Strings
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2Y2 | Midterms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
String
is a sequential collection of characters that is used to represent text.
String
In C#, a _ is an object of class string in the System namespace.
In C#, a string variable can be initialized by using either of the following:
• directly assigning a string literal; or
• using the new keyword and calling the String class constructor.
The most commonly used method for creating a string object is by assigning a string literal to a string variable.
The following example use assignment operator t assign the string literal to a string variable:
string strMessage = "Welcome to this course!";
string strPath = @"C:\Documents\Report.docx";
In the given example, the backslash () is used to escape characters with special use, such as newline (\n).
@
The @ symbol before the string literal is used to ignore the special use of backslashes.
Calling the String class constructor is the other method used to create a string object in C#.
The following statements show an example of how to use new keyword and String class constructor:
char[] word = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '!' };
string strGreet = new string(word);
In the given example, the String class constructor is used to create a string from an array of characters named word.
Note that in C#, there is no String class constructor that takes a string literal as an argument. The String constructors in C# only creates a string from characters and arrays.
The String class has two (2) properties that can be used to get some information of the string and can be used to manipulate strings. The following are the properties of the String class:
• char
This property is used to get the character at a specified index position of a string.
For example:
string word = "Computer";
char letter = word[2];
//the value of variable letter is character 'm'
• Length
This property is used to get the total number of characters in the string.
For example:
string word = "Computer";
int total = word.Length;
//the value of variable total is 8
The String class provides several methods that are used to perform operations on strings. Table 1 shows some of the methods of String class in C#.
Table 1. Methods in the class String (Harwani, 2015) Method Description
bool Contains(string value)
This returns true if the specified substring occurs within the string object; otherwise, it returns false.
For example:
string sentence = "The quick brown fox jumps.";
bool isContain = sentence.Contains("fox"); //returns true
bool Equals(string value, StringComparison comparisonType)
This determines whether the specified substring has the same value with the string object. The comparisonType parameter specifies the rules to use in comparing strings, such as ignoring the case version of the characters.
Example 1:
string word = "Computer";
bool isSame = word.Equals("computer", StringComparison.CurrentCulture); //this
returns false
Example 2:
string word = "Computer";
string strMessage = "Welcome to this course!";
string strPath = @"C:\Documents\Report.docx";
char[] word = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '!' };
string strGreet = new string(word);
string word = "Computer";
char letter = word[2];
//the value of variable letter is character 'm'
string word = "Computer";
int total = word.Length;
//the value of variable total is 8
Method Description
bool isSame = word.Equals("computer", StringComparison. CurrentCultureIgnoreCase);
//this returns true
int IndexOf(char value)
This returns the index position value of the first occurrence of the specified character within the string object if that character is found; otherwise, it returns -1 if not found.
For example:
string word = "Computer";
int index = word.IndexOf('p'); //returns integer 3
string Replace(char oldValue, char newValue)
This returns a copy of the string object except that all of the occurrences of an old character are replaced with a new character.
For example:
string word = "Color";
string strChanged = word.Replace('o', '#'); //returns a copy of string "C#l#r"
string ToString()
This returns a converted copy of object as a string.
For example:
double value = 105.25;
string strValue = value.ToString(); //converted 105.25 into string
string ToLower()
This returns a copy of the string object converted to lowercase.
For example:
string word = "COMPUTER";
string strConverted = word.ToLower(); //returns a copy of string "computer"
string ToUpper()
This returns a copy of the string object converted to uppercase.
For example:
string word = "computer";
string strConverted = word.ToUpper(); //returns a copy of string "COMPUTER"
The String class methods only create a copy of the string object and return a new string containing the result of the method operation.
Strings are immutable. This means that when a string object is created, its contents cannot be changed. Every instance of a string that has been modified is actually creating a new string in the computer’s memory.
For example:
string strComputer = "Computer";
strComputer = strComputer + " is a great invention.";
Figure 1. Memory allocation for String class
In Figure 1, the variable strComputer of String class will allocate a space in the memory with the string "Computer". When the content of this variable is modified by concatenating the string "is a great invention.", the compiler will allocate new memory space for the modified string instead of modifying the initial string at the same memory address. This behavior will delay the performance of the application if the same string is modified multiple times.
To solve this problem, C# provides the StringBuilder class that represents a mutable string of characters.
StringBuilder class
represents a mutable string of characters that allows the user to expand the number of characters in the string object without allocating additional memory space.
The following shows the way of creating a string using the StringBuilder class and using the new keyword and StringBuilder constructor:
The following syntax shows how to use Append() method to concatenate a string to the string object of StringBuilder class.
StringBuilder strComputer = new StringBuilder("Computer");
The example below will return the string ("Computer is a great invention.".
strComputer.Append(" is a great invention.");
Figure 2 shows how a StringBuilder class allocates a memory space when modifying a string object.
Figure 2. Memory allocation for StringBuilder class
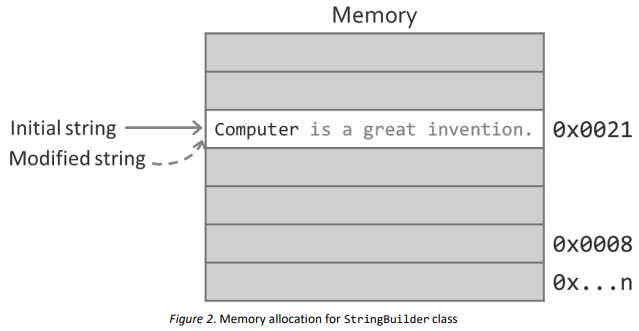
In the figure, the content "Computer" of the variable strComputer of StringBuilder class is allocated to a memory space.
When the Append() method is used to modify the content of the string variable, the content "Computer is a great invention." is allocated to the same memory address.
The StringBuilder class also contains two (2) main properties that can get and manipulate the information on a string. These properties are char and Length.
The following example shows how to use these properties:
StringBuilder word = new StringBuilder("Computer");
word[0] = '#'; //change the character at index 0 to '#'
for (int index = 0; index < word.Length; index++) {
Console.Write(word[index] + " + "); //gets the character at the specified index
}
Output:
# + o + m + p + u + t + e + r +
StringBuilder class
contains useful methods that can be used to perform operations on the content of the StringBuilder object.
Table 2 lists some of the methods of StringBuilder class.
Table 2. Some methods in the class String (Harwani, 2015)
Append(string value)
This appends a copy of the specified substring to the StringBuilder object.
For example:
StringBuilder word = new StringBuilder("Computer");
word.Append(" Ethics"); //returns the string "Computer Ethics"
Equals(string value)
This returns true if the specified substring is equal to the StringBuilder object; otherwise, it returns false.
For example:
StringBuilder wordA = new StringBuilder("computer");
StringBuilder wordB = new StringBuilder("computer");
wordA.Equals(wordB); //returns true because same content
Clear()
This removes all characters from the current StringBuilder object.
For example:
StringBuilder word = new StringBuilder("Computer");
word.Clear();
word.Append("Ethics"); //returns the string "Ethics" only
Replace(char oldValue, char newValue)
This replaces all occurrence of a specified old character of the StringBuilder object with a new character.
For example:
StringBuilder word = new StringBuilder("Color");
word.Replace('o', '*'); //returns the string "C*l*r"
ToString()
This converts the value of the StringBuilder object to a string.
For example:
StringBuilder word = new StringBuilder("computer");
string strWord = word.ToString();