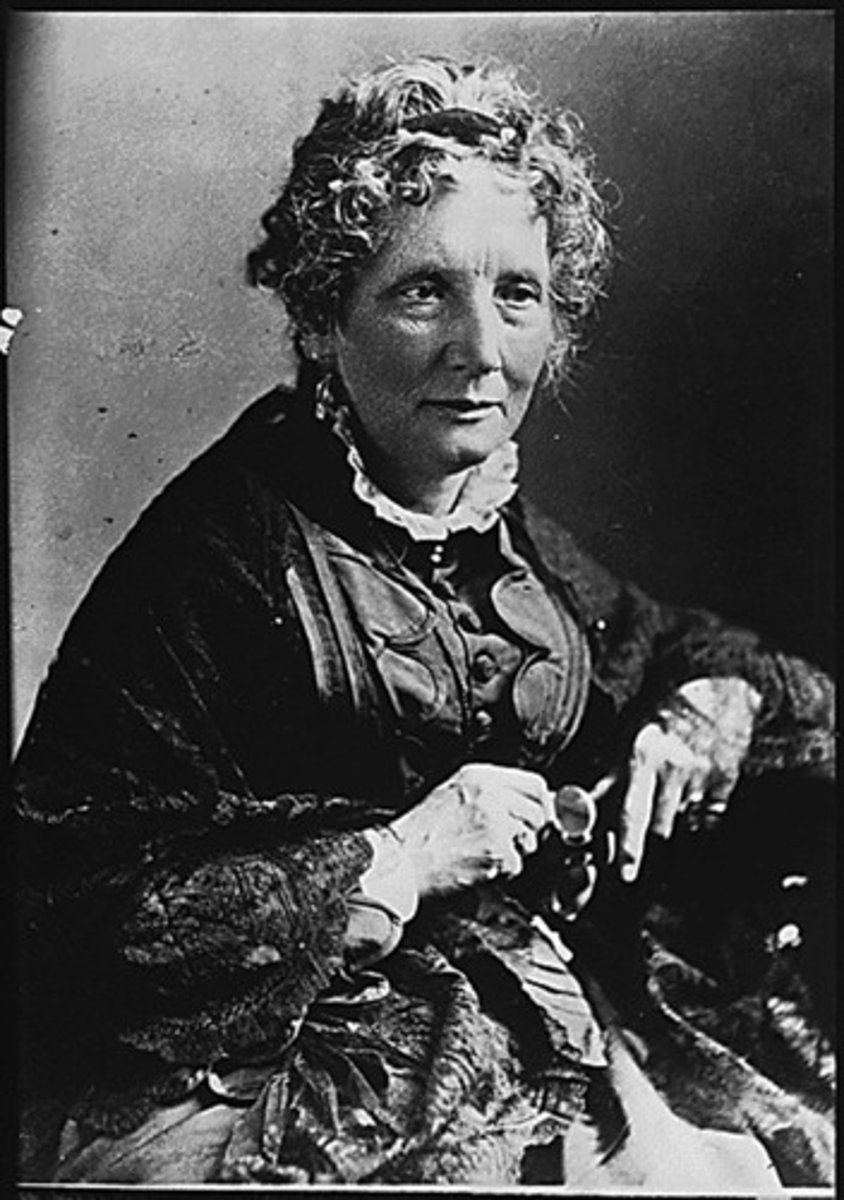

John Brown
Abolitionist who was hanged after leading an unsuccessful raid at Harper's Ferry, Virginia (1800-1858)
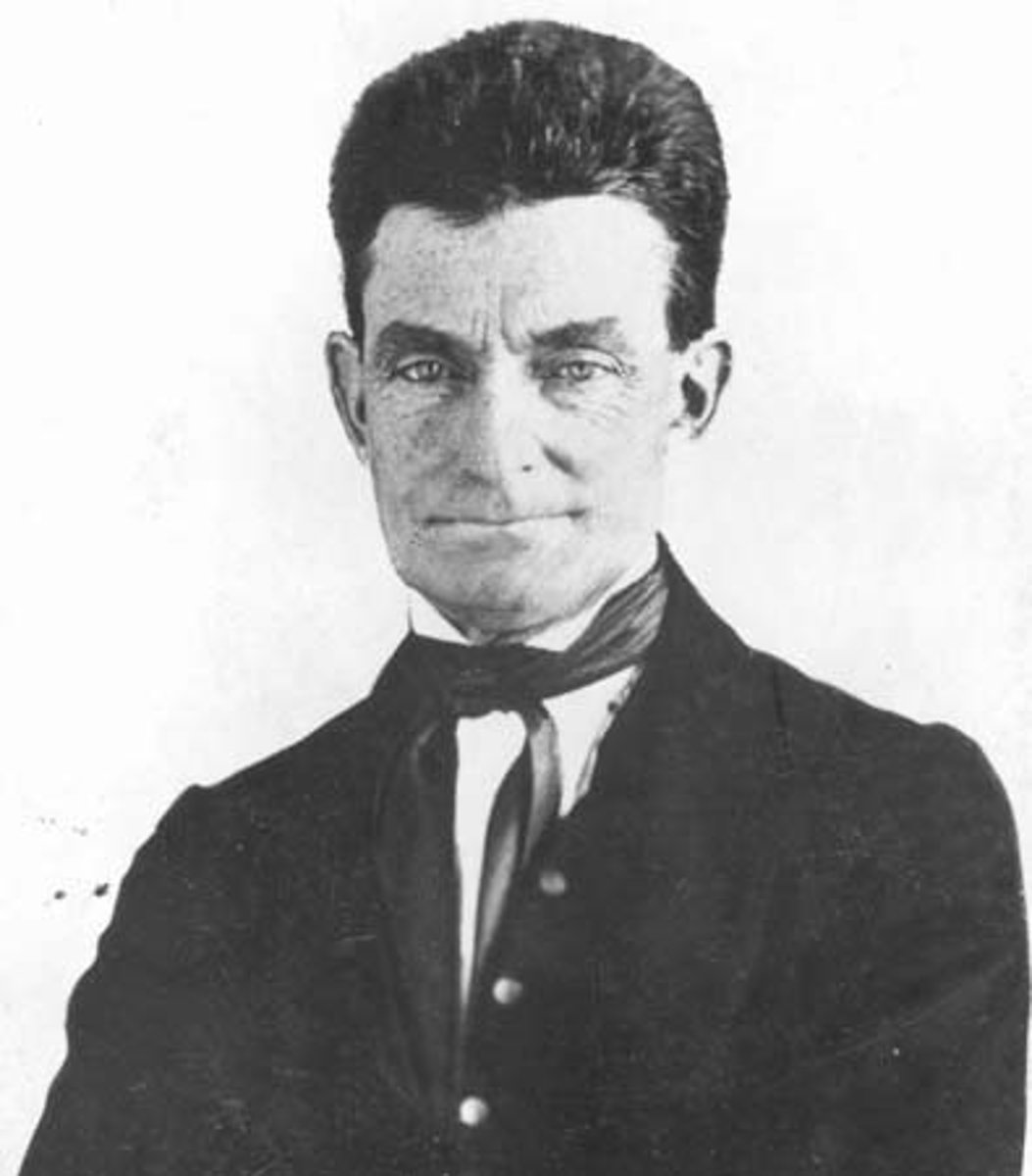

Abraham Lincoln
16th President of the United States saved the Union during the Civil War and emancipated the slaves; was assassinated by Booth (1809-1865)
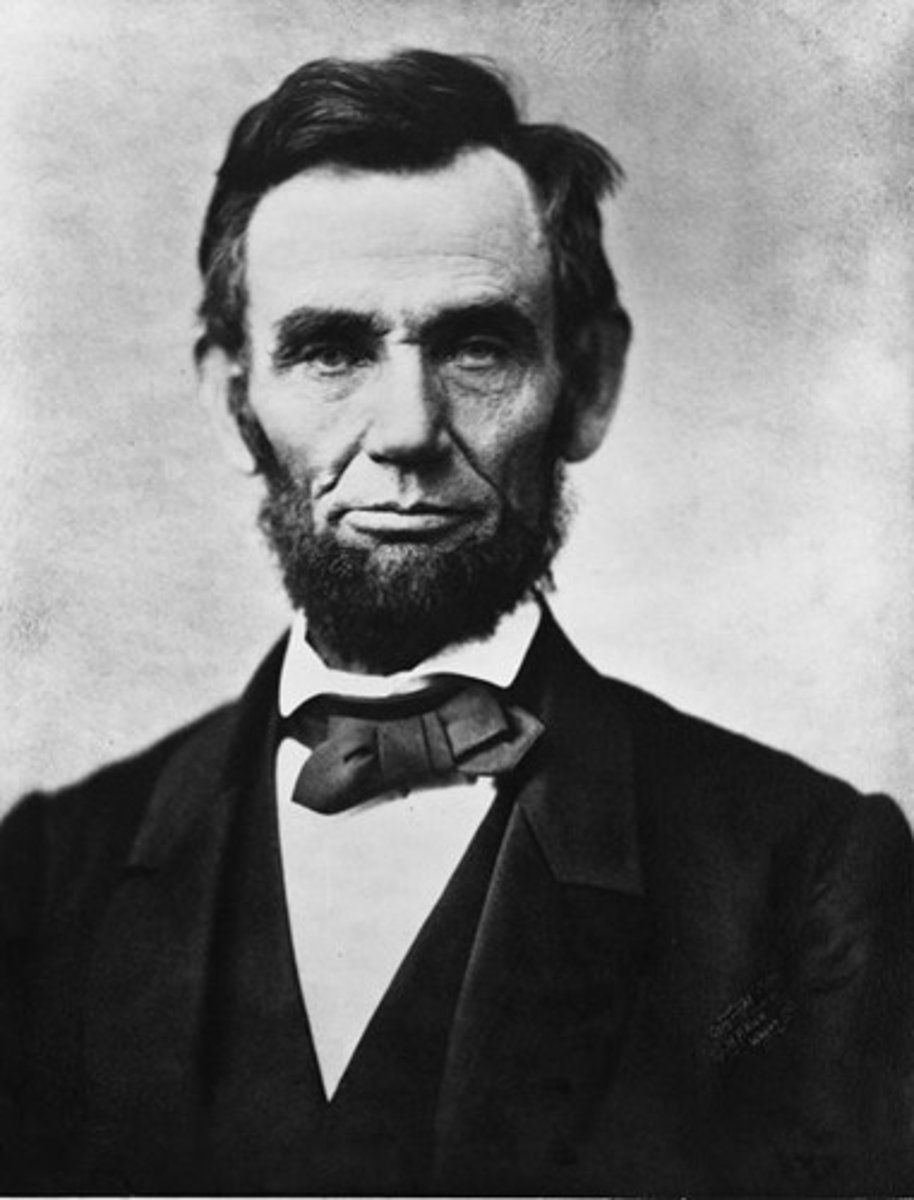

13th Amendment
Abolition of slavery
14th Amendment
Declares that all persons born in the U.S. are citizens and are guaranteed equal protection of the laws
15th Amendment
Citizens cannot be denied the right to vote because of race, color , or precious condition of servitude
Anaconda Plan
Union war plan by Winfield Scott, called for blockade of southern coast, capture of Richmond, capture Mississippi R, and to take an army through heart of south
Antietam
(AL), 1862, the first major battle in the American Civil War to take place on Northern soil. It was the bloodiest single-day battle in American history, with almost 23,000 casualties. After this "win" for the North, Lincoln announced the Emancipation Proclamation
Appomattox Court House
Famous as the site of the surrender of the Confederate Army under Robert E. Lee to Union commander Ulysses S. Grant
Black Codes
Laws denying most legal rights to newly freed slaves; passed by southern states following the Civil War
border states
in the civil war the states between the north and the south: delaware, mayland, kentucky, and missouri
Bull Run
1st real battle, Confederate victory, Washingtonian spectators gather to watch battle, Gen. Jackson stands as Stonewall and turns tide of battle in favor of Confederates, realization that war is not going to be quick and easy for either side
carpetbagger
A northerner who went to the South immediately after the Civil War; especially one who tried to gain political advantage or other advantages from the disorganized situation in southern states
Civil Rights Act of 1866
Passed by Congress on 9th April 1866 over the veto of President Andrew Johnson. The act declared that all persons born in the United States were now citizens, without regard to race, color, or previous condition.
Compromise of 1877
Ended Reconstruction. Republicans promise 1) Remove military from South, 2) Appoint Democrat to cabinet (David Key postmaster general), 3) Federal money for railroad construction and levees on Mississippi river
Confederacy
the southern states that seceded from the United States in 1861
Emancipation Proclamation
Executive order Issued by Abraham Lincoln which declared that all slaves in the Confederate states would be free
Freedmen's Bureau
Organization run by the army to care for and protect southern Blacks after the Civil War
Free Soil Party
Formed in 1847 - 1848, dedicated to opposing slavery in newly acquired territories such as Oregon and ceded Mexican territory.
Fugitive Slave Law
this law required that northern states forcibly returned escaped slaves to their owners.
Gettysburg Address
(1863) a speech given by Abraham Lincoln after the Battle of Gettysburg, in which he praised the bravery of Union soldiers and renewed his commitment to winning the Civil War; supported the ideals of self-government and human rights
Gold Rush
a period from 1848 to 1856 when thousands of people came to California in order to search for gold.
Harpers Ferry Raid
Occurred in October of 1859. John Brown of Kansas attempted to create a major revolt among the slaves. He wanted to ride down the river and provide the slaves with arms from the North, but he failed to get the slaves organized. Brown was captured. The effects of Harper's Ferry Raid were as such: the South saw the act as one of treason and were encouraged to separate from the North, and Brown became a martyr to the northern abolitionist cause.
Homestead Act
1862 law that gave 160 acres of land to citizens willing to live on and cultivate it for five years
Jefferson Davis
President of the Confederate States of America
Ku Klux Klan
A secret society created by white southerners in 1866 that used terror and violence to keep African Americans from obtaining their civil rights.
Know Nothing Party
Political party of the 1850s that was anti-Catholic and anti-immigrant
MA 54th Regiment
The regiment was one of the first official African-American units in the United States during the Civil War.
manifest destiny
A notion held by a nineteenth-century Americans that the United States was destined to rule the continent, from the Atlantic the Pacific.
popular sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people.
Radical Republicans
After the Civil War, a group that believed the South should be harshly punished and thought that Lincoln was sometimes too compassionate towards the South.
Reconstruction
the period after the Civil War in the United States when the southern states were reorganized and reintegrated into the Union
Robert E. Lee
Confederate general who had opposed secession but did not believe the Union should be held together by force
scalawag
A derogatory term for Southerners who were working with the North to buy up land from desperate Southerners
secession
Formal withdrawal of states or regions from a nation
sharecropper
A person who works fields rented from a landowner and pays the rent and repays loans by turning over to the landowner a share of the crops.
Sherman's March
(1864-1865) Union General William Tecmseh Sherman's destructive March through Georgia. An early instance of "Total war", purposely targeting infrastructure and civilian property to diminish morale and undercut the confederate war effort.
Stonewall Jackson
Brave commander of the Confederate Army that led troops at Bull Run. He died in the confusion at the Battle of Chancellorsville.
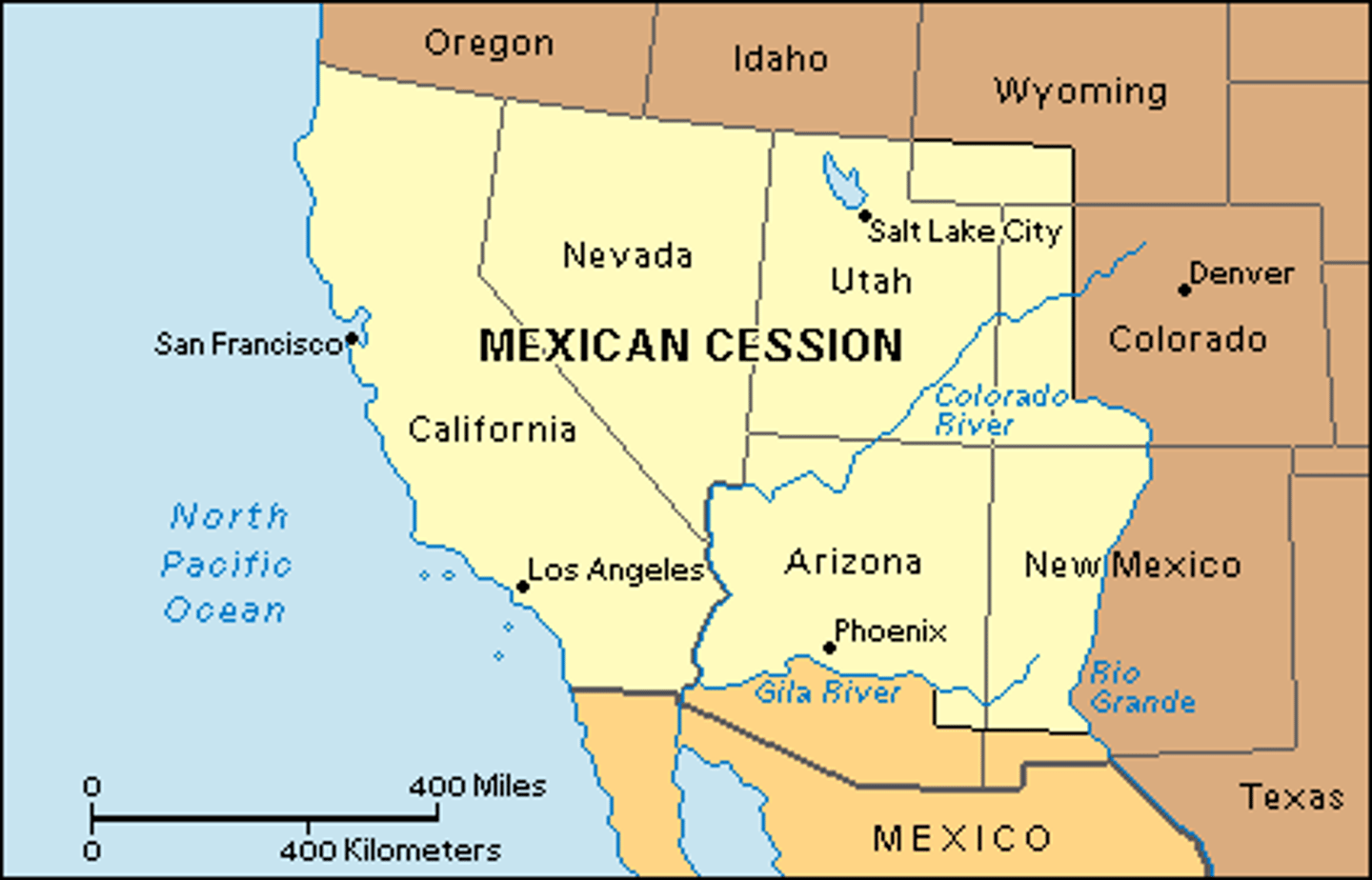
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Treaty that ended the Mexican War, granting the U.S. control of Texas, New Mexico, and California in exchange for $15 million
Underground Railroad
a system of secret routes used by escaping slaves to reach freedom in the North or in Canada
Reconstruction
the period after the Civil War in the United States when the southern states were reorganized and reintegrated into the Union
Wade-Davis Bill
a law that required a majority of prewar voters in Confederate states to swear loyalty to the Union before restoration could begin
Freedman's Bureau, 1865
a federal agency that was formed during Reconstruction to aid for emancipated slaves
Black Codes
laws that restricted African Americans' rights and opportunities
Civil Rights Act of 1866
a law that established federal guarantees of civil rights for all citizens.
Fourteenth Amendment
the constitutional amendment, ratified in July 1868 ,which guaranteed full citizenship status and rights to every born person born in the United States ,protected due process, and guaranteed equal protection under the law
Impeach
the act of bringing charges against a public official in order to determine whether he or she should be removed from office.
Fifteenth Amendment
1870 constitutional amendment that guaranteed voting rights regardless of race or previous condition of servitude
Scalawag
negative term for a southern white who supported the Republican Party after the Civil War
Carpetbaggers
A northerner who went to the South immediately after the Civil War; especially one who tried to gain political advantage or other advantages from the disorganized situation in southern states
Segregation
a forced separation, often by race
Integration
the act of uniting or bringing together, especially people of different races
Sharecropping
a system in which a farmer tends to a portion of a planter's land in return for a share of the crop
Ku Klux Klan
A secret society created by white southerners in 1866 that used terror and violence to keep African Americans from obtaining their civil rights.
Enforcement Acts
(1870-1871) Congress in response to the KKK and others, passed these acts to protect black voters. It created penalties on person who interfered with any citizen's right to vote. Outlaws the activities of the KKK
Poll Tax
A requirement that citizens pay a tax in order to register to vote
Literacy Test
A test given to persons to prove they can read and write before being allowed to register to vote
Civil Rights Act of 1875
law that banned discrimination in public facilities and transportation