Red meat slaughter - cattle
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Flow diagram of the cattle slaughter process
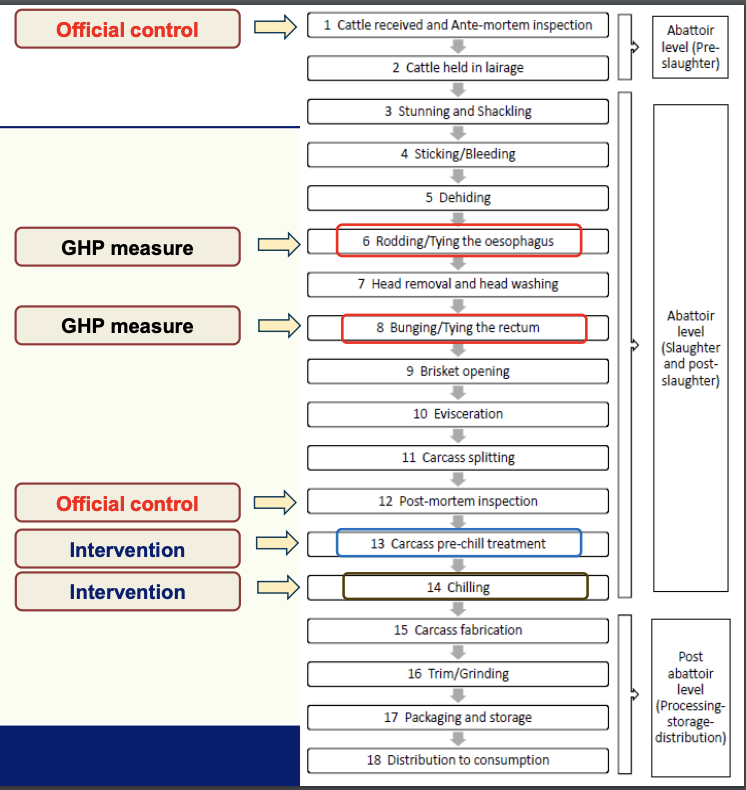
Who is responsible for:
Official controls
Process steps and controls
Official controls= OV
Process steps and controls= FBO
List what the FCI include
Animal ID
Disease status and foodborne hazards status as part of HACCP
Knowledge of residues
Movement restrictions (TB or other disease) to holding area
Why does the hide cross-contamination during stunning increase?
Due to cattle contact with contaminated floor in stunning box and landing area
How is sticking/bleeding performed in cattle?
Legs must be restrained due to involuntary kicking movements
Hygienic cut using "two knife system" first open hide then cut blood vessels
Neck cut: severing carotid and jugular veins (usually smaller abattoirs without hoisting equipment
or
Thoracic (chest) cut: preferable, severing brachiocephalic trunk (in all abattoirs where animal is hoisted)
What are the main sources/routes of microbial contamination during slaughter and dressing?
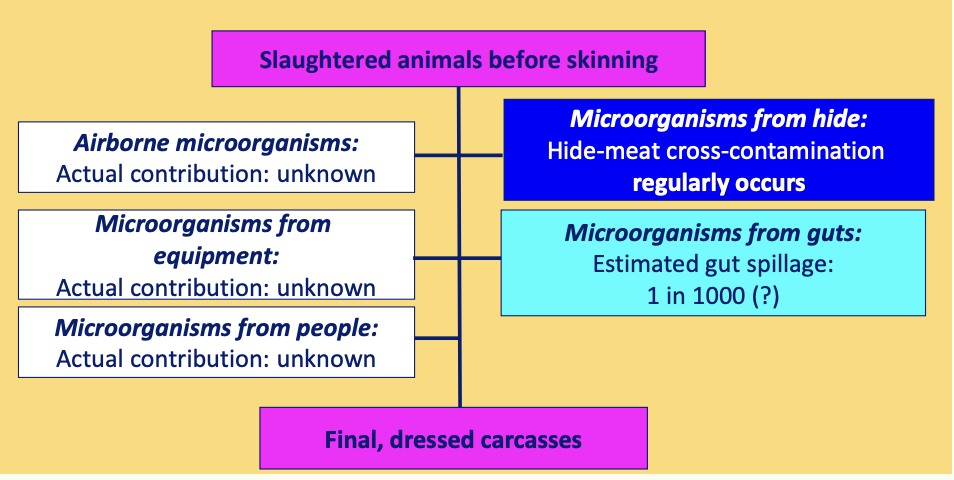
What are the names for the process of cattle hide removal?
De-hiding
Skinning
Flaying
What are the main foodborne pathogen in the beef chain and when is it highest on cattle hides?
E. coli, Salmonella
Highest on cattle hides at slaughter
What are the routes of transfer of microbial contamination from hide onto carcass during dehiding?
Direct transfer
Via accidental in-rolling of hide
Indirect routes
Via workers hands
Contaminated knives, equipment, aprons
Aerosols generated during manipulation
What are the three automated hide pulling methods?
Upwards
Downwards
Sideways

What should you do to decrease pathogen transfer during cattle hide removal?
Equipment, tools and knives sanitation between carcasses and whenever they get contaminated
How do you detect contamination on a carcass? What are the disadvantages of this method?
"Verifeye"

Based on spectroscopic imaging
Disadv- depends on diet, amount of derivatives of chlorophyll varies
When and how is rodding/oesophagus tying performed?
ASAP after stunning to prevent rumen spillage onto other carcass parts
Oesophagus released and clipped with plastic or rubber- then pushed up with the rod to the diaphragm to seal it
(Equipment and tool sanitation between carcasses necessary GHP)
How should head removal be performed?
In a manner that avoids contamination with gut content
Adequate washing but limit splashing and contamination of cheek meat
Who inspects the head post removal, what happens to each part if inspection is passed?
Inspected by Meat Hygiene Inspector
If passed:
Skull is specified risk material for BSE
Rest is fit for human consumption
What age cattle need to be BSE tested in UK?
Healthy: no testing
Emergency slaughter and sick at antemortem- Over 48 months
Fallen stock- Over 48 months
If imported to UK from other countries (^30,24,24)
What is bunging/rectum tying?
A process where a cut is made around the anus to free rectum from the carcass and then it is tied off and/or bagged to prevent faecal spillage
What is brisket opening?
Cutting through the sternum to open thoracic cavity to extract lungs and heart
What is evisceration?
A process to remove:
Red offal: heart, lungs, trachea, diaphragm, liver, kidneys
Green offal: stomachs, intestines and spleen
What is carcass splitting?
Splitting carcasses in middle with chain saw
Spinal cord removed afterwards (SRM)
What is the difference between the official controls of post mortem meat inspection in red meat and white meat?
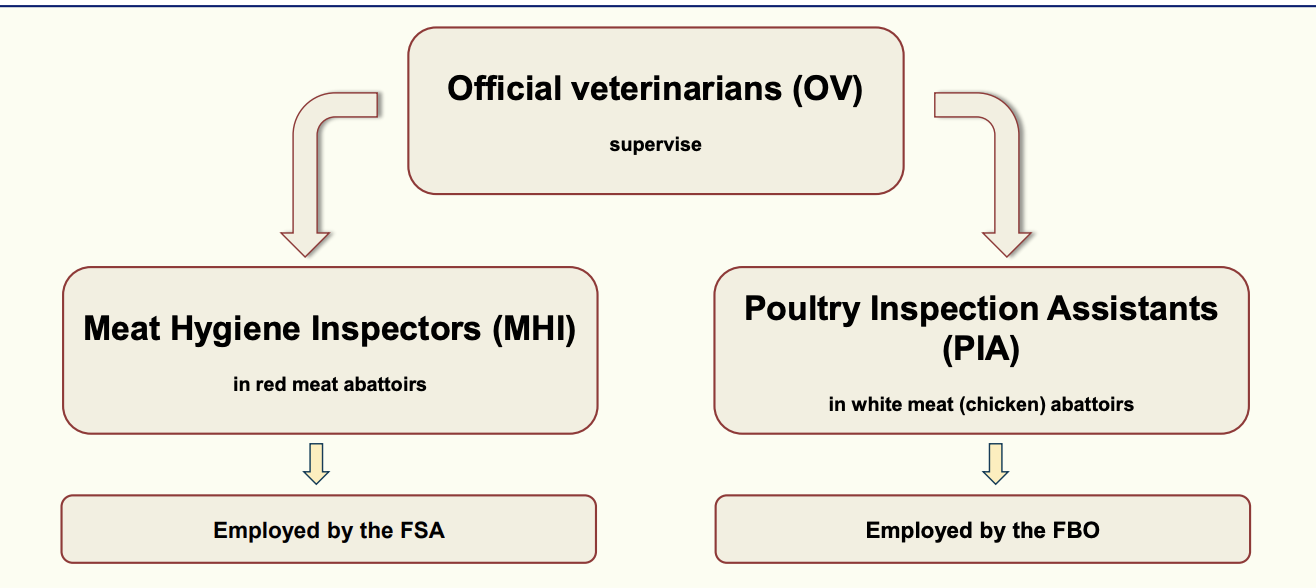
What are health marks?
Applied under responsibility of OV when meat deemed fit for human consumption
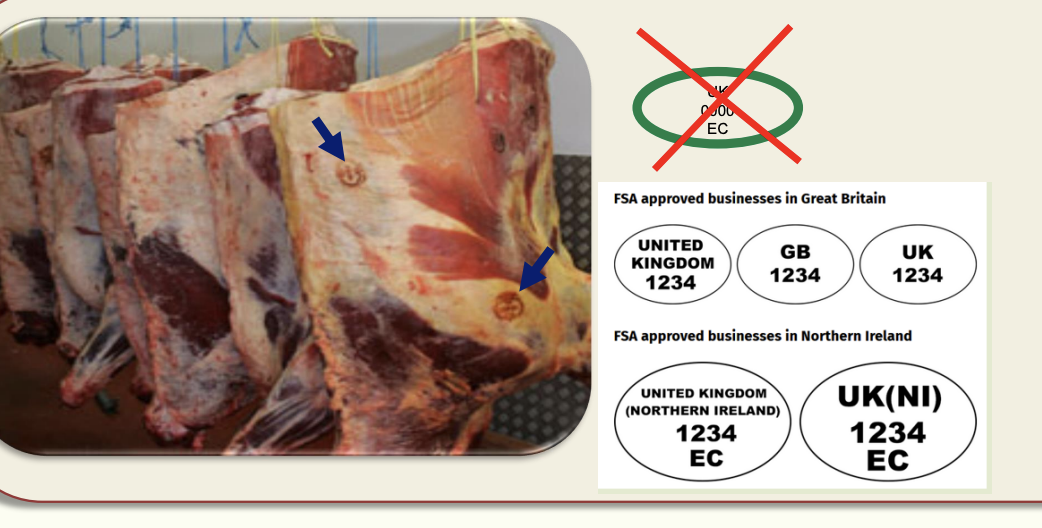
Explain how carcass pre-chill treatment (intervention) and chilling is used in abattoirs?
Interventions: in most abattoirs- most common knife trimming and steam vacuuming
Carcass washing with cold water: allowed but not recommended for beef and sheep
Chilling: regulatory mandated procedure
<7°C red meat
<4°C white meat
<3°C offal
What is involved in carcass fabrication? What temperatures does it occur at?
Cutting/boning
After chilling meat enters cold chain until consumption or processing into products not requiring chilling
In boning hall- temp most be low (<12°C), hot water not used for cleaning
What is involved in packaging, storage and despatch?
Packaging: aerobic, vacuum, modified atmosphere
Storage before despatch: temperatures low enough to maintain: <7°C in meat, <3°C in offal
Despatch: loading into refrigerated lorries